Signs Causes Types Complications Diagnostics Treatment Methods Prevention Doctors Work
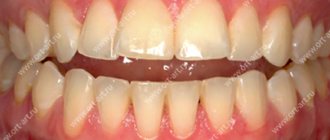
Malocclusion occurs in different forms. One of them is an open bite. It is recorded quite rarely - up to 2% of patients have such an anomaly. In 12% of children under one year of age, improper closure is noted, by 6 years - 5.6%, and in adults the percentage is very small - 1.8 - 2%.
What is an open bite
Open bite - incomplete closure of the frontal row of teeth or lateral sections. A vertical gap is formed, which causes not only an aesthetic problem, but also functional disorders. Quite often, this type of pathology can be combined with another form of occlusion, and it is necessary to treat a distal or mesial open bite.
Signs
Visual signs of an open bite:
- a downwardly displaced chin and an enlarged lower part of the face;
- half-open mouth;
- the upper lip is narrow and tense at the moment of closure;
- the sky is shifted down and back;
- the nasolabial fold is smoothed.
Intraoral symptoms:
- vertical interdental gap;
- the first molars close in their normal position, but the incisors do not;
- trapezoidal shape of the lower jaw;
- the jaw arches narrow;
- crowding of the lower incisors due to lack of space;
- the height of the lateral parts of the jaw is greater than usual;
- the mucous membrane is often inflamed, the gingival papillae are deformed;
- macroglossia (enlarged tongue).
Lisp and slurred speech are also one of the signs of pathology. The patient breathes frequently through his mouth. Swallowing is infantile. It is difficult for him to bite off due to a violation of the closure of the teeth and chew food.
Why does the jaws not close properly?
In addition to the above reasons, open bite can occur due to heredity. If a woman suffered from somatic or infectious diseases during pregnancy, the risk of malocclusion in the child increases.
Disruption of metabolic processes in the body has a strong impact on the formation of the described pathology. A lack of vitamins and minerals in a child leads to early loss of baby teeth and improper formation of the dentition.
Causes of open bite
An open lateral bite or improper closure of the front teeth can be a consequence of both acquired and genetic causes.
The occurrence of abnormal occlusion is influenced by the following points:
- heredity;
- abnormalities in intrauterine development (maternal illness, stress, medication);
- habits of sucking, chewing objects, or keeping the tongue half-protruded between the teeth;
- bone diseases;
- underdeveloped alveolar process;
- jaw injuries;
- ENT diseases and habit of mouth breathing;
- macroglossia;
- change of milk teeth early/late.
What is this disease
Open bite - this occlusion disorder is characterized by the absence of complete closure of the lower and upper incisors. With it, pronounced pathological changes in the dental system occur with loss of function, as well as gross aesthetic defects. Such malocclusion can be an independent disease; it is also often combined with other pathologies of occlusion and uneven dentition. There are combinations with distal and mesial disruption of teeth closure. It is recorded quite rarely, its prevalence among all occlusion anomalies is about 2%. The defect is most often detected in children under one year of age.
Classification
According to the etiological criterion, such disocclusion is divided into true (rickets) and false (traumatic). There are three degrees of open bite; the classification is based on the amount of space between the upper and lower teeth, due to the lack of closure (occlusion).
Degrees of severity of occlusion violation:
- The first is that there is a vertical interdental space of up to five mm, with a lack of closure in the area of the anterior teeth (canines, incisors).
- Second, this stage is characterized by the presence of a vertical gap with a size of five to nine mm, with the absence of contact between the incisors of the canines and molars.
- Third - there is a space between the teeth measuring more than nine mm; the front teeth, molars, and premolars do not touch each other.
Based on location, frontal (front) and lateral forms are distinguished. Lateral is divided into bilateral and unilateral. It is noted that this pathology can be asymmetrical as well as symmetrical.
Causes
The reasons for the development of this pathology are quite diverse. They are divided into acquired and congenital factors.
