- home
- Diseases
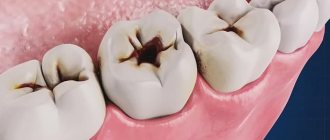
- Caries
- Deep caries
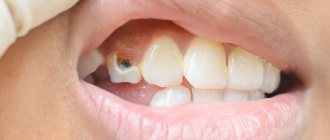
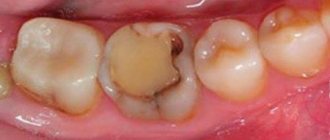
Deep caries is the fourth and final stage of destruction and demineralization of hard tooth tissues. Looking at the photo of deep caries, you can immediately notice the presence of a carious hollow. From the outside it may seem small, but inside there is always significant destruction of dental tissue.
With deep caries, the carious cavity is separated from the pulp by only a narrow layer of dentin, which with further development of the disease can lead to the development of pulpitis, periodontitis or periostitis. Thus, the main task of the dentist is to preserve all the functions of the tooth and minimize the risk of developing these diseases.
Etiology
The medical history of deep caries may indicate the primary or secondary development of the disease. In the first case, it occurs due to the lack of professional treatment of the middle stage of caries, in the second - after tooth preparation (incorrect treatment, chipped filling). Otherwise, the factors stimulating the development of the disease are the same as for caries in general: poor hygiene, lack of necessary cleaning of hard-to-reach places, disturbances in pH levels, saliva composition, genetic predisposition.
In our clinic you can get a free dental consultation!
Complicated caries in children
In children and adolescents, complications, like the caries that precede them, develop at lightning speed. This is due to insufficient mineralization of enamel in childhood and the tendency of young patients to infectious diseases caused by streptococci - sore throat, bronchitis, measles and scarlet fever.
Advanced forms of caries in children lead to:
- the development of its circular shape, when, starting from the neck of the tooth, decay spreads around its crown, and over time the tooth breaks off;
- spread of infection along the surface of the crown (planar caries). In this case, the tooth completely darkens, the child complains of aching pain;
- acute and chronic pulpitis;
- infection of the rudiments of permanent teeth, resulting in multiple caries after their eruption.
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2016, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
8 years of experience
Arzumanov
Andranik Arkadievich
Dentist-orthodontist
Graduated from Moscow State Medical University. Internship - Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics.
Residency at Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics. Member of the Professional Society of Orthodontists of Russia since 2010.
More about the doctor...
Factors and mechanics of development
One of the factors that determines the difficulty of treating secondary caries is the absence of severe symptoms. Determining the reasons that caused the re-development of the pathological process also poses a problem. Typically, such factors include:
- Mistakes made by the doctor who treated pulpitis of temporary or permanent teeth. A common problem is poor cleaning of the carious cavity before filling;
- Loose fit of filling material, leading to the formation of a free gap. The presence of space causes deformation of the structure under mechanical loads, provoking the appearance of cracks and chips. In addition, cavities in dental tissue contribute to the accumulation of pathogenic microbes and bacteria that cause caries;
- Wearing of a previously installed seal. The development of the service life leads to the launch of destructive processes that reduce the protective functions of the element and open access to the internal tissues of the tooth.
Secondary caries most often occurs at the junction of the filling with the dental tissue. In the initial phase, the problem is characterized by the formation of gaps and scratches, through which microbes and bacteria are introduced into the unit, and in the case of large cavities, food particles that gradually decompose in the oral cavity. Acidic elements released as a result of the development of pathogens corrode the enamel structure, damage dentin and provoke pulpitis - as a result, the patient is prescribed repeated tissue removal and root canal treatment.
However, it would be wrong to say that secondary caries is solely a consequence of medical negligence. Much depends on the patient’s compliance with the instructions given after the initial treatment. Common mistakes made during the recovery period include:
- Systematic consumption of excessively hot or cold food, which results in a tissue reaction to temperature changes, leading to the formation of cracks in the base structure;
- Including hard and hard foods in the diet, as well as maintaining bad habits, including smoking and love for toothpicks;
- Violation of the rules of hygienic oral care, leading to the accumulation of a significant amount of pathogenic bacteria that corrode weakened enamel.
