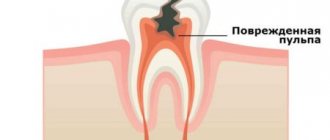
Chronic pulpitis is a form of pulpitis, inflammation of the pulp. Pulp is the soft tissue of the tooth, which is responsible for the blood supply to its hard tissues and consists of nerve endings, blood vessels and connective tissue. As a rule, chronic forms of pulpitis occur when acute forms are suppressed, but sometimes they can be a primary process without an acute stage.
Chronic pulpitis is an inflammatory process of the nerves and blood vessels of the tooth, which gradually causes severe changes in structure and function. If the disease is present, a person reacts sharply to cold and hot foods and experiences pain while chewing solid food. Pathology can be accurately determined using x-rays and electroodontodiagnosis. The development of the chronic form occurs in the absence of proper treatment of acute pulpitis.
Fact: the disease is much more often detected in the chronic form rather than in the acute form. People aged 20-50 years are at risk.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Causes of pulpitis
Photos of chronic pulpitis are presented in this article. This disease can occur for various reasons.
The pathology can become chronic if acute pulpitis is not treated for 12 weeks. The disease appears due to toxins and bacteria. They penetrate into the pulp through channels and through the blood. Complications of deep caries, increased abrasion of enamel, mechanical injuries and opening of the pulp can contribute to the development of pathology.
Advanced caries
Ignoring the symptoms of caries and the lack of professional treatment can lead to the further development of this disease with penetration into the deep layers of dental tissue, including the pulp. Once in it, pathogenic microorganisms will cause inflammatory processes.
Incorrect treatment of caries
Sometimes pulpitis occurs after caries treatment has been carried out. The reasons for its occurrence may be the following:
- Not all tissues affected by caries have been removed, and they continue to have a destructive effect on the tooth;
- During treatment, the pulp was burned due to insufficient cooling;
- The bottom of the tooth cavity was dried with an air jet before filling.
Tooth injuries
The integrity of the tooth enamel can be damaged due to a blow to it or contact with hard food. If, as a result, the crown splits and the nerve is exposed, inflammation of the pulp in the near future is almost inevitable.
Retrograde pulpitis
Sometimes the infection penetrates into the dental pulp not from the oral cavity, but through the apical foramen in diseases such as periodontitis, osteitis, osteomyelitis.
Indications
- Mechanical damage to the tooth and violation of the integrity of the crown.
- The appearance of complications of deep caries and the penetration of infection into the canals.
- Exacerbation of the disease and pain syndrome.
- Incorrectly installed filling and progression of pathology.
- Detection of inflammation on an x-ray.
Contraindications
- Cardiovascular diseases in the acute stage.
- Pregnancy and prohibition on taking medications.
- Mental and nervous disorders.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia, antiseptics, antibiotics.
How to treat pulpitis?
Knowing what it is, tooth pulpitis, you need to figure out how to treat this pathological process. The maximum effectiveness of pulpitis treatment at the Academy Dent clinic is achieved thanks to the highest classification of dentists, as well as the use of the latest equipment. Before starting treatment, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis based on the descriptions of the patient’s complaints, the results of an examination of the oral cavity, as well as diagnostic data.
Based on the information received, he draws up a treatment plan, in total there are 2 possible ways to solve the problem:
- Conservative treatment – used for acute pulpitis, especially effective in the early stages of the disease. The doctor drills and cleans out the carious cavity, after which he places medication over the pulp. In this case, antibiotics, antiseptics and proteolytic enzymes are used. After the use of drugs, a temporary filling is installed to block access to the pulp core and allow the drugs to act. In the future, when the infectious and inflammatory processes are stopped, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. This method preserves the vitality of nerves and other pulp structures, as well as the tooth itself.
- Surgical treatment is a radical solution used in cases where conservative methods of therapy do not bring results. Surgical treatment involves removal of the pulp core and thorough cleaning of the cavity. Depending on the course of the disease, the pulp can be removed only after killing the nerve. If there is large-scale destruction of bone tissue, the tooth must also be removed.
