July 30, 2020
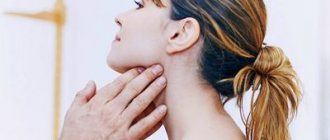
To talk about local inflammation, you must first understand what lymphadenitis is in general. This is an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, sometimes accompanied by suppuration
To talk about local inflammation, you must first understand what lymphadenitis is in general. This is an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, sometimes accompanied by suppuration. It manifests itself through enlargement of one or more lymph nodes and can occur in several regions of the body at once. Clinical signs of the disease depend on the form and type of lymphadenitis: acute or chronic, regional (damage to lymph nodes of one anatomical group) and generalized (involvement of several groups of lymph nodes), serous, purulent, gangrenous, hemorrhagic, phlegmonous.
In the body, lymph nodes create a protective barrier against viruses, infections, cancer cells, participate in the formation of lymphocytes (special cells that destroy foreign microorganisms) and the production of phagocytes, antibodies (immune cells), participate in digestion and metabolic processes, distribute intercellular fluid between body tissues and lymph.
Normally, the lymph nodes are not palpable or are palpated in the form of elastic, small-sized formations that are not fused with adjacent tissues or with each other. Depending on the prevalence, the following types of lymphadenitis should be distinguished:
- local - enlargement of one lymph node in one of the areas (single cervical, supraclavicular lymph nodes);
- regional - enlargement of several lymph nodes in one or two adjacent areas (supraclavicular and axillary, supraclavicular and cervical, occipital and submandibular lymph nodes, etc.);
- generalized - enlargement of lymph nodes in three or more areas (cervical, supraclavicular, axillary, inguinal, etc.).
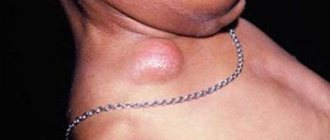
With axillary lymphadenitis, enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit are palpated. Symptoms of axillary lymphadenitis:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Painful sensations when palpating the affected area, turning the body, or moving
- Inflamed nodes are fused together with each other and adjacent tissues into one dense conglomerate
- The skin over the inflamed lymph nodes is hyperemic
- Symptoms of body intoxication appear - fever, weakness, headache, lack of appetite, feeling weak, muscle pain
Often the disease is accompanied by symptoms of the underlying disease; in addition, the patient may be bothered by:
- night sweats;
- weight loss;
- prolonged increase in body temperature;
- frequent recurrent upper respiratory tract infections;
- pathological changes on a chest x-ray;
- hepatomegaly;
- splenomegaly.
Causes of lymphadenitis
The function of the lymph nodes is to prevent the spread of infectious processes in the body. Any infectious agent that gets into them is destroyed by lymphocytes. When too many foreign microorganisms arrive, lymphocytes cannot cope with so many bacteria, the latter begin to actively multiply. This creates conditions for other types of leukocytes to penetrate into the site of inflammation, which causes an enlargement of the lymph nodes. One or more of them may become inflamed.
Inflammation can be nonspecific and specific. In the first case, the causes of the disease are bacteria and their toxins, viruses, and fungi. Lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes is caused by staphylococci and streptococci; they are pyogenic flora. The primary source of infection in the nonspecific form of the disease are boils, festering wounds, trophic ulcers, caries, erysipelas, and thrombophlebitis. In children, inflammation of the lymph nodes is often a complication of inflammatory processes in the ENT organs (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, influenza), childhood infections (scarlet fever, mumps, diphtheria) and skin diseases (diathesis, pyoderma).
A specific type of disease is triggered by certain types of microorganisms:
- tuberculous mycobacterium;
- plague stick;
- Brucella (the causative agent of brucellosis);
- Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis);
- tularemia bacteria (causing tularemia);
- actinomycete (the causative agent of actinomycosis).
When infected with these types of microorganisms, special symptoms characteristic of a particular disease develop. Lymph nodes undergo specific changes, since infectious agents enter them with the flow of lymph.
Is it possible to use traditional methods for treatment?
The craze for traditional medicine is bearing fruit. People are trying to replace pills with natural remedies. Alas, advanced lymphadenitis cannot be cured by this. Traditional methods can become an additional way to treat the disease in the initial stages of lymphadenitis and only in consultation with a doctor.
If you are undergoing treatment at the dentist, then take on board the following remedies to help cope with inflammation:
- ginger tea;
- compress with echinacea tincture;
- blueberry drink before meals;
- beet juice;
- vitamin C.
These remedies will help strengthen the body and activate forces to fight the disease. At least they won't do any harm.
Important: do not use traditional medicine without medical supervision. Not a single folk remedy can cope with purulent inflammation. As a result, you will still see a doctor, but it will take longer to be treated.
