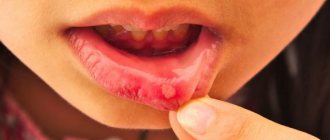
Causes
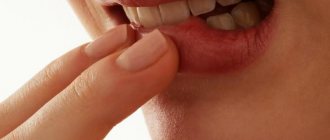
This is not to say that biting the cheek or lip inside occurs frequently and is a serious problem. In most cases, this happens due to inattention: a person tries to combine several things at the same time. It is not for nothing that there is a proverb: “When I eat, I am deaf and dumb.” After all, it is precisely because people talk while eating, or try to have a snack on the go, that damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity occurs. The listed situations can be classified as isolated, and the injury will be considered acute.
The second most common cause of soft tissue damage to teeth is anesthesia. If a strong drug was used for pain relief, the patient may feel numbness for several hours after the end of treatment at the dentist. Since sensitivity is lost, during a conversation or eating there are often cases when a person bites the mucous membrane until it bleeds.
Children are no less susceptible to such injuries than adults, which often happens during active play, when the baby is so carried away that he does not pay attention to the objects around him and does not control his movements.
However, in medical practice there are cases when patients constantly bite their cheek, which is facilitated by certain prerequisites:
- bruxism - grinding of teeth during sleep, caused primarily by spasm of the masticatory muscles, although the exact root causes of this phenomenon have not yet been studied;
- sharp edges of the teeth, formed as a result of trauma, pathological abrasion or imprecisely made restoration, contribute to the fact that the lip or mucous membrane of the cheek can be bitten from the inside;
- habit that occurs against the background of emotional overstrain and stress;
- pathological bite (lateral crossbite or deep);
- incorrectly performed orthopedic structures;
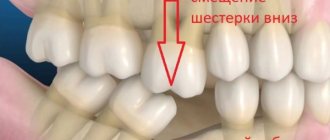
- wisdom tooth, located outside the dentition, the crown of which is directed to the buccal side, also constantly bites the cheek.
All of the above cases lead to chronic injury, which in some situations poses a threat to human health.
Signs of epulis on the gums
In everyday use, this disease is more often called supragingival due to its location directly above the mucous membrane between the teeth. According to the general classification, it is a tumor that is formed from epithelial cells of the gums. The neoplasm externally resembles a small bump or papilla; it may have a stalk and is attached to the interdental space. The main growth area is the area of the chewing teeth of the lower jaw; in more rare cases, it appears on the upper half.
There are several types of epulis on the gums and each has its own characteristic features:
- Fibrous: the most common form of the disease. The lump completely matches the color of the mucous membrane itself and does not have a thin base, so it looks like a seal at the neck of the tooth. It develops slowly and does not hurt or bleed when touched. If it reaches a large size, there is a problem with chewing and tightly closing the jaw.
- Angiomatous: this type of tumor has a whole network of tiny capillaries. They give it a red or bluish tint. Externally, such epulis on the gum is covered with tubercles and looks very unesthetic. It is easy to get caught by a toothbrush or denture, so minor bleeding often occurs.
- Giant cell: This form always causes concern among dentists due to its ability to destroy tooth roots and its tendency to become malignant. It has an unpleasant brown blood color and responds with pain to the touch. It is more common in patients over 40 years of age and requires constant monitoring.
Sometimes epulis is detected on the gums, which grows on the basis of bone tissue. This is an acanthomatous form of the disease, more commonly known as ameloblastoma. It occurs in young children and interferes with the exit of a molar tooth. The growth does not cause pain, but it affects the clarity of the baby’s speech.
First aid for damage
The first thing to do is to stop the bleeding and disinfect the injured surface, which will protect against the addition of pathogenic microflora and the development of an infectious process.
- Stop bleeding. It should be said that bleeding occurs in case of severe damage to soft tissues, but if the injury is minor, then a slight swelling appears. You should rinse your mouth with clean cold water, which helps to constrict blood vessels and thereby stops blood flow. If this does not help and the bleeding does not stop on its own, you need to moisten a sterile gauze pad with hydrogen peroxide and apply it to the wound.
- Relieving swelling. By applying an ice cube to the damaged area, you can reduce not only the swelling, but also the pain.
- Pain relief. If your home medicine cabinet contains lidocaine spray or gels that are used during teething in children, then these drugs can also numb a bitten lip or cheek on the inside.