By adhering to medical recommendations, you can promptly identify the prerequisites for the development of secondary caries, as well as avoid its development.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of deep caries, first of all, consist of a sharp toothache when exposed to thermal, chemical or mechanical stimuli. The pain is short-term and disappears after the stimulus is removed. If pieces of food remain in the cavity, the pain becomes aching and can last until the irritants are eliminated. If the carious cavity is extensive, the patient may develop an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth. Caries under a filling can develop for years and is characterized by the absence of clinical manifestations. Painful sensations occur only when the dentin is destroyed to the bottom of the tooth.
Prevention of caries
It is impossible to cure caries at home, but you can prevent its occurrence. To do this, it will be useful to resort to a number of preventive measures to strengthen tooth enamel, which will increase its resistance to chemical destruction. It will be useful:
- Avoid consuming sugary foods and drinks to prevent the growth of microorganisms in your mouth. Well, if you still decide to eat them, you should regularly rinse your mouth after eating.
- Regularly use toothpastes containing fluoride to brush your teeth. This microelement strengthens the enamel, making it resistant to acid and the formation of caries.
- Using dental floss daily will effectively remove food particles stuck between your teeth that cannot be removed with a standard brush.
Strict adherence to basic hygiene rules and proper balanced nutrition will help keep your teeth and gums healthy. It would be a good idea to make a habit of regularly visiting the dentist - the disease will be noticed in the early stages of manifestation, which will avoid the need for filling.
Diagnostics
Deep caries is diagnosed during an examination by a dentist, who takes into account the patient’s complaints, examination results, thermal diagnostics and radiography data. Differential diagnosis of deep caries requires distinguishing it from the following diseases:
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- average caries.
Diagnosis of deep caries
Making a primary diagnosis of caries usually does not cause major problems due to the abundance of external symptoms and other obvious manifestations. However, this disease should be distinguished from other dental ailments:
- Average caries
Medium and deep caries are different: the bottom of the cavity with moderate damage remains denser, sensitivity is moderate. A significant gap between the affected area and the healthy pulp is also visible on the x-ray.
- Chronic pulpitis (fibrous or hypertrophic)
If the infection has penetrated inside the tooth, inflammation of the pulp may develop. As a result, the pulp tissue changes and its growth may occur. The pain is usually mild.
- Acute focal pulpitis
Acute forms of pulp inflammation, on the contrary, are characterized by sharp shooting pain, usually occurring when pressing on the bottom of the cavity. The pain may worsen at night.
- Periodontitis
There are no periodontal changes with ordinary caries. If there are signs of such changes on an x-ray or during examination, we are most likely talking not about deep caries, but about periodontitis. Having patient history data also often helps in making a correct diagnosis. As a rule, periodontitis is a consequence of a previously occurring carious process.
Treatment
Treatment of deep caries is carried out in several stages and sometimes requires two visits to the dentist. The latter is necessary if the dentist is not sure that the disease has not affected the pulp. In this case, the treatment plan includes the following:
- treatment of the carious cavity and removal of all affected tissues;
- applying an insulating pad;
- installation of a temporary filling;
- a second visit after three to four days and installation of a permanent filling if there is no pain.
If pain symptoms are present and increasing, pulpitis is treated.
How to treat caries?
For treatment, you need to go to a dental clinic, since it is simply impossible to get rid of this disease at home. There is no point in postponing a visit to the dentist because early treatment will be faster, easier and cheaper.
This disease is very common, so the process of treating it at any stage does not cause difficulties for the dentist. At the initial stage, the entire procedure of medical intervention is limited only to cleaning the affected areas of the enamel using special tools and subsequent restoration of the structure.
At the middle stage, caries treatment involves removing the affected tissue, disinfecting the resulting cavity, filling it and subsequent processing, giving the restored tooth its original appearance.
Removing caries at a deep stage is often complicated by the fact that the walls of the tooth are too thin for which it is impossible to install a filling. In this case, you have to grind down the remaining parts in preparation for installing the crown.
Caries of the front teeth is treated in exactly the same way as in the case of other teeth, with the exception that photo fillings are necessarily used here, which can not stand out from the general background.
Where to treat?
You can undergo treatment for deep caries at the Good Hands dental clinic. Our specialists will make every effort to save the tooth and carry out its restoration, maintaining its appearance and functionality. It is very important to seek professional dental care in a timely manner in order to prevent the development of pulpitis and periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss. Our specialists use effective anesthetics and modern equipment in their work. Thanks to this, the treatment will be comfortable and painless. Book a free consultation with us by filling out the simple form on this page or calling us!
