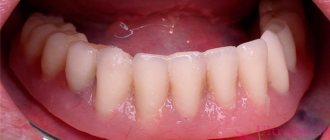
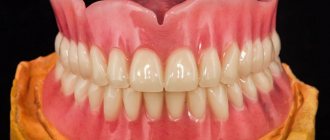
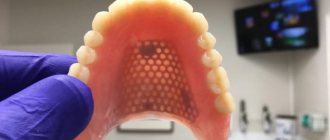
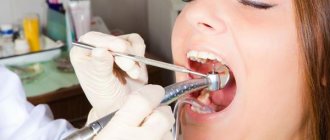
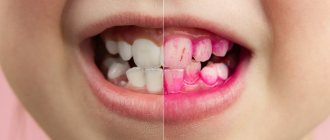
- When is denture relining necessary?
- Contraindications for prosthesis relining
- Laboratory relocation
- Relining the prosthesis price
- Features of the clinical method
- Laboratory method for relining a prosthesis
Attachment of removable dentures during prolonged wear with intense loads loses functionality.
Gradual weakening of locks or hooks requires relining of the removable denture. It is not difficult to determine that you need to contact a specialist for help. During a conversation or eating, gradually progressive discomfort begins to appear. Relining the removable denture will ensure a tight fit of the structure and will completely normalize the bite. By postponing a visit to the orthodontist, people expose the oral mucosa to danger and the likelihood of injury increases.
Symptoms that should not delay a visit to the dentist
You should make an appointment with an orthodontist if:
- changes in the alveolar process of the upper jaw appear;
- the prosthesis has received damage that is not visible to a specialist, or significant flaws have appeared after prolonged wear;
- the height of the lower third of the face has undergone atypical changes. At the same time, the minimum initial deviations rapidly increase;
- The relief of the oral mucosa changes dramatically during prosthetics or after prolonged use of a stationary prosthesis.
Indications for the procedure
Those who wear removable dentures need to visit a doctor once every six months for consultation and necessary relining. The procedure is necessary in the following cases:
- visible defects on the prosthesis;
- change in gum relief due to prolonged wear;
- unreliable fixation of the removable structure;
- transformation of the lower part of the face (height).
You cannot reline a prosthesis if it has significant defects and damage: in this case, a replacement is required. In case of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, relining is carried out only in laboratory conditions, but with the possibility of making impressions.
If the patient has an allergic reaction to plastic, a special laboratory will also be needed to reline the dentures.
Contraindications
Relining a removable denture is not done if:
- damage to the structure occurred due to a strong impact on a hard object or other mechanical impact that violated the integrity of the system;
- the prosthesis no longer meets the standards necessary for its continued wearing due to loss of integrity;
- there are one or more broken elements;
- anatomical retention is impaired, in which the prosthetic bed is not able to hold the prosthesis;
- The structure is unstable and can fall apart into its component parts at any moment.
The above reasons indicate the futility of relining a removable denture, since urgent production of a new system is required.
Advantages of the Denta-Labor team
- Many years of experience More than 20 years in the dental services market
- Modern equipment Expert class dental devices
- Denta-Labor's own training center conducts training courses for dental technicians in Moscow
- Individual approach The client’s wishes and existing orthopedic problem are taken into account
- No unnecessary additional services Completion of work according to a pre-agreed estimate
- Courier delivery We will deliver the dentures as soon as possible
Relocation technique
Orthodontists use two main types of denture relining.
- Clinical . It is limited by the patient’s intolerance to certain synthetic components that cause allergies, or chronic diseases of the oral mucosa.
- Laboratory . The most secure, reliable, convenient.
Only the attending physician chooses a technique based on the patient’s current condition, associated issues, and clinical picture.
What it is
Relining is the correction of an insert structure to improve the fit of the prosthesis to the gum and restore chewing functions. In addition, the rebased design should ensure the correct bite of the teeth when closing and opening the jaws.
