21.11.2019
Foreign clinics have never performed such a procedure as an injection to treat gums, because it causes enormous harm to both teeth and gums. Research has shown that antibiotic injections cause it to accumulate in the gum tissue and bone around the teeth. This leads to the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms and, as a result, to gum inflammation. Further, this is fraught with tooth mobility. In some Russian dental clinics, usually private, such injections are still practiced.
However, most clinics use antibiotic tablets and capsules to treat gum disease. The only injections that are given to strengthen gums are vitamin injections. The most commonly used are vitamin C and aloe. They are strong antioxidants. Thanks to this, a large number of microbes die. Injections are given with regular insulin syringes. You can also use folk remedies to strengthen your gums. This is a painless, cheap and effective method.
Folk remedies for strengthening gums
One of the most common folk ways to strengthen gums is the use of decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants. Commonly used are chamomile, sage, calendula, St. John's wort, yarrow, juniper, lingonberry and tricolor violet leaves. Decoctions of oak bark and linden blossom are very helpful in treating and strengthening gums.
Massage is also quite effective for strengthening gums. It can be done simply with your fingers. This will improve blood circulation and strengthen your gums.
To remove plaque from teeth at home, you can add sea or table salt to your toothpaste. You can also use a special toothpaste for bleeding gums. This paste contains not only a large number of medicinal herbs, but also fluoride, which helps prevent inflammation, strengthen tooth enamel and protect teeth from caries.
In addition, special gels and ointments are used in the treatment of gums. They heal foci of inflammation, forming an indelible protective film.
To keep your teeth and gums healthy, you need to consume various vitamins. If the body does not have enough vitamin A, it can lead to loose teeth. For the proper exchange of calcium and phosphorus, vitamin D is necessary. It helps the absorption and proper assimilation of these elements. Thanks to vitamin C, calcium is absorbed in the bone cells of the teeth. Vitamin B6 is prescribed in the form of medications or intramuscular injections for periodontal diseases.
A lack of calcium in the body can lead to various diseases of the teeth and gums. Therefore, it is better to take it in the form of dietary supplements.
Causes of gum disease
The main cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene. The processes of periodontal destruction begin at the moment of formation of a dental film of bacteria and the accumulation of soft dental deposits. If you do not remove all the bacteria in your mouth by brushing your teeth at this point, tartar will form.
In turn, the formation of stone on the teeth will lead to the formation of a periodontal pocket. In the absence of treatment, bone loss and destruction of the musculoskeletal system of the tooth occurs. This leads to exposure of tooth roots, loosening and loss of teeth.
Treatment of periodontal disease with injections: what kind of injections are used?
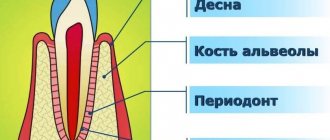
Periodontal disease is a disease of the oral cavity that is caused by exposure to pathogenic microorganisms. The affected area is the periodontium - the tissue surrounding the tooth. During the course of the disease, the gums and alveolar part of the jaw atrophy.
The initial signs of the disease are inflammation and bleeding of tissues. And this is already enough to contact a specialist, because periodontal disease is very dangerous and threatens a person with further health complications.
Injections into the gums are an important method of treating periodontal disease.
Consequences of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can lead to the following consequences:
- intoxication of the body with purulent secretions;
- periodontitis;
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bones;
- retrograde pulpitis;
- ulcerative gingivitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- increasing the load on healthy teeth;
- impossibility of prosthetics;
- the occurrence of stomach problems due to insufficient chewing of food and the presence of bacteria in the oral cavity.
The process of treating the disease is quite long and not very pleasant.
Correct comprehensive treatment, which is prescribed by a specialist depending on the extent of the inflammation, will help speed it up. The most effective method is to inject injections into the inflamed areas of the gums. This method is quite simple and relatively painless.
It is worth remembering that regular and high-quality oral hygiene can almost always prevent the occurrence of periodontal disease. You should not neglect it during the treatment process, it will significantly speed up your recovery time.
Features of injection treatment
Effective fight against the disease can only occur in a comprehensive manner, therefore the following types of drugs are prescribed:
- vitamins for teeth and gums containing zinc, iron and copper;
- immunomodulators;
- drugs that saturate the gums with oxygen - Lidaza;
- glucose;
- weak solution of hydrogen peroxide.
