An antibiotic (antibacterial drug, antimicrobial agent) is a drug that is effective in treating bacterial infections. Its effect is to directly affect the bacterium, it kills it. Its effect may also be to slow down the proliferation of bacteria, which allows the immune system to cope with it. The high prevalence of infections, a large selection of antibiotics for children, and the unjustified prescription of these drugs for diseases in children and adults have led to threatening consequences for human life—antibiotic resistance. According to the Eurasian recommendations, 25,000 deaths annually in the EU are associated with antibiotic resistance. At the moment, antimicrobial agents are an irreplaceable resource for humanity. Antibacterial resistance can be considered a threat to national security.
Before moving on to the choice of a children's antibiotic, consideration of dosage, duration of use, it is necessary to analyze and explain the main points in the formation of resistance to antibacterial agents. Only after this can one adequately judge the choice and approach to prescribing these medications.
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is the term for resistance to antibiotics. Who is to blame for this? The main reason is the excessive and uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents. This applies not only to medicine.
Prescribing antibiotics should always be justified.
Causes
- Application in medicine. Unjustified prescription on an outpatient basis, in a hospital, self-medication (over-the-counter). The main emphasis is on counteracting the unjustified prescription of antibiotics in primary care (at the outpatient stage). For this purpose, clinical recommendations and algorithms for prescribing antibiotics to children are specially developed and implemented in practical healthcare. Also, through the media, explanations are provided to the population about the need for the judicious use of antimicrobial agents and the dangers of their independent use.
- Use of antibiotics in veterinary medicine.
- Application in the agricultural industry.
Basic rules for the correct use of antibacterial drugs
- An antimicrobial agent is taken only in the presence of a bacterial infection that is suspected or documented.
- When using the drug, you must adhere to the optimal regimen. The first is the correct choice of medicine. Otherwise, it is necessary to maintain an adequate dose and duration of use.
- When choosing a drug, it is necessary to take into account the regional situation regarding antibiotic resistance of the most common pathogens and take into account the likelihood of infection of the patient with these bacteria.
- Do not use low quality antibiotics with unproven effectiveness.
- Do not use antibiotics for prophylactic purposes.
- The effect of using an antibacterial agent is assessed 48-72 hours after the start of treatment.
- Explain the harm of non-compliance with the medication regimen, and also explain the dangers of self-medication.
- Promote the correct use of the drug by the patient.
- In each case, it is necessary to use methods to determine the cause of the infection.
- When prescribing an antibacterial drug, doctors must adhere to recommendations based on evidence-based medicine.
Features of the clinical picture
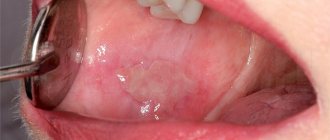
The symptoms of viral stomatitis at the initial stage of its development are easily confused with the symptoms of a common cold. The patient's body temperature rises and a headache appears. Gradually, the oral mucosa becomes very swollen and red, making it difficult for the patient to chew and swallow.
A few days after the onset of the inflammatory process, rashes characteristic of the disease appear:
- ulcers on the inside of the cheeks, palate, gums and tongue;
- groups of bubbles with clear liquid inside;
- “cold” on the lips, on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and in the nose;
- erosions that itch and hurt.
A whitish coating appears in the mouth of a sick person. The patient is concerned about general malaise, lack of appetite, bad breath and swollen lymph nodes.
Indications for antibiotics
A fairly common mistake is the use of antibiotics for diseases that develop as a result of a non-bacterial infection.
Antibiotics should not be used for viral infections.
Among these diseases:
- Acute pharyngitis.
- Acute laryngotracheitis.
- Rhinitis.
- SARS, only.
- Acute bronchitis. It is permissible to use antibiotics when bronchial constriction develops, as well as when fever lasts more than 5 days.
In these cases, the prescription of antibiotics is not justified, since the cause that led to these diseases is often viruses.