Reasons for the formation of epulis on the gums
In 80% of cases, the neoplasm occurs due to permanent damage to the mucosa. This is a common problem when wearing dentures, metal braces and other aligners. Sometimes the alveolar space is rubbed by the tip of a broken tooth or the edge of an incorrectly installed filling. The epithelium in one area is greatly irritated and cells begin to grow more actively.
In addition to frequent injuries to the oral cavity, the following features and pathologies lead to the appearance of epulis:
- various surges and disruptions in the endocrine system, exacerbation of diabetes mellitus or menopause;
- pregnancy and postpartum period;
- weakened immunity due to chronic diseases of the nasopharynx and endocrine system.
In children, mucosal growth almost always begins during the period of change of baby teeth. At this time, the child’s body is vulnerable to inflammation and complications. The situation is affected by an incorrect bite and the need to wear braces to straighten it.
How to speed up healing
In most situations, first aid, when a man or woman has bitten the lower lip and it is swollen, is enough to heal the wound on its own. But if the damage is deep enough or tissue infection occurs, then the use of medications cannot be avoided.
Application of gels - Metrogyl denta or Solcoseryl
To remove signs of inflammation and also to speed up wound healing, Metrogil-dent gel is used. The drug is applied to the damaged area after preliminary rinsing with water or a decoction of medicinal herbs 2-3 times a day for 7 to 10 days.
Solcoseryl dental paste has a similar effect.
Baths
D
To prevent infection, if an ulcer has formed, you can perform a mouth bath with an antiseptic. Miramistin, chlorhexidine or furacillin are best suited for these purposes. It is not advisable to use solutions containing alcohol (iodine, brilliant green) to treat the mucous membrane, as this dries out the tissue and causes irritation of the wound.
Treatment of wounds with oils
To ensure faster healing, keratoplasty – drugs that promote tissue regeneration – is successfully used for treatment 2-3 days after injury. Sea buckthorn and rosehip oil, caratoline, as well as a solution of vitamins A and E in oil have this effect. The products are applied directly to the wound with a cotton swab at least twice a day.
If the listed drugs do not help, then you need to consult a doctor: he will select medications to treat the damaged area.
What to do to speed up healing
After the first symptoms subside, it is necessary to create favorable conditions so that the wound heals quickly.
Women often ask: “If I bit my tongue, an ulcer formed and my lip became swollen, how should I treat it so that it heals faster?” The answer is very simple. If there are no complications, then often the use of medications is not required, because the body itself is able to cope with minor damage. The only thing is that you will have to be more careful about your oral hygiene.
- After each meal you should rinse your mouth with water.
- If an ulcer has formed, then oral baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs will help speed up its healing.
- You will have to exclude from the menu all dishes that irritate the mucous membrane (hot, salty, sour and spicy).
- Brush your teeth twice a day, and also remove plaque from your tongue and treat the interdental spaces.
Conservative therapy
The disease can be effectively overcome in a conservative way. In medicine, there are several methods of therapeutic therapy:
- Rinsing the mouth. The procedure is used only at the initial stage of the inflammatory process; in the future, this technique will be ineffective.
- Drug therapy.
It is carried out in case of development of a neoplasm on the mucous membrane due to bacteria or viral infection. The drugs prescribed are those based on interferon. This substance not only eliminates the cause, but also has a general strengthening and restorative effect on the body. List of necessary drugs: Roferon, Intron, Viferon, Altevir, Cycloferon, Lavomax. Additionally, it is necessary to take vitamins and antiviral medications. Treatment with tablets - Injections. Corticosteroids are used for manipulation, which reduce the inflammatory process and relieve the initial symptoms.
- Cryotherapy – liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the growth behind the cheek. The technique is used in cases where medications have not brought a positive result. The treatment has a side effect - the formation of blisters on the affected area.
- Laser therapy. Surgery is performed using a laser beam. There are no adverse reactions. The method is especially effective for the formation of growths on the lip, since no trace remains after the operation.
- Surgical intervention. A small incision is made on the surface of the mouth and the lump or fibroid is carefully removed. After a routine operation, a cyst or neoplasm may appear again, especially if the cause of its formation is a hereditary factor.