In the worst case, self-medication will lead to the appearance of chronic lymphadenitis - the accumulation of disease in the lymph nodes. In this case, the lymph nodes will become dense and painless. But the inflammation has not gone away - it is “dormant” and waits for the hour to strike the body with an acute attack under favorable conditions.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
Based on the nature of the inflammatory process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Acute lymphadenitis. The duration of the course is up to two weeks. Characteristic symptoms: pain and enlargement of regional lymph nodes, fever, headache, general weakness, loss of appetite, swelling and redness of the skin in the area of the affected node.
- Chronic lymphadenitis. The duration of the disease is 1 month or more. Develops with a sluggish infection or after untreated acute lymphadenitis. With this course, the pain syndrome is erased, but the lymph nodes themselves remain enlarged and dense. Lymphatic fluid retention and swelling are noted.
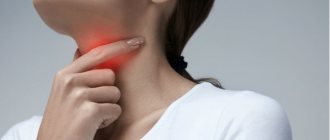
Lymphadenitis is classified according to the location of the inflamed lymph nodes into the submandibular, cervical, axillary and inguinal. All of them are characterized by similar symptoms: enlarged lymph nodes, pain, redness of the skin, intoxication syndrome. The differences are due to the location of the inflammatory focus.
Thus, with cervical lymphadenitis, there is a restriction in head movement; when turning or bending, the patient feels acute severe pain. If the lump is large, it can put pressure on the organs of the neck and cause difficulty breathing, changes in voice, and difficulty swallowing food.
Submandibular lymphadenitis is accompanied by pain in the jaw during talking or eating, but is rarely bothersome at rest. With the axillary type of the disease, hand movement is impaired, swelling of the upper limb on the affected side increases and its sensitivity is impaired.
Inguinal lymphadenitis is characterized by swelling of the legs on the affected side. This manifestation is due to a violation of the outflow of lymph and compression of large vessels in the groin area. If suppuration occurs, the body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, the patient feels weakness and pain in the lower abdomen.
How to prevent lymphadenitis?
Few people want to experience the symptoms of lymphadenitis. And to prevent inflammation from attacking you, follow simple rules:
- Treat all oral diseases in a timely manner, to do this, contact your dentist once every six months (online appointment) for a preventive examination;
- avoid injuries and scratches in the jaw area;
- treat all wounds with antiseptics.
DaVinci Aesthetic Dentistry Studio will help cure lymphadenitis at any stage. But we would be even more happy to help you warn him.
Add a comment
Leave your comment
Diagnosis of lymphadenitis
Recognizing acute lymphadenitis is not difficult. To make a diagnosis, anamnesis and a set of symptoms are studied. Difficulty can arise when infection of the lymph nodes is complicated by other concomitant diseases. In all cases, it is first necessary to determine the location of the primary purulent focus. In case of chronic disease, the patient is prescribed a puncture biopsy of the lymph node and histology.
To diagnose lymphadenitis, a general blood test is required. Based on its results, they judge not only the presence of the inflammatory process, but also its scale. Laboratory signs of lymphadenitis will be an increase in the total number of leukocytes and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. With an active purulent process, a decrease in the level of monocytes and eosinophils is detected.
Diagnostic examination involves instrumental methods - ultrasound. With its help, you can determine the shape and size of the lymph nodes, their connection with surrounding tissues, and the presence of an abscess. If necessary, computed or magnetic resonance imaging and x-ray contrast lymphography are used.
Nonspecific lymphadenitis should be differentiated from other diseases, such as lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, chronic granulomatous disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as metastases from malignant tumors.
Treatment of lymphadenitis
Treatment of inflamed lymph nodes is carried out in two directions:
- determining the source of the inflammatory process and eliminating it;
- relief of chronic and acute inflammatory process in the lymph node.
First of all, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the underlying disease that led to infection of the lymph nodes. If purulent inflammation develops, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, where the abscess is surgically opened.
Cervical lymphadenitis - symptoms and treatment
Elimination of the primary source of infection
Cervical lymphadenitis is often caused by acute or aggravated periodontitis and complications of advanced caries, such as acute purulent periostitis.
If the tooth can be saved, the root canals are cleaned and filled. If it is impossible to restore a tooth, it is removed. When a purulent focus has formed, the diseased tooth is treated or removed, and the abscess is opened. If cervical lymphadenitis has developed due to a disease of the ENT organs, the source of acute inflammation should also be eliminated.
Drug therapy
- Antibacterial therapy. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are usually used, mainly with a bactericidal effect. The components of such drugs destroy the cell wall of the bacterium or disrupt its metabolic processes, which leads to the death of the microbe. If the patient's condition does not improve, biological material obtained from the lymph node is examined and the sensitivity of microorganisms to drugs is determined.
- Antiviral drugs are used for viral origin of lymphadenitis, for example, herpes.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs suppress inflammation at the cellular level, reduce pain and reduce fever.
- Antihistamines reduce capillary permeability, which prevents the development of edema and congestive processes. They also prevent leukocytes from penetrating into the lesion and inhibit the production of substances that contribute to the development of inflammation.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
- UHF (ultra-high frequency therapy) is aimed at reducing swelling, inflammation and pain.