There are also controversial points when both viruses and bacteria can lead to the development of the disease. Such diseases include:
- Acute rhinosinusitis.
- Acute otitis media.
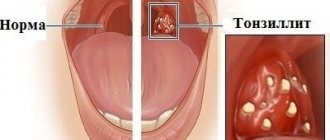
- Acute tonsillitis.
In such cases, an antibiotic is prescribed only after examination and observation by a doctor of the patient.
For viral infections (pharyngitis, rhinitis, laryngitis, tracheitis), the effectiveness of antibiotics is equal to the placebo effect. It is important to remember that the prescription of antibacterial agents does not prevent the development of bacterial superinfection (that is, the addition of a bacterial infection to an existing viral one). There are no effective remedies against ARVI. The use of antiviral immunostimulating agents common in pharmacy chains often does not have any effect. In this case, the antiviral agent can be considered as ascorbic acid or garlic. In such cases, adequate pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment is prescribed, which allows eliminating and eliminating the symptoms of ARVI. Used: paracetamol, ibuprofen, mucolytics (ambroxol, acetylcysteine, carbocysteine), vasoconstrictor nasal drops for a runny nose, nasal corticosteroid for rhinosinusitis. If there is a disease with a viral or bacterial cause (tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media), then in this case antibacterial therapy delayed by 2-3 days is recommended. Delayed antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infections has reduced the frequency of antibiotic prescriptions by 40%.
These statements are of an evidentiary nature and are described in more detail in the training manual “ Rational use of antimicrobial agents in outpatient practice of doctors , written on the basis and evidence base of the 2016 Eurasian recommendations.
Prosthetic stomatitis: treatment
Denture stomatitis can happen to anyone who has removable or fixed dental appliances. At the same time, pronounced areas of redness can be observed in the oral cavity at the site of the prosthesis, and lesions can also be remote when a secondary infection occurs.
Prosthetic stomatitis can be allergic or bacterial. Allergies develop when the material for prosthetics is incorrectly selected. This is a dentist’s mistake or a feature of the body when an allergy appears only after a while after exposure to the allergen.
The bacterial denture process is associated with improper oral hygiene, when the denture is not cleaned for a long time, plaque accumulates on it and causes irritation of the mucous membrane, which ends in inflammation. There are cases when the cause may be improper installation of the prosthesis or the characteristics of the dentition, when it is not possible to completely clean the structure.
The main treatment in this case will be eliminating the irritant. The prosthesis is replaced or corrected.
The main types of antibiotics and their common representatives on the market
Below we consider the most popular and frequently used groups of antibacterial agents:
- Beta-lactams . Among them are penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems. Among the penicillins, it is worth highlighting: amoxicillin, ampicillin, ticarcillin, carbenicillin, mezlocillin, mecillam. The most popular cephalosporins are: cefazolin, cephalexin, cefuroxime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefepime, ceftobiprole. Carbapenems are used much less frequently. Meropenem can be isolated.
- Macrolides . Macrolides include: clarithromycin, azithromycin (sumamed), josamycin.
- Tetracyclines . The most common: tetracycline, doxycycline, oxytetracycline.
- Aminoglycosides . Popular ones: gentamicin, amikacin, isepamycin.
- Levomycetins . Trade names: chloramphenicol, chloromycetin.
- Glycopeptide antibiotics . The most commonly used: vancomycin, bleomycin.
- Lincosamides . Used in medicine: lincomycin, clindamycin.
- Fluoroquinolones . Among them, the most commonly used are: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, gemifloxacin. They are a broad-spectrum antibiotic for children. These antibiotics are not contraindicated in pediatric practice, but their use in children is sharply limited.
It is important to remember that these drugs have their own indications and contraindications, and are also used against certain infections.
