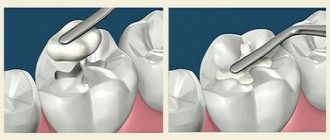
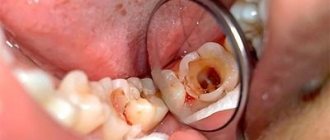
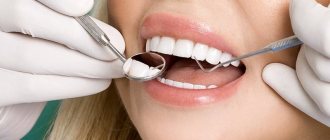
If caries appears on a tooth and it is not detected and treated in time, it can take on a more threatening form called pulpitis, which may be followed by periodontitis. Once the infection reaches the pulp, doctors can use a variety of treatment methods, both biological and surgical, and amputation or pulp extirpation is considered especially effective.
Dental pulp amputation is a gentle treatment method in which neurovascular tissue is partially removed. It is used primarily in the treatment of children's teeth. The maximum effect is achieved with slight damage to the dental tissue or in cases where the roots of the tooth are significantly curved. For adult patients, extirpation is mainly used, in which the dental cavities are completely cleansed.
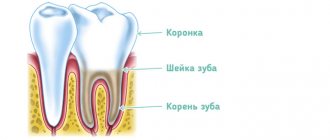
After the difference in the structure of the various sections of the pulp - root and coronal - was established, the very possibility of amputation arose. If the neurovascular bundle is damaged only in its coronal region, slightly or superficially, it can be removed. This procedure is of particular importance for children whose tooth roots continue to develop, and for their proper development it is necessary to preserve the possibility of their nutrition.
Pulp amputation can be performed by two methods - vital and non-vital. Let's take a closer look at both of these methods.
Vital method of pulp amputation
With this method of pulp removal, called pulpotomy, tissue damaged by caries is mechanically removed using local anesthesia. This technique is very popular. Using a bur, all damaged tissues are removed, after which the open cavity is treated with medications. The pulp is amputated before the root canals begin, in which it is kept alive. Its surface layers are fixed. The cavity is sealed with a temporary filling installed for six months. If after this time the patient does not complain of pain, percussion and palpation are painless, a permanent filling is placed in place of the temporary filling.
In children, the vital method of pulp amputation is most often used. This is due to the fact that permanent teeth, in the process of developing their roots, have winding canals in the form of ribbons, with many branches, and milk teeth need to preserve the ability of their root parts to resorption and at the same time the rudiments of future permanent teeth should not be affected.
Whether amputation can be performed using the vital method depends on how viable the part of the pulp located in the roots is, as well as on the presence of inflammation in the tissues surrounding the tooth. Deep amputation of the vital type differs from the ordinary one in that not only the coronal area of the pulp is removed, but also that located in the canals - at different levels of depth.
Acute pulpitis
The acute form of the disease causes severe paroxysmal pain, which becomes even more intense at night. Even without an external irritant, attacks of pain increase or decrease, but they usually occur when eating cold or hot food or drinks.
Due to the irradiation of the pain impulse along the nerves, sometimes the patient cannot say exactly which tooth hurts. If the pain becomes more and more intense, this may indicate the development of a purulent process. Its symptom is throbbing and almost constant pain, sometimes shooting and almost never subside.
A clear sign of pulpitis is a prolonged subsidence of pain after removal of the irritant. This takes about 15 minutes. This is its difference from caries, in which the pain disappears immediately if the irritant is removed.
Devital method of pulp amputation
Devital amputation involves preliminary killing of the pulp in its coronal part using special pastes. After which it acquires a fibrous structure that can be easily removed. In this case, the pulp located in the roots remains intact. After removal of the coronal part, the root pulp is mummified under the influence of drugs that impregnate it, dehydrates and becomes a sterile strand. There are a large number of antiseptic pastes based on various anti-inflammatory active substances that have certain advantages and disadvantages.
The devital pulp amputation technique is used for various types of pulpitis - acute and chronic. Or if the patient is afraid of syringes and injections or other phobias associated with dental treatment.
