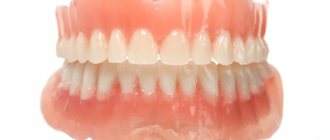
Even 20 years ago, it was difficult to restore teeth efficiently, since it was necessary to secure dentures to the few remaining units. The task became especially difficult with complete edentia. The only option was a removable structure, which was fixed on the gums with suction cups. But it causes a lot of inconvenience: it often rubs the mucous membrane, under the influence of stress it becomes deformed and displaced, does not allow you to smile, talk and eat normally, and can fall out of your mouth at the most inopportune moment.
There is no need to endure such discomfort now. Comfortable removable dentures with artificial roots have become a worthy and high-quality alternative to removable devices.
Types of prosthetics on implants
Implantation is significantly superior in quality to conventional prosthetics, as it restores not only the crown of the tooth, but also its root part, and also prevents bone tissue atrophy.
There are two types of prosthetics on implants:
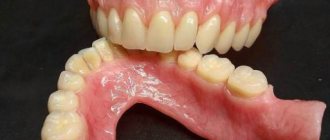
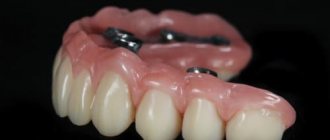
- Removable (more often called conditionally removable). By fixing dentures on implants, it is possible to get rid of all the disadvantages of false jaws. They do not fall out of the mouth, do not require daily removal, a few titanium rods are enough for fastening, and can be easily removed if necessary. Most often they are recommended for complete edentia, less often - in the absence of several adjacent teeth.
- Fixed. Depending on the number of missing units, crowns or bridges are used. In edentulous cases, the number of artificial roots (four, six, eight, ten or twelve) is determined taking into account the condition of the bone and the clinical situation.
Types of dental implantation
To date, there are no generally accepted standards for dental implantation procedures. In addition, implants are produced by several companies that produce models that differ in shape, structure, composition of components and installation protocols.
Experienced implantologists have to keep abreast of emerging new products and independently select types and methods of implantation depending on the specific situation, the individual anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient, as well as his requirements and financial capabilities.
Therefore, there are different types of dental implantation, differing in how the implants are placed, where and for what purpose.
Endosseous implantation
This is the most widespread modern method of intraosseous dental implantation, the essence of which is that a metal implant is implanted into a previously prepared bone bed. The shape of implants can be either root-shaped screw or plate-shaped, cylindrical, etc. But most often in endosseous implantation it is screw implants that are used - it is possible to install on them both a single crown and a bridge-like prosthesis and a complete prosthesis - using the All-on-4 or All-on-6 technology.
Therefore, when people talk about dental implantation today, they almost always mean endosseous implantation. The translation of this word from medical Latin means “inside the bone,” since implants are implanted precisely inside the bone tissue of the jaw. Titanium elements are used for this. Titanium is one of the most biocompatible metals, which is proven by the widespread practice of using titanium structures in a wide variety of fields of medicine. It is enough to mention that complex bone fractures are also corrected by installing titanium elements. Titanium prostheses, taking root and merging with the bone, provide strong fixation and ideal functionality of orthopedic structures.
Two-stage dental implantation
Prosthetics in 2 stages - 1) installation of an implant, and 2) installation of a crown or prosthesis - allows you to restore the integrity of the dentition in the most natural and gentle (for the body) way. The only drawback is the long time, which is even longer if it is necessary to do bone grafting, as well as in the presence of chronic diseases that slow down the process of engraftment of the material.
Typically, two-stage dental implantation involves the implantation operation itself in the first stage and the quiet engraftment of the implant under the tightly sutured gum. The penetration of infection is excluded here (if the operation is done correctly and carefully, and also if there is no accidental injury to the gums after the operation), and the absence of chewing load allows the titanium root to fuse with the jawbone more quickly and safely.
Although some experts believe that moderate and adequate chewing load stimulates bone tissue to regenerate and improves osseointegration, it is still most often considered as a risk factor.
One-stage dental implantation
It would be more accurate to call this type of implantation one-stage. With one-stage dental implantation, immediately after surgery, a gum former is installed on the implant - this allows you to shorten the entire procedure by several weeks (the period of time for the formation of a beautiful natural gum contour).