If you neglect this procedure, you can get the following complications:
- breakage of the prosthesis;
- deformation and loss of supporting teeth;
- inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Relocation cost
| Name | Price from | |
| Relining a partial denture | excluding cost of prints | 5500 rub. |
| Relining a complete removable denture | excluding cost of prints | 5500 rub. |
| Repair of acrylic prosthesis | simple, excluding the cost of prints | 3000 rub. |
| Repair of acrylic prosthesis | average, excluding cost of prints | 3000 rub. |
| Repair of acrylic prosthesis | complex, excluding the cost of prints | 3000 rub. |
| Taking impressions | Complex | 2000 rub. |
Nylon and polypropylene prostheses
Continuing the topic of removable dentures using injection molding, I would like to dwell on dentures made of nylon and polypropylene.
First, let's compare the advantages and disadvantages of nylon and acetal prostheses (Table No. 1).
Table No. 1. Advantages and disadvantages of nylon and acetal prostheses
Nylon dentures | Acetal dentures | |
| Advantages | 1. They don't break. 2. Do not cause allergies (except for cases of individual intolerance to nylon). 3. Do not require treatment of supporting teeth. 4. They do not damage the enamel of the supporting tooth. 5. Good cosmetics (not noticeable in the oral cavity). | 1. They do not break (fracture is possible when deformed at an angle of 90° or more). 2. Do not cause allergies (except for cases of individual intolerance to acetal). 3. Do not require treatment of supporting teeth. 4. They do not damage the enamel of the supporting tooth. 5. Good cosmetics (not noticeable in the oral cavity). |
| Flaws | 1. Plastic teeth do not chemically bond with nylon, frequent loss of plastic teeth, formation of dental plaque between the teeth and the nylon base. 2. Relining, repairing and welding of the tooth is impossible (in case of loss of one’s own teeth and changes in the alveolar process, which shortens the life of such a prosthesis to six months). 3. The chewing load is not distributed between the teeth and the alveolar process (jaw); as a result, atrophy of the alveolar process of the jaw. 4. Poor fixation with short teeth and an unpronounced equator. 5. It is poorly polished, and hence the next disadvantage: after about six months, the prosthesis changes color and becomes rough. Also, as a result of constant loads, the structural and optical properties of the material change. Thus, the main advantage of flexible nylon prostheses - excellent aesthetics - disappears very quickly. And the cost of a nylon prosthesis, mind you, is several times higher than that of a proven acrylic removable prosthesis. | 1. Insufficient transparency of the material, resulting in less aesthetics compared to nylon. 2. It cannot be used for the manufacture of denture bases, only for the clasp frame. 3. The need to use acrylic plastic as a base material. Possibility of fracture if deformed at an angle of 90° or more. 4. Poor fixation with short teeth and an unpronounced equator. These are disadvantages: they, of course, do not outweigh the advantages, but at the same time they exist. |
Next, as usual, I will start with indications and contraindications, as well as possible designs.
Removable dentures made of nylon and polypropylene have one significant drawback: their relocation is practically impossible due to the complexity and high cost of its implementation. Relining a nylon or polypropylene prosthesis is comparable in cost to making a new prosthesis, and the quality of the prosthesis after relining leaves much to be desired. That is why I would exclude the concept of relining nylon and polypropylene prostheses from the description of such prostheses altogether.
Taking into account the impossibility of simple relining of nylon and polypropylene prostheses, we will consider the indications and contraindications. Nylon prostheses have historically been intended for patients in dangerous professions, such as the US military and police, and these prostheses have also been successfully used for prosthetics for patients with epilepsy. This application was due to the fact that nylon prostheses cannot be broken and injured by fragments of the prosthesis, as is the case with acrylic prostheses.
The main properties: flexibility, strength, lack of allergies and transparency - determine the indications for the use of nylon prostheses.
But, oddly enough, these indications are quite narrow. First of all, these are patients with dangerous professions and conditions: military personnel, firefighters, police officers, and so on - and patients who cannot control their condition, such as epileptics. Secondly, patients with allergies to acrylic.
In other cases, the best result can be obtained by using other materials.