According to a number of experts, the technique of devital amputation for pulp in permanent teeth has low effectiveness, since in some cases it leads to inflammation of periodontal tissue. Such treatment is advisable only during the growth of tooth roots, and if they are already fully formed, their canals are cleaned by pulp extirpation.
Treatment of tooth pulpitis: prices, stages and treatment methods
If your tooth reacts to changes in temperature, hurts at night, or “pulsates,” see a dentist. There may be inflammation of the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth. Remember that early on the nerve can be treated.
The inflammatory process in the neurovascular plexus of the tooth, which is called pulpitis, can occur for many reasons. Most often it is provoked by advanced caries, injuries, as well as inconspicuous areas of carious lesions remaining after filling. The pathological process, occurring in acute or chronic form, can be quite dangerous, as it causes various complications. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a dentist.
When pulp removal is inevitable
The list of indications that determine the need for pulp removal includes the following clinical situations:
- Development of acute inflammatory processes affecting the pulp chamber;
- Acute form of pulpitis that occurs against the background of infection of the cavity;
- The need to open the chamber due to mechanical damage;
- Failure to comply with the dental intervention protocol, causing complications;
- Preparation for prosthetics, which requires eliminating the risk of infection of supporting units.
The decision on devitalization is made based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Prevention of pulpitis in children
Treatment of pulpitis in permanent teeth in children, as well as their “predecessors” - baby teeth - is a rather complex procedure that may require several visits to the doctor. Preventing a disease is easier than treating it - all you need to do is pay attention to hygiene procedures and teach your child how to brush their teeth correctly from a very early age.
It is also important to monitor the child’s diet - strengthen the enamel with solid foods (carrots, apples, etc.), provide a balanced diet to saturate bone tissue with minerals. It is better to limit sweets and give only water at night. Prevention of caries is the basis for preventing its complications, including pulpitis.
How to prepare a child for treatment?
Treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth in children is a rather complex task, so it’s great if the child is already familiar with the dentist’s chair. The first visit should be preventative - to familiarize yourself with the office environment, the doctor, and the instruments.
Also, the task of parents is to psychologically prepare the child. Required:
- talk to your child about doctors in a positive way - tell them that the dentist treats teeth and makes sure they don’t hurt;
- play dentist with toys and other family members;
- avoid mentioning pain or unclear, scary terms;
- do not deceive the child - explain that dental treatment may not be very pleasant, but it will not last long and the tooth will no longer hurt;
- remain calm, act gently but confidently if the child resists treatment;
- choose a suitable time for visiting - it is better in the morning, when the baby is alert and active;
- take a toy with you to calm the child;
- give the doctor the opportunity to establish contact with the small patient - do not rush him;
- Do not scare the child under any circumstances, do not threaten, do not blackmail.
If the situation cannot be controlled completely, you will have to reschedule the appointment for another day. However, the disease should not be ignored - treatment of pulpitis of baby teeth in children must be carried out one way or another. In special cases, treatment under general anesthesia may be considered, but this should be discussed with your doctor.
How is the operation performed?
Most often, dentists perform vital pulp extirpation. It includes the following steps:
- professional cleaning of the affected tooth,
- pain relief using local anesthetics,
- isolation of the working area from salivary secretions,
- incision in the arch of the dental cavity,
- removal of the neurovascular bundle,
- restoration of the correct shape of the root canal,
- antiseptic treatment of the tooth cavity,
- installation and grinding of the filling.
Possible consequences
If pulpitis is advanced and nerve removal is already required, then after 3-4 months the pathological process will make itself felt by darkening of the teeth. In addition, they will become brittle and dull. If the enamel has acquired a bluish tint, the dentist may have made a mistake when filling. This happens if there were traces of blood in the canal at that moment.
It is worth remembering that it is impossible in principle to cure pulpitis using traditional methods. Moreover, there is no single medicine that a doctor can prescribe to a patient for this diagnosis. Each case is individual, so treatment methods are selected taking into account the characteristics of the clinical picture: the degree of tooth damage, the presence of caries, purulent contents, diseases of the oral cavity, etc. Therefore, if signs of this disease occur, be sure to consult a doctor.
Techniques used
In modern dentistry, two methods are used to eliminate the affected pulp.