The main advantage is the ability to more quickly provide complete aesthetics of the dentition. The main disadvantage is a slight increase in the risk of complications, since the postoperative wound is not completely covered with a gum flap, but is adjacent to the protruding edge of the abutment - i.e. The risk of infection increases slightly.
Express dental implantation
The use of “fast” methods of dental prosthetics on implants allows the use of various methods of treating the surface of implants - giving them roughness, microporosity, simulating the properties of bone tissue, as well as increased hydrophilicity - wettability. This ensures better wetting of the implant surface with blood, faster deposition and attachment of cells that cause bone tissue growth.
In addition, various forms of thread have been developed and used to reduce drilling time (and reduce the risk of bone overheating), reduce trauma and improve the adhesion of the implant to the bone tissue - primary stability. Modern implants immediately hold well, so you can immediately install an abutment on them, as well as a crown.
The express dental implantation method makes it possible to obtain artificial teeth extremely quickly, literally in one visit to the implantologist. Most often, this method is used in cases where the patient cannot remain without teeth for several months.
Dental implantation in 1 day
The benefits of quick installation of implants and crowns (or dentures) are obvious: a reduction in the duration of prosthetics, a reduction in the number of visits to the dentist, and a reduction in time and finances. But there are also disadvantages that are not mentioned in advertising.
We can at least start with the fact that dental implantation in 1 day is not available to everyone. It implies more stringent requirements for the condition of the oral cavity, the volume of the jaw bone, and the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient. Those. in many cases it will not be possible for purely medical reasons.
The second important nuance is that there will still be more than one visit to the dental office. In the beginning, you will have to do tests, pictures of the jaw, take impressions, and wait for the crowns to be made. After the operation, it will be necessary to come for regular examinations so that the doctor can monitor the healing of the implants and take the necessary measures in time if there is a risk of complications.
In addition, permanent crowns and dentures are almost never installed immediately after surgery. They use temporary ones. And in a few months you will still have to come and replace them with permanent ones.
And most importantly, there is a higher risk of complications and the development of peri-implantitis - inflammation of the tissue around the implant, causing rejection of the artificial structure. With this development of the situation, there is a very high probability that the implant will have to be removed and the entire procedure will have to be repeated again.
Risks can be reduced not only by the highly qualified and extensive experience of the doctor, but also by the careful strict fulfillment of all his requirements by the patient, the cessation of bad habits (smoking, alcohol) during the healing period of the material, an extremely gentle regime for installed artificial teeth, and the complete elimination of increased loads. on them.
Implantation of upper teeth
Installation on the upper jaw has a number of features. Due to the fact that when chewing food, the upper jaw experiences less stress, its bone is less dense and more prone to resorption (atrophy) in the absence of teeth. Therefore, the first feature of implantation of the upper teeth is the almost obligatory bone grafting. It is most often not possible to install implants in the upper jaw without increasing bone volume.
The second important feature is the proximity of the maxillary sinuses to the jaw. As a result, implantation of upper teeth always requires special precision and care. With a slight deviation from the calculated position, the implant can easily pass through the bone and injure the sinus tissue located behind it. This is associated with a type of bone grafting for implantation in the upper jaw called sinus lift.
It consists in lifting the soft tissues and mucous membrane of the sinus, next to which the material will be installed, and placing a special osteoplastic material under them. After this, it is necessary to wait some time until the extended fragment is completely engrafted, and only then perform implantation. In some cases, installing an implant in the zygomatic bone can help avoid the need for a sinus lift or other bone grafting.
Zygomatic implantation
Currently, special implants installed at an angle into the zygomatic bone have been developed and are actively used. This makes it possible to perform implantation in the upper jaw for those patients for whom it is impossible to undergo a sinus lift or otherwise increase the volume of the upper jaw bone.
Zygomatic implantation is one of the most complex types of implantation. Due to the large length of the implant (up to 50 mm) and the complex shape of the bone in the upper jaw, the operation must be performed with maximum precision and accuracy. Therefore, the implantologist performing it must have experience not only in dental implantation, but also in maxillofacial surgery.
