From this article you will learn:
- what is zygomatic implantation,
- what complications can there be,
- patient reviews of zygomatic implants.
The article was written by a practicing implantologist.
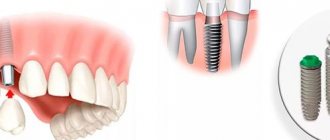
Zygoma zygomatic implants are a solution for patients with complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw (in the presence of a critical degree of bone volume loss), which allows them to obtain a permanent prosthesis and at the same time do without bone grafting. We will use them in situations where we do not have enough bone volume in the lateral areas of the upper jaw to install conventional classic dental implants.
How do zygomatic implants differ from traditional dental implants? First of all, the fact that zygomatic implants are significantly longer (there are options from 30 to 52.5 mm), and they are fixed mainly in the zygomatic bone. But these implants should not be used in all patients, and should only act as a “last alternative to bone grafting.” This is due to the high complexity of their installation, and the potential risk of complications (if the implant surgeon does not have sufficient experience in maxillofacial surgery).
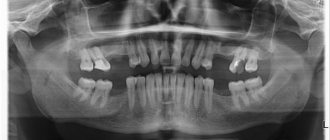
Zygomatic implantation (on the diagram and RG image) –
Nobel Zygoma implants are developed by ]Nobel Biocare[/anchor] (Switzerland), which is one of the most famous manufacturers of dental implants in the world. It was this company that developed such implantation methods as “All-on-4” and “All-on-6”, which allow patients with complete absence of teeth in the jaw to receive a completely permanent prosthesis (on 4 or 6 implants , respectively). Moreover, the prosthesis is fixed already 2-3 days after the operation.
It is for the All-on-4 and All-on-6 techniques that special implant models were developed, for example, “Nobel-Speedy Groovy”, “Nobel-Parallel CC”, as well as “Nobel-Zygoma” zygomatic implants. The latter are truly unique, because... no implant manufacturer offers anything like this, but as we said above, these implants should be used only as a last resort. And there are reasons for this.
Zygoma zygomatic implantation. What is this?
When a person remains without teeth for a long period of time, resorption of the jaw bone tissue occurs, and it is not always possible to install conventional implants. “Zygoma” supports were developed in Switzerland in order to carry out implantation even with severe bone resorption. These are specialized structures 2-3 times longer than the classic ones, allowing the implantation of titanium artificial roots into the zygomatic bones, which are not subject to resorption. Now the name “Zygoma” refers to all transzygomatic pins of different types and manufacturers. Zygomatic implants can only be used for prosthetic treatment of upper jaw teeth.
One of the types of transzygomatic implants is pterygoid. They are shorter than the Zygoma pins and are implanted into the pterygoid bone, rather than into the zygomatic bone. These include, for example, Swiss ROOTT “P” implants, which have a number of advantages. Firstly, they are suitable for use in almost any case due to their size and length (from 3.5mm to 4.5mm in diameter and from 16mm to 24mm in length). Such supports have a combined thread and ensure the stability of the structure. Another undoubted advantage of pterygoid implants is lower trauma to hard and soft tissues compared to zygomatic implants, and a minimal risk of rejection of the structures and various complications.
What brands do they represent?
Zygomatic implants are represented by two brands – Zygoma and Zygomatic (“Zygoma” and “Zygomatic”). The first ones were developed by Nobel Biocare - it was the company that first introduced such models to the world community in 1988. The Zygomatic model is a development of the Israeli company Noris Medical. In fact, this is already a copy of the Nobel Zygoma model. The second company has less clinical data and scientific research, so there are no clear recommendations for installing Zygomatic implants today. However, the models are very similar, so if we talk about usage, then in general terms it is identical.
What are pterygoid implants?
Pterygoid implants are a type of zigoma.
They are less traumatic, suitable for all clinical cases, and have fewer contraindications.
They penetrate not into the zygomatic, but into the pterygoid processes of the bone. The most famous types of implants of this variety are pterygoids of the ROOTT P
.
They have the ideal configuration and dimensions to suit almost any occasion.
When using them, the risk of developing bacterial complications and rejection of structures is minimized.
