What is local anesthesia
The main distinguishing feature of local anesthesia is that the person remains conscious during its effect. This type of anesthesia acts on receptors that are located below chest level. In addition to complete anesthesia, local anesthesia eliminates other tactile sensations, including temperature, pressure on tissue, or stretching.
Local anesthesia is possible in the following areas:
- on the surface of the mucous membranes of various organs - trachea, larynx, bladder, bronchi, and so on;
- in the thickness of tissue - bone, muscle or soft;
- in the direction of the nerve root extending beyond the boundaries of the spinal cord membrane.
- in impulse-conducting nerve cells of the spinal cord.
The main goal of local anesthesia is to block the occurrence of impulses and their transmission while maintaining consciousness.
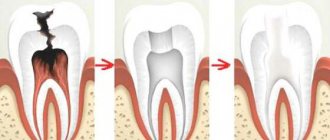
When is it reasonable to treat teeth under anesthesia?
In modern dentistry, anesthesia is often used not only for complex and lengthy operations, but also for routine dental treatment, grinding for dentures, tooth extraction, and in pediatric dentistry. However, it makes sense to use both general anesthesia and sedation in certain cases and for certain patient conditions:
- If long-term and complex treatment is planned (removal of several teeth at a time, bone grafting operations);
- If the patient suffers from a serious form of dental phobia or dentophobia (fear of the dentist and dental instruments);
- If the patient has diseases associated with an irresistible gag reflex, involuntary nervous convulsions;
- If the patient is allergic to local anesthetic drugs.
In dentistry, patients do not remain in the hospital after general anesthesia, but may well go home after
Types of local anesthesia
In medicine, there are the following types of anesthesia, differing in some characteristics and scope of application:
- terminal;
- infiltration;
- regional;
- intravascular.
Each type has a list of indications and contraindications that must be taken into account when conducting them.
Terminal anesthesia
This type is also known as topical or surface anesthesia. The main areas of application are dentistry, gastroenterology and proctology. Terminal local anesthesia (anesthesia) differs from other types in the method of administration: anesthetics in the form of a spray, gel or ointment are applied to the surface of the skin or mucous membranes.
In proctology, local anesthetic gels and sprays (Katetdzhel, Lidochlor, Lidocaine, etc.) are used during proctological examinations and diagnostic procedures: rectal examination, anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy. The examination becomes virtually painless. Also, local anesthesia in proctologists is used during certain medical procedures: latex ligation of hemorrhoids, sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids, infrared coagulation of internal hemorrhoids, as well as biopsy from the rectum.
Infiltration anesthesia
It is used in dentistry and surgery, and involves the introduction of special solutions into soft tissues. The result of the procedure, in addition to a pronounced anesthetic effect, is an increase in pressure in the tissues, and, as a result, a narrowing of the blood vessels in them.
Regional anesthesia
This type involves the introduction of an anesthetic near large nerve fibers and their plexuses, resulting in pain relief in localized areas. It is divided into the following types of local anesthesia:
- conduction, with the introduction of drugs near the trunk of a peripheral nerve or nerve plexus;
- spinal, with the introduction of drugs into the space between the membranes of the spinal cord and “turns off” pain receptors over a large area of the body;
- epidural anesthesia, with the introduction of drugs into the space between the spinal cord and the walls of the spinal canal through a special catheter.
Intravascular anesthesia
It is used mainly for surgical interventions on the extremities. Administration of drugs is possible only with the application of a hemostatic tourniquet. The anesthetic is injected into a blood vessel located near the nerve responsible for the sensitivity of the limb in the area below the injection site.
In recent years, due to the emergence of more effective local anesthetics, the number of proctological operations performed using local anesthetics has increased significantly. In addition, our specialists have developed a method of combined anesthesia - a combination of local anesthesia and intravenous anesthesia. This significantly reduces the toxicity of general anesthesia and reduces the severity of pain in the postoperative period, which allows the patient to recover faster after surgery.