For zygomatic implantation, implants from the Nobel Zygoma line are used. They have both a regular platform and an inclined platform, which allows you to install a standard straight abutment on such an implant. Zygomatic implantation most often involves the installation of 2 implants (one on each side). This makes it possible to perform complete prosthetics of the upper jaw using the All-on-4 system, installing the prosthesis on 4 implants, 2 of which will be zygomatic.
Implantation of lower teeth
The lower jaw is characterized by greater bone density and thickness, it is less susceptible to atrophy even with the loss of teeth, so it is very often possible to place larger implants on it without any bone grafting. Another feature of implantation of the lower teeth is due to the fact that it is on this jaw that the main load falls during chewing of food. It follows that implants in the lower jaw must be very strong and provide full functionality of artificial teeth. But the requirements for aesthetics here are not so stringent due to the fact that the teeth on the lower jaw, even in the smile zone, are usually less visible than the upper ones. Therefore, for implants in the lower jaw, the main thing is increased strength and functionality.
Dental implants in the lower jaw require more aggressive threading to facilitate insertion into the dense mandibular bone. The requirements for positioning accuracy here are also not as high as in the upper jaw. However, implantation in the lower jaw also has its own difficulties. In particular, the mental nerve passes through it, and when injured, various complications can arise - from pain to loss of sensitivity of the lower jaw. Therefore, installing implants in the lower jaw requires attention and more labor-intensive work from the implantologist.
Front teeth implantation
The installation of artificial teeth in the anterior part places increased demands on aesthetics. It is these teeth that are clearly visible when smiling (the upper ones are a little better than the lower ones), so it is especially important here to do everything carefully and select materials for abutments and crowns so that the structure does not show through the crown, for example, when choosing a zirconium dioxide crown, it is advisable to choose an abutment from the same material.
In addition, when implanting the front teeth, it is necessary to carefully perform gum plastic surgery, forming a beautiful contour that fits tightly to the neck of the implant so that the artificiality of the prosthesis is not noticeable.
When restoring one tooth using the classical two-stage implantation method, while the material is healing, a butterfly prosthesis can be installed in place of the missing tooth, which is attached to adjacent teeth using special dental glue.
However, in the absence of contraindications (and there is no need for bone grafting), it is often recommended to perform one-stage implantation with immediate loading. In this case, the overall implantation time is reduced, and the patient already on the day of surgery (or in the next day or two) receives a fully functional jaw and a beautiful smile.
Implantation of chewing teeth
Despite the fact that the posterior (chewing) teeth very rarely come into view and are usually not visible, terminal defects of the dentition (loss of the outer teeth) cause patients a lot of inconvenience, since it is these teeth that bear the main chewing load. The situation becomes more complicated if the outermost lateral teeth are missing, since it is impossible to install even a regular bridge prosthesis - there is no support for it on one side.
Implantation of chewing teeth can save the situation. Implantation with immediate loading can be considered as an option, but the optimal option in this case would be classic two-stage implantation.
Full dental implantation
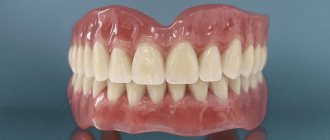
In case of complete absence of teeth, implantation is practically the only reliable alternative to constantly falling out dentures. It is reliable fixation, combined with excellent aesthetics and full functionality, that is the main advantage of full dental implantation.
It can be performed using All-on-4 or All-on-6 technology. Theoretically, it is possible to install 14 individual implants with separate crowns in each jaw, but the cost of such prosthetics will simply be off the charts. And the volume of bone tissue does not always allow this. It is much cheaper and easier to use the “all-on-four” or “all-on-six” technology, which involves (as is clear from the name) the installation of 4 (6) implants on each jaw and the fixation of a fixed prosthesis on them.
This technology makes it possible to obtain a fixed prosthesis within a few days, and in most cases it is possible to do without bone grafting even with severe atrophy of bone tissue.
Basal implantation
This type of implantation involves installing implants of increased length into the basal layer of bone - more dense and not subject to atrophy. Fixed prostheses can be installed on installed implants already on the second day thanks to a special thread design that ensures very high primary stability. In this case, special implants with a permanent abutment are used. Basal dental implantation allows for complete prosthetics, but All-on-4 or All-on-6 technologies are more often used, as they are simpler and more economical. Although basal implantation provides a more uniform load distribution and allows the use of a more anatomical shape of the prosthesis.