The main disadvantage of nylon prostheses is the difficulty of polishing and low abrasive resistance. What does this mean? It is difficult to polish a denture, and after a short period of wear, a polished denture loses its shine. The flexibility of the prosthesis and the lack of a chemical bond with artificial teeth lead to the formation of black microbial plaque between the artificial teeth and the base. However, despite the shortcomings, prostheses were and are in great demand among patients.
The demand is primarily due to the fact that nylon prostheses are flexible and, unlike acetal (which I wrote about in a previous article), transparent and, accordingly, more aesthetic. Patients are attracted primarily by the absence of metal support clasps, as well as the absence of the need for support crowns, as in clasp prosthetics with attachments and locks.
Although many dentists and patients believe that the flexibility of a removable denture is a benefit, this is actually not the case, especially when it comes to complete dentures. The fact is that the flexibility of nylon is needed in the manufacture of supporting elements (clasps and pelots), but a complete removable denture does not have them by definition. In addition, significant replacement of lost alveolar processes with the base of the prosthesis negates all the flexibility of the material. Well, the low abrasive resistance of the material and the unsightly appearance of such prostheses after a short time of wear make one think about the advisability of using nylon in each specific clinical case.
Most likely, it was the disadvantages of nylon that forced manufacturers of dental materials to intensify research in the search for a material that would combine the advantages of acrylic, acetal and nylon as much as possible. There are many varieties of nylon with varying degrees of hardness and abrasion resistance. Although they all leave much to be desired.
So far, the closest to this ideal is polypropylene. Although, like nylon, it cannot be relined as easily as acrylic.
Polypropylene has several distinctive features from nylon. Polypropylene is better polished and less likely to scratch during use. Due to greater rigidity than nylon, in polypropylene prostheses there are practically no gaps formed between artificial teeth and the base and no microbial plaque is formed in them, although, like nylon, polypropylene does not chemically bind to artificial teeth. In addition, the greater rigidity of polypropylene makes it possible to make retaining elements (clasps and pelots) of a smaller size than from nylon.
Let's look at what kind of prostheses can be made from nylon and polypropylene. The worst option for these materials is a complete denture.
But, fortunately, there are very few patients who need complete removable dentures made of nylon or polypropylene.
Partial dentures
Polypropylene is well suited for small removable dentures for one to three teeth with dentoalveolar pads. Such microprostheses are practically invisible in the mouth and adhere perfectly to the supporting teeth, of course, if these teeth have an equator. When making larger partial dentures, there are a number of rules that must be followed.
As with acetone dentures, polypropylene dentures can be used to treat any defect in the dentition that can be replaced with partial removable dentures. A complete contraindication is the absence of an equator on the supporting teeth, which can most often be observed on stamped crowns and quite often on fangs.
A relative contraindication is a deep palate, since the prosthesis may not fit tightly to the mucous membrane in the palate.
When making dentures from polypropylene, you should not use reversible clasps.
Prints and models
In my opinion, the best materials for taking impressions for polypropylene dentures are silicone impression compounds for removable dentures.
Models, including those for casting prostheses, must be made of class 4 supergypsum with a Brinell hardness of at least 250 N/mm2.
Stages of manufacturing polypropylene prostheses
We cast two models using a silicone impression. One is working, and the second is for casting the prosthesis. We remove from the model all the sagging and balls formed as a result of filling the print defects with plaster. We plaster the working model with the antagonist model into the articulator. We perform occlusal grinding of the working model and antagonists. We mark the model and draw the outline of the future prosthesis using a water-soluble pencil (Fig. 1, 2).
Rice. 1. We mark the model and draw a drawing of the outline of the future prosthesis using a water-soluble pencil.
Rice. 2. We mark the model and draw the outline of the future prosthesis using a water-soluble pencil.
Base wax with a thickness of 1.25 mm is excellent for modeling the arches of the upper and lower dentures. The modeling of the prosthesis itself does not differ from the modeling of a conventional removable denture, with the exception of the places where the clasp exits from the base of the denture. It is important to remember that when installing an artificial tooth next to an abutment tooth, you need to leave enough space for the clasp body, so we first model the full profile of the clasp, and then install the artificial tooth.
