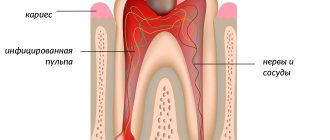
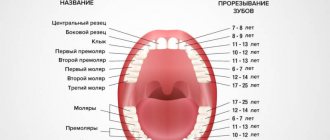
Regurgitation is the reflux of a small amount of gastric contents or gastric juice mixed with saliva up the esophagus. Regurgitation often occurs in infants and in the vast majority of cases is a variant of the physiological norm. They do not require therapy except in a few cases, which will be described below.
The younger the child is, the more often he can regurgitate. As the child grows, they gradually disappear until they disappear completely. In the first month, regurgitation occurs in 85% of children; this indicator does not depend on the type of feeding (formula or breast milk) and on the method of administration (bottle or natural feeding). After 3 months, regurgitation occurs much less frequently, and by one year it disappears completely.
At CELT you can consult a pediatrician.
- Initial consultation of a patient under the age of 17 inclusive - 2,500
Make an appointment
Causes and mechanism of regurgitation
The following reasons are identified:
- Filling the stomach with air, which the child can swallow while eating. This is the most common reason, which requires practically no special correction.
- Muscular weakness of the valve between the esophagus and stomach. It develops as the child grows and begins to function normally by the first year of life. Therefore, food can pass from the stomach into the esophagus without hindrance, which is what happens during regurgitation.
- Food allergies (or food intolerances). Most often it manifests itself as skin reactions, but in rare cases, regurgitation may be a symptom.
- Congenital defects of the gastrointestinal tract. The digestive system is quite complex; some disturbances in its structure can lead to digestive problems that begin to appear immediately after birth. Thus, narrowing in the area of the gastrointestinal junction can lead to frequent atypical regurgitation.
Next, we will provide recommendations on how to distinguish pathology from the norm, and when you need to see a doctor. If regurgitation is caused by a disease, then it is reasonable to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Vaccination against rotavirus
There are two vaccines - the Belgian Rotarix and the Russian RotaTek. Only RotaTek is registered in the Russian Federation. It contains the 5 most common strains. Vaccination against rotavirus infection is not included in the national vaccination schedule, but it can be done at the request of parents. RotaTek has strict age restrictions and intervals between revaccinations - be sure to consult your pediatrician.
“The effectiveness and safety of vaccines against rotavirus infection, subject to age limits, has been confirmed in many studies,” says Elena Kolganova, a pediatrician at the Fantasy children’s clinic. — After receiving the third dose of the vaccine, the number of hospitalizations decreased by 100%, and visits to the clinic decreased by 96%. Rotavirus, unlike influenza, rarely mutates, and therefore vaccination does not need to be carried out every year - immunity lasts up to three years.”
Regurgitation and vomiting
Regurgitation is in most cases a physiological phenomenon that does not require special treatment or observation. But it may look like vomiting, being a sign of dangerous diseases, in which case consultation with a doctor is necessary. Regurgitation and vomiting have a similar mechanism of occurrence, namely, the release of gastric contents into the oral cavity.
It is important to distinguish between them, since vomiting in newborns is very dangerous and can lead to aspiration of contents into the respiratory tract and respiratory arrest.
There are differences between regurgitation and vomiting:
- Regurgitation most often occurs after eating. Usually this is a single, non-repeating episode. The child regurgitates the food he has just eaten; there are no foreign impurities in it.
- Vomiting usually occurs repeatedly. It happens not related to food intake.
- Regurgitation does not affect the child’s well-being and mood - he is active, does not show signs of anxiety, smiles, and plays.
- Vomiting is accompanied by a deterioration in general health. The child is lethargic or restless.
- Regurgitation usually occurs suddenly, and vomiting is preceded by a decrease in activity and mood.
- Vomiting is rarely the only symptom; other problems with the functioning of the digestive tract or fever are also observed.
Vomiting in a child is a reason to see a doctor!
How to get rid of this?
First of all, you need to determine the causes of excessive salivation. If it is pathological, then you cannot do without the help of a doctor and drug treatment.
If increased salivation is a physiological process, then parents need to alleviate the baby’s condition and support him during the period of hypersalivation:
- The restoration of the baby’s health depends on quick and adequate treatment.
When pathological changes occur in the oral mucosa in a child, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The restoration of the baby’s health depends on quick and adequate treatment.
- To get rid of hypersalivation , the cause of which is stomatitis or gingivitis, dentists prescribe medications that destroy infectious agents and promote rapid regeneration.