Causes of caries
Multiplying carious bacteria, feeding on food debris on the teeth and releasing acidic products, slowly destroy the enamel. The disease develops at different rates in different people. It's connected with:
- Heredity.
It has a strong influence on the composition and structure of dental tissues, and if parents suffered from manifestations of the disease, then with a high degree of probability this will also be characteristic of their child. - Food.
Carious bacteria feed mainly on sucrose and a number of other complex carbohydrates, and eating sweets can lead to their rapid growth, an increase in the amount of waste products and to the decay of enamel. - Features of the immune system.
Often, caries develops after a person has suffered respiratory diseases, which is associated with weakened oral immunity, which causes the proliferation of microorganisms. - Brushing your teeth.
Many people neglect this hygiene procedure, or do it irregularly and for show. This leads to the formation of plaque, which is a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms. - Profession.
People who work in enterprises associated with the production of chemicals are statistically more likely to become ill. - Geography.
The percentage of fluoride in drinking water, which is responsible for strengthening tooth enamel, leads to an uneven spread of the disease depending on the region.
How does caries occur?
In advertising, caries disease is portrayed as certain bacteria that settle on the surface of the tooth and destroy it. This looks like reality.
Pathogenic microorganisms that come from the outside or are contained in the natural microflora of a person begin to multiply in a favorable environment where all the conditions are created:
- change in acid-base balance;
- acceptable temperature;
- humid environment.
Let's add here the activation of carbohydrate fermentation processes after eating. All this leads to the production of large amounts of organic acids, which attack tooth enamel and cause caries.
The main circumstances that lead to the occurrence of carious lesions include:
- lack of hygiene;
- improper oral care;
- predominantly unbalanced diet;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, both chronic and periods of exacerbation;
- decrease in the level of essential vitamins and microelements in the body;
- genetic predisposition
Hard plaque of bacteria
And if the problems listed above can be solved by adjusting nutrition and improving hygiene procedures, then you will have to fight the streptococcus bacillus.
The fact is that streptococcus is present in two states of aggregation: soft - in this case it will be easy to remove with a regular brush or dental floss, and hard.
The hard condition occurs due to an increase in the number of bacteria, their mineralization, resulting in the appearance of tartar, which cannot be removed at home.
Therefore, it is a good idea to undergo a hygienic professional cleaning procedure at a dental clinic to prevent caries.
A balanced diet is everything
You can use one rule - don't eat sweets. However, harmful carbohydrates, which lead to fermentation and the production of organic acids, are found not only in “delicious” foods. This includes any baked goods (including bread), added sugars (for example, in sauces and canned food), starchy foods (potatoes, carrots, tomatoes).
But this does not mean that you need to limit yourself in everything so that caries does not have a single chance. It is enough to add such foods to your diet in moderation; be sure to counterbalance them with whole grain cereals and green vegetables and fruits.
In addition, with age, the surface of the enamel becomes thinner and becomes more susceptible to what we eat every day.
Elemental composition of the body
A factor that is closely related to nutrition. If it is not balanced, most likely the body will not receive enough microelements necessary for the correct functioning of the body.
For example, calcium, phosphorus and fluoride are microelements that reduce the risk of dental caries. They are found in seeds, cottage cheese products, fatty cheese, canned red beans and some cereals.
Note! A diet enriched with microelements will not help if there is a genetic predisposition to demineralization, and “vitaminosis” can be observed during pregnancy - when the fetus “eats” the mother’s teeth, accumulating calcium, necessary for the proper development of the skeletal system. But this just means that in such cases you need to be even more responsible about your diet.
The work of the salivary glands
Water balance in the body has an interesting effect. It affects the full functioning of the salivary glands, which must secrete a sufficient amount of secretion to remove food debris and prevent the decomposition of bacteria.
Does your mouth often dry out? Try increasing the amount of water you consume, or analyze your diet - perhaps there is too much sweet or salty in your menu. Adjust this and let your saliva do its work.
Genetics and pathologies
Any disruptions in the body's natural metabolism - diabetes, gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers) and hormonal imbalance - have an impact.
In these cases, even with a varied diet, beneficial components may not be absorbed well enough and vitamin starvation still occurs.
What are caries?