Vital method
The procedure is carried out in one session, during which devitilizing drugs are used that can have a negative effect on the condition of the periodontium. The operation algorithm includes the following manipulations:
- Diagnosis of pathology and development of a treatment plan;
- Cleaning the mouth and affected area;
- Injection of an anesthetic that does not cause an allergic reaction in the patient;
- Installation of a rubber dam to drain secreted saliva;
- Excision of the dental arch and pulp extirpation;
- Correction of the position of the root canal followed by disinfection;
- Formation and fixation of a permanent filling.
To remove decayed tissue within the framework of this technique, evacuation can also be used to avoid the entry of destroyed fragments into the canal cavity.
Devital method
The method involves complete amputation of previously killed connective tissue filling the cavity. At the preliminary stage, the affected area is treated with a paste containing arsenic or a paraformaldehyde composition. In particularly difficult cases, characterized by obstruction of the canals, the technique of electrochemical necrosis is used, which makes it possible to kill tissue in hard-to-reach areas.
The operation will require two visits to the dental clinic. During the first session, the following manipulations are carried out:
- Diagnostics, cleaning and disinfection of the work area;
- Opening the crown cavity and applying a tissue killing composition;
- Installation of a temporary filling tab.
The second visit is scheduled depending on what material was used to process the pulp. If the fabric was treated with a paste with arsenic, two days is enough, if with paraformaldehyde, a week is enough. During the repeat session, the doctor:
- Removes the temporary filling tab;
- Provides access to the dental canal;
- Removes affected tissue and cleans the canal;
- Installs a permanent filling.
The devital method belongs to the category of cardinal methods, and is recommended only in cases where vital extirpation is impossible.
An important factor in avoiding complications is strict adherence to medical recommendations - both in preparation for the procedure and after the operation.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment involves removing the pulp in several stages. Depulpation is performed in the root and coronal zones in advanced cases. Sometimes it is impossible to cure a tooth without this procedure.
If the tooth is single-rooted, then it will have to be removed in two or even three visits to the dentist. And if this is a multi-channel case, then even more activities are needed. Therefore, the number of visits to the doctor is determined by the complexity of the lesion and the dynamics of treatment.
If a canal has been filled, the filling cannot be placed in one visit, since the material inside the canals must first harden.
Second visit:
- The doctor removes the temporary filling.
- The canal is washed with antiseptics and then dried.
- The canal is sealed. To do this, the dentist uses a gutta-percha point and paste. The pin is used to compact the filling compound.
- Finally, you need to take an x-ray to make sure that all actions were performed correctly and that the filling is tight to the top of the canal.
- A temporary filling is placed again. After this, painful sensations may persist for some time. To eliminate them, it is allowed to take ibuprofen, ketanov, nimesil and other drugs that the dentist should recommend.
Indications and contraindications
Pulp removal is recommended if the following factors preclude the possibility of tissue preservation:
- Developed pulpitis, which causes irreversible changes in the structure of the organ;
- Mechanical damage to the crown, including fractures;
- Periodontal diseases that cannot be treated with conservative methods.
In addition, surgical intervention is also performed in cases where the connective tissue is not susceptible to pathology, but prosthetics are planned.
The list of restrictions that exclude the possibility of carrying out the procedure temporarily or completely includes:
- Obstruction of root canals;
- Pathological deviations in root formation;
- Late stage somatic diseases;
- Presence of HIV or other severe diseases of the immune system;
- Intolerance to anesthetics used in surgery.
The decision to perform extirpation is made based on the results obtained during a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Chronic pulpitis
In the chronic course of pulpitis, there are no obvious symptoms. Sometimes a slight aching pain may occur, especially after cold or hot drinks or meals. Exacerbations, which are similar in their symptoms to acute pulpitis, are also possible.
When pus accumulates, flux appears. If a person is not provided with proper medical care, this can lead to phlegmon and related complications:
- damage to the jaw bones and facial nerve;
- abscess;
- apical periodontitis;
- sepsis;
- chronic hyperplastic pulpitis (occurs in childhood and adolescence).