These drugs have their own indications and contraindications, and have a narrow or broad spectrum of activity against bacteria. Some of the listed drugs can be used by children under one year of age. Children's antibiotics are available in tablets, suspensions, and ampoules for intravenous and intramuscular administration. Calculation of the dose, dilution of antibiotics and administration of the required dose to the child should be carried out by medical personnel in order to avoid unwanted reactions, as well as complications during injections. They should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
Duration of use of antibacterial agents
Parents often ask questions: “How many days are antibiotics given to children? What is the best antibiotic for children? What should I give my child when taking antibiotics? In most cases, 5-7 days of use are sufficient. There are exceptions in which the duration of use may increase to 10–28 days. The second question cannot be answered unambiguously. Each drug has its own indications and contraindications, so the use of a particular drug depends on the situation (age, diagnosis, concomitant pathology, etc.). To the third question, many doctors will answer the same: “Probiotics.” A probiotic will restore normal intestinal microflora that has been affected by an antibacterial agent. As a rule, they are prescribed in a course of 2 weeks to 1 month.
You can always consult your doctor if you have any questions regarding treatment.
According to the Eurasian recommendations, in order to overcome antibiotic resistance, experts emphasize the need to draw the attention of patients to strict adherence to the drug use regimen. It is necessary to use optimal dosage forms of antibiotics with high bioavailability, in particular, Solutab dispersible tablets, which is consistent with the current position of WHO and UNICEF. Advantages of Solutab dispersible tablets:
- Completely absorbed in the intestines. As a result, the effect is equal to the intravenous effect.
- Create a high concentration at the site of infection.
- Better portability.
- Good organoleptic properties.
- The ability to dissolve tablets, which allows the use of this dosage form in children.
- A minimal amount of liquid is required for swallowing.
- They have an advantage over a suspension - errors in preparation are eliminated.
Dispersible tablets recommended by WHO and UNICEF:
- Flemoxin Solutab
- Flemoklav Solutab
- Suprax Solutab
- Vilprofen Solutab
- Unidox Solutab
Parents of children should remember that an incomplete course of prescribed antibiotic treatment leads to the formation of bacterial resistance and a prolonged presence of the microbe in the body.
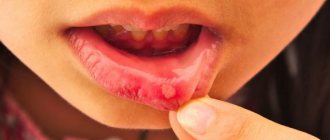
Symptoms of chronic stomatitis
Symptoms for chronic stomatitis are less pronounced than for acute stomatitis.
General symptoms (weakness, headache, fever, muscle aches) are almost always absent. It is important that the disease does not appear once, but recurs with a cold, decreased immunity, or has a constant frequency of relapses.
The herpes simplex virus can remain in our body for life, so once infected, a person remains a carrier for life - this explains the high prevalence of herpes.
Chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis
Appears after injury, hypothermia, acute respiratory viral infection, or during exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Rashes in the form of bubbles that burst with the formation of erosions (superficial defect of the mucous membrane) are most often located on the hard palate, cheeks, and tongue. On the first day, the rash is painful, there may be enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes, but the general condition is most often not disturbed. 7
Based on the number of relapses per year, the following forms are distinguished:
- mild 1-2 relapses in 3 years
- average 1-2 relapses per year
- severe 4-5 relapses per year
Chronic candidal stomatitis
It is observed in people who take antibiotics, in patients with tuberculosis, blood pathologies, diabetes mellitus and other diseases.8
It occurs in two forms:
1) Chronic pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis is difficult to treat and constantly recurs. Manifested by burning, dryness. All parts of the mouth are affected, the mucous membrane is covered with white films; if they are removed, the mucosa will appear bright red, bleeding and covered with erosions (superficial defect of the mucous membrane).
2) Chronic atrophic candidal stomatitis , as a rule, is found in elderly people wearing removable dentures. Manifestations: swelling, redness of the oral mucosa, seizures (cracks in the corners of the mouth).
Chronic ulcerative necrotic stomatitis
It occurs as a result of an acute form with ineffective treatment and most often occurs in a mild form.
