Pain after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed and the anesthesia wears off, the patient may experience minor pain, which usually goes away quickly. However, sometimes 1-3 days after surgery a sharp pain appears in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth .
Taking analgesics does not bring relief. This pain most often occurs due to disruption of the normal healing process of the tooth socket. In addition, the pain may be caused by the remaining sharp edges of the socket or by an exposed area of the alveolar bone not covered with soft tissue.
How pain goes beyond the norm
Sometimes the pain goes beyond the norm
The pain is intense, does not subside, increases or maintains amplitude, lasts more than 3-4 days, this ceases to fit into the framework of the body’s natural pain reaction, which must be endured. There are very specific causes of pathological pain after tooth extraction.
Poor quality treatment. The practice of dentistry is as susceptible to human error as any activity involving humans. Often the surgeon does not completely remove the root, leaving part of the dental tissue, cyst fragments, a piece of cotton wool, or a fragment of dental bone in the wound. All this becomes a source of inflammation. And after a few days the inflammatory process begins to actively develop.
If after removal a root fragment remains in the gum, an inflammatory process may begin.
Alveolitis. The cause of pain is the absence of a blood clot. Any wound, especially in the gum, needs a blood clot to close it to heal the tissue and block the path of infection. After a tooth is removed, this clot forms in the socket. But for various reasons it turns out to be broken or shifted. Patients also often wash out this clot, for example, when they begin to rinse the wound. As a result, the root hole remains open, infection gets into it, inflammation and swelling of the gums begin. All this is accompanied by pain, which normally should not be present.
In the photo there is alveolitis of the tooth
By the way. If a patient has to have a simple (single-rooted) tooth removed, according to statistics, alveolitis occurs in 3% of 100. When a complex tooth is removed, this figure rises to 20%.
Dry socket . This is the most common complication, also associated with the absence of a formed blood clot, but with it the hole from the root, upon careful examination, remains dry, despite the moist environment in the mouth, and bone is visible at the bottom of the hole. This problem is more likely to occur in smokers, older people, and those who have hormonal problems. The pain in this case will be quite severe. And you shouldn’t wait until it goes away; the doctor will help by putting a tampon with medicine in the wound that will moisturize and disinfect it.
Photo of a dry socket after tooth extraction
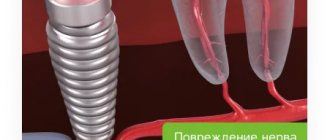
Trigeminal neuritis . This cause of ongoing and unrelenting pain is familiar to patients who have had a lower row tooth removed. The lower jaw serves as a receptacle for the branched trigeminal nerve. A dentist, diligently pulling out a deep-seated tooth root, can damage this nerve. The probability is low - only about 10%. But if you fall into this number, the pain after removal and the end of the freezing effect will be “shooting”, paroxysmal, not only in the gums and jaw, but also in the temples, around the eyes, even in the neck. Externally, the gums do not swell and do not look damaged, even redness is not observed. It is possible to identify neuritis only by the nature of the pain.
- How many days does a coma last after a stroke and is there a chance of survival?
Trigeminal neuralgia
Gum tumor
Often pain from an extracted tooth is accompanied by gum swelling. The phenomenon is not only not aesthetic, but, at times, dangerous.
In about half of removal cases, swelling after surgery is normal. It is associated with soft tissue injury. And if the swelling is temporary and transient. There is nothing to worry about, you just need to “get over it.”
Swelling of the gums after tooth extraction
But if the phenomenon is accompanied by atypical pain that lasts longer than expected. Perhaps this is a pathology that a repeat visit to the surgeon will help normalize.
- Inflammatory process. Often it is already present when the patient presents for tooth extraction surgery. And the source of inflammation is not always removed when the tooth is extracted. Trauma to the soft tissue allows inflammation to begin again. Plus insufficient antiseptic treatment of the hole or alveolitis.
