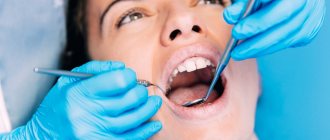
Who is a periodontist?
A periodontist is a highly qualified specialist involved in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases - the soft periodontal tissues that provide teeth with reliable fixation in the jaw.
The periodontist, as a highly specialized doctor, must have in-depth knowledge of the methods of treating various types of soft tissue diseases. In his practice, he uses antibiotics, special dental equipment, resuscitation agents and drugs to treat gums.
What diseases does a periodontist treat?
Periodontal therapy includes the following diseases:
- Periodontitis. Inflammatory processes of soft periodontal tissues of an infectious nature. It is characterized by difficult to bear, painful sensations, especially during chewing food, is accompanied by bleeding and the formation of ulcers, and can contribute to complete tooth loss.
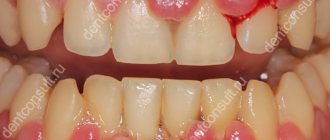
- Periodontal disease. A systemic disease that is non-infectious in nature and destroys the periodontal tissues. Periodontal disease is dangerous because in the first stages it is difficult to recognize it on your own. But some signs will still help to identify the need for examination: reduction of alveolar processes, constant itching in the gums and exposure of the area between the dental crown and root. If periodontal treatment is not started in time, periodontal disease will lead to tooth loss, and the poor condition of the soft tissues will not allow the installation of dentures or implants.
- Gingivitis. Gum disease with obvious signs by which you can easily understand that an inflammatory process has begun. These include: swelling, bleeding, pain in the gums, and unpleasant odor. It is not difficult to get rid of gingivitis; it is important to go to a dental clinic in time and be observed by a specialist and follow his recommendations.
- Tooth root cyst. A tumor appears deep in the gum, near the root of the tooth, has a round shape and is filled with a purulent accumulation. It is difficult to detect a cyst on your own; most often this happens after x-ray examinations during the treatment of other teeth. But it can cause constant aching pain that does not go away even after taking painkillers, periodontal swelling, headaches and increased body temperature.
- Stomatitis. Inflammation of the oral mucosa, accompanied by erosion, the appearance of ulcers, abscesses, blisters and the formation of white plaque. Most often it is infectious in nature, so if these signs are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When do you need to urgently visit a periodontist?
All of the above signs of pathologies are a good reason to make an appointment with a dentist. In these cases, self-medication is strictly prohibited, since treatment should be aimed at eliminating not the signs, but the causes of the disease. And only a professional specialist can identify them and prescribe effective therapy.
The main signs of the need for examination by a periodontist include:
- bleeding gums;
- the first signals of the onset of the inflammatory process;
- painful sensations in the gums;
- release of fluid when pressing on the gums;
- noticeable loosening of teeth;
- the appearance of periodontal pockets in the periodontal areas;
- peeling of soft tissues and their subsidence;
- exposure of the dental neck;
- putrid taste and bad breath that does not go away even after brushing or rinsing;
- suppuration;
- change in the angle of inclination of the teeth.
All of the above signs indicate dangerous changes that require immediate medical attention.
A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases - all tissues in which the tooth is located: jaw bones, tooth ligaments, mucous membrane.
Periodontists are experts in the treatment of oral inflammation. Only doctors who have received a certificate in therapeutic dentistry and surgical dentistry can master this narrow specialty. A periodontist treats diseases such as stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, and his work also includes the selection of preventive agents to prevent all these diseases in the future.
Periodontists treat people not only with incipient gum problems, but also with severe forms of gum disease (severe periodontitis and periodontal disease) or a complex medical history. Doctors offer a wide range of procedures for the treatment of gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. They can also treat patients with severe gum problems using a range of surgical procedures.
During the first visit, the periodontist will usually review the patient's complete medical and dental history. It is extremely important to know if the patient is taking any medications or undergoing treatment that may affect the teeth and gums, such as heart disease, diabetes, or possibly pregnancy.