Congenital causes of anomaly development include:
- unfavorable heredity for this trait;
- infections suffered during pregnancy;
- exogenous toxic effects on the fetus;
- somatic diseases of the mother;
- birth injuries;
- effect of medications;
- pregnant woman's injuries.
All these influences together during intrauterine development cause an atypical position of tooth germs, the formation of cleft palate, alveolar process and upper lip. Deformation of the facial skeleton occurs.
Acquired factors include:
- bad habits (prolonged use of a pacifier, sucking on foreign objects);
- consequences of rickets;
- hypovitaminosis;
- pathologies of mineral metabolism;
- early loss of primary teeth;
- shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- macroglossia (enlarged tongue);
- late teething;
- diseases that cause difficulty in nasal breathing (adenoids, polyps, deviated septum).
To determine patient management tactics, it is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology. A single pathological factor may play a major role in its development, and it is also caused by a complex of causes.
Symptoms
Malocclusion has characteristic signs: facial, functional, intraoral.
Facial manifestations include;
- lengthening the lower part of the face;
- there is no fold between the lips and nose;
- constantly half-open or open mouth;
- smoothing the chin fold;
- presence of a sloping chin.
When examining the patient's oral cavity, characteristic signs can also be identified.
These include:
- lack of closure of the anterior or lateral upper and lower units;
- crowding;
- the shape of the closure defect (it repeats the shape of the object held in the mouth);
- severe dental caries;
- hypoplasia of the enamel layer;
- narrowing of the arch, asymmetry of the alveolar process;
- pronounced tartar;
- the shape of the upper palate is disrupted;
- dryness of mucous membranes in the oral cavity;
- signs of hypertrophic gingivitis (bleeding and swelling of the gums, enlargement of the gum papillae).
The following functional disorders are typical for this disocclusion:
- inability to bite off pieces of food;
- difficulty chewing;
- violation of diction (interdental sigmatism, defects in the pronunciation of labial and lingual sounds);
- difficulty in nasal breathing.
The defect is usually accompanied by pathologies in the development of the paranasal sinuses of the skull, as well as the bottom of the nasal cavity.
Diagnostics
Before an open bite is corrected, a child will be thoroughly examined. The diagnosis is made by an orthodontist. He carefully examines the patient, listens, and analyzes his complaints. Studies and evaluates facial and oral signs of occlusion. The dentist measures the distance between the upper and lower teeth.
The doctor prescribes additional research methods.
These include:
- facial photometry;
- electromyography of the muscles of the head and face;
- orthopantomography;
- rheography;
- make casts of the jaws with subsequent study of diagnostic models;
- teleradiography of the skull with radiocephalometric analysis;
- tomography of the maxillary joint.
The patient requires consultations with specialized specialists: speech therapist, otolaryngologist.
Treatment
Methods for correcting open bite in children depend on the severity of the defect and the age at which correction begins.
Before the age of three years, mainly preventive measures are taken.
These include:
- stopping bad habits (sucking pacifiers, foreign objects);
- gymnastics for facial muscles;
- timely introduction of solid foods into the diet;
- consumption of foods rich in vitamins and microelements;
- prevention of rickets;
- timely treatment of caries;
- prevention of inflammation in the oral cavity;
- use of vestibular shields.
It is necessary to regularly visit the orthodontist and follow all his recommendations.
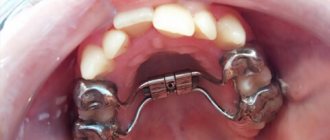
From the age of five to thirteen, corrective structures are prescribed.
The following devices are used:
- removable correction plates with tongue flap;
- Andresen–Goipl activator;
- Frenkel apparatus;
- trainers;
- Herbst-Cojocaru mouthguard device;
- Engle's apparatus;
- supradental vestibular arch.
To enhance the effect, continue to do gymnastics for the facial muscles. Children are recommended to visit a speech therapist to correct the pronunciation of sounds. Surgeries are performed to correct the lip frenulum. An otolaryngologist should treat diseases that make nasal breathing difficult.