For the treatment of the oral cavity, the following injections are distinguished:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antitoxic serums;
- biogenic stimulants;
- sclerosing therapy;
- Ribonuclease and Methyluracil.
Antibacterial drugs
The basic basis of periodontal disease treatment involves the administration of antibiotics. They are more effective in injections. The most commonly used drugs are Metronidazole and Doxycycline. When combined with Chlorhexidine, treatment becomes more effective. The course of such treatment takes place in just 5–7 days.
After the injection, inflammation goes away, pain decreases, and bleeding disappears. However, the use of antibiotics leads to severe tooth mobility due to the release of large amounts of toxins, leading to tissue death.
Antibiotics are used for moderate and severe disease processes. Use in milder forms can lead to complications: severe pain and increased sensitivity to the active substance of the drug.
Antitoxic serums
Such drugs lead to the complete destruction of pathogens in the oral cavity. The serum contains specific antibodies that eliminate exotoxins. Injections with this medicine increase immunity and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Treatment takes a record amount of time.
The dosage is selected individually, depending on age and weight. It is worth considering that these drugs can cause allergies and adverse reactions in the form of:
- anaphylactic shock;
- arthralgia;
- lymphadenitis;
- temperature rise.
Biogenic stimulants
In combination with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, stimulating drugs - aloe extract and FIBS - are necessarily prescribed. These medications regulate the metabolic process.
Aloe extract for periodontal disease
- Aloe extract is prescribed for severe inflammation. Use it for a month and a half, every other day.
- Injections of Filatov's biogenic stimulator are made into the upper and lower jaws, up to 30 injections are provided. The drug is contraindicated for high blood pressure and intestinal disorders.
- The drugs are prescribed in combination with agents of nonspecific action - Metacin, Pentoxyl, Biosed. Thanks to this, the treatment period is significantly reduced.
Sclerosing therapy
During this therapy, injections are given with chromium alum and quinine urethane preparations, which relieve looseness and swelling of the gums. A full course of treatment strengthens the mucosa and promotes the formation of new tissue. This therapy is contraindicated in people with gingivitis.
A deeper therapy process involves giving injections into the gum papillae, using a 40% glucose solution. The amount of solution is adjusted depending on the degree of swelling. The course of treatment consists of eight injections with an interval of two to three days between them.
Ribonuclease and Methyluracil for periodontal disease
Such drugs are prescribed additionally for a more effective treatment process. Ribonuclease is an enzymatic substance that promotes tissue repair and blood vessel growth. And Methyluracil is a drug that has an anabolic effect - stimulating the process of growth and restoration of tissue cells.
Antibiotics
Since the treatment is based on an antimicrobial method, taking antibiotics is inevitable for this disease. For periodontal disease, broad-spectrum antibiotics are usually prescribed, as they can destroy the maximum number of pathogenic bacteria.
Before starting treatment with tablets, it is necessary to do a special bacterial test to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to the prescribed antibiotic. If the patient does not tolerate antibiotics well, the doctor needs to find an alternative method of treatment. That is why it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and prescribe medications on your own.
Modern antibiotics come in various forms. It can be:
- tablets for oral administration;
- capsules for systemic treatment;
- gels for local use;
- special antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth.
Antibiotics may also be present in medicated toothpastes intended for the treatment of periodontal disease.
Despite such a variety of dosage forms, antibiotics are most effective in the form of tablets and capsules for internal use. In this case, they influence the entire body, allowing you to achieve maximum effect.
Most often, when treating periodontal disease, dentists prescribe the drugs metronidazole and doxycycline . They act specifically on those microorganisms that cause the disease. In combination with chlorhexidine, these drugs can almost completely get rid of the symptoms of periodontal disease.
Lincomycin
In recent years, treatment of periodontal disease with lincomycin has become increasingly common. This is a new generation antimicrobial drug with a broad spectrum of action. Lincomycin has a bactericidal effect.
Lincomycin is also prescribed in the presence of infectious diseases of the joints, bones (arthritis, osteomyelitis), respiratory tract (pharyngitis, tracheitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis), soft tissues and skin (furunculosis, abscess, erysipelas, mastitis). The therapeutic dose is set by the doctor, depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease in each specific case.
Usually this drug is taken for up to two weeks, but in exceptional cases the duration of use can be extended. Under no circumstances should you self-prescribe lincomycin! At a minimum, you can “earn” dysbacteriosis, and at a maximum – serious damage to the kidneys and liver. Therefore, treatment with lincomycin should be carried out only as directed by a dentist, who will select an effective and at the same time safe dose of the drug.