- If there is a helminthic infestation or a somatic disease , the symptom of which is increased secretion of the salivary glands, the child should be taken to see a doctor, examined completely and treated with medications that normalize salivation.
- Natural remedies will help improve the condition of the little patient. For stomatitis, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with table salt solution or herbal infusions, and for gingivitis - with sea buckthorn oil.
- You can reduce the secretion of saliva by strengthening the immune forces of the child’s body. For this purpose, they protect children from emotional stress, often take them for walks on the street, give them healthy food enriched with vitamins, and develop them physically by participating in various sports sections.
- Always use a bib. Treat the skin of the face with nourishing creams, and if necessary, dry the skin on the chin with the addition of zinc.
- Using pacifiers will help the baby reflexively swallow saliva when it is released in abundance.
Important! Self-medication of hypersalivation in children is strictly prohibited. Only the help of a qualified specialist will help to correctly establish the etiology of the pathology, on the basis of which appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Child behavior
The mechanism of regurgitation is such that components of gastric juice enter the esophagus along with the food eaten. As you know, it has high acidity and irritates the esophageal mucosa. As a result, the child experiences discomfort and can become quite restless. It’s very easy to check whether your baby’s anxiety is related to regurgitation - just lay him on his back. If the problem is regurgitation, then the baby will behave even more restlessly. If not, then the horizontal position will not bring him discomfort.
If regurgitation occurs frequently, it is called regurgitation syndrome. It can lead to complications - chronic irritation of the respiratory tract. As a result of the constant aggressive effect of gastric juice on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, the latter are susceptible to an inflammatory process. Therefore, it is important to monitor the child’s condition and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
How many times can there be a chair?
Diarrhea is also possible when teething
Quantity is one of the most important indicators. At first, the child may defecate up to 10 times per day. This is common in babies less than 4 months old. But there is one condition: the baby must feel good, the weight gain must be constant.
If the baby is breastfed, stool may be rare. There's nothing wrong with that. Even if the baby walks “largely” once every few days and feels good, there is no need to worry. However, you need to pay attention to the consistency of the stool; it should remain soft.
If the feces are hard, this is already a violation of the norm, which means there are digestive disorders. Diet violations made by a nursing woman can lead to this. Mom needs to monitor her diet more carefully, then everything will return to normal.
Tips for parents
Let's figure out how to avoid possible dangers associated with regurgitation. The main thing that responsible parents need to know is that most often children burp while lying down. This position is dangerous due to aspiration (inhalation) of gastric contents.
Preventing aspiration is simple - just bring the baby upright or turn him on his side or stomach immediately after he burps. Then the baby will be able to push food out of his mouth.
It is worth remembering that it is unacceptable to leave a child with regurgitation syndrome without adult supervision, especially when lying on his back.
What is it and how often does it happen
An intestinal infection is a disease that develops when viruses or bacteria enter the body and is manifested by diarrhea, vomiting, fever, weakness and dehydration.
According to WHO data for 2022, rotavirus infection accounted for 60% of cases of severe diarrhea in children under 5 years of age, and most of them were under one year of age. When the first symptoms appear in young children, it is necessary to seek medical help - up to 200 thousand children still die from rotavirus infection every year in the world, especially in developing countries.
Feeding rules
Frequent regurgitation can be prevented by following a few feeding rules.
- After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby upright. Even if your baby is tired or wants to sleep, you shouldn’t put him to bed right away. It is very comfortable to hold infants on your shoulder. After waiting for the air to burp, the child can be given any position.
- The same should be done before feeding. The thing is that in an upright position the child can release excess air from the stomach. If this is not done before eating, belching is guaranteed.
- There is a certain position recommended for breastfeeding. One of the main goals of correct positioning of a nursing mother and baby is to prevent regurgitation. The semi-vertical position of the baby with the head raised above the level of the body must be maintained during each feeding.
- Feedings should be frequent, but in small portions. Overfeeding is fraught not only with regurgitation, but also with other digestive problems.
- It is important not to feed your baby when he is crying or laughing, otherwise he will swallow excess air.
- If feeding is carried out using a bottle with a nipple, it is necessary to ensure that the hole in the nipple is not too large, and the position of the bottle is such that the nipple is always filled with mixture and not with air.
- You should refrain from active games in the first half hour after feeding.
