Causes
In many cases, the formation of ulcers in the facial area contributes to the appearance of inflammatory processes. Staphylococci and streptococci are among the most common pathogens. In accordance with the cause of development, specific and nonspecific lymphadenitis are distinguished. The development of the former can be caused by serious diseases such as tuberculosis. The second form develops due to direct penetration of infection into the lymph node. Entry may occur through lesions in the neck. Those people who are at risk include: patients with weak immunity; people whose field of activity is related to animals, dirty waters, etc. As a rule, people over 18 years of age experience this disease.
Types of lymphadenitis
Depending on the nature and duration of the disease, all lymphadenitis can be divided into subtypes:
- chronic;
- spicy.
Lymphadenitis can also be:
- Isolated – 1 lymph node is inflamed.
- Regional - the inflammatory process affects a group of neighboring lymph nodes.
- Total – lymphadenitis spread throughout the body.
The course of the disease is divided into specific and nonspecific: the first type includes inflammation as a result of tuberculosis, AIDS, toxoplasmosis or tumors, the second type includes all other types of lymphadenitis.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, better known as ICD-10, lymphadenitis is divided into groups according to location. They relate to diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (ICD-10 code - L04), as well as diseases of the circulatory system (code - I88).
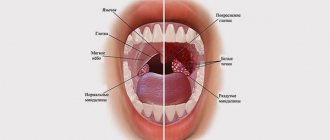
Acute lymphadenitis of the neck, head and face (L04.0)
About a third of the lymph nodes in the human body are localized in the head and neck area, which belong to group L04.0:
- submandibular;
- occipital;
- cervical;
- preauricular.
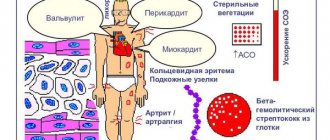
Inflammation of these lymph nodes occurs after tonsillitis and other bacterial diseases of the respiratory tract, with herpes, influenza and ARVI, due to dental diseases and inflammatory processes in the mouth. Lymphadenitis can also occur due to untreated wounds in the neck, face and cheeks. Another reason is infectious skin diseases.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis in this group include pain and discomfort in the affected area, difficulty swallowing, and fever in children. Lymphadenitis on the back of the head, behind the ears and under the chin is also visually noticeable: small spherical seals stand out on the skin and hurt when touched. You can see what the disease code L04.0 looks like in the photo.
Acute lymphadenitis of the trunk (L04.1)
This group includes inflammation of the lymph nodes of the body, which are located in the abdominal and thoracic region.
These include:
- abdominal or mesenteric lymph nodes;
- retrocrural lymph nodes;
- paraortic, paracaval lymph nodes;
- supraclavicular and subclavian lymph nodes.
This location of lymphadenitis may indicate viral and bacterial infections, as well as a specific type of disease resulting from tuberculosis, HIV infection, oncology of the abdominal and thoracic region.
Symptoms of the disease include severe chest or abdominal pain, increased body temperature, lethargy, and loss of appetite.
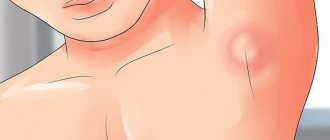
Acute lymphadenitis of the upper limb (L04.2)
Lymphadenitis of the upper limb includes inflammation of the lymph nodes of the elbow and armpit. Most often, the lymph node is enlarged on one side and visually appears as a swollen, reddish lump.
Axillary and ulnar lymphadenitis occurs due to infections of various etiologies:
- tonsillitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis and other bacterial diseases;
- influenza and herpes, ARVI;
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- infected wounds and abrasions in the armpit, chest and arms.
Also, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the axillary region can indicate mastopathy and mastitis that occur after childbirth and during feeding. In this case, the symptom manifests itself before menstruation, 2-3 days before the start of menstruation, and goes away on its own after a week.
Signs of the disease, in addition to noticeable swelling of the lymph node, include pain and discomfort in this area, possible itching, and fever.
Acute lymphadenitis of the lower limb (L04.3)
Lymphadenitis of the lower extremity includes inflammation of the inguinal and popliteal lymph nodes. They can develop as a result of inflammation of the soft tissues of the legs, from hypothermia, due to wounds and abrasions, infected calluses and uncomfortable shoes.