Trichopolum
The modern antimicrobial drug trichopolum is often used for periodontal disease. Trichopolum is also a broad-spectrum antibiotic, so it is used not only in dentistry. In particular, Trichopolum is prescribed for amoebiasis, trichomoniasis, giardiasis, vaginitis, urethritis, infectious diseases of bones, joints, central nervous system, bacterial pneumonia and other diseases.
Since Trichopolum has a wide spectrum of action, it effectively fights all known bacteria that are involved in the occurrence of the disease. Therefore, you should not be alarmed if the doctor prescribes you this particular antibiotic - it is used not only in general therapy, but also in the treatment of dental diseases, which include periodontal disease.
Possible complications from injections
The treatment process is not always easy and quick, and there is a risk of complications. If problems arise after the procedure, you must apply Solcoseryl ointment and consult a doctor.
If pathogenic microorganisms enter the injection wound, a small lump or lump may occur. It is also possible that the patient’s temperature may increase.
The injection may cause your cheek to swell when the facial nerve is hit. This will cause pain and stiffness in the facial muscles.
Plasmolifting in the treatment of periodontal disease
In dentistry, this disease is also treated with blood plasma injections. This method is quite young, but is already gaining popularity. It is distinguished by its safety and hypoallergenicity.
The essence of this method is that the required amount of blood is taken from a person and the plasma is separated from other components using a centrifuge. It is this plasma that is injected in the form of injections into the affected areas of tissue.
This treatment method has a number of positive properties:
- faster wound healing;
- elimination of bleeding;
- elimination of unpleasant odor;
- pain relief.
Plasmolifting is strictly contraindicated for HIV infections, Hepatitis and infectious diseases.
Despite the possible risks, the process of treating periodontal disease with injections is quite effective. In addition to getting rid of the disease, injections also get rid of the causes. They normalize the metabolic process, strengthen gums, restore microflora and increase immunity.
The course of treatment in this way is much shorter than taking conventional tablets and ointments. The thing is that the medicine gets to the site of inflammation faster in a higher concentration.
Worth remembering! Correct and effective treatment is prescribed only by the attending physician. You should not self-medicate, as this can only aggravate the whole process.
What is premedication and when is it needed?
Premedication is taking special sedatives in advance of visiting the dentist. It is also effective in children, so we draw the attention of parents to this method of relieving attacks of fear.
Pain has 4 factors:
- sensory sensitivity is the physical cause of pain,
- psycho-emotional mood of the patient,
- autonomic component, caused by overload of the autonomic nervous system,
- motor component.
That is, the more the child is afraid, rushes about and is in a state of stress (mobilization of the autonomic nervous system), the more painful it is for him. If you see that persuasion, stories and other tricks do not work on the child, then it is better to use medication than to cause irreparable harm to the child’s psyche.
It is best to discuss which sedatives are appropriate in this situation with your pediatrician. For safe home remedies, you should try a decoction of valerian or motherwort roots. You need to drink it 1-3 days before going to the dentist in accordance with the doctor’s instructions, according to the child’s age.
Injections for periodontal disease - injection treatment
The progression of the disease can be stopped and unpleasant symptoms can be eliminated with the help of injections of medicinal and restorative drugs. Agents that enhance cellular metabolism stimulate the formation of new tissue and strengthen the mucous membrane, eliminate the cause of the disease and strengthen local immunity.
At the same time, you need to understand that a severe form of the disease cannot be treated with injections, because No drugs can restore damaged tooth bone tissue and gums. In these cases, doctors suggest performing bone augmentation or flap surgery.
What is the difference between pediatric anesthesia and adult anesthesia?
Features of pediatric anesthesia are determined by the characteristics of the child’s body.
For example, a child’s body needs 2 times more oxygen than an adult. Also, the children's body is characterized by a rapid change in physiological states and an increased ability to adapt. At the same time, children are more sensitive to changes in ambient temperature, have increased emotionality, and find it difficult to remain in one position for a long time. There is a high probability of allergic reactions in children, and the smaller the child, the more caution you need to choose the drug.
Therefore, when performing pediatric anesthesia, the following rules must be observed:
Accurately select the anesthetic drug and its dose. There is some difficulty in treating pain in children under 4 years of age, because... Most local anesthetics are used from the age of 4. For a child prone to allergies, it is better to conduct special allergy tests to know exactly which drug is safe for him.