Regardless of the tactics and method of treatment, at the Academy Dent clinic, treatment of pulpitis is as comfortable and painless as possible. Dentists use the latest generation of anesthetic drugs and use modern expert equipment.
Clinical manifestations
Treatment of chronic pulpitis does not always begin on time, since this disease is very insidious. Acute pain is always the reason for seeking professional help, but with chronic pulpitis, pain symptoms are not pronounced and the patient prefers to postpone his visit to the dentist. In this case, the disease develops quite quickly and, at best, will lead to an exacerbation of chronic pulpitis with severe pain symptoms or to the occurrence of periodontitis, in which it can be very difficult to save the tooth from removal. No less pleasant consequences may include the formation of cysts, ulcers, phlegmons and even sepsis. This is why timely diagnosis of chronic pulpitis is so important!
The main manifestation is an acute reaction to cold and hot food. However, it occurs late (sometimes 5-10 minutes after consuming food or liquid). In a calm state, a person experiences heaviness inside the tooth.
The hypertrophied form is not accompanied by severe pain. Overgrown tissue appears that ruptures when eating food. Pain may occur when eating hard foods or when pressing on the inflamed area.
Gangrenous pulpitis causes severe pain when eating hot food, which does not go away for a long time. The pulp begins to rot, which causes bad breath. The color of the tooth enamel changes (it becomes dark gray).
An exacerbation is accompanied by severe pain even without mechanical and thermal effects on the affected area. There are positive symptoms of vasoparesis, swelling of the gums, and pain in the trigeminal nerve.
Routes of infection
Infection in the soft connective tissue rich in nerve endings with retrograde pulpitis can penetrate in several ways.
- According to the bloodstream of a patient suffering from chickenpox, rubella, sepsis, and influenza.
- Through the periodontal pocket in the destructive form of gingivitis, which provokes the destruction of the periodontal junction.
- Through the penetration of infection from neighboring foci of inflammation, such as sinusitis, chronic maxillary osteitis, osteomyelitis.
Types of chronic pulpitis
It is customary to distinguish the following types of chronic pulpitis:
- Hypertrophic – characterized by the formation of granulation tissue and dentin dystrophy. In this case, the overgrown granulations extend beyond the pulp chamber and enter the carious zone. If the form is polypous, then polyps are formed. Severe exacerbation can provoke pulp gangrene.
- Fibrous - differs from other types in that it leads to the appearance of coarse fibrous connective tissue. When examined, the pulp looks like a scar cord with a color change to white-gray. Gangrene, phlegmon and abscesses develop as complications.
- Gangrenous - represents complete tissue necrosis and tooth destruction (the color changes to gray-black). But in rare cases, it is possible to save small areas of the pulp.
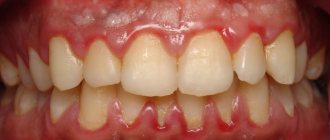
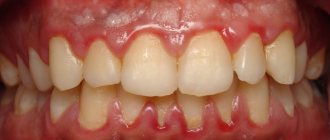
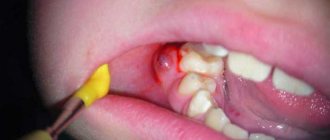
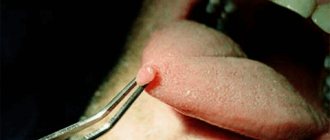
What does pulpitis look like in the photo?
In this section, clinic patients can see what tooth pulpitis looks like in the photo:
It is important to remember that dental pulpitis is a serious and dangerous disease that can cause a lot of discomfort and harm to health. However, with timely treatment of the disease, it is possible not only to save the tooth, but also to leave the pulp completely viable. Every patient can count on high-quality and effective treatment by making an appointment with a dentist. "Dent Academy", where the best specialists work, there is no place for negligence and mistakes.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Traditional medicine in the fight against pulpitis
Is it possible to cure pulpitis on your own, without going to a doctor, but resorting only to traditional medicine methods? Unfortunately no.