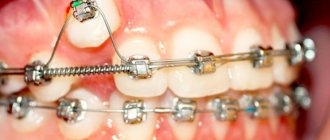
In adolescence, starting from the age of thirteen, this defect is corrected using braces, aligners, and aligners. They are usually worn for 2 years to achieve the desired effect. In severe cases, surgical correction of the alveolar process is used. If sufficient jaw closure cannot be achieved, the teeth are ground down and crowns are placed on them.
Complications
If a child's open bite is not treated, serious complications develop.
It can be:
- appearance defects;
- diseases of ENT organs;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of the maxillary joint;
- headache;
- severe psychological disorders.
These problems can be avoided with timely treatment from an orthodontist and following all his instructions.
Prevention
Prevention of the formation of closure disorders is aimed at preventing the causes that are responsible for the development of the anomaly.
Recommended:
- carrying out the prevention of pathologies that complicate the course of pregnancy;
- prevention of rickets;
- elimination of diseases that impede nasal breathing;
- it is necessary to monitor the timely eruption of teeth;
- treat them for caries in a timely manner.
If there is a suspicion that a child has a closure anomaly, he should be regularly taken to the orthodontist for examination.
Forecast
The disease has a positive prognosis with early orthodontic correction of the defect. In this case, it is possible to make the appearance more attractive and prevent the formation of complexes and the emergence of psychological problems.
Types of open bite
Before an open bite is corrected, it is classified.
By etiology (causes of occurrence):
- false.
A common cause is premature loss of baby teeth. And also bad habits. A false open bite is also called traumatic. The anomaly has the character of an increasing complication. And, if correction is not made at an early age when changing the primary bite, hardware treatment may be required. - true.
Treatment of open bite teeth of this type is more difficult. Since it is based on a bone disease, rickets. Patients have difficulty breathing, dry mucous membranes, more obvious speech defects and facial signs of the disease. Sometimes, to correct an open bite in an adult, it is necessary to involve not only an orthodontist, but also other specialists.
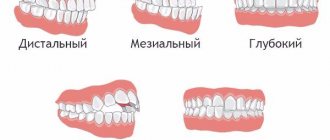
By location:
- lateral
open bite. Non-occlusion of teeth in the lateral region. Occlusion can be unilateral or bilateral. There are 2 or several units in the problem area. - anterior
open bite. The most common type. 4-8 teeth of the frontal group are involved in the problem.
There are mandibular open bite, maxillary and combined. Symmetrical, asymmetrical.
Another classification:
- dentoalveolar
open bite. The roots of the teeth are shortened; - gnathic
_ The disturbances occurred due to changes in the shape of the jaw.
The degree of occlusion pathology is noted based on the size of the vertical gap: up to 5 mm - I degree, up to 9 mm - II degree, more than 9 mm - III degree.
Treatment in children and adults - a fundamental difference
No matter how scary and unpleasant a malocclusion may look, it can still be treated.
Of course, we are not talking about a magic pill that will solve all problems.
This is a long and painstaking path that the patient must go through under the clear guidance of a specialist.
It is advisable and correct to begin treatment in childhood, when the bite is at the stage of formation. In this case, a special set of myogymnastic exercises for the muscles of the face and tongue is prescribed. A correctly selected complex at the right age makes treatment of open bite in children as effective as possible. The orbicularis oris muscles become stronger and exert the necessary pressure on the bones of the jaw and teeth, forming the necessary bite.
It is advisable to do such exercises with a child who can repeat them and perform them correctly, without turning the procedure into pampering
It is not always possible to solve a problem with gymnastics. Then a whole arsenal of orthodontic devices comes to the rescue. At a young age, it is easiest for a child to suck on a special orthodontic pacifier. It is made from ordinary latex and differs from the usual one only in shape.