Key Features
- The length reaches 52.5 mm
, despite the fact that conventional implants are no longer than 25 mm; - The pin design consists of a smooth part and a screw at the end. The thread is needed to stabilize the implant in the bone, and the smooth part reduces the risk of bacterial complications
; - The special surface treatment of TiUnit accelerates osseointegration
and ensures an influx of platelets - the bone immediately receives nutrition and tissue exchange begins.
Indications for installation
| Name | Pterygoid implants | Zygomatic implants |
| Complete or partial loss of teeth in the upper jaw | Yes | Yes |
| Severe cases of bone degradation | Yes | Yes |
| The maxillary and nasal sinuses are too close | Yes | Carefully |
| The need to restore the dentition without bone grafting and sinus lifting | Yes | Yes |
| The inability or unwillingness of a person to wear removable dentures | Yes | In cases where other measures are untenable. |
Risks
Zygomatic implants are long, they run along the edge of the maxillary sinus, coming close to the nerve endings and eyes. Installation of such implants requires pinpoint precision from an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Common complications:
- Sinusitis. A titanium pin can cause inflammation of the maxillary sinus.
- Rejection. The survival rate of zygomatic implants is high
[2], but still some of them do not take root and a complex operation is carried out in vain. - Fistula formation. A fistula is a “passage” between the oral cavity and the sinus. Through it, microbes penetrate the sinus and cause inflammation.
- Paresthesia (feeling of pins and needles on the skin). If the doctor touches the infraorbital or zygomatic-facial nerve during implantation, the consequence may be long-term paresthesia.
- Orbital injury. A rare complication caused by a surgeon's error.
- Complications of TMJ (temporomandibular joint)
Of course, zygomatic implants are a breakthrough in dentistry, but their installation requires extensive experience, special training, and modern equipment. Complications after surgery can develop into a serious problem. A psychological factor cannot be ruled out. Many patients, seeing a photo of a jaw with such pins, literally panic. Therefore, implantologists offer alternatives:
- removable prosthetics;
- bone plastic;
- pterygoid implants.
Contraindications for installation
| Name | Pterygoid implants | Zygomatic implants |
| Pregnancy and lactation | Yes | Yes |
| Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, diseases of the ENT organs | The implementation process does not depend on the condition of the mucous membranes | Installed close to or through the maxillary sinus |
| Uncompensated diabetes mellitus | Yes | Yes |
| AIDS and other immune diseases | No | Yes |
Possibilities of subsequent prosthetics
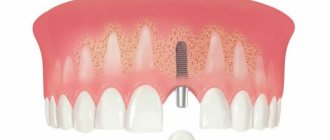
Titanium implantation rods are first implanted into the bone tissue. Over the course of several days (the exact period depends on the individual physiological characteristics of the body), they will be fixed with special structures. Please note that they are designed for each patient individually so that the jaw structure is maintained or straightened if required. The structures are necessary so that the person continues to use the jaws, but the load does not move the titanium rods.
Bridge and bar construction on zygomatic implants
The full adaptation period takes approximately six months. During the process, you can screw in any prostheses. However, the installation process must be carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist, just as he must observe the condition of the jaws for some time. And only after this permanent dentures are installed.
Possible complications and risks when installing Zygoma and ROOTT P
| Name | "Zygoma" - degree of risk | ROOTT P - degree of risk |
| Violations of structural stability | Average | Minimum |
| Risk of rejection | Average | Minimum |
| Development of problems with vision or ENT organs | Average | Absent |
| Nerve trauma | Absent | Absent |
| Rejection rate | 23% | 2% |
Possible consequences after installation
Complications after implantation can occur due to incorrect actions of the doctor, as well as neglect of his recommendations by the patient. The most common consequences of poor quality care and technological errors during the implantation procedure:
- pain;
- swelling;
- bleeding;
- increased body temperature;
- seam divergence;
- numbness;
- inflammation of bone tissue, soft structures;
- rejection.
The last point is rather an exception to the rule. The first three are a normal reaction after surgery. The gums may hurt, the stitches may bleed, and swelling may last up to a week. If the symptoms do not disappear, you should urgently contact the clinic. All other issues must be urgently resolved.
Features of Zygoma implantation. How does the installation work?