The periodontist examines the gums, checks the condition of the teeth and bite. To do this, the mucosal specialist uses a small measuring device called a periodontal probe and places it between the teeth and gums to determine the depth of this space. If its depth is more than 4 mm, then it is assessed as a periodontal pocket; this helps the periodontist assess the health of the gums, which, together with other research results, will allow him to choose the right treatment. An orthopantomogram or panoramic X-ray must be taken to determine the condition of the bone below the gum line. Based on the patient’s complaints, examination of the oral cavity, X-ray data and measurement results of periodontal pockets, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Periodontal treatment can be conservative (periodontal cleaning, scaling, medications, physiotherapeutic procedures) or surgical (bone and tissue grafting using bone preparations, membranes).
When should you make an appointment with a periodontist?
Often, the treatment of patients with periodontitis and periodontal disease is undertaken by ordinary dental therapists who have read several books and attended courses on the treatment of gum inflammation. Their tactics are to maintain visible “gum health” with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs - absence of bleeding, suppuration, and reduction of bad breath. But! These methods cannot in any way affect an already formed pocket, into which food, plaque, etc. continue to fall. Therefore, relapses of the disease constantly occur, which again, in a circle, brings the patient to the doctor.
Especially as people age, more and more patients are showing signs of periodontal disease, coupled with research that points to a link between periodontal disease and other chronic diseases, periodontal treatment may require greater understanding and increased knowledge by a qualified professional. For patients with moderate or severe disease, it is better to consult a periodontist who also knows surgical treatment methods. Ask your periodontist for surgical certification! After periodontal sanitation, how should it be used?
Research has shown that effective brushing and flossing, along with regular professional dental cleanings, helps prevent tooth decay and gum disease. But sometimes, even people who are very careful about their oral hygiene cannot protect themselves from diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis. Your dentist may recommend a visit to a gum specialist if he notices a problem. Additionally, you can talk to your periodontist about improving the appearance of your smile using some of the options of plastic surgery.
Treatment by a periodontist
Treatment with a doctor begins with an initial consultation. The doctor draws up a treatment plan.
Periodontists have a wide range of tools available to combat gum disease. Treatment usually begins with the least invasive measures, which are not surgical procedures.
- Removing plaque and tartar
- Antimicrobial drugs and the use of antiseptics for washing periodontal pockets, their treatment with anti-inflammatory gels
- Depulpation of teeth
- Using technology for splinting mobile teeth with fiberglass
- Manufacturing of removable temporary dentures for periodontal treatment
Choosing a periodontist
A great way to find a qualified periodontist is to request a referral from your general dentist. Additionally, there are several points to consider when choosing a periodontist, including:
- The length and experience of a periodontist, how long has he been working in this specialty?
- Reviews from patients (preferably whom you know personally)
- Education and/or courses completed by the periodontist? How long ago were they completed?
- What diagnosis did the periodontist make and what treatment plan did he propose? Ask about all of your periodontal treatment options and the pros and cons of each. Periodontists have different treatment philosophies. While some focus closely on treating the disease with surgery, others prefer more conservative non-surgical alternatives. Make sure you fully understand why your periodontist is recommending a particular treatment and that you agree with the proposed plan.
- What are the estimated costs of the treatments? Does your periodontist treat under compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance? In cases where dental insurance does not cover treatment costs, what forms of payment are available?
- What types of dental technology/equipment does the clinic provide?
- What medications and pain management options are offered?
- Pleasant communication and professionalism of the support staff?
- Does the doctor work alone, or is he one of many specialists in a dental practice that can provide you with comprehensive oral care?
- What types of emergency medical care are available?
How not to fall for deception and determine that a specialist is not competent?
- The doctor recommends antibiotic injections directly into the gums.
In the case of injections into the site of inflammation (for example, an antibiotic such as Lincomycin), especially in large doses, a one-time destruction of pathogenic organisms occurs, which results in the release of toxins and mediators responsible for inflammation. As a result, the formation of a large amount of these substances leads to necrosis or necrosis of the periodontium of the tooth (the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone). As you might guess, the tooth gradually becomes looser, which may even be much greater than before treatment. Such teeth actually cannot perceive chewing pressure. The treatment method is not used in countries such as the USA, Europe, Australia, Japan or Israel - which are known for their high level of development of dentistry and medicine in general.
- Recommendations for applying applications using ointment forms of preparations.
An absolutely useless exercise due to the fact that ointments do not remain on the wet mucous membrane and are very quickly washed off with saliva. Moreover, the active substances of ointments do not penetrate deeply (through the oral mucosa), but remain on the most superficial layer - the mucosal epithelium, which is often insufficient for full treatment.