Also, the causes of inguinal lymphadenitis include diseases of the genital organs:
- urethritis;
- prostatitis;
- vaginitis;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia.
Most often, inflammation of the lymph nodes of this group occurs in adults.
Acute lymphadenitis of the lower extremities is accompanied by severe pain at the site of inflammation, discomfort, noticeable compaction and swelling of the lymph node.
Nonspecific mesenteric lymphadenitis (I88.0)
Nonspecific mesenteric lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes resulting from a bacterial or viral infection.
The causative agents of mesadenitis include:
- streptococci and staphylococci;
- enteroviruses;
- salmonella;
- mononucleosis.
The disease is characterized by severe abdominal pain, fever, vomiting and nausea. Disorders of stool and gastrointestinal functioning are also often observed: diarrhea, constipation, hiccups.
Chronic lymphadenitis (I88.1)
Chronic lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph nodes that occurs over a long period of time. It can be unilateral or bilateral, specific or nonspecific, and localized in different parts of the body.
The chronic course of the disease may be due to:
- complications of tonsillitis, bronchitis and tonsillitis;
- purulent boils and ulcers on the body;
- oral infections;
- fungal infections;
- tuberculosis;
- AIDS and HIV infection.
As in the case of acute lymphadenitis, the disease is accompanied by thickening and enlargement of the lymph nodes. At the same time, a swollen and hard lymph node practically does not hurt and remains mobile. Other symptoms, such as fever, redness, pain and weakness, are also less pronounced.
What contributes to the development of the disease?
There are several factors that contribute to the spread of lymphadenitis in children and adults:
- infection of the nasal and oral cavities,
- dysfunction of the endocrine system,
- HIV,
- severe allergies,
- metabolic disorder,
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Cervical lymphadenitis is not transmitted from one person to another, since it is only an additional process that appears as a complication. In accordance with the diseases occurring against the background of this pathology, treatment is prescribed by a certain specialist in his field (surgeon, infectious disease specialist, and so on). Initially, lymphadenitis occurs in an acute form, gradually turning into a chronic form.
causes of cervical lymphadenitis
Varieties
Types of cervical lymphadenitis:
- Penetration of infection into the lymph node (quickly cured, practically does not lead to complications).
- Presence of serious illnesses. In this situation, diagnosis is carried out in the acute form of the pathology.
There are several stages of the disease in acute form:
- Serous. Does not cause intoxication or severe fever. The initial stage of penetration of harmful organisms into the lymph node.
- Purulent. Indicates bacterial infection. Promotes the appearance of high temperature. In this case, surgical intervention is a necessary condition.
- Complicated. In this situation, we are talking about immediate surgical intervention, since the disease can cause infection of the entire body. The disease occurs along with the spread of infections through the lymph nodes. It is worth noting that this form is highly curable and does not cause complications. The development of pathology in other nodes can cause the spread of a serious disease, which is called generalized lymphadenitis.
Why is lymphadenitis dangerous?
{banner_banstat10}
If the infection is not treated, it will continue to spread throughout the body. Prolonged inflammation of the lymph nodes can lead to tissue necrosis, destruction of the lymph nodes, sepsis and serous purulent pathologies.
Complications arising from lymphadenitis:
- thrombophlebitis;
- lymphostasis;
- osteomyelitis;
- encephalitis and meningitis;
- abscesses.
Important! Serious consequences of the disease can include purulent pathologies, disability and even death.
Symptoms
The main symptoms that indicate the presence of lymphadenitis are the following: increased body temperature, insomnia, fatigue, nervous system disorders; indifference to life, poisoning, etc.
In the initial stage of acute lymphadenitis, thickening of the lymph nodes can be observed. When pressed, discomfort and pain occur. Such signs are considered dangerous, so patients should immediately consult a doctor for advice. Otherwise, further development of a dangerous disease may occur.
Symptoms of the chronic form of the studied lymphadenitis in adults and children include: hardening of the lymph nodes, high body temperature, weakness and fatigue, insomnia, pain when pressing the lymph nodes.
