Foods that may cause a bitter taste in your mouth
A good place to start is to take stock of what you've recently eaten. Some foods cause a bitter aftertaste:
- Pine nuts;
- Fatty meats;
- Strong coffee or tea;
- St. John's wort decoction;
- Pasta;
- Sea buckthorn oil;
- Alcohol.
Typically, a bitter taste occurs immediately after eating or after several hours. Bitterness in the mouth can also be caused by taking certain medications - antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, blood pressure medications, and others.
What to do
- It is necessary to avoid “bitter” foods or not eat them before bed.
- Diversify the menu with fruits, especially citrus fruits.
- Add buckwheat porridge to the list of dishes.
- If the bitterness is caused by taking pills, it disappears a few days after the end of treatment.
Complications after dental prosthetics
- Sores and chafing after installation of dentures;
- Inflammatory process on the gums under dentures. Stomatitis;
- Diseases of supporting teeth (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- Allergy to materials used to create prostheses;
- Galvanic syndrome;
- Loosening the fixation of removable structures;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Let's look at each of the complications in more detail.
Sores and chafing after installation of dentures
A common phenomenon, especially typical for removable structures.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations, pain while eating;
- Feeling of a foreign body in the mouth;
- Profuse salivation.
Treatment
The next day after the installation of a removable structure, there is always a follow-up appointment at the dentist's office. Regardless of the presence or absence of unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to come to the clinic for an examination, otherwise, if this is not done, bedsores will form .
If necessary, the doctor will correct the prosthesis and set a date for the next visit. At least two amendments are required for everyone.
During the first two to three weeks, you get used to the dentures, and discomfort is completely normal. Full adaptation usually occurs by the end of the third week.
Prosthetic stomatitis
Prosthetic stomatitis
One of the most common complications.
Symptoms
- In the first time after installing the prosthesis, in addition to discomfort, excessive pressure on the mucous membrane and pain are felt. Redness of the gums appears, and possibly the formation of pustules on the mucous membrane. Small blood vessels are pinched, and the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted at the site of contact - bedsores form;
- The fixing elements of partial dentures can also irritate the surrounding periodontal tissues and contribute to their inflammation.
Treatment
It is necessary to visit your doctor, who will carry out antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and dentures, prescribe local anti-inflammatory therapy (rinses, mouth baths, ointments, gels), as well as a set of procedures aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration.
Diseases of supporting teeth
In the case of partial dentures, there are teeth in the oral cavity that perform the important function of supporting and securing the denture. Whether the supporting teeth are healthy, covered with crowns or restored with fillings, in any case it is necessary to take care of it and maintain hygiene of the entire oral cavity.
Symptoms
- Visible accumulations of food debris, plaque on teeth, as well as on removable structures;
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth and from the prosthesis;
- Bleeding gums around supporting teeth;
- Painful sensations during meals, from temperature stimuli, night pain.
Treatment and prevention
- Maintain regular and thorough care of dentures and teeth;
- Visit a doctor for professional oral hygiene;
- If pain occurs during chewing, as well as aching, sharp pain, contact your dentist.
Allergy to dentures
Allergy to dentures
An allergic reaction to denture materials can occur when the dentures come into contact with the tissues of the patient's body.
Currently, scientists are trying to minimize the occurrence of such reactions, and today many different materials for the manufacture of removable dentures.
The rate of occurrence of an allergic reaction can vary - from several minutes to several hours, and sometimes days after installation of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- Rashes on the skin of the face;
- Redness and swelling of the oral mucosa;
- Attacks of bronchial asthma. Suffocation;
- Inflammation of the salivary glands;
- Dry mouth;
- Burning sensation of tongue.
Treatment
- Remove dentures;
- Contact an orthopedic dentist as soon as possible;
- Carry out repeated prosthetics with structures made of a different material.
Galvanic syndrome
This complication after prosthetics is the formation of galvanic current in the oral cavity.
The cause of the occurrence is the presence of dissimilar metals in all structures installed in the oral cavity (for example, used as the base of a prosthesis and as part of crowns) if a particular patient is predisposed to this disease.
In modern dentistry, in the manufacture of dentures, metals and their alloys are used, such as stainless steel, cobalt-chrome, silver-palladium alloys, alloys based on precious metals and others.
It is known that any alloy immersed in an electrolyte solution (in this case, saliva acts as this) acquires a potential unique to it. If metals with different potentials are present in the patient’s oral cavity, then all the conditions necessary for the formation of galvanic current arise.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations while eating;
- Metallic taste in the mouth;
- A bitter and acidic taste in the mouth, especially aggravated when a metal spoon touches the dentures;
- Headache;
- Sleep disorders;
- General malaise;
- Allergic manifestations on the oral mucosa (swelling, erosion);
- Darkening of metal prostheses.
Treatment
- Repeated prosthetics, excluding the presence of dissimilar metals in the oral cavity.