- A complex tooth - impacted or dystopic - its removal will almost certainly involve the fact that the surgeon will open the mucous membrane over a large area and will spend a long time “pulling out” the tooth. Of course, the cheek, gums, even the neck and skin near the ear can become swollen and painful.
Atraumatic tooth extraction
- Gum section. Sometimes the surgeon sees suspicious swelling of the gums already during the operation, and mistaking it for an abscess (in most cases, rightly) cuts the gum. Thus, the extracted tooth will hurt much stronger, longer, and with accompanying swelling of nearby soft tissues.
Photo after tooth extraction. During the operation it became necessary to apply sutures
There is nothing to worry about if the swelling is expressed as follows:
- the swelling is not pronounced and decreases over time;
- the temperature is not elevated;
- moderate pain;
- there is no unpleasant odor from the mouth.
By the way. There are exceptional cases when there is no severe pain from the extracted tooth, but there is a swelling of the cheek, and it is growing. It does not happen often, mainly after the removal of a tooth with pulpitis, if the root canals are not very thoroughly cleaned. In this case, you need a second visit to the surgeon to prevent the formation of a cyst.
If your cheek is swollen, you need to visit the dental surgeon again
If the condition does not improve, but worsens at least slightly or the pain remains stable. If new aggravating symptoms appear that were not present immediately after removal. You shouldn’t delay visiting a doctor; it’s better to play it safe and make an appointment for an examination.
It's time to go to the doctor
If you observe the following symptoms in yourself or your loved ones for several days after tooth extraction surgery (more than three days):
- pain intensifies;
- the pain changes in character or is specific;
- gums become red;
- gums have acquired a bluish tint;
- swollen gums;
- there is a bad smell from the mouth;
- cheek swollen;
- body temperature increased;
- Pus comes out of the root socket of the tooth.
If your cheek is swollen, your temperature has risen, or your condition is worsening, then you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Important! The area in the gum begins to hurt after tooth extraction three hours later. Normally, pain can be intermittent or constant, subsiding or recurring. Starting from the third day, the pain decreases and disappears completely.
Video: Cheek swollen after tooth extraction - what to do
Difficult case
All previous characteristics relate to conventional tooth extraction, with one or more roots. But there are times when the operation goes beyond the standard surgical procedure. These include the removal of a dystopic wisdom tooth. During this operation, which takes longer, all tissues are injured much more than during standard removal. Here, pain is allowed in the postoperative period for up to one and a half weeks. The pain may also be accompanied by swelling of the gums, a swollen cheek, headaches, and neck pain. All these symptoms are considered not dangerous and go away without medical or other intervention.
Wisdom tooth removal
Alveolitis
Inflammation of the walls of the socket.
- In the initial stage of alveolitis, an intermittent aching pain appears in the socket, which intensifies while eating;
- The general condition is not disturbed, the body temperature is normal;
- The tooth socket is only partially filled with a loose, disintegrating blood clot.
With further development of inflammation:
- The pain intensifies and becomes constant;
- Transmitted to the ear, temple, corresponding half of the head;
- The general condition worsens, malaise and fever appear.
Limited osteomyelitis of the tooth socket
Inflammation of the bone tissue in the area of the extracted tooth :
- in the socket of the extracted tooth , and pain occurs in the adjacent teeth;
- Weakness, severe headache;
- Body temperature is 37.6-37.8°C and above, sometimes there is chills;
- Loss of sleep and performance;
- The bottom and walls of the hole are covered with a dirty gray mass with a fetid odor;
- Touching the gum is sharply painful;
- When you tap adjacent teeth, pain occurs;
- The perimandibular soft tissues are swollen, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, dense, painful;
The symptoms of acute inflammation last 6-8 days, sometimes 10 days, then they decrease, the process passes into the subacute and then into the chronic stage.