Most often, when performing proctological operations (hemorrhoidectomy, excision of anal fissures, small pararectal fistulas, rectal polyps), pararectal blockade, as well as spinal anesthesia, are used.
Allergy to local anesthetics
Allergy to local anesthesia is extremely rare and in practice it is not possible to detect it using immunological tests.
The reaction to local anesthetics is pseudo-allergic in nature and is associated with the mechanism of degranulation of mast cells and basophils upon contact with Toll-like receptors on their surface. In terms of external manifestations, pseudoallergic reactions are no different from true intolerance to local anesthetics. They can be local or generalized. Appear on the second to fifth administration of the drug and are manifested by urticaria, edema, anaphylaxis or an attack of suffocation. The problem of modern medicine is related to the fact that reliable laboratory tests for determining pseudoallergic reactions have not been developed.
Much more often in practice there are allergies to anesthesia to additional components of the solution or packaging.
One of the leading places is occupied by latex allergy. Some manufacturing companies use latex to make pistons and plugs for glass cartridges. Doctor's gloves are also made from it. Therefore, if you have noticed a reaction to medical gloves, warn your doctor about it. The RuDenta clinic uses exclusively anesthetics in a cartridge with latex-free rubber.
Some manufacturers add stabilizers, preservatives and vasoconstrictors to the anesthesia solution.
Vasoconstrictors include adrenaline, norepinephrine and fellipressin. It is to these substances that we owe the strength and duration of anesthesia. They also prevent the rapid entry of the drug into the bloodstream and thereby reduce its toxic effect. However, there is also another side to the coin. They are oxidized too quickly by atmospheric oxygen. Therefore, sodium bisulfite must be added to their solutions. It reacts more actively with oxygen and thus prevents the oxidation of active substances. Bisulfites can cause allergic reactions and bronchospasm, more so in patients with hypersensitivity to sulfur-containing drugs (bronchial asthma). In such cases, the drugs of choice will be similar anesthetics without a vasostrictor: mepivacaine (Scandonest, mepivastezin) or ultracaine D.
An allergy to local anesthesia can develop to parabens , a preservative for drugs in ampoules and in some carpule anesthetics (Ultracaine D-S). Parabens are widely used in the food industry and in toothpastes.
Preparations for local anesthesia
The following drugs are used to provide local anesthesia:
- Novocaine;
- Dicaine;
- Lidocaine;
- Trimecaine;
- Bupivacaine;
- Naropin;
- Ultracaine.
Each of them is effective when carrying out a certain type of anesthesia. Thus, Novocaine Dicaine and Lidocaine are more often used when it is necessary to anesthetize the skin and mucous membranes, while more powerful drugs, such as Naropin and Bupivacaine, are used for spinal and epidural anesthesia.
What to eat immediately before the procedure
One day before the test, you need to follow a more specialized diet. It is advisable to exclude solid foods; after the middle of the day, do not eat at all; you can take water or clear drinks (non-carbonated).
The nutritional order should be as follows:
- Morning
. Light breakfast of dishes prepared according to the list of permitted products. - Until 13.00
. You can have lunch, it is advisable to take a minimum portion of food. - Dinner
. Only clear liquids; after starting preparation with the drug, you should not eat.
You should also not eat food on the day of the test. You can consume the clear liquid in any quantity. Drinking liquids 1 hour before the procedure is not advisable, but not prohibited.
Indications for local anesthesia
All methods of local anesthesia have the same list of indications, and are used if necessary to numb a specific area for a short time (up to an hour and a half). It is recommended to use them:
- for performing surgical non-abdominal interventions or small abdominal operations, the duration of which does not exceed 60-90 minutes;
- with intolerance to general anesthesia;
- if the patient is in a weakened state;
- if it is necessary to carry out diagnostic procedures against the background of severe pain;
- if the patient refuses general anesthesia;
- in elderly patients;
- when general anesthesia cannot be used.
Anesthesia for pregnant women during dental treatment
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the patient needs to select an anesthetic drug especially carefully. Many drugs can harm the unborn child, so in the early stages (the first two months), when the fetus is forming, it is better to refrain from visiting the dentist if an operation with anesthesia is to be performed. Also, dental operations are not performed in the last two months of pregnancy.