Only in case of exacerbation, general phenomena are observed - rise in temperature, headache, weakness, soreness of the lymph nodes. Symptoms: moderate pain, bleeding, thickening of the gum edge, the presence of ulcers that are covered with necrotic plaque.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis
a disease with an unknown cause, the probable cause is an allergy.
Aphthous stomatitis has a chronic course, the frequency of relapses depends on the severity of the disease. Symptoms: burning of the mucous membrane, formation of painful aphthae (rounded erosions), periodic relapses of the disease.
Chronic mechanical stomatitis
Develops as a result of chronic injury.
Reasons: malocclusion, unpolished crown or filling, old fillings, crowns, low-quality dentures, trauma from an orthodontic device when it breaks, tartar.
As a rule, it does not bother a person much, manifesting itself as barely noticeable swelling, redness, mild pain, and possible thickening of the interdental gums (gingival papillae). But persistent trauma can also lead to the formation of a chronic ulcer, which is prone to malignancy; older people who use old or poor quality dentures are at risk.9
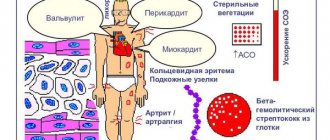
Complications of antibiotic use
When using antibiotics, there is a risk of developing unwanted reactions. Such complications include:
- Hepatotoxicity – liver damage. Most often observed when taking moxifloxacin, macrolides, and clavulanate.
- Cardiotoxicity is damage to the heart. Such a reaction can occur when using fluoroquinolones, azithromycin, clarithromycin.
- Neurotoxicity is damage to the nervous system. Occurs with fluoroquinolones.
- Allergy . Characteristic of penicillins and cephalosporins.
In fact, the wider the spectrum of antimicrobial activity, the higher the risk of adverse reactions..
Classification of chronic stomatitis
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane: | a comment: | 1) superficial - there is redness, slight swelling, single superficial defects of the mucous membrane - aphthae. 2) deep - deep defects are observed - ulcers; in more severe cases they can be covered with a necrotic coating. |
| classification: | Due to the occurrence: | a comment: | 1) infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal) 2) traumatic (mechanical, chemical or physical injury) 3) allergic |
Choosing an antibiotic in a child
Previously, we reviewed the main diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract, for which antimicrobial agents can be used. Now we will analyze the main drugs that can be used for this or that pathology, and also indicate the required dosage of the drug.
Do not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
Do not use medications yourself! The medications and dosages listed below are for informational purposes only and are not equivalent to treatments prescribed by a physician.
Acute otitis media
The drug of choice is amoxicillin 40-90 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. Duration of therapy is 10 days in children <5 years old, 5-7 days in children >5 years old. The second-line drug is amoxicillin/clavulanate. The third-line drug is josamycin.
Acute rhinosinusitis
Similar to the use of antibacterial agents for acute otitis media.
Acute tonsillitis
The drug of choice is amoxicillin 45-60 mg/kg in 3 doses, phenoxymethylpenicillin 25-50 mg/kg 3-4 times a day. The second-line drug is cefixime. The third-line drug is josamycin. Duration of therapy is 10 days.
Community-acquired pneumonia
The therapy of choice is amoxicillin IV 45-90 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. The second line drug is amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefuroxime IM, ceftriaxone IM. The third line drug is josamycin 40-50 mg/kg/day in 2 doses.
Antibiotics are indispensable drugs in the fight against bacterial infection. These medications should be prescribed solely for medical reasons. It is very important to adhere to the prescribed regimen of using the antibacterial agent. Do not self-medicate. If signs of infection occur, contact your pediatrician, who will help establish the diagnosis, cause of the disease, and prescribe adequate treatment.
Causes of viral stomatitis
The occurrence of the disease is caused by a complication of the primary disease (chickenpox, herpes, etc.). The following may cause signs of the disease:
- poor oral hygiene;
- untreated caries;
- gingivitis, periodontal disease;
- unbalanced diet;
- avitaminosis;
- general weakening of the body;
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
Inflammation in other organs and systems of the body also causes viral stomatitis in children and adults.