- The pain becomes dull and weak;
- General condition improves;
- Body temperature normalizes;
- After 12-15 days, the tooth socket is filled with loose, sometimes protruding pathological granulation tissue, which, when pressed, releases pus.
Please note that pain relief during a complication does not mean that the process has begun to heal; perhaps it has entered a chronic, more dangerous stage. As a rule, the surgeon schedules a follow-up examination for the patient after removal; ATTENDANCE IS MANDATORY!
Online consultations with doctorsAll about coronavirus
February 4, 2022, 10:21 pm doctor001 · February 4, 2022, 10:21 pm Thank Reply
Hello! In order . 1.Erosive reflux esophagitis, grade A according to LA. Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus! Reflux - esophagitis, this is esophagitis, the cause of which is gastroesophageal reflux! Normally, there is a sphincter (valve) in the area of the cardia (cardia is the place where the esophagus enters the stomach), which opens and allows food to pass in only one direction - from the esophagus into the stomach and immediately after that it closes, preventing the acidic gastric contents from passing back into the esophagus! This is normal! But it happens that the sphincter does not close completely, i.e., there is insufficiency of the cardia or it closes completely, but when the stomach contracts, the valve does not hold, it opens towards the esophagus and the acidic contents, which should not be in the esophagus, enter there, i.e. That is, gastroesophageal reflux occurs, as a result of which the esophageal mucosa becomes irritated and inflamed, i.e. reflux occurs - esophagitis! The degree of reflux disease can be different: from the entry of stomach contents only into the lower third of the esophagus with the occurrence of esophagitis in such a limited area of the esophagus, to its extensive entry throughout the entire esophagus to the pharynx, as well as from mild inflammation in depth and area, as in your case , to a deeper and more widespread! Grade “A” according to LA, this is the mildest degree of inflammation (esophagitis) according to the VOC - ANGELES CLASSIFICATION (LA), according to which, according to the degree of severity, there are 4 degrees (A, B, C, D.)! You have the first “A”, i.e. the mildest degree, in which there is one or more damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, each of which is no more than 5 mm long, limited by folds of the mucous membrane. 2. Erythematous diffuse gastropathy. Erythema is redness! This just means that the gastric mucosa is slightly red and thickened, i.e. signs of gastritis! 3. Lymphollicular hyperplasia of the antrum of the stomach, signs of HP contamination. Lymphollicular hyperplasia of the antrum of the stomach is common, which means that against the background of redness and thickening of the mucosa there are foci of lymphofollicular hyperplasia! No, it's not precancer! The reason for their appearance is not fully understood; it is believed that the reasons may be both the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach and the regular entry of bile from the duodenum into the stomach as a result of duodeno-gastric reflux! The process is reversible; when the above reasons are eliminated, the picture returns to normal! With the conclusion, contact a gastroenterologist, get a course of treatment and repeat after 2 months for FGDS and make sure that everything has returned to normal! This is all that can be written about your question! Good luck to you !
Thank Reply
Sharp edges of the alveoli
Socket pain can be caused by protruding sharp edges of the socket, which injure the mucous membrane located above them. Pain appears 1-2 days after tooth extraction , when the edges of the gums above the socket begin to approach each other.
- The pain intensifies during chewing and when touching the gums;
- When you feel the hole with your finger, a protruding sharp edge of the bone is detected, and a sharp pain occurs.
This pain can be distinguished from the pain of alveolitis by the absence of inflammation in the socket area and the presence of an organizing blood clot in it.
What to do after removing a baby tooth: general recommendations
In dental clinics, milk teeth are removed under anesthesia. An exception is made only for moving, strongly swinging units. Anesthesia is selected differently:
- local - a small injection with preliminary anesthesia of the gums;
- nitrous oxide sedation - delivering laughing gas through a mask to reduce anxiety;
- under anesthesia - with multiple removals or individual indications for treatment during sleep.
