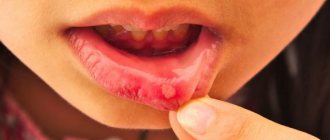
How chickenpox begins and develops Chickenpox is an acute infectious disease characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes. It does not appear instantly: the incubation period can range from 10 days to 3 weeks.
Chickenpox is highly contagious. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with a carrier. Children often get sick in entire groups (groups in kindergarten or classes at school). We will tell you how to recognize the disease in the shortest possible time to prevent its spread.
What causes chickenpox?
The causative agent of this disease is human herpesvirus type 3. It belongs to the subfamily of alphaherpesviruses, which have the following features:
- a wide range of hosts (humans and animals);
- short reproductive cycle;
- rapid reproduction;
- volatility;
- rapid decay of affected cells;
- death under the influence of UV rays.
When the chickenpox virus enters the human body, for the first three to four days it is contained within blisters covering the skin. On the eighth day it ceases to be detected. Outside a living organism, type 3 herpesvirus dies in 15 minutes.
The rash usually appears 48 hours after infection. The carrier remains infectious for another five days. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Contact-household infection is also possible.
How to recognize chickenpox?
To get sick, two conditions are enough: to be near someone with chickenpox and not have a history of it. Everyone gets infected with it, regardless of age and immunity strength. Nothing can be done during the incubation period. All we have to do is wait for the first signs:
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- general malaise;
- decreased appetite;
- the appearance of a characteristic rash.
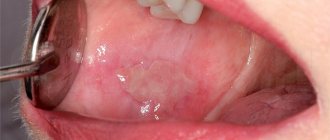
At first, the rash is rare and looks like spots or pimples. Under no circumstances should you squeeze them out: the scar will be very deep. The volume of the rash gradually increases, covering all parts of the body.
In the early stages, chickenpox can be mistaken for an allergic reaction. But contact dermatitis rarely spreads throughout the body and never develops into blisters.
In this case, the person feels severe itching. Scratching chickenpox is also not advisable. This will not bring relief, but there is a risk of getting a lot of scars on the skin or causing a secondary infection.
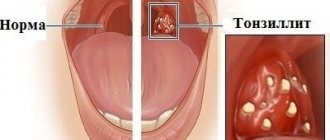
Main symptoms of the disease:
- pain, itching, dryness;
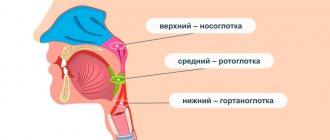
- sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat and pharynx;
- attacks of coughing and sneezing;
- nasal congestion (runny nose);
- discharge of mucous formations from the oropharynx;
- itching in the eyes (especially when combined with conjunctivitis), sore throat, nasal passages;
- the back wall of the larynx becomes red or even purple;
- weakening of the voice (hoarseness, hoarseness);
- feeling of “heat” in the throat area.
Fever is an uncharacteristic sign of the disease, which usually indicates the addition of a secondary infection.
The pathology is considered dangerous due to the possibility of pharyngitis turning into otitis media, sinusitis, and tonsillitis. Otolaryngologists at MedicCity, using the most advanced treatment methods and modern equipment, will be able to diagnose, treat you and relieve you of unpleasant symptoms. Don't develop allergic pharyngitis and don't let it ruin your life!
The acute form occurs with long-term or short-term exposure to allergens on the body. It usually goes away quickly. The long course of the disease and possible complications appear with prolonged contact with allergens. Inflammation can affect not only the throat, but also the respiratory tract, as well as the entire body.
Periods of chickenpox
Quite a long time passes between infection with the herpes virus and complete recovery. There are four periods:
- incubation (up to three weeks);
- prodromal (up to two days before the appearance of rashes);
- rashes (several waves for two to five days);
- crust formation.
During the prodromal period, the patient experiences general malaise. It is expressed in weakness, nausea, headache. Sometimes the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, and vomiting occurs. In some patients, there is no prodromal period, and rashes immediately appear some time after infection.
Chickenpox in adults causes severe complications. They do not appear immediately. Some appear after the tenth day of the disease, others after a month.
How does chickenpox occur in children?
Chickenpox is considered a childhood disease, since it mainly affects children of preschool and primary school age. In children, the illness period is relatively short (about 10 days), while in adults it can last three weeks or more.
During this time, the rash goes through several stages:
- erythematous spots;
- nodular rash (papule);
- ulcers (pustules);
- crusts.