The anesthetic should be administered to the child as gently as possible. Children are often afraid of tools, and even more so of syringes. Before the injection, the needle insertion site should be treated with a tasty anesthetic gel, which “freezes” the gum. Today, a large selection of such drugs is available.
Due to increased sensitivity to ambient temperature, a child may feel cold during treatment in a cool room, or vice versa - hot if the room is poorly ventilated and too small. This factor must be taken into account.
Do not neglect the method of premedication before visiting the dentist. Taking a sedative will help your child relax and be less afraid.
A very important component is the doctor’s personality. A good pediatric dentist finds an approach to parents and children and turns fear into interest. Advice to parents: help him with this to the best of your ability.
Contraindications to injections for periodontal disease
For effective treatment, the doctor prescribes a set of drugs, each of which has contraindications for use. Therefore, it is important to undergo examination and identify possible diseases before starting therapy. For example, in case of autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, glomerulonephritis, multiple sclerosis), immunomodulators are strictly prohibited. Cardiac decompensation and pulmonary failure are contraindications to the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment is not started in the presence of foci of inflammation in the body or in the acute stage of any disease. During pregnancy and lactation, injections are prescribed with caution; if possible, opt for non-drug treatment (massage, rinsing).
Precautions after anesthesia
In order for the rehabilitation period to proceed safely, some points should be taken into account:
- Eliminate hot, spicy, salty foods from your diet.
- Do not take solid food for the first 3 days.
- Maintain oral hygiene (temporarily eliminate the toothbrush and replace with mouthwash).
- Give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Keep records of changes in the general condition of the body (body temperature, general well-being).
- Avoid emotional disturbance.
Taking all these points into account, the patient significantly reduces the risk of complications during the rehabilitation period. The pain that arose after the treatment should not worry the patient on the first day. If your gums hurt for a long period after an anesthesia injection, this is a reason to seek medical help from a dentist again.
Category Miscellaneous Published by kosmetik-dent
How are injections performed?
Injections into the gums do not cause much discomfort and most often do not cause severe pain. They are performed with special syringes with a very thin and short needle. If you need to undergo a course of injections (and for periodontal disease, up to 20 injections are sometimes prescribed daily), first the gums are anesthetized with an anesthetic: ultracaine, ubistizin, scandonest or another.
The drug is administered using a special carpule syringe. If the patient complains of increased sensitivity of the gums, the injection site can be pre-numbed with special anesthetics in the form of a gel, ointment or spray.
What types of anesthesia are used in pediatric dentistry?
Application anesthesia in the form of a gel with an anesthetic.
This is the least scary method of pain relief for a child, but also the weakest. It is enough to perform professional hygiene, remove a loose tooth or “freeze” the injection site. But its use should not be underestimated.
Classic injection local anesthesia.
It is mainly used from about 4 years of age, but has few contraindications. The main thing is to find out whether the child is allergic to the proposed drug. The dentist chooses the type of anesthetic substance based on the child’s age, his condition, and even his mood. Articaine preparations are widely used for dental pain relief in children - its effect is 5 times stronger than the familiar novocaine, it is non-toxic and does not provoke allergic reactions.
General anesthesia is treatment under anesthesia.
You can often find parents wanting to treat their child’s teeth under anesthesia. It’s easier for the parents and the doctor, but for the child?
Two strict rules for the use of anesthesia during dental treatment in children:
- Anesthesia is NOT USED without very good reasons.
- Treatment under anesthesia is possible ONLY in rooms specially equipped for this, where there is a full set of equipment for resuscitation, and there is an anesthesiologist and resuscitator on staff. Or such equipment can be deployed by a visiting anesthesia team.
Indications for dental treatment in a child under anesthesia:
- Age up to 4 years.
- Developmental features: autism, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy or epilepsy.
- Large volume of dental intervention.
- Allergy to local anesthetics.
A strong, insurmountable fear of treatment, if other methods have been tried and did not work.
Sedation
Sedation is not anesthesia in the classical sense. This is a relatively new method in which the small patient breathes a mixture of nitrous oxide, a “laughing” gas, and oxygen. This method has a good relaxing effect; the child calms down, plunging into a shallow sleep, but can answer questions and remains conscious. Sedation goes well with local injection anesthesia.
What medications are prescribed for periodontal disease?