The level of complexity of installing Zygoma implants is many times greater than all other types of implantation. The lack of truly qualified specialists in the field of maxillofacial surgery, who are ready to work with Zygoma supports and at the same time have sufficient knowledge in working with computer programs, is a problem with this type of implantation.
Initially, transzygomatic implants were installed through the maxillary sinus into the zygomatic bone by creating an opening in the side wall of the sinus and displacing the mucous membranes to the side. Now this technique has been improved, and implementation is used without involving the sinuses. There is also a surgical technique where a channel is made in the lateral part of the maxillary sinus for the implant inside the bone, so the implant does not fall into the sinus, but is adjacent to it. All three methods are used in treatment; depending on each specific case, the optimal method is selected.
Zygoma zygomatic implants, in case of complete restoration of the dentition, are used in the All-on-4 and All-on-6 systems with immediate loading with their prosthesis. When replacing partial teeth with prosthetics, transzygomatic implants are used in quantities of up to 4 pieces.
When introducing Zygoma implants, careful preparation for the operation is carried out. Consultation with a dentist, drawing up a treatment plan, performing CT scans and diagnostics using x-rays. Possible contraindications are identified, therapeutic actions are modeled in 3D format in specialized programs. Surgical templates are created, according to which the accuracy of the future design is worked out. Zygoma are implants with immediate loading; accordingly, a temporary prosthesis is fixed on them immediately after implantation. After the end of the osseointegration period, permanent crowns are installed.
Types of Zygoma zygomatic implants –
Zygomatic implants Nobel Zygoma come in several types.
- “Brånemark System Zygoma” line – implants in this line have a modern TiUnite surface, which allows for rapid and controlled implant healing. The advantage of this line is the huge number of orthopedic components that make it possible to perform prosthetics even in the most difficult clinical situations. Below you can see what such a zygomatic implant looks like.
- “Nobel-Zygoma 45°” line – these implants have a 45° inclined platform, and thanks to this beveled edge they are used with straight multi-unit abutments. In addition, these implants also feature a TiUnite surface as well as a specially designed apical portion of the implant to provide multicortical anchorage. The advantage of this line is a wide selection of orthopedic components for prosthetics, similar to the Brånemark System Zygoma.
- The Nobel-Zygoma 0° line also has a TiUnite surface, plus a special design of the apical part of the implant, providing multicortical fixation. Implants in this line are distinguished by the fact that they are used with angled Multi-unit abutments 45° or 60°, which simplifies prosthetics when the axes of the implants diverge. Zygomatic implantation using Nobel-Zygoma 0° will cost more than using Nobel-Zygoma 45°, which is due to the use of more expensive angular versions of multi-unit abutments.
Important: Please note that the implants of the NobelZygoma 45° and NobelZygoma 0° lines have threads only in the lower third. This is important when installing these implants through the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses, when the mucous membrane of the sinuses will be adjacent to the surface of the implants. Therefore, the absence of threads in this area of Zygoma implants makes sense.
Possible alternatives
There are cases when Zygoma zygomatic implantation is not possible. In this situation, experts advise considering alternative options. This:
- Pterygoid implants ROOTT P;
- Carrying out a sinus lift procedure;
- Bone grafting;
- Implantation with basal implants;
- Use of removable dentures.
The use of zygomatic supports is considered a last resort measure of treatment when the bone tissue is severely atrophied and the maxillary sinuses are located so close that it is not possible to install classic pins. In other situations, you can get by with a sinus lift or bone grafting in combination with classical implantation. In addition, much depends on the financial capabilities of the client. If there are not enough funds for implantation, removable dentures are recommended, which, unfortunately, will not prevent further atrophy of bone tissue.
Recommendations for the recovery period
During the recovery period, you need to follow some rules in nutrition, oral hygiene, use of medications and lifestyle.
Do not eat too cold/hot foods and drinks, avoid sour and spicy foods, drink up to 1.5–2 liters of water per day. In the first 3-4 days, you can do mouth baths to prevent inflammation. For complex procedures, antibiotics, ointment for treating sutures, vitamins and antihistamines are prescribed to reduce swelling.
During the rehabilitation period, you should not include solid foods in your diet, use dental floss, or brush your teeth with an electric brush.