Following these simple rules will help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
Currently, dysarthria is a widespread disorder in childhood. For example, according to Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Special Pedagogy and Psychology Vakulenko L.S. Murmansk State Pedagogical University, dysarthria occurs in 40.8% of 240 preschool children with speech pathology aged 4 to 7 years. The speech defect in question inhibits the development of speech as a whole and significantly lengthens the time required for correctional work.
The purpose of this article is to consider traditional and non-traditional techniques for one of the characteristic symptoms of dysarthria - hypersalivation, i.e. profuse salivation. The problem of eliminating increased salivation is too complex and cannot be solved only through exercises in speech therapy classes.
Preliminary work
It is necessary to teach the child to suck with closed lips, swallow saliva with his head thrown back and in a normal position. Before performing any articulation exercise, the teacher reminds the child to swallow saliva and blot the inside of the mouth with a napkin.
Recommendations.
- People around you should constantly monitor the position of the child's mouth and remind him to keep his mouth closed when he is not eating or talking.
- It is important that the child develops a differentiated sensation of dry and wet chin.
- During classes, it is necessary to pause at certain intervals and invite the child to swallow saliva.
The main stage of work
1. Cryotherapy.
Applying a piece of ice along the contour of the lips, taking into account 6 points (see Fig. 1). The duration of ice retention at each point is from 5 seconds to 1 minute (V.A. Kiseleva [4]).
| Fig.1. Diagram of the location of active points in the lip area. |
2. Rinse the mouth.
- Rinse using medicinal herbs: infusion of rose hips, oak bark, yarrow. You must first make sure that your child does not have allergies.
- Step-by-step gargling with mineral water, liquid jelly, kefir, thick jelly.
3. Speech therapy massage.
- Acupressure is performed in the area of the submandibular fossa, using the index finger to make light vibrating movements under the chin for 4-5 seconds (E.F. Arkhipova [1]).
- Acupressure is performed in the recesses under the tongue, at two points simultaneously (see Fig. 2). Massage is carried out using the index, middle finger or rake probe. Rotational movements are performed counterclockwise, no more than 6-10 seconds. Movements should not cause discomfort to the child.
Fig.2. Massage in the recesses under the tongue. - Point massage. Find parallel points under the tragus of the ears, where the jaw bones meet (correctly found points are painful). With our index fingers we make circular movements along the points for 5 minutes clockwise (2.5 minutes with the mouth open, 2.5 minutes with the mouth closed) and 5 minutes counterclockwise (similar) (V.A. Kiseleva [4] ).
- Massage of the soft palate. Stroking and kneading movements with a finger along the midline of the hard and soft palate from the upper incisors to the uvula to obtain a pronounced pharyngeal reflex (V.A. Kiseleva [4]).
4. Chewing solid food.
Instructions for parents of dysarthric children:
- We gnaw, chew, swallow - carrots.
- We gnaw on crackers, bagels, dryers.
5. Static and dynamic facial and articulation exercises (E.M. Kosinova [5], O.A. Novikovskaya [7]).
- Imitation of yawning, chewing, swallowing with the head thrown back. (Chewing and swallowing is recommended to be done with the mouth closed).
- “Chicks” (“Window”). Open your mouth wide and hold it in this position for 3-5 seconds. Close your mouth. When performing the exercise, the tongue lies calmly at the bottom of the mouth. Keep your mouth open for 5-10 seconds.
- "Mustache." Hold a strip of paper, cocktail tubes of different diameters, a wooden or metal spatula, and medicine bottles of different diameters with your lips.
- "Fat guy - skinny guy." Puffing up both cheeks at the same time. Retraction of the cheeks into the oral cavity with the mouth open and lips closed.
- "Balloons". Inflate one cheek - deflate. Then inflate another and deflate. Inflate alternately 4-5 times.
- “Yogi exercise” - the mouth is open, the child rotates his tongue in front of the mouth, then the speech therapist invites him to swallow saliva.
- "Dry your tongue." Roll your tongue into a tube and suck air into yourself through the tube.
6. Activate muscles using honey or bread ball.
- Place a bread ball (crushed vitamins, drop 1-2 drops of syrup from a pipette) on the tip of your tongue, and forcefully make swallowing movements.
- Place a drop of honey on the tip of your tongue. Do the “Clock” exercise or move your tongue back and forth.
7. Breathing exercise “Storm in a glass.” Pour water into a glass. Take a juice straw and blow through it. Be careful not to puff out your cheeks.