The goal of therapy is to strengthen the gums and stimulate metabolic processes. This problem needs to be solved comprehensively, so the dentist prescribes treatment with several drugs simultaneously.
Immunomodulators
Stimulation of the immune system allows you to accelerate tissue regeneration, resist the development of the inflammatory process and increase the overall resistance of the body. Since periodontal disease is often associated with disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, the administration of immunomodulators allows for a faster complete recovery. The choice of drug is always made by the doctor after studying the medical history. Immunomodulators such as:
- Timalin. It is a complex of polypeptides. Stimulates the body's immunological reactivity, helps increase cellular immunity, regulates the number of lymphocytes, and enhances the activity of phagocytes.
- Thymogen. A synthetic dipeptide that activates intercellular metabolism, stimulates the activity of bone marrow cells, and has an antioxidant effect.
- Galavit or sodium salt of luminol. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, restores the body's protective functions, increasing its nonspecific resistance to infectious diseases.
- Pyrogenal. Lipopolysaccharide, which activates the body's defenses and stimulates recovery processes. Suppresses the development of scar tissue.
Contraindications to the use of drugs that activate the immune response are the presence of liver and kidney diseases, disorders of the thyroid gland, and any autoimmune diseases.
Vitamin complexes
Vitamins play an important role in the treatment of periodontal disease. One of the reasons for the development of this disease is considered to be metabolic disorders, since the lack of vitamins affects the protective functions of the body and promotes tissue atrophy. In case of periodontal disease, it is advisable to prescribe vitamins in injections, this way the required concentration of substances in the gum tissues is quickly achieved. The following vitamins and complex preparations are indicated:
- Aevit. Contains fat-soluble vitamins A and E. Retinol (vitamin A) is necessary for reproductive function, promotes tissue regeneration, and stimulates metabolism. Tocopherol (vitamin E) ensures the normal functioning of muscle and nerve fibers and acts as an antioxidant.
- B vitamins (B6, B12, B1). They improve cellular metabolism, participate in the processes of carbohydrate metabolism and hemoglobin synthesis. Promotes rapid healing of wounds and the formation of new tissue.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Increases the number of lymphocytes, enhances their activity. It has an immunostimulating effect, therefore it is often prescribed to elderly people and patients after surgical operations. Prevents the development of infectious lesions.
Vitamins are prescribed with caution to patients with severe atherosclerosis and a history of myocardial infarction. In the absence of contraindications, the administration of vitamin preparations can quickly achieve visible improvement in periodontal disease.
Biostimulants
Biogenic stimulants are preparations of plant or animal origin that enhance metabolic and regeneration processes in the body. In case of periodontal disease, the choice is most often made in favor of liquid aloe extract. It has a local anti-inflammatory effect, stimulates healing, accelerates tissue regeneration and strengthening. In addition to this drug, doctors prescribe:
Contraindications to the prescription of biostimulants are allergic reactions to the components and individual hypersensitivity to the drug. Prescribe with caution for cardiovascular diseases and hypertension.
Sclerosing therapy
To reduce swelling and sagging gum tissue, injections of 40% glucose solution or 5% hydrogen peroxide are prescribed. These substances cause tissue compaction and swelling reduction. In the absence of individual contraindications, the drug of choice is glucose. Such injections are painless and well tolerated by patients. Contraindications: desquamative (geographic) gingivitis.
Reference. Before sclerosing therapy, dental plaque must be removed and the oral cavity must be sanitized.
Antibacterial therapy
Despite the fact that periodontal disease itself does not cause inflammation, periodontitis often develops simultaneously with it. In order for the treatment of the underlying disease to show good results, it is necessary to eliminate acute inflammation. Antibiotics may be prescribed for this. The choice of drug and the duration of the course depend on the stage of the disease and medical history.
In recent years, dentists have noted a decrease in the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics. This is due to the formation of resistant strains of microbes. Therefore, when choosing a drug, you should pay attention to new agents to which the pathogenic flora has not yet lost sensitivity. It is advisable to use:
Antibiotics can be used not only in the form of injections, but also in the form of a solution for applications, gels, rinsing solutions, and tablets.
What causes gum pain?
Diseases are classified according to several criteria:
- According to the size of the focus of the disease (local process or large-scale).
- Based on the type of disease, the most convenient classification is:
- Gingivitis;
- Periodontitis;
- Periodontal disease;
- A separate point should be made about microtrauma of the gums and the consequences of other oral diseases (stomatitis, cyst, periodontitis).