If in the process of making dentures it is necessary to try on the arrangement of teeth on wax, then first we make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture, and then we reduce the wax composition and model the clasps or pelots (Fig. 3-12).
Rice. 3. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 4. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 5. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 6. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 7. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 8. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 9. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 10. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 11. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture. Rice. 12. We make a wax composition that is absolutely similar to a standard removable denture.
The final modeling is carried out on the second model, intended for casting the prosthesis. To do this, we transfer the wax composition with teeth from the model, plastered in the articulator, to the second model and very carefully bring the shape of the wax composition to the final form of the prosthesis (Fig. 13-14).
Rice. 13. Final modeling on the second model, intended for casting the prosthesis.
Rice. 14. Final modeling on the second model intended for casting the prosthesis.
The edges of the wax composition should be well adhered to the model, there should be no excess wax on the artificial teeth, and the wax should be polished (Fig. 15-16).
Rice. 15. The edges of the wax composition must be well molded to the model.
Rice. 16. The wax must be polished.
Before plaster casting the model into the casting ditch, we file down the plaster teeth so as to eliminate undercuts (Fig. 17-18).
Rice. 17. Before plaster casting the model, we file down the plaster teeth into the casting cuvette.
Rice. 18. Before plaster casting the model, we file down the plaster teeth into the casting cuvette.
Lubricate the inner surface of the casting cuvette with petroleum jelly and mix 300 grams of third-class gypsum and 90 ml of distilled water in a vacuum mixer. While mixing the plaster, place the model in water. After filling the lower part of the cuvette with plaster, we immerse the model with the base down to the beginning of the base of the prosthesis, as close as possible to the casting entrance. If necessary, we cover some parts of the plaster model with plaster to eliminate undercuts (Fig. 19-20).
Rice. 19. After filling the lower part of the cuvette with plaster, immerse the model.
Rice. 20. After filling the lower part of the cuvette with plaster, immerse the model.
After approximately 40 minutes, you can begin installing the gating system and pouring the second part of the cuvette (Fig. 21).
Rice. 21. Installation of the gating system.
To maintain uniform coloring of the prosthesis, it is advisable to use a wide flat sprue that smoothly converges to the hole of the cuvette, which is intended for injection of plastic (Fig. 22-24).
Rice. 22. To maintain uniform staining of the prosthesis, it is advisable to use a wide, flat sprue.
Rice. 23. To maintain uniform staining of the prosthesis, it is advisable to use a wide, flat sprue.
Rice. 24. To maintain uniform staining of the prosthesis, it is advisable to use a wide, flat sprue.
Mix the gypsum mixture in a vacuum mixer.
Before filling the cuvette, it is lubricated with Vaseline and collected. Water is poured into the cuvette for a few minutes, and before pouring the gypsum mixture, the water is poured out and the residue is thoroughly shaken off. After filling the second half of the flask with plaster, I recommend placing the cuvette in a vessel under pressure of 1 atmosphere. This is necessary so that air does not escape from the first plaster half and from the model, which can lead to the formation of pores in the plaster of the second half of the cuvette.
After 40 minutes, the cuvette, without disassembling, must be placed in boiling water.
After waiting until the wax begins to flow out of the hole in the cuvette, remove it from the water, disassemble it and rinse with boiling water.
After the cuvette has cooled, an insulating varnish can be applied.
For this article, I decided to use two methods of isolating plaster from plastic.
The lower jaw was insulated with a standard insulating agent from thermomolding polypropylene, and the upper jaw with a non-standard agent suggested to me by C. He suggested covering the plaster with photopolymer varnish (Fig. 25-28).
Rice. 25. Isolation of the lower jaw.
Rice. 26. Isolation of the lower jaw.
Rice. 27. Isolation of the upper jaw.
Rice. 28. Isolation of the upper jaw.
After isolating the gypsum, we assemble the cuvettes and proceed directly to casting.
