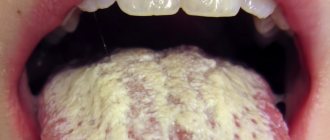
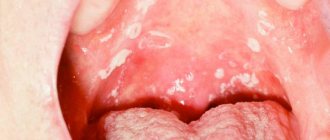
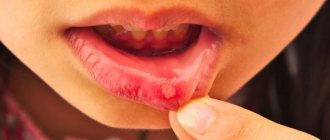
Typically, yeast fungi indicate that there is a severe malfunction in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The doctor may indicate the need for tests, based on the results of which he will make the appropriate diagnosis - intestinal candidiasis.
Intestinal candidiasis refers to a common deviation of the digestive system, which is expressed in the presence of a yeast fungus that has settled on the intestinal mucosa. It is present in every person in the mucous membranes (in the mouth, in the large intestine and even in the vagina) and is intended to maintain homeostasis.
However, under certain conditions, it can cause serious harm to the body, since the process of rapid reproduction of the fungus is activated, that is, the development of the disease starts. Candidiasis acts as a complication of dysbiosis. Anyone can get this disease.
Intestinal candidiasis. Causes
It is generally accepted that the gastrointestinal tract is the main endogenous reservoir of Candida, from where the subsequent spread of infection throughout the body occurs. Candida albicans belongs to the opportunistic flora and is a component of the normal intestinal microflora. Determination of the presence of Candida albicans in 10x4 degrees in a bacteriological analysis of stool, according to official requirements, is not an indication for making a diagnosis of “intestinal candidiasis,” much less for antifungal therapy. In practice, the clinician has to deal with candidiasis, which is observed in the intestines up to 80% and it is better for Candida to be below the detection level in the analysis (0).
Risk factors for the development of candidiasis infection are varied, they are also caused by various diseases of organs and systems of the body, in which signs of impaired intestinal microflora develop, in particular diabetes mellitus, oncopathology, inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis), irritable bowel syndrome, anemia , AIDS, decreased immune defense, stress. Therapy for underlying diseases can also contribute to the development of intestinal microbiocenosis disorders and excessive growth of candida - this is the use of cytostatics, immunosuppressants, radiation therapy, antibiotics, and surgical interventions in the treatment.
The physiological periods of a person’s life, neonatality, pregnancy, menopause, old age, and deteriorating environmental conditions that reduce a person’s anti-infective resistance are also important in the occurrence of overgrowth of Candida fungi, which leads to an imbalance between the normal flora and the body’s immune response. (Burova S.A., Kurbatova I.V., 2006). All the reasons that were described above, in which a violation of the microbiocenosis of the gastrointestinal tract develops, can lead to candidiasis. The most significant conditions should be highlighted: gastric surgery, disorders of the secretory and motor functions of the stomach and intestines, colonic diverticulosis, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Poor nutrition and, in particular, steroids contained in food and supplements and food intolerance seem to be important for the development of dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal tract.
Ways to prevent thrush in infants
By following preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing thrush:
- Wash your child's hands regularly, especially if he puts them in his mouth and sucks his fingers. The mother and everyone who comes into contact with the baby should also wash their hands regularly.
- Regularly sterilize pacifiers, teethers, bottle nipples, and anything else that goes into your baby's mouth.
- Wash towels, diapers, and clothes that may have been in contact with fungus at a temperature of at least 50 degrees.
- Sterilize all parts of the breast pump that touch the breast and milk after each use.
- Remove expressed breast milk from the refrigerator immediately before feeding to prevent fungal growth.
- If you suspect that stored expressed milk may be contaminated with fungus, it is better to get rid of it.
- Practice good breast hygiene by changing your disposable breast pads regularly and changing your bra every day.
Preventing the recurrence of thrush
Oral thrush in children can be difficult to get rid of, especially if you are breastfeeding, also because the fungus is so contagious. Thrush can be transmitted between mother and baby through the nipple. You can get the fungus from your household and infect them through bedding, dishes and cutlery.
Therefore, it is extremely important that mother and baby (and other family members if infected) are treated at the same time.
It is also useful to follow all preventive measures while treating the cause of thrush.
Intestinal candidiasis. Indications for examination
Indications for examination of the gastrointestinal tract to exclude fungal infection should be the following:
- the presence of 2 risk factors for the possible occurrence of candidiasis,
- double superficial colonization of candida,
- the presence of reasons that can lead to disruption of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract with excessive growth of fungi of the genus Candida.
- febrile conditions of unknown origin, resistant to antibiotic therapy,
- skin and allergic diseases, because Candida is a trigger for allergic diseases and a factor favoring their development.