Recovery occurs when all the scabs fall off. Until this point, the person is still contagious and can pass the chickenpox virus to others. The first wave of rashes usually passes quickly, but it is replaced by several more.
As a rule, there are no complications in children. The main thing is that the baby does not scratch the rash to avoid secondary infection and scar formation. Severe disease occurs in newborns. When the first signs of chickenpox appear in an infant, you should immediately call a doctor.
Scarlet fever - symptoms and treatment
Early complications
In the case of a severe course with a toxic form, a terrible complication develops - toxic shock .
Purulent-septic complications may occur: peritonsillar (next to the palatine tonsil) abscess, neck phlegmon, purulent otitis and mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone), sinusitis and sepsis. In these cases, immediate resuscitation and surgical actions are needed. But the most disabling complications are associated with autoimmune reactions when acute rheumatic fever . The full picture includes five symptoms: inflammation of the tissues of the heart, migratory polyarthritis, chorea, annular erythema and rheumatic nodules on the skin. It develops more often in children 7-15 years old, this is due to the epidemiology of scarlet fever and streptococcal infections. In adults, chronic forms are more often detected. According to the State Statistical Report in Russia in 2014, the prevalence of rheumatic fever is:
- 1.8 per 100 thousand children from 0 to 14 years - acute forms;
- 11.8 per 100 thousand children and 118.4 per 100 thousand of the total population are chronic forms [12].
Late complications
Late complications include diseases that are not directly related to the pathogen and are caused by impaired immune response: carditis, arthritis, chorea and glomerulonephritis.
Carditis occurs with inflammation of the heart valves, the mitral and aortic valves are most often affected, valvular insufficiency and regurgitation develop (backflow of blood through the valves). On examination, an organic systolic murmur is heard. Treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs does not always lead to improvement, and in some cases chronic heart disease develops. Against the background of blood volume overload, the symptoms of heart failure intensify. Then the patient requires surgical treatment with valve surgery.
Arthritis is an inflammation of mainly large joints, accompanied by pain, swelling, and stiffness in movement. It is characterized by damage to several joints, most often the knees and ankles, and migratory inflammation. Good response to anti-inflammatory therapy. In case of inadequate treatment and genetic predisposition, a chronic course of arthritis develops with repeated attacks and joint deformation.
Chorea sometimes occurs after 6 months. A person develops gait disturbances, involuntary, uncontrolled movements of the arms, legs, body, and facial expressions, which are usually excessively expressed. From the outside, the condition resembles dancing, hence the name. On examination, muscle tone is reduced, reflexes are animated, sweating is pronounced, temperature is unstable, and excessive emotionality is present. Long-term antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsant drugs are effective in treatment.
PANDAS syndrome stands for Pediatric Neuropsychiatric Autoimmune Disorder. The complication was discovered relatively recently, at the end of the 20th century. The characteristic symptoms of this disorder are obsessive-convulsive seizures. The patient develops obsessive thoughts and movements, motor or vocal tics, emotionality and memory impairment may appear. With antibacterial and immune therapy, improvement occurs, but with repeated streptococcal infection or a stressful situation, the symptoms return.
Glomerulonephritis is an autoimmune kidney disease. Characteristic symptoms are edema, dysuria (impaired urination), hematuria (blood in the urine), increased blood pressure, and renal failure. Assessing a general urinalysis helps in diagnosis, especially with mild symptoms. In therapy, water and salt are limited, antibiotics, diuretics, antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory drugs are used, and in case of renal failure - dialysis [12][13].
Atypical forms of chickenpox in adults
In adults, chickenpox is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication of the body. Atypical clinical forms are also possible:
- Rudimentary. The rash is either absent or does not develop beyond the blotchy stage.
- Hemorrhagic. A bloody impurity appears in the blisters, and small hemorrhages appear on unaffected areas of the skin. Black crusts form.
- Bullous. Along with the usual chickenpox, other blisters appear. They are filled with a cloudy yellowish liquid and take a long time to dry. If such blisters burst prematurely, the area of skin underneath them becomes wet for a long time and does not heal.
- Gangrenous. The tissues inside the blisters die, and ulcers form underneath them. Cleaning of pus is often required.
The generalized form of chickenpox is considered separately. It is characterized by damage to internal organs. It is difficult to tolerate and there are deaths. At risk are patients taking steroid hormones.
How to help with chickenpox?
