From this article you will learn:
- when the first teeth appear
- sequence of teething in children,
- terms for baby and permanent teeth (scheme),
- reasons for delayed eruption.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Teething in children is the process of gradual appearance of tooth crowns above the surface of the gums. Teeth are considered fully erupted when their chewing surface begins to contact the antagonist teeth of the opposite jaw, and the gums cover the crowns of the teeth only in the area of their neck. Eruption always occurs in 2 stages. First, temporary milk teeth erupt, and only when the jaws reach the desired size do permanent teeth appear in place of the fallen milk teeth.
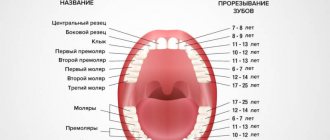
The eruption of primary teeth in a child usually begins at 5-6 months and will continue for up to 24-30 months, and during this time a total of 20 primary teeth will appear. The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones begins at the age of 6 years. The eruption of permanent teeth occurs up to 14 years of age inclusive - with the exception of wisdom teeth, which usually appear after 18 years of age. There is a strict sequence of teething in children, which you can see in the diagrams below.
Gums during teething: photo
Traditional symptoms of the eruption of baby teeth are swelling and redness of the gums, increased salivation and drooling, in addition, the child becomes restless and sleeps poorly. Sometimes indigestion and a slight increase in temperature may occur. In some cases, 2-3 weeks before eruption, a lump filled with clear or bluish liquid may appear on the gum, which does not indicate inflammation or any pathology (Fig. 2).
→ How to relieve teething symptoms in a child
How teeth are formed
The appearance of the first tooth is a milestone in a child's development. Now he's almost an adult! After all, his teeth will help him chew solid food and develop speech.
Baby teeth begin to form in the fetus as early as the 6th week of pregnancy. Between the 3rd and 6th months, enamel has already formed on the teeth. All this will be hidden under the gums for the time being. At the same time, deep in the jaw bone there are already the rudiments of molar teeth.
For most children, their first tooth appears between 4 and 7 months, but for some it happens later. With early development, it can erupt at 3 months or earlier. If the child grows normally and has no problems with skin and hair, then it’s okay. But if your baby is already 1.5 years old, and teeth have not appeared, you may need the help of a dentist.
The lower teeth usually appear about a month earlier than the upper teeth.
Approximate order of appearance of baby teeth:
- Lower central incisors (at 6 – 7 months).
- Upper central incisors (at 8 – 9 months).
- Upper lateral incisors (at 9–11 months).
- Lower lateral incisors (at 11 – 13 months).
- Upper small molars (molars) (at 12 – 15 months).
- Lower small molars (molars) (at 12 – 15 months).
- Upper canines (at 16 – 18 months).
- Lower canines (at 18 – 20 months).
- Lower large molars (molars) (at 24 – 30 months).
- Upper large (root) (at 23 – 30 months).
By age 3, your baby should have all 20 teeth, which will last until he is about 6 years old, when his first baby tooth falls out.
Don't be discouraged if your teeth grow crooked at first. Over time they will all fall into place.
Deviations in teething
Minor changes in the timing and sequence of dental growth should not cause alarm. However, significant deviations from the norm in teething are a cause for concern.
- The tooth does not appear for a long time. Reason: genetic predisposition to long eruption or lack of rudiments.
- Too early appearance of teeth. Caused by disruption of the endocrine system.
- Black or brown enamel surface color. Indicates high iron levels, poor salivation, or chronic inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
- Incorrect row position. Bite pathologies indicate a hereditary factor or deformation of the maxillofacial bone.
How to understand that your baby is teething (symptoms)
Many people believe that the process of teething must necessarily be accompanied by general anxiety of the baby, fever and diarrhea. However, not all experts share this point of view. Some consider this a mere coincidence. There is an opinion that children, when they start teething, are more likely to put dirty objects in their mouths to scratch their gums, and cause an infection.
Some lucky people go through this period painlessly.
But most children still experience some discomfort:
- Anxiety;
- Increased salivation, which can lead to facial irritation;
- The gums swell and become more sensitive;
- Refusal to eat;
- Bad dream.
If your baby has a fever or diarrhea, consult a doctor.
Painful teething: advice for parents
When faced with teething in children, many parents are at a loss. First of all, you need to call an ambulance and determine the reason for the baby’s poor health. If symptoms are confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medications for teething - antipyretics and painkillers.
You can treat your gums yourself with an anesthetic gel with a cooling effect to reduce itching and swelling of the mucous membrane. Ice will also help. To reduce gum irritation, there are special silicone fingertips made of hypoallergenic material.
Folk remedies for teething will effectively relieve painful sensations - a decoction of chamomile, sage, tincture of valerian and honey will soothe inflamed tissues.
Painkillers for teething are contraindicated in children; this can worsen their health.
Important!