Algorithm for diagnosing intestinal microflora disorders with overgrowth of Candida flbicans:
- Analysis of medical history, identification of risk factors,
- analysis of clinical data,
- microbiological and gas chromatographic methods for studying disorders of the microflora of the intestinal tract (various biological environments),
- smears - impressions from the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus,
- if systemic candidiasis is suspected, it is necessary to culture blood and biological fluids and tissues for the presence of a fungal infection,
- serological diagnosis and assessment of the effectiveness of treatment based on the levels of antibodies to candida,
- inflammatory markers (lysozyme, a-antitrypsin, elastase),
- secretory immunoglobulin A, which allows assessing the degree of activity of the intestinal-associated immune system,
- immunological status (screening) level 1.
All laboratory data should be assessed and analyzed in conjunction with the patient's current clinical situation.
Intestinal candidiasis. Symptoms
Disturbances of intestinal microbiocenosis with excessive growth of fungi of the genus Candida or candidal dysbacteriosis are clinically manifested by fermentative dyspepsia, abdominal pain, more in the sigmoid region, flatulence, frequent abundant foamy loose stools with mucus are noted up to 6-10 times a day, accompanied by disturbances in vitamin metabolism, low-grade fever fever, severe weakness, headache. Symptoms of damage to the mucous membranes in the form of stomatitis, glossitis, and vulvovaginal thrush are often observed. Fungal infection sharply reduces immunity, which leads to a deeper development of visceral candidomycosis with damage to the upper respiratory tract, lungs, genitourinary and digestive systems. In the blood - moderate leukocytosis, accelerated ESR, with sigmoidoscopy - catarrhal hemorrhagic proctosigmoiditis.
Indications for therapy are subject to clinical, microbiological, serological or histological confirmation of candidal infection, detection of candida with clinical manifestations from two or more surfaces of fungal colonization.
Breastfeeding with thrush
If you are breastfeeding, thrush can cause a lot of discomfort for you and your baby.
It is important to start treatment as soon as possible, so go to the doctor as soon as possible to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Please note that symptoms may not go away immediately.
Experts recommend not stopping breastfeeding if you have thrush. Here are some ways to relieve discomfort without interfering with your milk supply:
- Try to have shorter feedings, but more often.
- Wash your nipples with water after each feeding and dry them before putting on a bra.
- If cracked nipples make breastfeeding painful for you, try expressing milk and giving it to your baby from a small cup.
- Pain can be relieved with medications. Talk to your doctor about which medications are safe to take while breastfeeding.
Other reasons
Sore breasts and nipples are not always caused by thrush. If you experience sharp pain in your breasts during or after feeding, or severe pain in your nipples, try changing your feeding position or letting your baby latch on again. Sometimes this is enough to relieve the pain.
If cold compresses or air baths increase the pain, the cause of the pain may be contraction of the blood vessels in the nipple area.
Another cause of pain may be mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland due to stagnation of milk, poor emptying of the mammary gland, as well as a cracked nipple.
These conditions are often confused with thrush, so you should visit a doctor who can pinpoint the cause of your discomfort.
FAQ
- In some babies, thrush causes inflammation in the mouth, as well as pain and discomfort during feeding. But many babies do not experience any discomfort.
- In some cases, thrush may go away on its own, but it is important to see a doctor as he or she may prescribe antifungal treatment.
- If the corners of your baby's mouth are cracked or you notice white spots on the tongue, lips, or inside the mouth, it may be thrush. Another sign of thrush is discomfort or pain during feeding.
- Doctors usually prescribe antifungal medications to treat thrush in children. If thrush appears in the mother or one of the family members, it is important to treat everyone at the same time to avoid transmitting the infection to the baby.
Life with a baby is full of surprises. One minute you are touched by that first toothless smile, and the next minute you look anxiously into the baby’s mouth.
Thrush in infants is a common problem that parents face. Just follow the doctor's recommendations, and everything will gradually pass, and you and your baby will be able to enjoy moments of closeness during feeding again.
Localization of Candida
It should be noted that Candida primarily affects the stratified squamous epithelium of the oral cavity and esophagus and, less often, the single-layer cylindrical epithelium of the intestine. As a result, Candida fungi cause invasive lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract and colonization (adhesion) in the areas below the stomach. At the same time, clinical symptoms discussed above as signs of non-invasive candidiasis may appear in the intestine, even at the adhesion stage. (Burova S.A., 2006). Consequently, among all localizations of candidiasis of the digestive tract, oropharyngeal candidiasis comes first, followed by candidal esophagitis, gastric candidiasis (often it can be suspected with ineffective Helicobacter pylori therapy and prolonged healing of the ulcer), intestinal candidiasis, which must be differentiated from pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile and acute process in the intestines caused by rotoviruses and Escherichia coli.