Diagnosis of caries involves dividing the disease depending on several factors: symptoms, source of occurrence, and so on. Let's consider the most understandable ones for the average patient without special medical education.
Areas of distribution
Everything is quite clear here:
- single - a carious cavity is localized on one tooth, begins with a harmless spot on the enamel, is not accompanied by pain until it goes deeper
- systemic (or multiple) - develops very quickly, affects several units in a row, has a depressing effect on the immune system.
According to the flow and emerging consequences:
- without complications - no special violations have been identified, dental intervention will not lead to a negative outcome;
- complicated - at the diagnostic stage, including studying an x-ray and opening the affected cavity, a violation of the internal tissues, pulpitis and periodontitis were revealed.
Stages of caries
This classification is most often found in the vocabulary of dentists, as it is used to describe the level of development of carious disease.
Let us arrange them in order of increasing complexity of treatment and the level of consequences of surgical intervention:
- darkening of the enamel or stain - accompanied by a change in the uniform color of the surface in the form of a small whitish or gray spot or stripe. At this stage, the patient does not experience pain, and if the pathology is invisible to the eye, the person himself will not notice it;
- initial superficial lesion - a small, almost imperceptible hole of a dark shade appears in place of the spot, which grows over time. The tooth reacts to temperature changes, drinking too hot or too cold drinks and foods;
- medium caries - the disease affects dentin - the part that is located directly under the enamel layer, so the pain is no longer periodic, but permanent, and the quality of life decreases;
- deep caries is a diagnosis that requires urgent intervention and treatment, as the pulp (nerve endings) is affected. Most likely, you will have to perform depulpation - in fact, depriving the tooth of nerve endings, which means that the tooth will be less protected from mechanical influences from the outside. Moreover, a tooth with advanced pulpitis must be removed and replaced with an implant or crown.
Separately, you can take out a type that differs in localization directly on the tooth. That is, the process usually begins from the affected edge of the tooth, or from the center.
However, if there is the presence of tartar, which in turn provokes bleeding gums, an increase in the colony of pathogenic bacteria and accelerated development of gingival lesions, then cervical caries occurs. It is located right next to the gums, where the most mineralized residues are found.
Diagnostic methods
Regardless of the severity of the pain, you should immediately consult a doctor at the first suspicion. You need to choose a dental clinic where they will conduct a full diagnosis and staging of the disease.
The main ways to determine the level of “neglect” of the oral cavity include:
- visual check - using a mirror and probe
Additional Information. Find out from the administrator or on available resources on the Internet whether the clinic uses microscopes in its work - a doctor with special microscope glasses will see more minute changes in the enamel than one who uses his own vision, no matter how sharp it is.
- digital images (this can be a regular X-ray, or a full-fledged computed tomography or popular 3D recognition);
- functional study;
- thermal testing
A high-quality diagnosis will give the doctor an understanding of how to treat caries in order to avoid the unpleasant results of untreated pathology, which affects the pulp under the filling and brings even more problems.
How to get rid of carious disease
The type of therapy directly depends on the stage of the disease.
In case of minor damage, conservative intervention is performed without preparation (drilling, cutting the gums or interfering with dentin and pulp):
- Visual diagnostics;
- Isolation of the tooth from the gingival fluid
- Gently cleans the surface from dark spots;
- Application of a mineralizing composition that will prevent re-injury, for example, with the Icon system
The mineralization composition will stop the spread of caries if all actions are performed accurately.
Traditional drill
If the pathology has turned into holes and with all subsequent deteriorations, they resort to the only method of treatment - mechanical exclusion of the affected areas using a drill or, simply, a drill.
This process is considered a surgical intervention and, if necessary and a low pain threshold, treatment of caries is carried out using anesthetics:
- Pain relief (if necessary, if the affected area is shallow, the patient may refuse the injection);
- Isolation of tooth with rubber dam.
- Mechanical cleaning of carious and softened tooth tissues - drilling;
- Application of medications to remove bacteria and prevent the formation of new caries;
- Complete repetition of the anatomical shape of the tooth;
- Polishing the filling.
If caries turns into pulpitis, this will complicate tooth treatment. Under anesthesia, it will be necessary to remove the nerve and seal the tooth canals with an inert substance. Otherwise, the inflammation will go further into the bone, into the jaw, into the blood, which can lead to very serious consequences, including tooth extraction and hospitalization.