Without a doctor's recommendation, antibiotics and other strong teething medications can cause an allergic reaction.
How to help your baby when teething
- Give your baby something to chew on, such as a teether, which can be pre-chilled in the refrigerator.
- Massage your baby's gums with a clean finger. You can first wrap your finger in clean gauze. This will relieve the pain for a while.
- If your baby is already eating solids, give him cool foods (applesauce or yogurt).
- You can give your child something hard to chew on, such as a cracker. Just make sure your baby doesn't choke.
- If all of the above does not help, you can give your child a baby pain reliever or a special teething gel - strictly after consulting a doctor.
Vomiting, runny nose and diarrhea are not always symptoms of teething. If your baby appears unwell, call the doctor.
Formation of permanent bite
The development of permanent teeth is a long and complex process. The formation of permanent teeth begins at approximately 3 years of age, when the child’s primary bite is already fully formed.
Preparations for their eruption are ongoing, but changes occur gradually, so most often we don’t even notice them. Meanwhile, the child:
- jaws grow and expand;
- the distance between baby teeth increases (this is important, since permanent teeth are larger and by the time they erupt there should be enough space for them in the dentition).
Timing of eruption of permanent teeth in children
The order of growth of permanent teeth in children is mainly hereditary. In approximately 50% of cases, the molars (sixes) grow first. Second molars appear at 7-8 years of age. Around the same time, the incisors are replaced.
The first permanent tooth appears in children at 6 years of age, and the complete formation of the permanent dentition of the lower and upper jaw is completed at 12-13 years of age. After this, the roots of permanent teeth continue to form and this process ends by the age of 15.
Teething symptoms
Unlike baby teeth, permanent teeth in children erupt almost always painlessly and with virtually no symptoms.
In rare cases, during the teething period the child’s well-being may deteriorate:
- the child gets tired quickly;
- drowsiness appears;
- gums become inflamed;
- salivation increases, a runny nose appears;
- The gums itch where the tooth grows, and when chewing, painful sensations appear.
Problematic eruption of permanent teeth in children
Problems that may arise during the eruption of permanent (molar) teeth:
- 1
Growth retardation – after a baby tooth falls out, the permanent one is in no hurry to appear for 6 months or longer.
- 2
Bite pathology. It may be associated with premature eruption of permanent teeth (if the baby teeth have not yet fallen out), or lack of space on the jaw for normal tooth growth.
- 3
Hyperdentia - permanent teeth grow second row behind the milk teeth. The reason is the strong fixation of the temporary tooth in the socket, as a result of which the permanent tooth “chooses” a more convenient direction for growth.
- 4
Caries and its complications.
Choosing a toothpaste and brush
Has your baby cut his first tooth? Congratulations!
- Until one year of age, parents need to brush their baby’s teeth without toothpaste using a special silicone brush placed on their finger at least once a day.
- At one year old, the baby needs to pick up his first children's toothbrush - without toothpaste for now. It is better if the child chooses it himself. She should interest him, but not scare him away.
What should you pay attention to when choosing a children's toothbrush?
- Decor - kids love bright colors and funny characters.
- The handle should be comfortable, preferably made of non-slip material with a protective ring to avoid injury. Its length should correspond to the age of the child.
- It is important that the brush head is not too large and awkward. The optimal size is 2–3 teeth of a child. To avoid damaging your gums, it is better to choose a brush with a rounded head.
- Soft brushes with a bristle height of no more than 11 mm are suitable for children. It should be even so that the pressure on the surface of the teeth is uniform.
- From 2 to 2.5 years old, it’s time to start using toothpaste and teach your child to brush his teeth on his own. You need to choose a special baby toothpaste without fluoride, because the baby may want to eat it. You can switch to fluoride toothpaste when he learns not to swallow it.
Formation of the dentition
The article tells how to understand that a child is teething, and about ways to help him with pain and inflammation of the gums. But first, a few words about the process of dentition formation.
The formation of absolutely all teeth occurs in the fifth month of intrauterine development. They remain in a “frozen” state and begin to grow immediately before eruption. Therefore, if a child has no teeth by 9-12 months, radiography is prescribed - a study that allows one to evaluate their formation and location.
How to brush your teeth correctly
- Your baby's teeth need to be brushed 2 times a day - in the morning and in the evening before bed.
- Use a small amount of toothpaste at first, about the size of a grain of rice, then work up to a pea-sized amount.
- If you use such a small amount of toothpaste, there is no need to rinse your mouth.
- Brush your teeth gently from the outside and inside.
- The tongue also needs to be cleaned, because bacteria accumulate on it, causing bad breath.
- Remember to change your toothbrush every 3 months.
At this stage, it is too early to floss because the teeth are usually far apart.
How to keep children's primary and permanent teeth healthy?