For better casting results, the cuvette can be heated to 130 degrees, but even without heating it turns out quite well.
Polypropylene casting
Polypropylene is sensitive to heat: if you heat the polypropylene just 5 degrees higher than necessary, the color of the prosthesis will not be pink, but orange. And at the same time, it is worth underheating by 5 degrees to the optimal temperature, and we will end up with underfilling of the thin parts of the prosthesis. For each casting machine, it is necessary to experimentally select the casting temperature by casting several plates and assessing their color and the quality of the thin parts (Fig. 29).
Rice. 29. For each casting machine, it is necessary to experimentally select the casting temperature by casting several plates.
My J-100 is set to 265 degrees final temperature and 7 minutes of preheat. Press pressure 7.5 atmospheres.
Please note that diotic holes must be made in the teeth for fixation in the prosthesis (Fig. 30).
Rice. 30. Diotary holes must be made in the teeth for fixation in the prosthesis.
After casting and cooling the cuvette and removing the prostheses from the plaster, we can see the result of casting. The upper denture shines like a Christmas tree decoration, and the lower denture is matte. However, both prostheses have virtually no plaster residues. Both methods of isolation are clearly effective, but the method of Grigory Alekseevich Shalik is certainly more effective, and the prosthesis practically does not need to be polished (Fig. 31-34).
Rice. 31. The denture practically does not need to be polished.
Rice. 32. The denture practically does not need to be polished.
Rice. 33. The denture practically does not need to be polished.
Rice. 34. The denture practically does not need to be polished.
After fitting on models plastered in the articulator and polishing, the finished dentures can be sent to the clinic.
Polishing polypropylene requires some skill and patience from the dental technician. It is important to carry out processing and polishing at low speeds of the abrasive tool. After sanding, use a sharp scalpel to remove any fibrous material from the edge of the denture. For polishing, use water- or oil-based pastes designed for polishing plastics with a fine filler.
To add shine, use thread brushes.
Features of the clinical method
- Complete examination of the oral cavity, checking the integrity of the prosthesis.
- After analyzing the bite, the size of the marginal area is adjusted. The long one is cut off. Short - extended using quick-hardening plastic substances.
- A small layer of 1 mm will be removed from the prosthesis. The edge fragment loses polishing.
- Thorough impregnation of artificial elements with Vaseline.
- The boundaries of the marginal area are completely treated with a liquid polymer mixture.
- After the outer layer becomes dull, the prosthesis is put on by the patient. It is necessary to close your jaws tightly and hold in this position for a couple of minutes.
- The system is then polymerized in special equipment.
- After ten minutes of treatment, the prosthesis is removed to be adjusted manually. In the finale, he is immersed in hot water.
The advantages of clinical relining of a removable denture include the rapid elimination of existing deficiencies, as well as ideal accuracy. The disadvantages include the high porosity of the material, which reduces the hygiene of the system, and color changes.
Material used
Gasket materials used for relining are classified into three groups:
- solid permanent – their average service life is about 4 years;
- soft semi-permanent – recommended for use in clinical cases when the patient experiences discomfort while using prostheses while observing all parameters and characteristics.
Most often, this is the lower jaw, since it is there that there is less space to evenly distribute the load; - temporary soft ones - their service life is no more than 2 weeks. The materials are specially developed for use for medical reasons.
The most common:
- Sofreliner S;
- Mollosil;
- Rebase II;
- GC Coe-Soft.
The process of processing prostheses made from various materials is presented in the video.
Permanent Solid Padding Materials
To ensure a tight fit of the prosthesis to the mucous membrane, a solid lubricant is used.
There are two methods for restoring the fastening of the structure : cold-curing acrylic plastic, used during the restoration of a removable jaw, and hot-curing acrylate applied in the laboratory - a fabric identical to materials for the manufacture of dentures.
The first type of cold-curing resin contains methyl methacrylate , which injures soft tissues and causes discomfort in patients. Hot-curing plastics contain other components (polyethyl methacrylate - PEMA and butyl methacrylate), which do not harm the mucous membrane, but at the same time reduce the glass transition temperature.