Loosening the fixation of removable structures
Weakening of fixation of removable structures
This complication develops gradually, as the design of lamellar prostheses approaches the end of their service life.
In the case of clasp prosthetics, it is also possible for the plastic parts of the locking prostheses to wear off and the clasps to loosen .
Causes
- Daily use, regular removal from the oral cavity, changes in the anatomical structure of the prosthetic bed (loss of bone tissue with age).
Symptoms
- Sensation of displacement, movement of the prosthesis in the mouth;
- Lack of adherence of the prosthesis to the gums and teeth;
- Loss of structures from the mouth during eating and talking.
Treatment
- Making a new removable denture;
- Using special dental adhesives for fixation.
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
Relining of the prosthesis - correction, restoration of a removable structure in order to obtain a denture base adapted to chewing pressure, clarifying its fit to the prosthetic bed.
Over time, atrophy of the mucous and bone tissue occurs under the base of the removable denture. Atrophy leads to uneven distribution of chewing pressure between the supporting teeth (if any) and the mucous membrane. Failure to reline a removable denture can lead to its breakage and loss of supporting teeth.
Relining can take place either directly in the patient's mouth or in the laboratory.
Method of relining a removable denture in the clinic
- The dentist removes a thin layer of plastic from the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed and applies an even layer of self-hardening plastic to the treated base. After some time, the prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity, installed and pressed, after which the patient closes his jaws. Excess plastic is removed with a spatula. After this, the prosthesis is removed and placed in a special apparatus, where the final polymerization of the plastic (hardening) takes place;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Causes
- Errors at the stages of prosthesis manufacturing: excessive or insufficient thickness of the base in the frontal region, incorrect determination of the height of the lower third of the face and the centric relation of the jaws, inaccurate placement of artificial teeth in the base of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- “Failed” or, conversely, excessively protruded lips;
- Biting cheeks with removable dentures;
- Deep nasolabial folds;
- Drooping corners of the mouth;
- The ability to close your lips only with force, while in a relaxed state your teeth are visible;
- Feeling of tightness in the cheeks.
Gallbladder and liver problems
If bitterness causes you anxiety every day for a long time, it's time to get your liver and gallbladder checked. Perhaps, as a result of a malfunction or inflammation, the gallbladder does not have time to remove bile from the body on time, and it ends up in the esophagus. This is where the unpleasant taste comes from.
What to do
- A blood test is mandatory; it is advisable to do both a general and biochemical one, as well as an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- As a rule, the doctor recommends taking anti-inflammatory and choleretic drugs (prescription only).
- For patients with cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, a diet is prescribed: milk and light vegetable soups, low-fat cottage cheese and kefir, boiled fish, marmalade, and tea are allowed.
- It is recommended to drink about 2-3 liters of liquid per day
- Decoctions and infusions of chamomile and calendula are useful, for the preparation of which 1 tsp is used. dried inflorescences are brewed with a glass of boiling water for 15-20 minutes. Take the decoction 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. half an hour before meals.
Stomach problems
The appearance of bitterness in the mouth also indicates stomach problems. It is often complicated by additional indications: bloating, nausea, heartburn, stomach pain, belching and a yellow-white coating on the tongue.
What to do
- Restore proper functioning of the digestive organs: remove heavy fatty and smoked foods, spices, salty and fried foods from the diet.
- Take medications that normalize the functioning of the stomach and intestines (as prescribed by a doctor).
Attention!
Bitterness in the morning, together with pain in the right side, more often indicates problems with the liver and gall bladder, short-term and after meals - about problems with the duodenum and gastrointestinal tract, hormonal disorders.
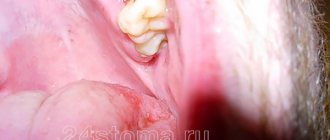
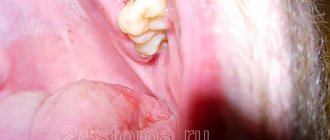
Causes of alveolitis
Normally, after a tooth is removed, a clot of blood cells and fibrin, the protein from which a blood clot is built, forms in the socket. It almost completely covers the bottom and walls of the alveoli. The clot serves as a mechanical barrier, biological protection against infection and additional injury to the wound surface. In this case, healing occurs by primary intention. The wound is slowly filled first with loose tissue, then with denser connective tissue, and later with young bone.
But there are situations when the healing process is disrupted.
Inflammation of the socket occurs if:
- The operation was highly traumatic, which reduced the protective capabilities of one’s own tissues;
- The blood clot, as the main defense, is broken or completely absent (“dry socket”):
- prolonged bleeding;
- early destruction of the clot;
- non-compliance with the rules of care (for example, increased rinsing, eating hard or too hot food soon after surgery);
- Tooth extraction was carried out for emergency reasons due to an acute infectious process: periodontitis or periodontitis with complications;
- There are common reasons:
- reduced immunity;
- blood clotting disorder;
- elderly age;
- lack of proper dental hygiene.