Pulpitis is a stage of caries development, characterized by the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the pulp. If caries has occurred on a tooth, it can only be removed by drilling and nothing else. Therefore, the affected areas must be drilled out and the tooth filled.
Bacteria entering the pulp cause inflammation. Cariogenic organisms are resistant to even powerful antibiotics, not to mention the herbs used by fans of alternative medicine. It is for this reason that no folk remedies can not only cure pulpitis, but even slow down its development, alleviating the patient’s suffering.
Do not waste time on ineffective self-medication: you must immediately consult a doctor!
Treatment of chronic pulpitis
Since chronic pulpitis leads to irreversible changes in the pulp tissue, it is removed from the crown and root parts of the tooth. Treatment involves surgical intervention with depulpation and can be carried out using the following methods:
- vital - the pulp is removed under anesthesia, the root canals and tooth are filled;
- devital - a special paste is applied to the pulp, and then the already dead pulp is removed, the canals and the tooth itself are filled.
Vital extirpation is carried out in one visit and is considered a gentle method, but it cannot be used due to the patient’s allergic reaction to anesthetics or in case of obstruction of the dental canals. It is in these cases that the devital method is used, which requires 2, and sometimes 3 visits to the dentist.
Retrograde pulpitis – Prices
| Services | Price |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canal | 1050 rub. |
| Placing a light polymerization filling | 3800 rub. |
| Unsealing 1 channel, sealed with paste | 1100 rub. |
| Unsealing of 1 channel, sealed with cement for 2/3 of the length | 4000 rub. |
| Permanent canal filling (gutappercha, paste) | 1500 rub. |
Recommendations after treatment
The only way to avoid relapse is to maintain proper oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly. The appearance of pain in a tooth at rest or while eating is a good reason to visit a specialist, as this reflects an inflammatory process in the pulp. Professional cleaning of the oral cavity and visiting the dentist 2 times a year will help you prevent the recurrence of chronic pulpitis. If, after treatment from a specialist, you notice an acute reaction to cold and hot food, experience pain when pressing on your gums and teeth, or notice swelling and discoloration of the enamel, be sure to make an appointment with your doctor.
In the dental department of the CELT clinic, treatment of chronic forms of pulpitis is carried out using modern diagnostic equipment and high-quality filling materials.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Tooth pulpitis: symptoms
So, we now understand what dental pulpitis is, and we move on to the symptoms of this disease. With pulpitis, different severity of symptoms can be observed - from acute paroxysmal pain to minor pain. In this regard, there are 2 of its forms: acute and chronic.
- Acute form of pulpitis – signs of pulpitis in this case are reduced to the appearance of acute paroxysmal pain (especially at night). The pain is spontaneous and occurs spontaneously without any irritants. However, during “pain-free intervals” pain can be provoked by thermal irritants, mainly cold water, although it is also possible from hot water.
An important point: after eliminating the irritant, the pain does not go away for about 10-15 minutes. The latter circumstance makes it possible to distinguish pulpal pain from pain due to deep caries, because with the latter, the cessation of pain occurs immediately after the cessation of the stimulus.Often patients cannot correctly identify the diseased tooth, because pain can radiate along the nerves to the entire jaw. The severity of the pain increases as the inflammation transitions from serous to purulent. As the purulent process develops, the pain becomes pulsating, shooting, tearing, and the pain-free intervals shorten until they disappear completely (24stoma.ru).
- Chronic form of pulpitis - pain in this form of pulpitis is usually aching, not expressed, and is of a rare periodic nature. Very rarely, pain may be completely absent. Periodically, chronic inflammation can turn into acute, with the appearance of corresponding acute symptoms.
Important: what form of pulpitis will occur depends solely on the virulence (level of pathogenicity) of microorganisms, as well as on the characteristics of the body’s immune response to infection. With increasing age, the frequency of acute forms of pulpitis decreases - due to a decrease in the capabilities of the body's immune response.