When local anesthesia is used, the lip and cheek in the area of the tooth being removed lose sensitivity. Sensations are restored within 1.5-3 hours, and during this period of time parents should keep an eye on the baby and distract him.
Strange sensations of numb tissues lead to the fact that children begin to bite them with their teeth. And since there is no sensitivity, the bite can severely injure the lip or cheek from the inside. To prevent this from happening, you should keep your child busy with something interesting - watch cartoons or play your favorite games.
Nutrition after baby tooth extraction: how much you can’t eat, choice of foods
The second point that adults need to consider is nutrition. And this is not only the traditional question of how much you can’t eat after a baby tooth is removed. Dietary restrictions apply to:
- fasting interval time - 2 hours after removal;
- choice of products - for several days you need to remove solid foods from the menu, offer the child purees, jellies, omelettes, instant baby cereals.
The drinking regime also has its own peculiarities:
- Avoid drinking through a straw and carbonated drinks;
- give up fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, drinking yogurt;
- remove excessively cold or hot drinks;
- drink a lot during the first 24 hours.
Rodikova Tatyana
Children often ask what a baby tooth looks like after removal. I show. Many guys ask to take the tooth with them. Children place their extracted teeth under their pillow at night and receive gifts from the “tooth fairy.” A pleasant fairy-tale tradition that turns removal into a small adventure.
Do's and Don'ts after tooth extraction in a child
The child leaves the doctor's office with a sterile swab in place of the extracted tooth.
The cotton wool is removed after 20 minutes. The first three days after the surgical procedure you cannot:
- actively engage in sports - experience significant physical activity;
- warm up the area of the extracted tooth - apply compresses, visit a bathhouse, sauna;
- pick the hole with sharp objects (toothpicks, matches), touch with your tongue or hands;
Correct behavior after tooth extraction;
- chew food on the side opposite the removal site;
- Gently rinse your mouth after meals (take some water, hold it and spit it out);
- brush your teeth with a soft brush, avoiding the socket.
- take medications prescribed by the doctor in a dosage appropriate to your age;
- Apply ice to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth to reduce pain.
Adults are advised to distract the child from thoughts about the removed tooth. It is best to keep your baby busy with calm board games, watching a favorite fairy tale, or reading books.
This approach will reduce stress and relieve the child from worrying about the dental procedure. It will also help to avoid unnecessary investigative curiosity and studying the wound in the gum.
How to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction in a child
Rinsing in the first days after removal is strictly prohibited. Aggressive active movements can cause a clot to fall out of the socket and cause bleeding.
Instead of rinsing, the pediatric dentist-surgeon will definitely recommend oral baths. They are easy to make. The child puts an antiseptic solution into his mouth, holds it at the removal site for several minutes and gently allows the liquid to flow out by simply opening his mouth slightly.
The composition for the baths can be almost any. A weakly concentrated saline solution or soda solution is recommended for children. For older children, you can offer Miramistin, Chlorgesidine solution - sold in any pharmacies.
Soldatenkova Alina
Most recommendations after tooth extraction are aimed at preserving the blood clot in the socket. It is very important that it does not fall out. The clot serves as a natural protection for the wound from bacteria and accelerates healing. It is especially important to monitor the socket when removing the 4th milk tooth in children (chewing). Healing of wounds after extraction of incisors or fangs occurs faster and usually without consequences.
Toothache after caries treatment
Constant pain after filling can occur for many reasons. A common cause of discomfort is the application of an insulating lining made of glass ionomer cement (GIC) and filling on the same day with a composite. The polymerization times of GIC and composite differ, which can result in displacement of the gasket and its pressure on the pulp.
If the pain is short-term in nature as a reaction to cold, sour or sweet and quickly passes after removing the irritant, it may be due to the fact that during the treatment there was a mechanical effect on the pulp. After 2-3 days, the pulp will return to normal functioning and the pain will stop.
If you experience pain when biting, you need your dentist to grind the filling to fit your bite.