Other types of dental implantation
In the past, other types of dental implantation were used, such as endodontic-endosseous implantation - an attempt to preserve a natural tooth, reducing its mobility by implanting special implants through the tooth canal. Today, this technology has fallen out of use, since preserving a tooth in this way is unreliable and very artificial, leaving the possibility for tooth remains to become a source of inflammation at any time.
Subperiosteal implantation involves placing a kind of metal frame with protruding supports under the soft tissues of the gums and periosteum, onto which the orthopedic structure is later fixed. Today this technology is also considered obsolete.
Transosseous implantation involved the installation of pins that pass through the jaw and are fixed to the lower part of the jaw with a special bracket. Due to its great complexity and traumatic nature, this technology is also not used today.
Contraindications
You will have to refuse prosthetics on implants if there are contraindications to the implantation of titanium rods:
- violation of blood clotting properties;
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus;
- weakening of the tone of the masticatory muscles;
- tuberculosis and other serious respiratory diseases;
- inflammatory processes, benign and malignant tumors in the oral cavity;
- presence of untreated teeth;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- nervous disorders;
- AIDS, HIV;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- undergoing radiation therapy;
- inability to use anesthesia.
Types of fastening structures
There are two ways to fix a removable denture on an implant:
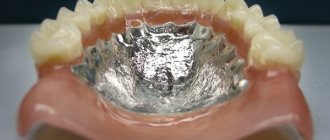
- Beam connection.
Pins (at least four) are screwed into the jaw bone and a metal beam is placed on them. Thanks to it, it is possible to unite and stabilize artificial roots, avoid loosening and falling out of the structure, which ensures long-term operation. In addition, this method allows you to evenly distribute the load and restore the jaw.
On the inside of the beam, metal locks are installed that secure the removable device. If necessary, it can be easily removed.
- Ball-shaped fixation
Holes are made at the base of the structure, with the help of which it is secured to an abutment with a round head. This option, despite its lower reliability, is in high demand among patients due to its low price. A removable denture of this type gradually loosens and becomes mobile, and therefore requires frequent replacement. In addition, it unevenly distributes the chewing load, which can cause discomfort and restrictions in food choice (due to the inability to chew hard foods).
Dentures for completely edentulous upper jaw
Up to 8 implants are implanted into the jawbone from above, since the bone here is loose and subject to atrophy (compared to the lower jaw). In some cases, removable prosthetics of the upper jaw are organized on 4-6 implants, if the density and size of the bone allows.
If there is a significant deficiency of bone tissue, there is a risk of injury to the maxillary sinuses, then a sinus lift is performed first or mini-implants are used.
Mini-sized artificial roots are not the best option for fixing removable dentures on the upper jaw. Titanium roots will not stick to loose fabric. If mini-products are implanted, the Locator fixing mechanism is used.
How many artificial roots are needed?
Theoretically, two titanium rods are enough to secure the removable system. In this case, it is possible to significantly reduce the cost of treatment, but at the same time the performance properties of removable appliances are significantly deteriorated: the fastenings become loose, the structures do not fit tightly to the gum (it often atrophies) and are displaced. As a result, the aesthetics of the smile deteriorate, discomfort and pain arise, and you have to give up solid food. Therefore, dentists recommend screwing four screws into the lower jaw, and six into the upper jaw.
Planning
After analyzing the collected information, the implantologist evaluates the examination results and presents available treatment options. The patient receives information about possible alternative solutions, stages and timing of upcoming dental implantation. The cost of the treatment plan and prices depend on the number of implants, the brand of the manufacturer, and the characteristics of the clinical picture.
Prosthetics on mini-implants
In addition to conventional pins, minimally invasive smaller models can be used to attach removable devices, allowing prosthetics to be performed immediately after implantation. Patients choose them if it is impossible to install classic artificial roots or if they want to save money. Miniature products have almost no contraindications; they can be installed even with significant thinning of the bone tissue.