Intestinal candidiasis. Therapy
Therapeutic approaches to the treatment of gastrointestinal dysbiosis with overgrowth of Candida fungi include the following:
- A balanced diet excluding sugar and the consumption of complex carbohydrates, foods with prebiotic properties, and probiotic foods.
- Antifungal drugs.
2.1.Polyene antibiotics (nystatin, natamycin, levorin).
- Nystatin is most appropriate to use in the presence of candida in the esophagus, stomach and is practically ineffective when candida is localized in the intestine, which makes it also not effective when administered prophylactically along with antibiotic treatment.
- Pimafucin (natamycin) is the most effective drug for overgrowth of Candida in the intestines. The drug has an antifungal (fungicidal) effect. Interacts with sterols in fungal cell membranes, disrupting their structure and function and causing their death. Active against many pathogenic yeast fungi, especially Candida albicans. No resistance to natamycin was observed. For intestinal candidiasis, 1 tablet is prescribed. 4 times a day after meals for 7-10 days.
2.2. Triazole derivatives (flucanazole, Diflazon, Diflucan, Mikosist, Flucostat, rumicosis, intraconazole, terbizil, etc.), caspofungin derivatives - Cancidas (for administration of the drug), Noxafil (posaconazole) suspension for oral administration.
2.3. MPH (copper derivative of chlorophyll) is a plant antiseptic from brown algae, a natural immunomodulator due to stimulation of phagocytosis and the activity of copper cations, enhanced by the influence of alcohol, has a bactericidal effect against staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, fungi, putrefactive bacteria and E. coli and an antiviral effect. MPH protects and stimulates hematopoiesis, the anti-inflammatory effect is due to an excellent complex of microelements. Prescribed by a doctor orally, 1 drop per 5 kg of body weight daily in a small amount of water. The course of treatment is 30 days,
2.4. Citrosept is a herbal antimicrobial agent made from grapefruit seed extract, which has a bactericidal effect, including. and against fungi of the genus Candida and Helicobacteriosis of the stomach, promotes the absorption of vitamin C, contains bioflavonoids that strengthen the vascular wall of capillaries and prevent blood clots and cholesterol plaques, stimulates the body's natural resistance. It is prescribed as drops diluted in water or juice in different dosage regimens depending on the disease.
2.5. Self-eliminating bacillary preparations (B subtilis, L.bulgaricus) - Flonivin-IS, Baktisubtil, Sporobacterin, biosporin, Baktisporin, Gastrofarm, etc.
2.6. Saccharomyces boulardi - Enterol, 1 capsule contains 250 mg Saccharomyces boulardi, suppresses the growth of opportunistic flora and fungi Candida Krusei, Candida pseudotropical
2.7. Probiotics – lactose-containing preparations (Lactobacterin, Gastrofarm, Primadophyllus, Acidophyllus, Narine, etc.)
- Enterosorbents.
- Hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Hofitol, Karsil, milk thistle preparations, Floravit, etc.)
- Immunomodulatory drugs (Kipferon, Polyoxidonium, Dopolan, Marispan, etc.)
How to treat thrush in a baby
If you notice possible symptoms of thrush in yourself or your child, contact your doctor to confirm the diagnosis. The doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Sometimes thrush will go away on its own within a few weeks, but your doctor may also prescribe antifungal medications.
Thrush: treatment with folk remedies
It is not recommended to buy medications to treat thrush in infants without consulting a doctor.
Mothers often resort to folk remedies: they treat spots in the baby’s mouth and their nipples with a soda solution, remove sugar, dairy products, and products containing yeast from their diet.
There is no scientific evidence that these methods are effective, and they should only be used in conjunction with treatment prescribed by your doctor, and not instead of it. Do not use over-the-counter medications or home remedies without your doctor's approval.
If the inflammation does not go away after a few weeks of treatment or goes away and starts again - especially if the baby is over nine months old - talk to your doctor about the possible causes.
Intestinal candidiasis. Prolonged treatment
The duration of treatment is at least 6 weeks, and then prolonged pulse therapy in short courses with individual selection of drugs for 6 months, but observing the principles of prolonged treatment of gastrointestinal dysbiosis with overgrowth of Candida fungi.
- Rational nutrition continues mainly with the limitation of sugar-containing foods and dishes.
- Repeated courses of citrosept.
- Lactose-containing probiotics 10 days each month.
- Immunomodulatory drugs (repeated courses after 3 months)
- Hepatoprotectors – 2 courses over 6 months.
Assessment of the treatment effect according to the clinical and laboratory data discussed above, during treatment and after 6 months.