A definite disadvantage of cold-curing plastic is an unpleasant taste, loss of color over time, and an increased exothermic reaction. It is also quite difficult for the dentist to measure the required amount of material when removing a denture or to determine the thickness of the layer for relining.
Important. Since the permanent adjustment of the artificial jaw is performed for a long time (two years), it is worth giving preference to the method carried out in the laboratory.
Semi-permanent soft lining materials
Such materials are used when the patient is unable to wear a prosthesis with a solid base due to the destroyed edge of the alveolar process.
Among soft gaskets, there are silicone polymers , which have a low glass transition temperature, and plexiglass - or in other words polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), a thermoplastic plastic. To lower the temperature of the latter, plasticizers are used - substances that add plasticity to polymers.
Silicone polymer (rubber) hardens when heated using an organic compound - benzoyl peroxide, or at room temperature using tetraethyl silicate ether.
The weak point of the material is considered to be insufficient adhesion to the base of the PMMA prosthesis, which threatens the destruction of the connection. Silicone rubber also leads to the development of stomatitis.
Another type of soft spacers is acrylic , which is firmly connected to the base of the dental chewing device.
There are polymers that can be dissolved by plasticizers and systems of copolymerizing plasticizers..
In the first group, the polymer is a powder - a mixture of PEMA and PMMA and a liquid - MMA (methyl methacrylate ether), containing 25-50% plasticizer. Organic compounds of polymers are gradually leached and the substance ceases to be flexible. To protect the material from destruction, follow the denture cleaning regimen.
The second type of compounds withstands dissolution . The liquid is combined with either PEMA or copolymers (l-butyl and ethyl methacrylate). At room temperature, the substance is solid, which helps to process it better, and it softens at oral temperature.
Reference. The duration of wearing soft cushioning materials is no more than six months.
Temporary soft cushioning materials
Tissue conditioners are temporary extremely soft dentures applied to the base of the dental structure in order to equally distribute chewing force and pressure and cope with the inflammatory process of the oral cavity.
The substance consists of PEMA powder , which when mixed with ethyl alcohol, an aromatic ester and a plasticizer creates a gel. Alcohol and plasticizer are leached, so the conditioner is periodically renewed to speed up the healing of the mucous membrane. You should clean your denture regularly, otherwise bacteria will appear.
An alternative is to reline the prosthesis from polyamide, polyurethane, polycarbonate, etc. Their difference is increased flexibility, which is why they are often referred to as “flexible prostheses.”
There are modern removable dentures that have the advantages of classic acrylic dentures and flexible nylon ones - among them, the relining of the Acri Free prosthesis stands out.
Like nylon structures, they are elastic and comfortable to wear , and, like acrylic ones, they are strong, durable, adjustable and repairable.
Removable dental structures are made from non-allergic material.
They are fixed on the teeth using pink plastic clasps that match the color of the gums.
Relining of removable dentures using the laboratory method
- The work is performed by a technician in a laboratory.
- The degree of wear of the prosthesis, quality of manufacture, and tightness of fit in the mouth are assessed.
- A control impression is made for transmission to the doctor.
- The surface of the prosthesis undergoes special treatment.
- A copy of the impression and the system are lowered into a ditch, after which they are filled with diluted plaster.
- The cast is taken out, and the resulting void is filled with polymerizing plastic.
- The excess is cut off, after which the product is polished.
The main advantages of the laboratory technique include the absence of contact between the mucous membrane and the plastic, a strong connection between the old and new layers, and an excellent aesthetic appearance. The disadvantages include the length of the process. The patient is forced to go without a prosthesis for several days; errors are possible that require additional time to eliminate defects.
A special case
It is worth talking separately about the relining of the prosthesis when the bite is reduced, since this process has some peculiarities.
During the procedure, you should always pay attention to the central occlusion ratio, since it can change due to ongoing atrophic processes.
The interocclusal gap is determined as follows:
- A small amount of thermoplastic polymer is placed between the patient's teeth.