It is important to maintain oral hygiene after surgery. You need to talk a little, and for the first fourteen days eat only pureed and soft food. Drink more fluids.
By following all the rules, the tissues of the lip and cheek are minimally injured, and the process of recovery and rehabilitation occurs much faster.
When medical help is needed
If the biting happened once, and the wound does not hurt much, but heals quickly, then there is no reason to see a dentist. However, there are situations when the wound was so severe or the condition of the ulcer worsens every day, then medical intervention cannot be avoided.
- During the bite, a through wound of tissue occurred, the normal healing of which will require sutures.
- The patient bit his lip, after which a lump more than 5 mm in diameter formed, or a hematoma occurred at the site of injury.
- The bleeding cannot be stopped on its own, or it resumes after some time.
- Extensive damage to the tongue with torn edges.
- The pain persists for more than 3 to 4 days, with no signs of improvement.
Types of neoplasms
Classification of neoplasms:
- Papilloma is the most common phenomenon in this area.
The cone has a convex shape with a stalk. It can be localized in one place and grow throughout the tongue, cheek, palate, gums and even neck. The structure of the growth is soft and has a distinct pink color. There is no pain. It only causes discomfort when eating. With each bite, the papilloma increases, and bacteria accumulate, which increase inflammation. Mucocele - Atheroma is a new formation of the sebaceous gland. If the slightest blockage of the iron ducts occurs, their secretion accumulates under the skin and is expressed in the form of a cyst. The growth is a dense transparent ball with a diameter of one to seven centimeters. The atheroma rotates during palpation, without causing pain. Pain syndrome occurs when the condition is neglected, when a purulent mass accumulates inside the growth. An additional sign of deterioration is elevated temperature.
- Mucocele is an internal bubble of the oral mucosa. The formation is cyanotic, and a cloudy bacterial fluid accumulates inside. The cyst is soft, there is slight pain. When opened, the liquid flows out on its own. Young patients suffer from this disease.
- Growths of vascular origin: lymphangioma and hemangioma. These neoplasms, when compressed, change their original shape and decrease in size. They do not cause any particular discomfort.
- Malignant growths – oncology of the salivary gland. First, a small lump forms behind the cheek, then similar growths form behind the ear, under the jaw. Additional signs will be: numbness in some areas of the face, muscle weakness, acute pain in the larynx and tonsils.
The main thing is to establish the cause in time using computed tomography, and the doctor will prescribe a biopsy. Treatment is carried out immediately.
Self-medication is not acceptable; there is a risk of life-threatening complications!
The gums near the wisdom tooth hurt, what to do: treatment of gums and teeth
What is prohibited to do
Some actions can be harmful and cause the inflammatory process to worsen. Particular attention must be paid if the child has severely bitten his cheek or tongue, since children are not always able to adequately assess the severity of the injury.
- use alcohol solutions (Lugol, iodine tincture, brilliant green) to disinfect the wound;
- touch the bite site with dirty fingers;
- rinse the mouth with hot decoctions, which will only increase bleeding;
- try to puncture the resulting bubble, especially if the child bites his tongue;
- without a doctor's prescription, take antibacterial drugs internally, as well as apply antibiotic ointments or powders to the wound surface.
Possible complications
Wounded areas of the cheeks or tongue can become a prerequisite for the development of an infectious process on the mucous membrane, therefore, when an ulcer or extensive wound forms, a mandatory dental examination is required, followed by treatment of damaged areas of soft tissue.
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, the following complications may develop:
Aphthous stomatitis
This is a disease of the oral cavity that tends to have cyclical exacerbations. Small ulcerations appear on the mucous membrane, which are very painful. They are also called aphthae;
Herpetic stomatitis
The main cause of its occurrence is the herpes simplex virus. By the way, it is present in the blood of 99% of the population. Many factors, including biting your cheek and decreased immunity, lead to this disease occurring. Small bubbles with clear liquid, grouped into 10–20 elements, form on the affected area. After opening them, the ulcerated surface is covered with a weeping crust;
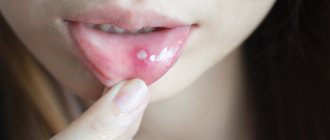
Traumatic ulcer
This is the most common consequence if an adult or child bites their cheek. It is characterized by pain of moderate intensity and redness of the damaged area. With adequate treatment and the absence of regular injury, it quickly resolves;
Afta Bednara
This is a disease that occurs after a person begins to frequently bite his cheek or lip. Children who have special bacteria living in their mouths are more susceptible to pathology if the child does not brush their teeth well. The lesion on the mucous membrane is covered with a grayish-yellow coating;
Ulcer malignancy
This is the most terrible consequence that can occur in those who often bite the mucous membrane. In other words, due to regular damage, the structure of tissues is restructured and their uncontrolled growth begins, which leads to cancer.