But mini-implants also have a significant drawback. Due to their small size, they are unable to withstand significant loads for a long time, which reduces their service life to 2–3 years. In the future, they will cause the same discomfort as conventional removable dentures.
Complete removable lower jaw prosthesis
For lower jaw prosthetics, up to six artificial roots should ideally be used. But if the bone tissue allows, 2 to 4 implants (whether classic or mini-products) are permissible to fix a removable denture. This is due to the increased density and thickness of the lower jaw bone.
When implanted with titanium roots into high-quality jawbone, structures of any length and diameter have excellent primary stability.
The use of traditional implants is always preferable, but in the case of the lower jaw, the installation of mini-implants is justified for the patient.
Installation steps
Before inserting a pin into the gum, the specialist carries out preparatory measures, which include a diagnostic examination and sanitation.
First, the dentist directs the patient to:
- orthopantomogram (if there are a large number of missing teeth, a computed tomography scan will be needed);
- general blood test (if there are chronic diseases or implantation under anesthesia is planned, then an extensive diagnosis is performed).
Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines whether there are any contraindications to the procedure, and also examines the structure of the bones and the structure of the jaws. If necessary, he can give a referral to a specialist to determine the possibility of surgical intervention.
You should not refuse sanitation, which significantly reduces the number of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. Otherwise, the risk of implant rejection increases.
In case of bone tissue atrophy, osteoplasty is performed (only with classic two-stage implantation) to ensure reliable fixation of artificial roots. After the procedure, you will have to wait about six months for the bone material to take root well.
The installation of removable systems on implants is carried out in two stages:
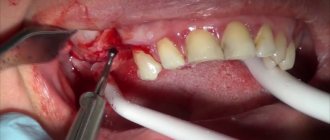
- a titanium screw is inserted into the gum (the process takes no more than 40 minutes). In the classic protocol, a patchwork method is used: the gum is peeled off, a bed is formed, a pin is screwed in and sutures are applied. Mini-models are fixed without incisions, which ensures minimal invasiveness of the procedure;
- perform prosthetics. With two-stage implantation, prostheses are installed only after high-quality implantation of the supports in the bone (after 3-6 months), and when using mini-models - after 2-3 days.
Alternative Methods
All options considered involve the implantation of screws into the bones. Nowadays all implantation materials are screwed in this way. An artificial metal root completely replaces the natural one. The implant has a similar appearance and is placed in almost the same area. Additional segments may be affected at greater depth.
Intramucosal technology for installing dental implants
The pin is not screwed into the bone structures, but directly into the gums and a little deeper. This way the installed structure will not fall out. Outwardly, it resembles buttons, and not an imitation of the root part of the unit.
The technique is gradually becoming a thing of the past due to its fragility. There is a high probability of complications (injury, inflammatory processes).
Endodontic-endosseous method
This option is also outdated. A device in the form of a small awl is inserted into the root canal, then it is moved slightly beyond its limits and fixed in hard tissues. It was used mainly in the presence of a mobile or broken incisor, canine, or molar. Such fixation is difficult to implement and becomes loose over time. The technology is not suitable for long-term restoration and is indicated for patients with narrow-shaped canals.
Mini implantation
How dental implants are inserted: tooth installation technology involves shallow immersion into bone structures. Over time, the pins become loose, the fastenings wear out, which means the prosthesis becomes mobile and causes severe discomfort.
This method is welcomed only as a short-term method while the patient is undergoing long-term therapy. For example, this happens when restrictions are discovered on the use of more “long-lasting” techniques. The treatment period is up to 5 days. The prosthetics are removable; screws can be inserted even in cases of complete edentia.
Advantages of orthopedic structures on implants
Prostheses that are installed on artificial roots are characterized by several advantages:
- lightweight, compact in size;
- provide a highly aesthetic smile;
- restore the proper functioning of the maxillo-oral apparatus;
- are securely attached and do not fall out of the mouth;
- do not require the use of fixing creams and daily removal;
- relieve complete edentia;
- evenly distribute the chewing load, thereby preventing atrophic processes in bone tissue;
- have a reduced palatal overlap, due to which they promote rapid addiction, do not provoke a gag reflex, and do not distort the taste of food;
- last twice as long as conventional structures (7–10 years);
- are inexpensive.
