A couple of years ago, an outbreak of the “extremely dangerous” new Coxsackie virus, as the media dubbed it, occurred in Turkey. In fact, this virus is not new at all and has existed for many, many years. And this virus is not dangerous at all, only very contagious. The causative agent of hand-foot-mouth disease is the Coxsackie virus of the enterovirus family. Most often, children under 10 years of age are susceptible to the disease, but adults can also get sick. Coxsackie enterovirus multiplies in the gastrointestinal tract. In total, about 30 serotypes of the Coxsackie virus have been studied. Today in this article we will tell you what is important to know about it and how to treat it.
What is important to know?
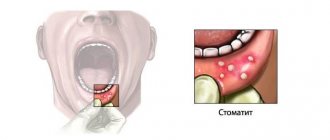
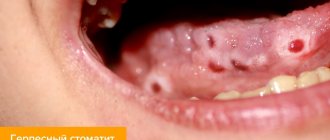
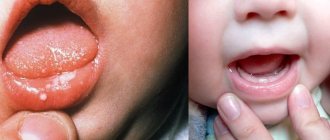
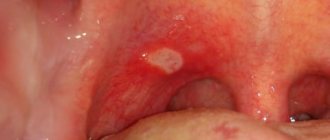
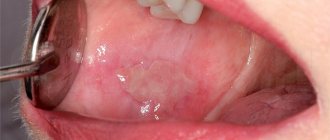
The incubation period lasts from 3 to 5 days and is rapid. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are high fever, reaching 40 degrees, and a rash in the form of red spots with blisters in the center. Most often, the rash is located in the mouth (tongue and gums), on the arms and legs, it can also affect the buttocks, especially in the anus, and single elements of the rash can appear on any part of the body.
The duration of the disease is on average about 10 days. According to statistics, the peak incidence occurs in summer and autumn. The Coxsackie virus does not cause immunity, that is, it is quite possible to become infected again, but the course of the disease will be easier than the first time.
You can become infected from a sick person or from a carrier of the virus. Infection most often occurs in resorts near the sea during the season.
The Coxsackie virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, household contact and food, that is, you can become infected through dirty hands or shared utensils, dirty toys, sand, water, unwashed vegetables and fruits. You cannot get infected from animals.
Three outcomes of the disease:
- The child recovers completely
- The disease becomes chronic when organs retain the virus for an indefinite period of time.
- The patient becomes a carrier of the virus
Two groups of Coxsackie virus:
- Viruses of this group infect mucous membranes and skin. Characteristic features for this type of virus are herpangina, serous meningitis, vesicular stomatitis, acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis.
- Viruses of this type infect the pleura, heart and pancreas. The liver suffers greatly.
Routes of transmission of the virus
Virus transmission occurs:
- respiratory route,
- fecal-oral route,
- through contact and everyday life,
- vertically (from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth).
Viral particles are released into the environment through breathing, saliva, and defecation in feces.
If the rules of personal hygiene are not observed sufficiently, infection can occur very easily. This explains the widespread spread of infection in crowded groups - kindergartens, summer camps, on hotel grounds (especially in swimming pools). Playing with shared toys, licking them, or putting unwashed hands in their mouths is common among young children. And few preschoolers know how to wash their hands correctly: long enough and washing out all the creases between the fingers and under the nails.
The virus is highly contagious, meaning that a small amount of viral particles enters the body for the disease to develop.
Symptoms of the disease
As we said above, the incubation period of this enterovirus infection is rapid and lasts from 3 to 5 days. In this case, the temperature can reach 40 degrees and decrease extremely poorly, even with the help of antipyretics.
Nausea and vomiting, pain in the labor and throat, and refusal to eat may occur. An important symptom is a skin rash or exanthema and a rash on the mucous membranes or enanthema. The rash is localized in the arms, legs, less often the buttocks and genitals, as well as on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue. Symptoms of enterovirus infection may be mild, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
The disease affects children under 10 years of age, with 95% of cases most often affecting children under 5 years of age. Adults are very rarely affected; the disease is most severe in pregnant women, the elderly and people with immunodeficiency. If the Coxsackie virus is detected in a pregnant woman, then first of all it will be dangerous for the baby, and not for the mother. In this case, the child will be born with symptoms of the virus.
The contagiousness of the disease is very high; several family members or even a class can become ill at once. Despite the fact that epidemics occur mainly in the summer and autumn, it is quite possible to get sick throughout the year.
Stages of the disease:
On days 1-2, the child may feel a sore throat, abdominal pain, possibly a decrease in appetite or a slight increase in temperature. One or more conditions may be present.
After 3-7 days or longer, these symptoms disappear and ulcers appear in the mouth, a rash on the arms and/or legs that begins to itch, and the lymph nodes in the neck become enlarged.
On days 7-10 , the disease usually goes away on its own.
Very rarely, a child may begin to peel off his fingernails and toenails, which goes away within 3-6 weeks after the illness. In this case, fingernails grow back within 3-6 months, and toenails within 9-12 months.
During illness, it is important to leave the child at home and not attend kindergarten, school or other public places.
Important! The blisters will remain contagious until they dry, which is a few days after they appear. Another month after the illness, the stool will be contagious.
You should consult a doctor immediately if:
- the rash blisters become painful or filled with pus, as there is a possibility of secondary infection;
- the rash on the child’s oral mucosa has become too painful that the child cannot open his mouth and refuses to eat and drink.
Call an ambulance immediately if:
- the child does not pee for more than 8 hours;
- the baby's fontanel becomes sharply sunken;
- the baby cries without tears;
- The child’s lips were cracked and dry.