Starting from the age of 2, it makes sense if the pacifier is replaced by an elastic plate, which will allow you to give up not only the pacifier, but also a number of bad habits. Starting from the age of 4, vestibular plates have shown their effectiveness. At an older age, when a permanent bite begins to form, various orthodontic trainers are prescribed, which not only combat childhood habits, but also directly affect the formation of the facial skeleton.
Myogymnastics must be performed every day. You don’t have to set aside special time for this by doing a series of exercises while watching your favorite TV shows. You can increase the effectiveness of exercises using special devices. Rogers shock absorber, Friel interlabial disc, Dass activator - a whole “gym” for the muscles around the mouth.
The main goal, which is achieved through the use of these devices, is to change the tone of the masticatory muscles, return the growth of bone tissue to normal, normalize the function of the tongue, and improve the swallowing function.
There are also a number of systems and devices for permanent wear that correct the bite at the bone level:
- Klammt activator
- Frenkel apparatus
- Herbst apparatus
- Expansion plates on springs
- Vestibular arches, etc.
This is not the entire list of activators and devices used to correct bites. The specialist knows and makes a decision for each individual case. Sometimes you even have to resort to plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue to restore its mobility.
Although the problem of open bite is typical for children, adult patients often come to the clinic. Some, for unknown reasons, did not go to the dentist on time, and for some, the bite changed due to a number of traumatic factors.
Treatment in adults is a more complex and protracted process. The whole problem is that the dentition has already been formed, and jaw growth has stopped. But this does not mean that nothing can be done. There are many methods and devices for correcting an already formed bite in the later stages of development of the anomaly.
You can use removable aligners and devices, but they are significantly inferior to non-removable structures, such as braces or the Engle device. Treatment with braces is carried out in combination with the installation of special rubber rods.
But if after braces there is no visible result, and this happens, then you have to wear special crowns that change the height of the bite.
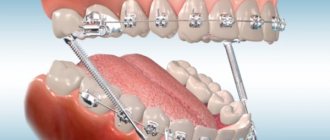
Good results are achieved using the Engle and Cojocaru apparatus. A special arc made of thin wire with special hooks for elastic shock absorbers (rods) is placed on the upper or lower, or both, with the help of which it is possible to achieve the necessary jaw traction.
The movement of the anterior teeth can be achieved not only through rods, but also using an expansive Angle arch. To do this, the target teeth are covered with crowns with hooks, the arch is bent in the direction of the required displacement and fixed in the hooks. A special metal with a memory effect strives to return to its original position and thus gradually pulls the teeth along with it to the level we need.
These methods still have a small drawback; they do not solve the aesthetic component of the problem. They don't change their face. And if the patient has a shortened lip, then after such traction, he simply will not close his lips and will be in a state of permanent smile, which is also not the best option.
Correction of the situation is achieved by using bite plates, which allow you to reduce the height of the bite to the required distance.
Their particular advantage is that they make it possible to reduce the height of the jaw on the sides and significantly improve the patient’s appearance.
And all this without the help of plastic surgeons and scalpels. But this is not always possible.
In some cases, radical surgical intervention cannot be avoided. This affects adult patients more than children due to stunted jaw growth. Then decortication is performed and the jaw bone is excised in the shape of a triangle to change the angle of its inclination.
The operation involves the removal of the first molars and filing of the cortical layer and is performed through the oral cavity under anesthesia. Before excising a section of the jaw, the orthodontist is faced with the task of preparing an apparatus for postoperative correction of the jaw. The strongest teeth – the last molars – are prepared for crowns. Special rubber rods will be attached to them, the other end of which is attached to the front teeth.
In the postoperative period, under the influence of traction, the jaw will gradually change its bend in the area of decortication (where the tooth was removed).
A distraction device is used in a similar way. It requires activation and constant monitoring in the inpatient setting of the maxillofacial surgery department. The device is activated at 0.2 mm per day in the first week after surgery. Then it is necessary to correct the plastic part of the device so that it acts as a retention device for the next two months.
After any type of surgery, patients are advised to wear an external device, similar to a soft sling, on the chin and secured to the back of the head. Over the next 6-8 months, the patient will need to remove the permanent retainer and use the removable one only at night to allow the jaw to wean itself off the device.