8. Pronunciation of vowels: a, e, and on a solid attack (V.A. Kiseleva [4]).
- a a a; uh uh; and and and;
- ae, ae, ae; ea, ea, ea; ai, ai, ai; hey, hey, hey;
- aei, aei, aei.
Based on our practical experience, with systematic work, salivation disappears after 3 months.
Danger signs
Responsible parents should be aware of dangerous symptoms that require consultation with a doctor:
- The baby is very restless and often turns around and arches his back when burping or feeding. This symptom may indicate chronic irritation of the esophagus.
- Regurgitation is frequent, abundant, observed after each feeding.
- The child is showing signs of dehydration.
- Regurgitation that first appeared after the first half of the year.
- Prolonged regurgitation without improvement (the same frequency and the same volume of regurgitation in a child 1 year and older).
- Regurgitation is accompanied by an increase in temperature.
- The child does not gain weight or even loses it.
- You cannot independently determine whether your baby is spitting up or vomiting.
There are even more dangerous symptoms, when they appear, you need to call an ambulance:
- The child stopped breathing after burping.
- A bluish tint appears on the lips and face.
- After regurgitation, the child lost consciousness.
- Reflux (stomach contents) that is green or brown can be a sign of intestinal obstruction or stomach bleeding.
Aspiration is extremely dangerous in infants who are unable to clear food from their airways on their own. The only thing parents can do is call an ambulance. It is not recommended to try to help your child on your own.
What should “normal” stool look like?
In the first months, infants have loose stools - this is the norm!
In the first months of life, all babies have loose stools. This is considered normal. You should not react to the advice of “well-wishers” who claim that the chair should be decorated. Perhaps such people simply don’t remember how it should be or don’t know anything, but want to seem knowledgeable on this issue.
A newborn baby cannot have formed feces; in this case, he simply would not be able to perform an act of defecation. The child cannot yet sit or stand and receives only liquid food, so he should only have loose stools. The body cannot form normal feces for an adult, because solid food particles do not enter and formed feces simply have nowhere to come from.
Therefore, parents should be calm about loose stools, which in adults is considered a deviation from the norm. There is nothing wrong with this for babies. But if the baby has hard feces, constipation will begin, which you will have to fight with your own means. After all, delayed bowel movements cause no less problems than diarrhea.
Parents need to monitor the consistency and color of stool; these indicators may change with age. Moreover, changes can occur every day. Such mobility of indicators is more common in breastfed children. Mom's diet will have a noticeable effect on the color of her stool. Therefore, even if an unfamiliar color appears, there is no need to panic; you must first analyze what the nursing woman ate. Standard indicators are given below.
Treatment
Treatment is required if respiratory complications occur or if irritation of the esophageal mucosa is suspected. In this case, the specialist will prescribe medications that reduce the acidity of gastric contents. This will not help with regurgitation, but will prevent further trauma to the esophagus. Specific medications are selected individually at an appointment with a pediatrician.
If the cause of regurgitation is an anatomical defect, surgical treatment may be required. Indications for surgery and its scope are specified by the surgeon.
For advice on infant feeding, please contact the specialists at the CELT clinic. Extensive experience, highly qualified clinic doctors and modern equipment are the key to the health and successful development of your children.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What happens when a virus enters the body
With food or saliva - if a child licks his dirty hands - rotavirus enters the mouth, then into the stomach and intestines. There it penetrates the cells of the superficial layer lining the intestines from the inside and damages them. Unlike bacteria, viruses do not lead to significant inflammation of cells; they disrupt the functioning of the body's enzyme systems to a greater extent.
Carbohydrates stop being broken down and accumulate in the intestines - the balance of fluid, potassium and sodium in the body is disrupted. A lot of water, electrolytes, organic acids and carbon dioxide collect in the intestine, which normally should not be there. Because of them, vomiting and diarrhea begin and gas formation increases. At the age of up to 5 years, intestinal cells are not yet mature enough - rotavirus affects up to 2/3 of them, so children get sick more often and more severely than adults.
Most often, the first symptom is vomiting. It occurs simultaneously with or precedes diarrhea and usually lasts 1-2 days. The stool is usually watery, foamy, yellow in color with a small amount of mucus. In infants it can occur up to 20 times a day. The duration of diarrhea is on average 3-7 days, but there are cases of up to two weeks - usually in children under one year old. Sometimes the infection begins with a fever of up to 38-39 ° C, symptoms of ARVI - cough, runny nose, sore throat. Children can also refuse to eat and literally collapse.