Let us consider the etiology and clinical manifestations of each of these pathological conditions.
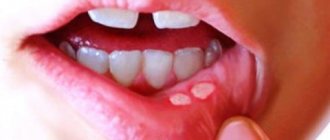
Gingivitis
This is a disease of the gum margin and interdental papillae. The reason for this is food debris that is not removed from the source of inflammation, rots and provokes the abundant proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms. Typical for adults and children.
The enamel near the gums begins to darken and is covered first with a soft coating, then with hard stone.
The more plaque, the higher the likelihood that the gums will begin to bleed.
With a long process, the gums grow and turn red.
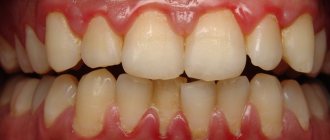
In the photo above: healthy gums, below: the initial stage of gingivitis - tartar
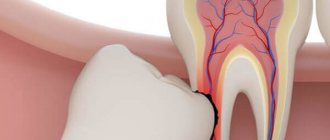
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis causes inflammation to spread to nearby tissues. Periodontal and bone tissue suffer.
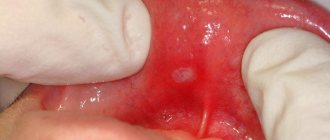
Over time, the tissue between the tooth and gum is destroyed, leaving the tooth exposed. This is how periodontal pockets form. Pus accumulates in them.
Symptoms: discharge of pus from the pockets, crimson-red mucous membrane, bad breath.
Gingivitis and periodontitis are 2 stages of the same process, starting with plaque and ending with tooth loss. These diseases are not age related.
Before visiting a doctor, we recommend rinsing your mouth with decoctions of chamomile and calendula.
Periodontal disease
Attention! In this variant of gum disease, pockets do not form! And gum inflammation does not occur here.
The nature of the disease is dystrophic in nature.
This condition is associated with age and is caused by hardening of the blood vessels that supply the gums. Every year the disease occurs earlier and earlier: today people over 35 years of age suffer from periodontal disease. The process is treatable only in the early stages. At a later stage, it remains possible to control the rate of degeneration. Periodontal disease is associated with systemic diseases of the body (disruption of the endocrine system, atherosclerosis). Its treatment is aimed at ridding a person of systemic diseases and maintaining or restoring blood supply to the gums. For this purpose, nutritional pastes and microbial additives are used. It is necessary to care for the oral mucosa and enamel to avoid inflammatory complications.
Stages of development of periodontal disease:
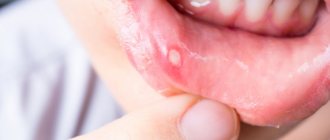
Stomatitis
This is an inflammation of the oral cavity, localized on the surface of the gums, cheeks, and tongue. Unlike stomatitis and injuries, the rest of the listed diseases are characteristic exclusively of the gums.
There are several types of stomatitis. One of them is typical for older people - this is denture stomatitis. The rest can affect children and adults.
Home treatment for stomatitis is replacement of dentures, antihistamines and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions. For the viral variant, ointments containing acyclovir salts are used.
Features of stomatitis are transparent blisters, in place of which pink sores remain.
Microtraumas and gum cysts
Frequent causes of injury are foreign bodies and wisdom teeth.
The risk group is children who transport into their mouths everything that can fit there.
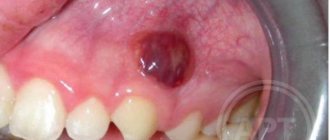
At the site of microtrauma, a purulent sac may form - a gum cyst.
Wisdom teeth are of particular interest. Their growth is accompanied by high fever and throbbing pain.
You can try rinsing your mouth with antiseptic solutions (chamomile, calendula, chlorophyllite). If you have a cyst, be sure to see your dentist.
Possible complications in the treatment of periodontal disease
Injections into periodontal tissues can lead to unwanted complications. When giving an injection with a non-sterile instrument, an abscess may form. In this case, the resulting inflammation is opened and sanitized. Rinse with disinfectant solutions is prescribed.
If the needle touches the facial or trigeminal nerve, neuralgia may develop, a disease manifested by sharp pain in the areas of innervation of the corresponding nerves. In severe cases, novocaine injections may be prescribed to relieve pain.
Sometimes injury to soft tissues with a needle causes pain that does not go away for a long time. In this case, dentists recommend applying Solcoseryl gel to the gums.