Do not be afraid of the depulpation process. With enough attention and care, the tooth will function just like other teeth with nerves. The main thing is to cover such a tooth with a crown.
Caries in children
Dental problems are not limited to adults only. Kids are not yet used to or have not learned to pay enough attention to hygiene, and some really love sweets.All this leads to caries disease on temporary milk teeth. But do not take their temporary nature as a reason not to treat milk caries.
Damage to the milk row can lead to the same complications in the form of pulpitis and periodontitis, and you will have to resort to real general operating anesthesia to cure fidgety teeth.
In addition, deep caries can affect the formation of permanent dentition, so a preventive examination by a dentist is required for children once every six months.
Prevention is the key to health
This applies to both adults and children:
- maintain regular oral hygiene - brush your teeth twice a day with a toothpaste enriched with fluoride and calcium, use dental floss and brushes, mouth rinses, and if you cannot use a toothbrush, take chewing gum;
- Supplement your daily care with an appointment with a dental hygienist at least once a year to get rid of tartar;
- maintain a sleep schedule, diversify your diet, drink more water and engage in physical activity.
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to suffer from pain and then spend money and time on treatment in professional dentistry.
Complications
Untimely treatment of caries leads to inevitable complications:
- development of pulpitis (the carious process gradually spreads to the deep layers of dentin surrounding the pulp of the tooth);
- if pulpitis is not treated, necrosis of the pulp occurs (i.e. it dies), as a result, a focus of inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root;
- development of gum “flux” (a purulent process occurs between the jaw and periosteum);
- the appearance of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root (the bone tissue is resorbed, and inflammation forms in its place).
PREVENTIVE ACTIONS
To reduce the risk of pathology formation, it is important for patients to perform secondary prevention of caries:
- install composite inlays and crowns from modern materials;
- follow all the specialist’s recommendations during and after treatment;
- when identifying the first violations of the structure of the material, it is important to make an appointment with a doctor;
- come for preventive examinations once every six months, even without obvious complaints.
Compliance with all simple rules will make it possible to minimize the risk of a secondary process. It is important to find an experienced doctor to perform treatment. That is why, when choosing a clinic, you should pay attention to prices, patient reactions after an appointment, and the qualifications of doctors.
By making an appointment with us at West Dental, you make your choice to use the best specialists and high-tech equipment and perform treatment procedures with modern materials, so the occurrence of secondary pathology will be minimal.
CONSEQUENCES OF UNTIME TREATMENT
If you suspect the presence of a carious process under a filling, you should immediately make an appointment with a dentist. To register with West Dental, you can go to our website and fill out the feedback form or call the numbers provided. Failure to eliminate the pathology in a timely manner can be dangerous due to:
- Damage to the jaw bone. Inflammation can affect all bone structures.
- Destruction of the tooth root with a root canal. If the roots are damaged, the only answer to solve the problem is to extract the unit.
- Transfer of the pathological process to neighboring units that were completely healthy.
- Large area of destruction of the crown and root parts of the tooth.
A great danger in the secondary process is inflammatory diseases of the pulp chamber and its further death. This can occur due to the use of chemical solutions during drug treatment and traumatization with burs.
WHEN SHOULD OLD FILLINGS BE CHANGED?
Replacing old fillings is a method of treating and preventing secondary caries. This makes it easier to prevent the disease from getting worse and treat it conservatively in one visit to a specialist. Therefore, old fillings that have stood for more than 5 years should be changed if:
- the tight fit of the filling to the tooth is broken, i.e. pieces of food get stuck between the material and the walls of the cavity, there is a high risk of damage to hard tissues;
- there is excess material and it “hangs” over the neighboring unit or gum, which causes a local inflammatory reaction on the gum, bleeding and the risk of destruction of the root system of the unit due to the accumulation of food and pathological microorganisms;
- abrasion of the filling has occurred, which over time leads to bite pathology and problems with the TMJ;
- The filling material did not restore the anatomy of the chewing surface, i.e. has changed the natural shape, and thus increases the risks of joint diseases;
- the aesthetics are impaired, especially the frontal group of teeth, which are visible when smiling;
It turns out that replacing fillings is important because of maintaining the health of teeth and gum tissue. If the attending physician considers it necessary to replace an outdated filling, you should agree for the sake of continued oral health.