- The specialist takes measurements of the height of the lower third of the patient’s face at rest and when the jaws are closed.
- Based on the obtained measurement results, the optimal variant of the interocclusal gap is determined.
In accordance with the results obtained, polymer is applied to the prepared surfaces of the prosthesis, and the boundaries are re-processed using special molding tests.
After this, the prosthesis is installed in the patient’s oral cavity, where the normal closure of the dentition is checked.
Frequently asked questions - answers:
Which prosthesis is better to choose - domestic or imported?
Perhaps, from an aesthetic point of view, our products are inferior, but in practice they turned out to be much stronger and more reliable than imported dentures.
Why is the denture, which I have been using for less than a year, constantly getting in the way and falling out? This has already begun to cause psychological discomfort.
The implant was simply not adjusted to the end. We advise you to do a relocation; do not worry, there is nothing painful or scary in this procedure.
Why do I need to reline the prosthesis if nothing bothers me?
Reliable fixation of the prosthesis is an extremely important condition for the full functioning of the entire dental system. And, of course, comfort. Any artificial teeth need to be looked after - cleaned and regularly shown to an orthopedic dentist.
To order denture relining in the dental laboratory Denta-Labor, send a request from the website or call the number: +7(495) 162-08-25.
Dyatlov Evgeniy Valerievich
Head of the Denta-Labor laboratory and teacher at the training center organized at the laboratory.
Graduated from Stavropol Basic Medical College.
Author of the article: Scientific team of the dental laboratory Denta-Labor
- Studied in Germany with Dr. Karl Peter Meschke in the course of complete removable prosthetics.
- I attended a course of lectures at the German Dental Academy based at BEGO (Bremen).
- Completed a week-long internship in Germany at the BEGO company on new technologies and materials for removable prosthetics.
What is denture correction?
The procedure that improves the fit of the denture to the mouth and provides maximum retention is called correction or relining.
- Dentures are first adjusted during the manufacturing process to eliminate design errors and defects. The material used for production may be deformed. The procedure helps remove discrepancies and ensure that the artificial teeth fit the patient.
- The need for correction arises during a person’s adaptation to the structure. In the first days of wearing it, an unpleasant sensation is felt in the mouth. The new prosthesis gradually settles and puts pressure on the mucous membrane. The dentist must grind down the material in the area of excessive pressure and remove roughness.
Over time, any prosthesis requires adjustment. The bone mass of the gums decreases, and natural changes occur in the oral cavity. Gradually, the structure loses its fixation and begins to adhere poorly to the tissues. In addition, impacts and prolonged use may cause damage.
Each prosthesis requires correction over time
Reviews
— Albert
I really liked the level of service and attitude of the staff.
- Eugene
They saved me, there’s no other way to put it. Thank you for the speed and decency. Everything as promised!! I recommend to all!!!
- Svetlana
This is not the first time we have used denture repair services. As always FAST AND HIGH QUALITY! Thank you for your promptness and understanding!!
— Ksenia Vladimirovna
My daughter’s denture broke on the eve of her wedding, I was very upset, but Denta-Labor managed to fix it very quickly and efficiently, thank you.
Delivery areas:
- Altufyevo
- Bibirevo
- Biryulyovo East
- Central Administrative District
- Chertanovo
- Golyanovo
- Krasnopresnenskaya
- Kuntsevo
- Kuzminki
- Odintsovo
- Lyublino
- Medvedkovo
- Mitino
- Otradnoe
- Pavshinskaya floodplain
- Printers
- Polezhaevskaya
- River Station
- Ryazan Avenue
- SAO
- Northern Butovo
- Sokolniki
- NEAD
- SZAO
- Tushino
- Southern Administrative District
- SEAD
- South-Western Administrative District
- Voikovskaya
- Vykhino
- Company
- Zhulebino
- Aprelevka
- Dubki
- Krasnoznamensk
- Krylatskoe
- Cuban
- Nazaryevo
- Barvikha
- Vlasikha
- VNIISSOK
- Vnukovo
- Larks