Bridge or implant
Bridges are a non-removable type of prosthetics. The dentures rest on the ground down crowns of adjacent teeth and are glued to them with special cement. They are made of metal ceramics, zirconium or pressed E-max porcelain. With the help of such structures, you can restore one or several teeth in a row, a maximum of four.
Advantages of bridges:
- cheaper than implants;
- look natural;
- do not require lengthy preparation or surgical intervention;
- simple care, preventive examination every six months.
Flaws:
- depulpation of supporting units is possible;
- preparation of healthy enamel of supports;
- jaw bone atrophy;
- wear out, service life is 10-20 years.
If there is a financial opportunity, we recommend installing implants. With this method, a titanium root is inserted into each hole and a metal-free crown is placed on it. Such structures are much stronger than fixed bridges and there is no need to damage adjacent units of the dentition. It should be remembered that under the “empty hole” an atrophic process develops. With an implant, this is excluded: pressure is constantly created, and bone tissue degradation does not occur. You can install a bridge supported by implants, in which case the treatment will be cheaper than implanting each tooth.
Dental restoration price
It is impossible to indicate the exact cost of installing removable structures on implants, since it is influenced by many factors: brand and type of implants, their number, prosthesis material, type of fastening. If rehabilitation or bone grafting is required, you will have to pay additionally for the procedure.
For example, restoring teeth using Korean mini-models can cost from 100 thousand rubles, while restoring the entire jaw using classic rods will cost at least 150 thousand rubles.
Advantages and features of the technology
| Advantage | How is it achieved |
| Used for edentulous lower jaw | The method is used in cases where there is not a single tooth left on the lower jaw. If there are sick or mobile ones, they must be removed |
| Teeth in 1 day with permanent denture | The protocol, like all methods of one-stage implantation, requires immediate fixation of the prosthesis in order to stabilize the implants and provide a load on the bone tissue to accelerate the process of its regeneration |
| Ideal aesthetics and comfort | The denture, which consists of a maximum of 12 crowns, is created from an acrylic base and crowns. It is attached immediately, which allows the patient to avoid wearing removable structures and almost instantly begin to smile and eat normally without feeling pain and discomfort from pressure on the gums and lack of fixation of the prosthesis. |
| No bone grafting required | Like any of the one-stage implantation methods, the Trefoil complex allows you to do without the bone augmentation procedure. However, due to the small number of implants, this protocol places increased demands on the quantity and quality of bone in the frontal zone |
| High degree of primary fixation of implants | Achieved due to the cylindrical shape of the implants and instant fixation of the titanium beam. It is attached to the implants themselves using long screws and specially designed fasteners, which together ensure stabilization of the implants and protect them from displacement even with increased chewing load |
| Precise positioning of implants | This protocol involves the use of 3D diagnostics and modeling of the entire process, which eliminates inaccuracies at any stage of treatment |
| Fast adaptation | The prosthesis is positioned on the implants, not on the gums, so there is no risk of injury or chafing when chewing |
Patient reviews
Most people who have installed removable structures on implants admire their superiority compared to conventional removable devices and their affordable price. Such dentures will not fall out during lunch or a business meeting.
But at the same time, patients note the fragility of the products, since after 2-3 years their quality begins to deteriorate, which causes psychological and physical discomfort.
It should be noted that the success of implantation is influenced by various factors, among which the doctor’s professionalism plays a central role. At the Uni Dent dental clinic, only qualified, experienced doctors practice with extensive knowledge in their field and the necessary skills, which guarantees a high-quality result.
Rehabilitation period
After implantation, it is important to follow the recommendations of doctors so that rehabilitation is as easy as possible:
- Do not eat for 2 hours or until the anesthesia wears off completely.
- Avoid eating hot foods for the next two days. Liquid or semi-liquid foods are recommended (avoid chewing or chewing food at the dental implant site until the wound has healed). Smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol are also prohibited.
- Intense physical activity is not recommended for two consecutive weeks after dental implantation. Do not touch the implant or its immediate surroundings.