- Ultrasound is used to speed up the resolution of the inflammatory process.
- UVR (ultraviolet irradiation) is indicated to reduce inflammation.
- Laser therapy is aimed at reducing pain, improving nutrition and blood supply to the affected area.
- Electrophoresis is a method in which a medicinal substance penetrates tissue using a direct electric current. For lymphadenitis, electrophoresis with potassium iodide and proteolytic enzymes is usually performed.
- Magnetic therapy is aimed at reducing pain, inflammation, swelling and congestion in tissues.
Physiotherapeutic methods are used in Russia to reduce the duration of drug treatment, but there is insufficient scientific evidence of their effectiveness.
Surgical intervention
Opening a purulent focus is indicated for purulent forms of lymphadenitis and adenophlegmon. Depending on the size of the lesion, the operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. During surgery, the purulent contents and tissue of the disintegrated lymph node are removed.
After surgical treatment, a drainage is placed in the wound, which ensures the drainage of pus and prevents the edges of the wound from healing. Then the wound is treated, its edges are renewed and sutured.
Detoxification therapy
Reduces the level of toxins in the body by diluting them, absorbing breakdown products and increasing diuresis. To do this, drink more fluid, and in severe cases, Hemodez and Reogluman are administered intravenously.
Diet
It is recommended to eat a balanced diet and consume enough vitamins, macro- and microelements.
Features of treatment of lymphadenitis
Treatment of cervical lymphadenitis directly depends on the stage and form of the disease.
In acute serous lymphadenitis, special attention is paid to the primary source of inflammation: inflammatory diseases of the teeth, oral cavity and ENT organs. If the primary inflammatory process is stopped in the early stages, then the symptoms of acute serous lymphadenitis also become less pronounced.
In almost 98% of cases with acute lymphadenitis, it is possible to identify the primary lesion [10]. It is eliminated and antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory or antihistamine therapy is prescribed.
When a purulent form develops, the primary focus is eliminated, the abscess is opened and the tissue of the disintegrated lymph node is removed. The patient is usually kept in the hospital under 24-hour observation. Daily dressings are performed, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and detoxification therapy is prescribed.
In case of chronic hyperplastic lymphadenitis, the affected lymph node is removed, and treatment is also carried out in the hospital. Tissue fragments are sent to the laboratory, processed and examined under a microscope. This procedure allows you to exclude cancer and prevent its development.
Drug treatment: drugs most often prescribed
Treatment is complex and includes the use of various groups of medications. It is customary to use the following drugs for lymphadenitis:
- Antibiotics. To eliminate the source of infection (Amoxicillin, Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Vancomycin, Lincomycin).
- Analgesics. To eliminate pain syndrome (Tramadol, Trimeperidine).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects (“Ketoprofen”, “Ibuprofen”, “Paracetamol”).
- Antihistamines. Helps relieve the inflammatory process (Cetirizine).
- Antiseptics for topical use (Vishnevsky ointment).
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy methods are used - UHF. Ultrahigh-frequency therapy accelerates the elimination of the inflammatory process and enhances local tissue immunity. This method of treatment is contraindicated when the patient has a persistent increase in body temperature, has a tumor process, tachycardia, or muscle pain.
Frequently asked questions about lymphadenitis
What is submandibular lymphadenitis?
This is an inflammation of the lymph nodes that are located under the lower jaw. This form of the disease develops in the presence of an infectious focus in the oral cavity. This could be caries, periodontitis, gum disease, tonsillitis. It is accompanied by symptoms such as pain at the location of the node and redness of the skin above it, increased body temperature, pain during eating and during conversation, general malaise, and headache.
How long does it take to treat lymphadenitis?
The duration of treatment for the disease depends on a number of factors: the form of the disease; the presence of a purulent process; causative agent of lymph node inflammation. To completely eliminate the inflammatory process and eliminate pathogenic microbes in uncomplicated lymphadenitis, the course of treatment will be about two weeks. In the chronic form of the disease, therapy is long-term.
Is it possible to warm a lymph node?
Thermal effects on the inflamed lymph node are allowed when the inflammatory process has not yet been complicated by the formation of pus. It is believed that warming compresses with camphor oil or infusion of medicinal herbs help relieve pain and inflammation. However, you should consult your doctor before undertaking warming procedures, as such actions may worsen the infection. If the skin over the inflamed lymph node is red, then warming it is contraindicated, as this is a sign of suppuration.
Why does lymphadenitis occur?
Like any inflammation, lymphadenitis occurs due to the activity of bacteria: streptococci and staphylococci. The causes of submandibular lymphadenitis are diseases of the oral cavity and infection that enter directly into the lymph nodes as a result of diseases such as:
- caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- gum disease;
- chronic diseases (for example, tonsillitis);
- syphilis bacteria;
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- external infections that enter the body as a result of injury.