Possible complications
Open vertical occlusion does not remain without consequences. The aesthetics of the face and smile suffer, difficulties develop in other functional departments:
- Digestion is disrupted due to problems with biting and chewing;
- the person has a lisp, and with a large gap, speech is slurred;
- The TMJ (temporomandibular joint) experiences difficulties, muscle tone decreases;
- the condition of the periodontium worsens (it experiences excessive load);
- the abrasion of the enamel of the teeth, on which all the work “falls”, increases, they are more loaded and experience increased pressure;
- Mouth breathing develops problems with the ENT organs and respiratory system.
Diagnostics
In addition to a visual examination, the orthodontist can measure the gap and assess the degree of open bite for further treatment. There is a possibility of direction for more in-depth research that will give a complete picture:
- teleroentgenogram;
- orthopantomogram;
- taking impressions.
Often a specialist sees the presence of a combination of disocclusions: distal open bite, mesial.
To collect information about the patient and the progress of the correction, before and after photos are taken.
Options and stages of treatment for open bite
In Moscow dental clinics, doctors offer various open bite treatment systems. But, as a rule, they are based on generally accepted correction principles.
Important!
The first stage of any treatment is to eliminate bad habits. This includes thumb sucking, the need to chew something and put the tongue back in its place so that it does not put pressure on the teeth. There is a special design for this with mini-spikes; when you try to push the tongue forward, the resulting discomfort teaches you not to do this.
Treatment of open bite in children
- myogymnastics.
A set of selected exercises will allow you to correct the position of your teeth and train the muscles of the jaw apparatus. Gymnastics are done regularly, independently or with devices: Friel disk, Rogers shock absorber. - activator.
When changing the bite, the activators are fixed so that the front teeth do not exert pressure, everything is aimed at correcting those elements where the pathology is located. A tongue rest is provided. The designs come in different varieties and are supplemented with screws, etc., depending on the complexity of the pathology. Activators of Rogers, Klamt, Schwartz apparatus, etc.
Correction of occlusion in mixed dentition:
- myogymnastics;
- fixed systems;
- Engle's apparatus.
Plates with a vestibular arch, springs and a lock have proven themselves well. Metal hooks and rings are attached to the teeth that need to be moved. This happens due to tension.
Correction of open bite in adults
For patients with permanent dentition or at the end of the shift period, the emphasis is on jaw extension:
- orthodontic plates;
- braces with reversible arches;
- trainers, aligners.
A - braces, B - plates, C - trainers, D - mouthguards
Patients of the same age category may be prescribed different methods for treating occlusion disorders. It depends on the specific clinical picture, etiology, and degree of deviation from the norm.
Sometimes the only option left is surgical treatment. As a rule, the work of orthodontists comes first. With the help of a braces system, teeth are rotated into the correct position, if necessary, removal occurs. Then the maxillofacial surgeon begins. The jaw bone is dissected and returned to its normal position using plates and structures. After healing, braces are used again. The treatment is long, but this is the only way to achieve an excellent result and consolidate it with a strong degree of pathology and complicated accompanying deviations from the norm.
Prognosis and prevention
There are no clear opinions regarding the prognosis of treatment for open bite. It all depends on the nature of the pathology, as well as the therapy that is used. Often, with proper treatment, the patient can completely or partially get rid of the defect. Typically, doctors strive to eliminate functional malocclusions, restoring the patient’s ability to chew food and speak normally. After this, they begin to correct aesthetic defects. With a competent approach, it is possible to achieve high-quality results.
As for the prevention of open bite, it includes the following steps:
- In the prenatal period – giving up bad habits, eating a balanced diet, monitoring test results, etc.
- In the postnatal period - ensuring that the child does not suck his finger or other foreign objects, breathes through his nose and does not stick out his tongue.
It is also very important to regularly visit a dentist, who can always identify a malocclusion at an early stage and prescribe effective treatment.