At the stage of the chronic form of the disease, the symptoms become somewhat muted. This is due to the fact that the body reduces the number of mechanisms spent on fighting pathology. As a result, the body is poisoned. Purulent inflammation leads to an increase in the number of external symptoms of the disease, which leads to exacerbation. Purulent inflammation is indicated by intense pain and swelling of the lymph nodes. A similar condition is life-threatening and requires urgent intervention.
lymphadenitis symptoms
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the lymph nodes, preventive measures should be followed.
These include:
- Timely treatment of bacterial and viral diseases.
- Treatment of purulent skin lesions of any origin.
- Oral care: routine dental consultations, hygiene.
- Breast hygiene, especially during breastfeeding.
- Protection during sexual intercourse to avoid STDs.
- Antiseptic treatment of cuts, abrasions and wounds.
- Correction of immunity with vitamins, diet and special medications.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is not a full-fledged disease, but an unpleasant symptom that indicates a serious pathology in the body. If not treated on time, lymphadenitis can lead to serious complications and consequences.
Diagnostic methods
neck lymphadenitis detected ? During the examination, the doctor presses on the lymph nodes to determine the cause. A general blood test will provide the necessary information about the course of pathological processes, which are characterized by an increase in the number of lymphocytes.
If the diagnosis is established without the presence of certain complications, the doctor immediately prescribes therapy. However, in cases where the doctor notes disturbances in other systems, it is necessary to conduct additional examinations, which include:
- general and biochemical blood test,
- histology examination,
- x-ray of the chest area,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity,
- immune system examinations and blood tests to check for hepatitis.
In any case, consultation with a specialist is mandatory. An exacerbation of the disease can occur at any time.
Possible complications
This diagnosis is a good reason to consult a doctor and carry out urgent treatment. In the worst case, dangerous consequences may occur through:
- purulent pimples,
- thrombophlebitis,
- septicopyemia.
When purulent fluid is released into the esophagus or bronchi, then there is a high risk of the spread of dangerous complications (for example, fistulas in the esophagus).
As a result of the chronic form of the disease, inflammatory processes in the form of sepsis or adenophlegmon are often observed.
Therapy
Lymphadenitis is treated in an adult using traditional methods. These include:
- bed rest,
- treatment with antibiotics,
- UHF,
- electrophoresis,
- galvanization,
- no impact on damaged areas of the body,
- vitamin complexes.
Among other things, they may also prescribe special products and ointments.
Importance is attached to lymphadenitis treatment with antibiotics . Before prescribing this type of treatment, the specialist is obliged to conduct an examination to determine whether harmful organisms have reacted to such drugs. It is clear that the doctor prescribes to the patient those medications to which the pathogens give a reaction.
When it comes to urticaria lymphadenitis with purulent processes, then to cure it is necessary to open the purulent pimples and remove all the liquid from them.
If a tuberculosis bacillus is detected, the patient is transferred to hospital treatment. Within the clinical center, strict monitoring of the patient’s condition is carried out, as well as his isolation from healthy people to prevent the development of infection.
treatment of lymphadenitis
To treat chronic lymphadenitis, it is necessary to detect and eliminate the main factor of lymph node compaction. Only this will allow you to get rid of the pathology 100% forever.
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes
The symptoms of pathology can be eliminated with the help of medications, traditional methods of treatment and physiotherapy.