There is currently no cure for chickenpox. Usually the disease goes away on its own, and therapy is limited to smearing the rash with aniline dyes with bactericidal properties. A solution of brilliant green (“zelenka”) is usually used. You can take an antipyretic to relieve your general condition.
To relieve itching use:
- solution of iodine tincture (2-3%);
- solution of potassium permanganate (1:5000);
- hydrogen peroxide (3%);
- glycerol.
In some cases, antihistamines can help relieve itching. But you should not take them uncontrollably: it is better to call a doctor at home and determine acceptable medications. Showering is allowed, but without a washcloth to avoid damaging the bubbles. The same applies to the use of towels - after water procedures, you need to carefully pat your body dry with a cloth.
Features of treatment
Treatment of skin diseases of an allergic nature requires an integrated approach. First of all, therapy should be aimed at the absolute exclusion of harmful pathogens, as well as at improving symptoms. Itching, swelling and redness cause patients severe discomfort, both physiological and emotional. Itchy spots make it difficult to sleep and work fully. In addition, the affected areas disrupt the aesthetics of the skin, so patients often hide them under clothing, which can only aggravate the situation. In addition, allergic reactions on the skin cannot be wetted, so patients are deprived of the opportunity to take a bath, visit the pool or sauna.
To eliminate a rash on the hands, it is necessary to use topical external agents in the form of ointments or creams. In the treatment of allergic dermatoses, drugs based on topical glucocorticosteroids have proven themselves to be effective.[10] Such products have wide application possibilities, since they have several effects on the inflammatory focus:
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- antiallergic effect;
- vasoconstrictor properties;
- antipruritic effect.
One of the representatives of local glucocorticosteroids prescribed for the treatment of allergic dermatoses are the drugs "Akriderm GK".
Complications of chickenpox
In most cases, this disease is not dangerous; children tolerate it easily. The only threat is infection of the wound when combing with dirty hands. In such cases, staphylococci or streptococci may be ingested and a purulent infection may develop.
The chickenpox virus does not disappear from the body after recovery. Temporarily neutralized, it is localized in the spinal cord. As years pass, it can become more active and cause shingles.
In adults, complications may include:
- stomatitis (if a rash appears in the mouth);
- conjunctivitis (on the eyelids);
- inflammation of the middle ear.
The greatest danger is chickenpox pneumonia with a mortality rate of 40%. The consequences of infection with the chickenpox virus can manifest themselves in the form of neurological disorders, heart disease, and joint damage. A month after recovery, there is a risk of developing retinal inflammation and cranial nerve palsy.
Mononucleosis: myths and reality
Common myths about mononucleosis.
The article was prepared by Elena Kolganova, a pediatrician at the DocDeti clinic.
Mononucleosis is a viral disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Transmission of this virus occurs through close contact. For example, through saliva on shared utensils or during a kiss - this is what another name for this disease is associated with - “kissing disease”.
The symptoms are:
1. Tonsils affected by a white coating, as with a sore throat.
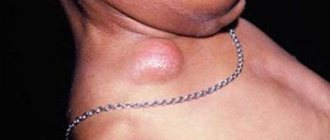
2. Enlarged liver and spleen
3. Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, in some cases to such an extent that they can prevent the head from turning.
4. Adenoids - difficult nasal breathing, snoring.
As a result of a general blood test (CBC), special cells are identified - monocytes (a type of leukocyte) - mononuclear cells.
A number of nonspecific symptoms of intoxication in mononucleosis:
- High fever that lasts for a long time (2-3 weeks).
- Weakness.
- Lethargy.
- Decreased appetite.
- Drowsy state.
In most cases, the course of this disease is not accompanied by symptoms, and by the age of 5, in 50% of cases, children already have antibodies to EBV.
If we talk about the adult population, then in 90-95% of cases, the body has protective titers of antibodies against mononucleosis, because they suffered this infection at an early age.
As stated earlier, mononucleosis is a viral infection, so there is no specific treatment. It is necessary to eliminate the symptoms that interfere with life.
To combat the symptoms of infectious mononucleosis, your pediatrician may prescribe the antibiotic amoxicillin/ampicillin. In children who receive these drugs, in 85% of cases, a rash appears on the body, which is accompanied by spots and itching. This rash can linger for a long time (up to three months).
Even after complete recovery, EBV may appear in saliva for a couple of months. Throughout life, without any symptoms or clinical changes, EBV can be isolated from a person. This causes transmission of the virus.
If EBV is found in the saliva of a healthy person, then no therapeutic action is necessary!