It is impossible to diagnose diseases on your own, so if you have the slightest suspicion of the development of complications, you should consult a dentist or therapist for advice.
Symptoms of epulis in the mouth
Each type of this dental disease is different in appearance. The tumor grows quite slowly, so most patients do not immediately notice a lump near the tooth. It can protrude from only one side or from both. The main symptoms of epulis on the gums:
- A soft bulge of pink or dark cherry color appears on the mucous membrane closer to the neck of the tooth.
- The lump ranges in size from 3 mm to several centimeters and fills the space in the mouth.
- A person feels that the tongue does not have enough free space.
- Sometimes there is external asymmetry of the face and protrusion of the cheeks outward.
- Bleeding occurs after brushing teeth, eating, or biting.
Any epulis, the photo of which resembles a shapeless growth in the oral cavity, looks like deformation of the gums from the inside. If the process is severely advanced, a person may feel loosening of the chewing teeth. With constant injuries from a prosthesis or a brush, bacteria enter the wounds. Therefore, the disease is often complicated by inflammation and the appearance of an abscess, cyst and pulp death.
What to do if you bite your cheek from the inside? Causes of the problem
You can often hear from women that she bit the inside of her cheek, and now she is wondering how to treat it. Before engaging in therapy, it is necessary to identify the causes of the problem. Often, injury occurs if they try to eat and talk at the same time, or eat while actively moving. Such cases occur occasionally, but if teeth regularly injure soft tissues, you should look for the source of what is happening.
Oral health is about more than just healthy teeth. Well-being is also judged by the condition of the soft tissues, gums or mucous membrane of the cheeks, vestibule and tongue. Regular biting causes permanent changes in the soft tissue structure, which can lead to serious consequences.
What is epulis on the gum?
Epulis is a benign tumor-like formation that appears on the gum, usually in the area of the molars. Outwardly, it resembles a mushroom: it has a stem and a cap. The pathology has different sizes and shades, this is largely determined by its shape - from a few millimeters to 2 cm in diameter.
Epulis itself does not pose a threat, but it does cause discomfort to the patient. In addition, the formation is prone to growth, and under unfavorable conditions it can degenerate into a malignant tumor. The disease affects patients of all ages, but most often occurs in people 25-40 years old.
Epulis itself is not dangerous, but under unfavorable conditions it can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Causes of cheek biting from the inside
To understand why mucosal bite occurs, you need to understand the prerequisites that cause such an action and why the cheek gets caught between the teeth. With a single bite and regular injury to soft tissues, the treatment method will be completely different.
Despite the seeming banality of the problem, when soft tissue is constantly injured, the variety of causes is great.
- A habit that occurs against a background of frequent anxiety or stress.
- Violation of the arrangement of teeth in a row, which is most typical for the sixth and seventh teeth (about tooth numbering).
- Bite pathology.
- Inaccurate manufacturing of tooth replacement structures.
- A single bite during the period of anesthetic injection after dental treatment.
Reasons for the formation of a lump
Inside the mouth, thickening occurs on the mucous membrane for many reasons. Most often, the reason for this is the inflammatory process that develops after dental treatment. Pus or infectious pathogens come out from the root cavity of the tooth, which affects the delicate tissue of the palate and cheeks. If the mouth is not treated properly, a dense ball will soon form inside the cheek. The infection also spreads with reduced immunity. After visiting the dentist, after the period recommended by your doctor, be sure to disinfect your gums and palate to protect yourself from discomfort in the future.
Extensive growth
A neoplasm can appear due to inflammation of the lymphatic system and salivary gland. This condition can occur during colds, mechanical blockage of the saliva channel and exposure to harmful microorganisms. If you react late, the inflammation process will affect the eyes and the entire cheek from the inside.