Medicines
| Group name | Effect on lymphadenitis | Representatives |
| Antibacterial drugs | Antibiotics destroy the cell membrane of bacteria, which leads to their death. Used for bacterial infections. | Amoxiclav, Clindamycin, Azithromycin |
| Antiviral drugs | They inhibit the development of the virus by suppressing DNA replication or inhibiting neuraminidase. Used for viral lymphadenitis. | Amantandine, Remantandin, Tamiflu |
| Antifungal drugs | Drugs that increase the permeability of the fungal membrane, which prevents their reproduction and destroys the fungus from the inside. | Fluconazole, Amphotericin B |
| Antiseptics | Prevent the development of infection that occurs when the skin is injured. | Vishnevsky ointment, |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Medicines that suppress the formation of prostaglandins and have a strong anti-inflammatory effect. | Ibuprofen, Ketorol, Nimesil |
| Antispasmodics | They are used for mesenteric lymphadenitis of viral, bacterial or tuberculous origin. Relieves pain. | No-Shpa, Drotaverine |
| Antihistamines | They constrict blood vessels at the site of inflammation, reduce capillary permeability, weaken and nullify the inflammatory process. | Cetirizine |
How to treat with folk remedies at home
If an accurate diagnosis has not been established and there are no medications at hand, you can use traditional methods of treatment. They include compresses and drinks made from vegetables, herbs and herbs, as well as echinacea tincture.
Uses of Echinacea
To get rid of lymphadenitis, a compress is made from echinacea - an effective remedy that resolves inflammation:
- 50 ml of tincture is mixed with 100 ml of water. The mixture is infused for half an hour.
- Gauze or a napkin is moistened with the solution and applied to the inflamed area.
- A small layer of cotton wool or soft cloth is laid on top.
- The compress is secured to the area with a bandage and held until it dries.
Beet juice
Beetroot juice, obtained from the vegetable or its tops, has a strong cleansing effect and also improves the functioning of the lymphatic system.
To cure lymphadenitis, it should be consumed as follows:
- Extract juice from beets using a juicer. It is advisable to pre-cut it into pieces.
- Let the juice steep for half a day.
- Drink 100 ml of the drink on an empty stomach, morning and evening.
If the product is given to a child, the volume of juice should be reduced by half. It is also advisable to add a little carrot juice to make the drink more palatable.
Anti-inflammatory collection
Herbal infusions that relieve inflammation - you can use either ready-made pharmaceutical ones or mix the following ingredients yourself:
- peppermint;
- raspberry leaves and berries;
- dandelion root;
- Linden blossom;
- wormwood grass.
The components must be dried and mixed in equal proportions. 4 tbsp. l. the resulting collection is poured with 1 liter of boiling water, the infusion is allowed to brew for half a day, and then drunk half a glass 3-4 times a day.
Celandine compress
Celandine is an effective disinfectant and anti-inflammatory agent. To combat lymphadenitis, it can be applied to fresh leaves; they must be scalded with boiling water, cool slightly and applied to the affected area for 30-40 minutes.
A celandine compress is made as follows:
- 25 ml of celandine is diluted in 100 ml of water. The mixture is infused for half an hour.
- Gauze is soaked in the solution and applied to the lymph node.
- The compress is covered with cotton wool or a soft cloth, secured with a bandage and left for an hour.
Horsetail infusion
{banner_banstat9}
Horsetail is a blood purifier that improves the functioning of the lymphatic system.
An infusion of it is taken orally and prepared as follows:
- A tablespoon or 1 pharmaceutical bag of herbs is brewed in 250-300 ml of boiling water.
- The mixture is infused for 20-30 minutes, then filtered.
- Take 3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
To enhance the effect, it is worth making a decoction of knotweed herb according to the same recipe. Taking infusions should be alternated at intervals of 2 days.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is the use of physical factors on the body to treat a disease. The use of the method for lymphadenitis reduces inflammation, accelerates tissue regeneration, and also alleviates the patient’s general condition.
Physiotherapeutic methods used for inflammation of the lymph nodes:
- Ultra-high frequency or UHF therapy. It affects the body with a high-frequency electromagnetic field, increasing temperature and dilating blood vessels. This helps leukocytes quickly reach the site of inflammation, which speeds up recovery.
- Laser therapy. It affects the body's tissues with light waves, improving microcirculation, analgesically and relieving inflammation in the lymph node. Accelerates regeneration, helps with all types of lymphadenitis.
- Galvanization. It affects the body with a weak low-voltage electrical tone, relieving pain, restoring tissue and nerve fibers, stimulating microcirculation inside the lymph node.
When using these methods, lymphadenitis goes away faster, but they cannot completely replace drug therapy. Physiotherapy should be used as an adjuvant and only under the supervision of a physician to avoid complications.