Common myths:
1. If you have suffered from mononucleosis, then you can forget about a vacation at sea.
2. Previously, there was an opinion that EBV, under the influence of UV rays, takes on oncogenic activity and increases the possible risks of developing blood cancers - leukemia. But such a connection has not been confirmed in modern clinical studies. The possible involvement of EBV in the development of Burkett's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma and certain types of gastric cancer has been noted. But these are independent diseases, and not a manifestation of mononucleosis. They can develop in people who have a predisposition to this and concomitant severe pathology: AIDS, malaria, primary immunodeficiencies. Burkett's lymphoma is common in Africa, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma is common in China.
3. Rupture of the spleen, as a result of its enlargement, is possible, but only in very extreme cases. For safety reasons, you should avoid blows to the abdominal area for three weeks from the moment of recovery.
4. Another common misconception is that you should avoid visiting children’s groups and vaccination is contraindicated within 6-12 months. These tips have not been confirmed in international studies, and therefore have no justification. Previous mononucleosis is not a contraindication to vaccinations, and you can be in children’s groups immediately after the child’s well-being improves.
5. A big misconception is chronic mononucleosis, which a child suffers from for several years and can only be cured with a complex regimen of immunomodulators. Infectious mononucleosis is an acute infection that lasts 3-4 weeks. After the illness, a condition similar to chronic fatigue (lethargy, pallor, drowsiness, lack of interest in games, apathy) may be observed for 3-4 months. There is no need to treat this condition, you just need to survive it.
What is chickenpox pneumonia?
This is a lung lesion that occurs in 16% of cases of chickenpox and in almost all cases if the disease occurs in a generalized form. The first symptoms may appear simultaneously with the rash:
- dyspnea;
- chest pain;
- cough with sputum (often with blood);
- bluishness of the skin.
Multiple focal nodules spread in the lungs, which on x-ray look like tuberculosis. Antibiotics do not help in this case. Against the background of chickenpox pneumonia, bronchitis often develops; in severe cases, pulmonary edema is possible.
Pneumonia that develops in the later stages of chickenpox is considered separately. It is caused by a secondary coccal infection and is a common pneumonia. The disease is treated according to the standard regimen - penicillin.
Rashes on the hands: the most common diseases
In order to choose the right treatment, it is important to distinguish one type of allergic dermatosis from another. Therefore, let’s look at the symptoms of skin diseases in more detail:
- With atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis), a rash often appears on the skin of the fingers and hands. The acute period of the disease is characterized by severe itching, redness and swelling of the skin. Itchy spots can come in different shapes and sizes. Without proper treatment, crusts may form at the site of the rash. In the chronic form, symptoms such as dry skin and flaking are observed.[3]
- Urticaria is divided into several types: immunological, physical, drug and idiopathic. The development of the first two is based on the body’s reaction to external stimuli, including food and household allergens, as well as high or low temperatures, sunlight and other factors. Taking certain medications can trigger drug-induced urticaria. Idiopathic is a rash whose cause cannot be determined.[4] All types of hives present more or less the same way: redness, swelling of the skin and the appearance of itchy blisters.
- Contact dermatitis often affects the skin on the fingers, especially when coming into contact with harmful substances such as rubber and metal products, household chemicals, cosmetics and perfumes, topical medications, certain plants and insects.[5] The disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms. The acute course is characterized by redness of the skin and the appearance of itchy blisters. The chronic form is accompanied by dryness and flaking of the skin, increased skin pattern.
- Eczema is an acute and chronic inflammatory disease that affects both the upper and lower extremities. It may also affect various parts of the body. As a rule, eczema rashes are symmetrical, accompanied by redness and limited swelling of the skin. Small blisters filled with clear liquid often appear on affected surfaces.[6]
Neurological complications of chickenpox
The consequence of infection with a herpes virus in an adult can be secondary encephalitis. Inflammation develops from the fifth to tenth day of the rash, sometimes even after recovery. The pathological process can be localized in different places:
- membranes of the brain (meningitis form);
- cerebellum (atactic form);
- spinal cord (myelitic form).
- Combined damage to the brain and spinal cord (encephalomyelitis, meningoencephalitis) is also possible.
In mild cases, damage to the central nervous system by the chickenpox virus leads to loss of coordination, involuntary eye movements, hand tremors, and dizziness. In more severe cases, vision suffers (up to its complete loss). The most dangerous complication is paralysis. Mental damage, even mental retardation, is also possible.