The optimal time for dental treatment with anesthesia is the second trimester of pregnancy. For treatment, injection anesthesia is chosen, and the injection is given very precisely, with a small amount of the drug.
During lactation, if the mother has to undergo dental treatment with anesthesia, it is recommended to temporarily transfer the child to artificial nutrition until the drug is completely eliminated from the body.
Not available for pregnant women:
- General anesthesia.
Possible complications when using local anesthesia
The use of local anesthetics carries certain risks, which include several types of complications:
- damage to the central nervous system and conduction system of the heart;
- damage to spinal tissue, nerve roots and spinal cord membranes;
- suppuration at the site of anesthetic injection;
- allergic reactions.
In most cases, the listed problems arise when the anesthesia technique is violated, or when the anamnesis is not collected completely.
Is anesthesia harmful in dentistry?
Properly administered anesthesia, in which the immersion in and out of sleep is carried out by an experienced anesthesiologist, does not have any further harmful effects on the body. Contrary to terrible rumors, it does not take away 5 years of life, does not affect potency, is not addictive, and in general, modern drugs allow you to perform an operation under anesthesia with a minimum of side effects. Yes, the load on the body during general anesthesia is quite high, but in cases where anesthesia really needs to be used, it is justified.
However, discomfort after anesthesia, unfortunately, is inevitable and continues for 12-24 hours after surgery. These include:
- Nausea and vomiting. The most common effect, which is most clearly manifested in women, young people under 30 years of age, as well as non-smokers and those suffering from seasickness;
- Chills - manifested due to anesthesia, which suppresses the body’s thermoregulation and slows down metabolic processes, due to vasodilation and a decrease in pressure;
- Headache, dizziness and drowsiness, clouded consciousness and difficulty thinking - arise due to the effect on human consciousness. This is a normal reaction of the body, more pronounced in older people.
Only an anesthesiologist can tell you the exact time when the side effects of anesthesia will go away. This depends on many factors: the gender and age of the patient, the condition of his body, his height and weight, etc.
How to use drugs to cleanse the intestines
It is necessary to take special products to clean the intestinal lumen at home. Before using any such tool, you should study the instructions. This will avoid the development of side effects and clarify the order of taking the drug.
It is not advisable to eat food directly during bowel cleansing, but it is necessary to consume a lot of water. This is necessary to compensate for the liquid losses that inevitably occur during the cleaning process.
You should start taking medications 2-3 hours after a light breakfast. Some medications must be taken strictly on an empty stomach. The most common means of preparing for a colon examination include:
- Fortrans
. It begins to act 2 hours after administration. Able to effectively cleanse all parts of the intestines. One sachet of the product is designed for dilution in 1 liter of cold water. 1 sachet per 20 kg of patient weight. For a patient weighing 80 kg, 4 sachets will be required. The resulting solution must be divided into 2 parts. Drink half between 18-20 hours, in portions of 0.25 liters every 15 minutes. The second half should be consumed between 6 and 7 am on the day of the study. - Lavacol
. Osmotic colon cleanser. Available in powder form. You need to take it according to the regimen indicated in the instructions. Standard dosage is 15 sachets per procedure. - Endofalk
. macrogol, sodium chloride, potassium chloride and sodium bicarbonate. The medicine is a mixture of different salts and macrogol to obtain a homogeneous isotonic solution. - Picoprep
. It has a complex effect - it helps soften stool, accelerate its excretion, and retains fluid in the intestines. It begins to act 2-3 hours after administration. - Moviprep (recommended)
. The product begins to act 1-2 hours after the first dose. It is necessary to divide the reception into 2 parts, evening and morning! read more here! It retains fluid well in the intestines and is well tolerated by patients due to the small volume of the drug (only 2 liters).
Important to remember
Please note that before using any laxatives, you should consult your doctor. Only a specialist will be able to prescribe the correct remedy and show the exact regimen for its administration.