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The health of future permanent teeth depends on how healthy the child's baby teeth were. The main concern of parents is quality care, timely treatment and preservation of baby teeth until the time comes for their natural replacement with permanent ones.
What should you do for this?
- Carefully monitor the condition of your baby’s teeth and regularly take him for examinations to the dentist in order to diagnose caries in time.
Prevention of caries is one of the main conditions for the health of a child’s future permanent teeth. You can protect your teeth by ensuring regular high-quality oral hygiene. One of the most effective measures to prevent caries in children is the dental procedure of sealing the fissures of baby teeth.
- Treat caries in a timely manner.
Unfortunately, temporary teeth have very thin enamel and not a very dense structure, so when affected by a carious infection, they are quickly destroyed. With timely diagnosis, caries is treated quickly and without complications - in dentistry, baby teeth are filled with safe materials. Thanks to modern materials and technologies in dentistry, it is even possible to restore baby teeth with severe destruction. In some cases, if the baby tooth could not be saved, and there is still a lot of time left before the permanent teeth erupt, prosthetics of temporary teeth is used.
- Take care of proper nutrition.
Food is an important source of useful vitamins and microelements, so it is important that the child’s diet is varied and balanced.
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The habit of brushing teeth and observing the rules of oral hygiene is formed in children from the appearance of their first teeth. Maintaining the health of children's teeth requires very little time and effort, but all this effort will help your child keep his teeth healthy for a long time!
Creating a good habit
The habit of brushing your teeth should be established in childhood. If you don’t force your child, but figure out how to turn this activity into an interesting game, your baby will brush his teeth with pleasure. Here are some tips:
- Children love to copy adults, so lead by example by brushing your teeth with your child.
- If you brush your teeth with your baby, at the end open your mouth and show each other how you handled this “task.” If necessary, clean your child's teeth yourself.
- Don't scold him, no matter how badly he cleaned it. Children at this age have not yet developed fine motor skills, so do not expect precise movements from them.
- Let your child associate brushing his teeth with something joyful. Play his favorite children's music, tell him stories about teeth, and draw on a dental theme.
- Keep a piece of paper with a schedule for brushing your teeth. Divide the day into morning and evening (you can draw the sun and moon there) and check the box when you brush your teeth.
- Finally, talk to your child like an adult. Explain to him why brushing his teeth is good. Draw scary microbes on a piece of paper and together figure out how you can fight them.
If your little one refuses to brush his teeth, try buying him a new toothbrush with his favorite cartoon character on it. Get him interested. Get several toothbrushes and let him choose a new one each time.
Experts' opinion
The effectiveness of ASEPTA wipes has been proven in the laboratories of the VERTEX company. Products have:
- Certificate of Conformity No. ROSS RU.AG81.N01070;
- Certificate of Conformity No. ROSS KR.AG81.H01815;
- Certificate of state registration No.RU.47.01.05.014.E.000002.01.18.
In addition, a study of the clinical effectiveness of the use of therapeutic and prophylactic agents of the ASEPTA series in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases in children and adolescents, conducted at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry of the Novosibirsk State Medical University, proved that after the use of Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic agents in children There was a decrease in signs of inflammation in periodontal tissues (disappearance of swelling, bleeding gums).
What microelements are needed for teeth growth?
Fluorine
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to acids and harmful bacteria. Thus, it helps prevent the development of caries.
Fluorine is found in:
- Toothpaste - however, remember that toothpaste with a small fluoride content can only be used by children over 4 years old;
- Fluoride-enriched water;
- Chewable tablets or drops;
- Some fruit juices.
Remember that too much fluoride can lead to fluorosis, which is when white spots appear on the teeth. Therefore, it is important not to use too much toothpaste, especially if the child has not yet learned to spit it out.
Calcium
Calcium takes an active part in the mineralization of teeth. A 3-year-old child should receive 800–1100 mg of calcium per day.
Products containing calcium:
- Milk, yogurt;
- Spinach and other green leafy vegetables;
- Broccoli;
- Fish.
In order for calcium to be better absorbed, it needs helpers. One is vitamin D and the other is vitamin K2.
Vitamin K
Calcium is collected and transported into bone tissue using the protein osteocalcin, which normally “dormants” peacefully in the blood. In order to activate it, you need natural vitamin K. It is found in dairy products (milk, yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese - for example, Agusha K2 cottage cheese).
Formation of milk bite
The process of building a human bite has 5 stages, and all of them occur in childhood.
Each of the five stages is important for the final formation of the entire dental system and dental occlusion:
The first stage is from birth to 6 months (before the appearance of the first teeth).
The second stage is the period of eruption of all baby teeth in a child (6 months - 3 years).
The third stage is the period of jaw growth, preparation for the natural change of milk teeth to permanent ones (3-6 years).
The fourth stage is the time of active growth of the jaws and the eruption of permanent teeth (6-12 years).