These are all signs of dehydration!
You should also call an ambulance if:
- stiff neck is observed, that is, the baby cannot press his chin to his chest;
- Strong headache;
- backache;
- fever above 38 degrees.
Pathogenesis
For Coxsackievirus A and B, the entry gates are the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, upper respiratory tract and intestines. Enteroviruses freely overcome the “gastric barrier” and penetrate the cells of the small intestinal mucosa. Subsequently, the process of virus replication occurs in the cells of the intestinal epithelium, lymphoid tissue and mesenteric lymph nodes. The virus then enters the bloodstream and causes primary viremia. The Coxsackie virus exhibits the greatest tropism for cells of the central nervous system/muscle tissue, but a variety of organs are also involved in the pathological process.
Dissemination of the pathogen occurs in the heart, liver, lungs, kidneys, eye vessels, pancreas, where it multiplies and accumulates. Clinical symptoms, severity and outcome of the disease are determined by a number of factors - the biological properties of the virus serotypes, their tropism, the state of the humoral/cellular immunity of the human body. Swelling, inflammation and areas of necrosis develop in the affected organs.
The stages of pathogenesis are shown schematically in the figure:
Stages of pathogenesis of the Coxsackie virus
Persons who have recovered from the disease develop long-lasting (over several years) type-specific immunity.
Treatment and prevention
As a rule, the disease goes away on its own within 10 to 14 days after its onset. There is no cure for Coxsackie virus as such, so therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms.
It is quite possible to mistake the symptoms of hand-foot-mouth disease for a cold or even chickenpox. Therefore, treatment is often started if the child does not feel well.
Since the symptoms are usually mild, this infectious disease occurs without serious pathologies and consequences, and can end in recovery without treatment. But the earlier the disease is detected, the more the duration of the disease will be shortened, and in this case it is possible to prevent complications.
Symptomatic treatment of enterovirus infection includes drinking plenty of fluids, antipyretics if necessary, sprays for the throat and mouth, and if the rash is itchy, then the use of antihistamines is possible.
Prevention of the disease includes hand hygiene after going outside and visiting public places, ventilating the room in which the child is located during the day, buying only bottled filtered water for the child, washing fruits and vegetables before eating, and regularly washing children’s toys. Also, during periods of epidemic, you should not allow your child to visit public places.
So, Coxsackievirus or hand-foot-mouth syndrome is a highly contagious disease of the enterovirus family. Mostly children under 10 years of age are affected; in 95% of cases, these are children under 5 years of age. Important symptoms of the virus are a rash in the form of blisters on the arms, legs, mucous membranes of the mouth, and less commonly, the buttocks. The disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets, household contact and food. As a rule, it goes away on its own within 10-14 days. Treatment for the virus is aimed at relieving symptoms. If a baby has symptoms of the Coxsackie virus, then he should be isolated from other children, that is, not taken to school or kindergarten, and also call a pediatrician home. Be healthy!
What antiviral agents for Coxsackie virus are recommended for patients (at the INN level)
For any disease, comprehensive treatment under the supervision of a doctor is necessary. And enterovirus infection is no exception. As a rule, when characteristic signs of the disease are detected in a small patient, both antiviral antiviral and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Among antiviral drugs, drugs containing interferon are used. Such drugs include Viferon Suppositories.
Suppositories containing human interferon do not give the virus a head start of several days until the body itself begins to fight the infection, but begins to act immediately, thereby reducing the recovery time. For symptomatic treatment, the following is used:
- Antipyretic syrups or suppositories containing paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- To avoid dehydration and alleviate the symptoms of intoxication, you should drink plenty of water (boiled or bottled), water with lemon;
- For diarrhea, it is advisable to take absorbent agents, such as activated carbon;
- To relieve pain in the mouth, you can use gels used for teething in babies.
- To speed up healing and prevent infection of mouth ulcers, antibacterial sprays are used;
- Although the rash usually does not cause itching in children (unlike chickenpox), if it bothers the baby, antihistamines can be used.
List of sources
- Bondarenko, V. I. Enteroviruses in river water Text. / V. I. Bondarenko, V. I. Zadorozhnaya, K. V. Yashchenko // Hygienic aspects of biological pollution* of the environment: materials of the X All-Union Conference. -M., 1988. Part: 2. - P. 79.
- Kozhevnikova, N.V. Increasing role of enteroviruses in modern infectious pathology Text. / N.V. Kozhevnikova, T.N. Karavyanskaya, E.B. Golubeva // Far Eastern Journal of Infectious Pathology. 2007. -No. 10. - P. 52-53. — Bibliographer: p. 53.
- Kokoreva S.P. Modern complex therapy of viral neuroinfections in children / S.P. Kokoreva, N.P. Kuprina, O.A. Panina // Children's infections, 2007. – T. 6, No. 4. – P. 47-53.
- Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated July 27, 2011 N 106 SP 3.1.2950-11 “Prevention of enterovirus infection.”
- Sabitova A.M., Alexandrova T.A. Modern clinical and epidemiological features of enterovirus various clinical forms of infection // Collection of materials of the X Russian conference “Pediatrics and pediatric surgery in the Volga Federal District”, Kazan, November 26-28, 2013. - P. 60.
Diet
Diet for influenza, ARVI, colds
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 4-7 days
- Terms: 5-12 days
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
A balanced dairy-vegetable diet with plenty of fluids. When treating enteroviral exanthems , foods that irritate the oral mucosa (fried foods, spices, pickles, citrus fruits, hot foods/drinks) are excluded from the diet.