If a small ball rolls when you press on it with your finger, then it is a wen or a lipoma. It occurs due to a disease of the endocrine system, toxic infection or heredity.
The next reason is damage after injury. The resulting lump is the body’s protective reaction to the negative impact on the tissues of the mouth. In this case, you do not need to touch the growth with your hands or tongue, because of this the infection will increase and healing will take even longer.
Ulcers can occur after taking certain medications. For example, in large dosages, aspirin can burn the mucous structure of the oral cavity.
The cause can only be determined by consulting a specialist and undergoing certain tests.
Possible consequences of injury
Wounded areas of the cheeks or tongue can cause the development of an infectious lesion of the mucous membrane. The course of diseases of this type is manifested by all kinds of wounds and ulcers, which requires a dental examination followed by treatment of the lesions.
During examination, doctors discover the following consequences of biting soft tissues:
- aphthous stomatitis is a chronic disease of the oral cavity that periodically worsens. In this case, small ulcerations called aphthae appear on the membrane; they can be located in any place in the oral cavity. The main diagnostic sign is considered to be a severe pain reaction in the ulcerated area;
- herpetic stomatitis - the main cause of the disease is the herpes simplex virus, found in the bloodstream of almost 99% of people. With weakened immunity and injury to the soft tissue membrane of the mouth, the pathogen is able to become active and colonize the injured area. The disease looks like small bubbles filled with liquid and located in groups of 10-20 elements. Young women and children are more susceptible to the disease;
- traumatic ulcer is the most common consequence of a bite of the mucous membrane inside the oral cavity. It may appear after careless brushing of teeth, after treatment at the dentist, when biting, or from a burn. Characterized by severe pain, with appropriate therapy and the absence of permanent injury it quickly resolves;
- Bednar's afta is a disease that appears after biting the cheek. Occurs in children under the influence of a special type of bacteria due to poor hygienic status of the oral cavity. The lesion on the mucous membrane has a white-yellow coating.
General symptoms
Signs of growth are obvious:
- The tumor grows quickly, so it is immediately felt by the tongue.
Over the course of seven days, it reaches a diameter of more than two centimeters. Pain inside the cheek - Severe pain (in some cases there is no pain).
- Bleeding.
- Swelling of the mucous system.
- Temperature increase.
- Decreased appetite.
- In rare cases, the voice disappears and difficulty breathing occurs due to swelling.
- The growth has a red tint, which over time turns purple.
- The shape is slightly convex.
- There are white cysts, but over time they turn into red ulcers.
You should not neglect the symptoms; it is better to make sure that there is nothing serious and carry out therapeutic therapy using folk remedies.
First aid
If you receive an injury of this type, do not put off visiting the dentist for too long, because it can be caused by various reasons. Sometimes ulcerations in the oral cavity occur as an indicator of a serious disease in the body.
- When bleeding occurs, rinse your mouth with cold, clean water. Under the influence of low temperature, blood vessels spasm, which helps stop bleeding. This also helps reduce pain.
- In cases of severe pain, medication may be used. Apply a couple of drops of anesthetic solution to a sterile gauze pad and apply to the affected area.
- To speed up healing, you can rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution or a decoction of anti-inflammatory plants.
Video: habit (biting lips and cheeks).
I bit my cheek from the inside: how to treat it?
When an injured cheek hurts and an ulcer has formed, treatment of the lesion consists of several actions:
- in case of severe pain, redness and lump formation, anti-inflammatory tablets are used - they relieve discomfort and help fight inflammation;
- to prevent infection, you should rinse, irrigate the mucous membrane with a decoction of St. John's wort or chamomile, you can use an antiseptic;
- To speed up healing, ointments and gels with a regenerative effect (Solcoseryl, Metrogil-denta) are suitable.
When the wound does not heal for several days, the first thing to do is visit a doctor. It is possible that the occurrence of lesions is provoked by general diseases.
First actions after biting
If an ulcer forms after biting your cheek, you need to remember whether it was in that place before the soft tissue was injured. If you do, don’t put off visiting the dentist, because this could be a symptom of a serious illness.
If after biting your cheek there is bleeding from the inside, you need to rinse your mouth with clean water. The low temperature that affects the wound causes spasm of the blood vessels, which helps stop bleeding. In addition, this will help reduce the intensity of the syndrome.