Expert opinion
Tupikov Alexey Sergeevich
implant surgeon
Experience: more than 8 years
People have many fears and misconceptions about zygomatic implantation. When a patient takes a responsible approach to his health, he will choose a clinic where such operations are successfully practiced and where experts in their field work. If the doctor has extensive experience, has the necessary knowledge, and the dental center has all the necessary equipment, you can be sure that this will be one of the conditions for a successful procedure. Of course, we should not forget about possible complications and contraindications that must be excluded. In my work, I usually try to use traditional or pterygoid implants (implanted into the pterygoid processes, and not into the zygomatic bone), and only in cases where a person has severe bone degradation and other serious indications, do I resort to transzygomatic implantation.
Stages of treatment
- Diagnosis and history taking. Based on the test results, contraindications and the possibility of surgery are identified;
- Implantation planning: location of implants, choice of shape, required number of pins;
- Sanitation of the oral cavity, medical and therapeutic;
- Implantation. Anesthesia. Installation of zygomatic implants at an angle in the cheekbone or pterygoids in the pterygoid process;
- Prosthetics with a temporary structure.
After the operation, the patient comes for follow-up examinations and photographs. Once osseointegration is complete, the temporary prosthesis is replaced with a permanent one.
Where to go for installation
Not every clinic provides installation services for Zygoma zygomatic implants and ROOTT P implants. Below are dentists that perform this type of treatment.
| Clinic name | Clinic website | Price |
| Restoration of a full dentition using pterygoid implants in the dental implantation center of the ROOTT MCDI | dentalroott.ru |
|
| Restoration of a complete dentition using Zygoma implants in Ladent dentistry | ladent.ru |
|
| Restoration of a complete dentition using Zygoma implants at Akademstom | akademstom.ru |
|
| Restoration of a full dentition using Zygoma implants at Bionic Dentis | bionicdentis.ru |
|
| Restoration of a full dentition using Zygoma implants at the Dynasty of Doctors clinic | dinvrach.ru |
|
The decision about what type of implantation will be used is made by the dentist together with the patient. The doctor examines diagnostic materials and medical history, and the client expresses his wishes. It is also important when choosing a clinic to pay attention to the guarantees offered. Reputable centers provide a lifetime guarantee on the products and on the work of the specialists performing the operation.
Prosthetics on zygomatic implants –
Prosthetics with a completely fixed bridge will begin immediately after installation of the implants and, thus, you will receive your prosthesis within 2-3 days after surgery. The important point is that at first you will only receive a temporary fixed prosthesis, which is also called an adaptation prosthesis. You can use such a temporary prosthesis for an average of 2 years (maximum up to 3 years) - after which it will need to be replaced with a permanent one.
Price of zygomatic implantation in Moscow –
- All-on-4 technique on “Nobel Biocare” implants (2 of them will be “Nobel-Zygoma” zygomatic implants and 2 more classic “Nobel-Speedy Groovy” implants) - together with an adaptive prosthesis on a metal frame will cost you about 500,000 rubles .
- All-on-6 technique on “Nobel Biocare” implants (2 of them will be “Nobel-Zygoma” zygomatic implants and 4 more classic “Nobel-Speedy Groovy” implants) - together with an adaptive prosthesis on a metal frame will cost you about 600,000 rubles .
Zygomatic implantation (All-on-4 technique) –
As we said above, permanent prosthetics are carried out over a period of 2 to 3 years, and the patient is offered a huge selection of options for permanent fixed prostheses. This can be an acrylic or ceramic composite fixed prosthesis on a titanium frame, or bridges made of metal ceramics and zirconium dioxide, as well as other options. You can read more about the options and cost of the permanent prosthetics stage in the article at the link below:
→ Prosthetic options for All-on-4 and All-on-6
Disadvantages of zygomatic systems
The disadvantages include the high cost of Zigoma models, due to their size and manufacturing difficulties. But this drawback disappears if we imagine that installing classical implants in an atrophied bone will require additional paid operations. Another disadvantage is possible complications - perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, damage to large nerves and blood vessels. But if the surgeon performing zygomatic implantation using the Zygoma system has significant practical and theoretical experience and has undergone additional training from implant manufacturers, then the risk of complications tends to zero.