The fifth stage is 12-15 years old, when the child’s baby teeth have already changed and all teeth are permanent.
Correct formation of the primary dentition is one of the main conditions for the development of a correct permanent dentition in a child.
When should I take my child to the dentist?
The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation recommends showing a child to the dentist once a year starting from 12 months.
The purpose of the first trip to the dentist is prevention. The doctor checks whether teeth are growing correctly and gives recommendations on oral hygiene. It is better to do this no later than your first birthday, so that the specialist does not miss caries and possible problems with your bite.
The first trip to the dentist should not frighten your child.
Here are some tips to make it painless:
- Do not pay too much attention to this event, do not prepare your child on purpose;
- Don’t worry yourself so that your baby doesn’t get nervous along with you;
- If possible, arrive early to your appointment to give your baby time to look around.
What complications may arise?
Baby teeth did not fall out on time. The cause of the problem must be determined by the dentist. This usually requires an x-ray. In the image, the specialist can see the degree of development of the molars.
The appearance of caries and the occurrence of pulpitis. In this case, there is a change in body temperature, the appearance of severe pain and a general deterioration in the child’s well-being.
A very common situation occurs when a molar tooth (one or more) has already begun to appear, but the milk tooth does not fall out. As a result, the new tooth will look for other ways to grow, which will lead to a change in its direction and displacement. The result is a violation of the bite and the even position of the dentition. To eliminate the problem, you will need to consult an orthodontist.
The completion of tooth root formation occurs at approximately this age:
| Teeth | Upper jaw, age | Lower jaw, age |
| Central incisors | 9-13 | 7-11 |
| Lateral incisors | 9-12 | 8-11 |
| Fangs | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| First premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| Second premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| First molars | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| Second molars | 14-15 | 14-15 |
Since the eruption of third molars does not occur at a specific time, it is impossible to establish a clear age at which their roots are formed.
X-ray results confirm the completion of the process of tooth root formation. The key signs are the absence of an opening at the apex, as well as a pronounced periodontal contour.
Thus, completion of dental growth, including full maturation, usually occurs only between the ages of 15 and 18 years. It is at this time that the maxillofacial apparatus already has the same dimensions as in adults.
Possible problems
Despite the fact that changing teeth is a natural physiological process, some children and their parents may encounter a number of problems that require contacting a pediatric dentist.
No molars
The absence of permanent units can be caused by congenital edentia - the complete or partial absence of tooth buds.
Another reason for the absence of molars is previous inflammatory diseases - periostitis or periodontitis, resulting from progressive caries. Inflammatory diseases of the periosteum and periodontal tissues have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the tooth buds and can lead to their death.
Important! It is absolutely necessary to treat baby teeth for caries. You should not assume that the problem will go away on its own with the change of teeth. The progression of the disease can negatively affect the health of the tooth buds.
Molar tooth hurts
The enamel of newly emerging permanent teeth is still poorly formed. The low level of its mineralization makes teeth vulnerable to cariogenic microflora. This can lead to the development of caries and cause pain.
Due to poorly formed enamel, tooth sensitivity to external irritants (cold, hot, sour, sweet) may increase, which is also accompanied by painful sensations.
Important! Normally, permanent teeth do not hurt. If pain occurs, you should contact your pediatric dentist. The specialist will determine the cause of the pain, carry out the necessary treatment, fluoridation or remineralization of tooth enamel.
Molars grow crooked
The incorrect position of permanent teeth can be caused by two reasons - the growth of the permanent unit outpaces the process of loss of baby teeth or they were removed ahead of schedule, which led to incorrect formation of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
In this case, there is only one way out - orthodontic treatment of malocclusion.
Important! A malocclusion must be corrected. The sooner you contact a dentist, the more successful the treatment will be. The child will be prescribed to wear removable or fixed orthodontic appliances that will help straighten the permanent teeth and bite.
Injuries
Due to their activity and lack of experience, children can accidentally injure a newly emerging permanent tooth. Due to mechanical damage, cracks and chips may appear on it. The damage looks unattractive. Caring for such teeth is complicated, since food debris can get stuck in the cracks, which will certainly lead to the development of caries.
Important! If a child accidentally injures a permanent tooth, it is necessary to seek help from a dentist. The specialist will assess the complexity and depth of the damage and will build up the missing volume of tooth tissue with composite materials.
Tooth loss
Loss of healthy permanent teeth can only occur as a result of severe trauma to the jaw, for example, during a child’s fall or fight. A diseased molar may fall out on its own. In this case, you will also need to consult a specialist. Most likely, the child will undergo temporary prosthetics for the lost unit, which will not disrupt the formation of a correct permanent bite.
The tooth is loose
Looseness of a permanent tooth is an alarming symptom indicating a pathology of the dentofacial apparatus or the presence of inflammation. Consultation with a specialist is required!