Swelling and bruising are a normal consequence of the dental implant procedure and disappear after a few days. They can be reduced by using cold compresses for 2 hours after the procedure. You should not clean the dental implant area for 10 days after the procedure unless your doctor recommends otherwise. The remaining teeth should be thoroughly cleaned. You should also not rinse your mouth for 8 hours after dental implantation, as this may cause severe bleeding.
Comparison of possible options
An alternative to the described method of restoring teeth are removable dentures and fixed structures on implants. Which option should you choose?
| Types of prostheses | |||
| Characteristics | Regular removable | Removable on implants | Fixed on implants |
| Fixation quality | Unreliable. They require frequent correction and relining, and the use of fixing creams, as they often fall out of the oral cavity. | At first they hold well, but gradually begin to loosen and shift due to the fact that the fasteners wear out. | Very high. The splinting beam, which serves as the base of the structure, does not allow the orthopedic structure to move and provides high stability. |
| Mounting methods | They are fixed with suction cups on the mucous membrane or with hooks on the supporting teeth. | They are connected to titanium pins with a beam or spherical abutments. | They are secured with screw connections or dental cement. |
| Support for devices | Soft tissues of the oral cavity - gums and palate (for conditionally removable structures - abutment teeth). | Artificial roots (two are possible, but the optimal number is 4–6). | Implants (from 3 to 14). |
| Dimensions | Massive structures blocking the palate, which can provoke a gag reflex, disrupt the sense of taste, and change speech. | They have a reduced palatal overlap, which makes them lighter and more comfortable. | Lightweight and compact. They do not block the palate, which means they do not change the taste of food and promote rapid addiction. |
| Need for removal | It can and should be removed daily to perform hygiene procedures. | You are allowed to shoot at any time, but you should not do this more than twice a month. | It is impossible to remove it yourself; if necessary, you should consult a doctor. |
| Bone atrophy | The process cannot be prevented; it constantly progresses, disrupting aesthetics and functionality. | Atrophy slows down, its speed is affected by the number of supports. | The volume of bone tissue stops decreasing, and active regeneration begins. |
| Comfort level | Short. | Pretty good. | High. |
| Eating | Difficulties arise, you have to follow restrictions and eat food with a soft consistency. Solid foods deform the device, causing pain and discomfort. | With a small amount of support, you need to stick to a diet and give up solid food. | The design works like teeth, so you don’t have to limit yourself when choosing products. |
| Duration of service. | 2.5–7 years (depending on the type of prosthesis). | 5–7 years, when installing mini-implants – 1.5–3 years. | 10–15 years, and sometimes longer. |
| Price | From 20 thousand rubles. | From 100 thousand rubles. | From 150 thousand rubles. |
Requirements for dental restoration methods
When renovating, two things are important - aesthetics and functionality.
Aesthetics - the appearance of the prosthesis. It should not differ from neighboring crowns and should resemble natural ones in anatomical shape and color. If artificial gum is present, it should be invisible when smiling - the contour is thin and neat.
Functionality consists in restoring the bite - tightly closing the chewing rows and correct positioning of the jaws relative to each other. The load should be distributed evenly.
When choosing a method, take into account that prosthetics is inferior to implantation. The pressure on the supporting teeth increases, and the bone tissue under the prosthesis atrophies. Atrophy will lead to deterioration of hygiene and the risk of inflammatory processes. Implants do not have such problems. The role of the root is played by an artificial rod in the bone, so when chewing, the same force is applied to the jaw as with a healthy tooth. This type of prosthetics is better in terms of functional restoration. In terms of aesthetics, implants also benefit.
How to care for orthopedic systems
Hygienic maintenance of removable devices on implants is easier compared to conventional removable dentures. They are not removed daily, but only once a month. Cleaning is carried out twice a day. In this case, you should clean not only the artificial teeth, but also the acrylic base. Particular attention is paid to areas adjacent to the mucous membrane and interdental spaces. It is best to use an irrigator, which, unlike a brush, efficiently removes dental plaque from hard-to-reach places. After eating, rinse the mouth with special means.
Timely preventive examinations are important for maintaining the freshness, whiteness and aesthetics of teeth. Uni Dent dental specialists will promptly identify and eliminate inflammatory processes that can cause implant rejection and other pathological changes in the oral cavity.