- Lack of proper oral hygiene communication and instruction.
As we have said more than once, the only reason responsible for gum inflammation is gingivitis and periodontitis. The doctor must carefully convey to the patient that improper oral care leads to an abundant accumulation of soft microbial plaque on the teeth, which subsequently forms tartar and hard supra- and subgingival dental deposits. If the doctor did not insist that hygiene is where you should start, did not select the right toothbrush, toothpaste and did not show how to use dental floss - such a doctor is worthless.
- Lack of certificate in dental surgery.
It is important to understand that complex flap operations or curettage of periodontal pockets can only be performed by an experienced dental surgeon who has the proper education, skills, experience and diploma. Highly qualified operations involving the grafting of synthetic bone or plastic surgery along the edge of the gingival margin, which is in an inflamed state, should not be carried out by a dentist, otherwise complications are guaranteed.
- State clinics.
Today, unfortunately, it is virtually impossible to receive qualified dental care - this is primarily due to the low qualifications of the staff, the lack of modern equipment and the lack of courses, lectures or trainings for doctors.
{jlcommentspro}
What stages does an appointment with a periodontist include?
Treatment in the periodontist’s office can be divided into 3 main stages:
- Elementary. This stage includes a visual examination of the oral cavity and the necessary diagnostics. If the pathology is not serious and manifests itself only as mild inflammation, then the doctor can only prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and special hygiene.
- Surgical. Actually the treatment itself, the methods of which differ and depend on the type of disease. It is necessary to wash the formed pockets in the periodontium with special solutions and remove subgingival deposits, if any. In difficult situations, the periodontist resorts to surgical methods.
- Prophylactic. The specialist talks about prevention methods at home and prescribes a follow-up appointment for maintenance therapy.
Advice from periodontists
In order to preserve the health of your gums, you need to use dental services twice a year and scrupulously follow the rules of hygiene.
Advice from doctors on oral care:
- Hygiene procedures must be carried out daily, morning and evening, without any exceptions. This is the main guarantee of periodontal health.
- During the day, after each meal, rinse your mouth; if you don’t have a special mouthwash on hand, you can use plain water. Any remaining food particles between the teeth must be removed using dental floss.
- The toothbrush should be chosen correctly; it should have a rounded end and medium-hard bristles, which will prevent damage to the gums during brushing.
- The toothbrush should be changed quite often, at least once every 4 months, otherwise it becomes an ideal place for the accumulation of dangerous bacteria.
- The choice of toothpaste should also be taken seriously, since it is its composition that determines how effective the cleansing of all components of the oral cavity will be. There are special pastes containing useful components and additives that will help eliminate problems with soft tissues.
Periodontist treatment methods
If necessary, the specialist will wash the inflamed area of the mucous membrane with a special solution, which will help eliminate pain and relieve swelling.
Inflammation of the gums may cause tooth mobility, which is treated with splinting (tying together several teeth or the entire dentition along an arch).
Treatment of gums can occur through surgery (at the acute stage of periodontitis). This method includes removal of damaged soft tissue, transplantation of a gum flap, and replacing it with a biological bone membrane.
All these methods of treatment and therapy do not provide a lifetime guarantee, but they can bring the condition of the gums back to normal.
Where can you go in Ivanteevka if you have gum disease?
If you need the help of a periodontist, you can contact the Sanident dental clinic, one of the best in Ivanteyevka, as confirmed by reviews from our satisfied patients. We employ only professionals with extensive experience who use modern treatment methods, the best equipment and reliable drugs. With us you can quickly and inexpensively restore health to your teeth and gums.
Complex dentistry "Sanident" is located at the following addresses:
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4 (Ivanteevka railway station);
- Shchelkovo, st. Central, 80 (railway station Voronok).
Prevention by a periodontist
Many people turn to a periodontist when the disease has already begun to progress and the patient feels serious discomfort in the oral cavity. To eliminate complications, preventive measures should be followed.
- You should take care of your teeth and gums every day, rinse your mouth several times a day (before and after meals). Dental floss should always be on hand to help remove food debris from the interdental spaces.
- The toothbrush should be used for no longer than 3 months, after which you should purchase a new one.
- A scheduled consultation with a specialist who will provide individual recommendations on oral hygiene is recommended at least 2 times a year.
A timely visit to a periodontist will help maintain healthy gums and teeth.