If the pain is so severe that a person cannot even chew food normally, you can take any painkiller. A compress made from a piece of gauze previously soaked in an anesthetic (solution) will also help reduce the intensity of pain. Any antiseptic can be used to rinse the mouth, which will help speed up healing.
Medications
Treatment of ulcers, which often form after a bite, can also be done at home. If the damage is minor, doctor's help is not required. A wound on the oral mucosa heals quite quickly without an inflammatory process, which occurs due to increased humidity and specific components of saliva. As an exception, we can name a regular bite and the initial stage of abscess formation.
It is recommended to rinse the mouth with any antiseptic, for example, Chlorhexidine
To eliminate the wound, you can use special medications that are available in any pharmacy. These include solutions and ointments with an antiseptic effect. One of these is the drug Chlorhexidine, released in the form of a solution. It is necessary to rinse the mouth with this product in case of existing wounds in order to neutralize pathogenic microorganisms.
Local bactericidal preparations include Cholisal gel.
In addition to treating damaged mucous membranes from the inside of the cheek, this remedy can also treat gums with the development of gingivitis and other diseases. In addition, the drug is used in the treatment of stomatitis. The gel is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day, leaving for 30 minutes until absorbed.
If a sore appears after biting your cheek, it can be treated with a brilliant green solution, that is, brilliant green. The product has a drying effect and helps eliminate pathogenic bacteria from the affected area. The solution is applied as it is washed off from the mucous membrane.
Tablets such as Furacilin are used as an antiseptic, dissolved in warm water in a 1:1 ratio. The mouth should be rinsed every few hours. If there is severe bleeding, it is recommended to pre-treat the affected area with hydrogen peroxide. Eating and drinking are allowed 1 hour after using the solution.
In case of severe pain, you can take a tablet of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, for example, Ibuprofen or No-shpa. Such drugs help reduce the reaction of tissues to mechanical damage and eliminate pain.
Causes
The most common causes of bumps on the gums are:
- illiterate and irregular dental care;
- n injuries in the oral cavity;
- n consequences of wearing dentures.
Lack of regular dental care causes plaque to appear on them, which becomes a suitable habitat for pathogenic bacteria. As a result of their reproduction, a lump with pus often appears on the gum.
Often the tumor appears after injury or unprofessional installation of dentures. This occurs after the use of low quality materials and insufficient antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
Lumps on the gums in most cases indicate the presence of dental diseases. Most of them can cause significant discomfort, which necessitates immediate contact with a specialist.
Folk remedies
If biting your cheek causes an ulcer to form, you can use folk remedies to eliminate it:
- milk and chicken yolk (dissolve the yolk and one teaspoon of honey in 100 ml of warm milk; use the prepared product to wipe the affected area several times a day using a cotton swab);
- calendula (pour a tablespoon of dried flowers into a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for an hour; use the finished product to rinse the mouth 3 times a day);
- chicken egg white (dissolve 1 white in half a glass of warm water and use as a mouth rinse every few hours);
- yarrow (obtain juice from the plant by finely chopping it, mix it with honey and lubricate the affected area with the resulting product, securing it with a cotton pad on top for 20 minutes; carry out the procedure every 3 hours);
- cinquefoil root (pour 20 g of raw material into a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for several hours; the finished product is used to rinse the mouth 4-5 times a day);
- salt (pour 1 teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water, stir and rinse the mouth with the solution several times a day);
- thyme (1 tablespoon of the herb is poured with boiling water in a volume of 1 cup and left to infuse for half an hour; strain the finished product and rinse the mouth with it several times a day).
You can rinse your mouth with regular saline solution
Other recommendations
If an ulcer forms on the inside of the cheek after improper biting, you should reconsider your diet. So, it is recommended to remove hot drinks and food of the same temperature from it. This can be explained by the fact that exposing the wound to high temperatures slows down healing. It is also necessary to exclude cold foods, for example, ice cream, cold juices, etc. Low temperatures act similarly to high temperatures.
It is recommended to include as many vitamins as possible in the diet, which will help increase the body’s protective function and thereby speed up recovery. These include vitamin C and vitamins included in group B. These can be contained both in food products and in ready-made vitamin preparations.
If you constantly bite your cheek, the formation of an ulcer is inevitable. The main thing is to provide first aid correctly and prevent such injuries in the future.