Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antimycotic or antifungal agent. The antimycotic properties of clotrimazole were discovered in the late 1960s. The drug belongs to the category of imidazole azole antifungals. It is available in a variety of dosage forms, including creams, ointments, tablets, and slow-dissolving capsules.
Clotrimazole may be used to treat anemia
In addition to its antifungal activity, clotrimazole has become a drug of interest for the treatment of a number of other diseases, such as sickle cell disease, malaria and some types of cancer. This drug's minimal side effects and uncomplicated metabolic profile have led to its widespread use for the treatment of fungal outbreaks, such as vaginal infections caused by yeast spores (candida vulvitis or thrush), as well as athlete's foot.
The main risk factors for the development of candidiasis include:
- improper oral hygiene;
- wearing orthopedic structures or removable dentures;
- long-term inhalation therapy;
- decreased salivation due to certain pathologies;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- taking antibiotics;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- decreased immunity, including due to chronic diseases;
- endocrine pathologies, including obesity, diabetes;
- smoking;
- carrying out chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Oral candidiasis occurs much more often in children than in adults. Newborns can become infected even in utero if the mother has thrush - infection occurs during natural childbirth. After birth, the infection can be transmitted to the child through the skin of the mother's nipples and hands, and from her oral mucosa. The source of infection is unsterile pacifiers and oilcloths, and medical personnel who do not follow the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during invasive procedures. In an older child, oral candidiasis is often caused by a weakened immune system or improper dental care.
Indications and contraindications for use
The list of pathologies for which the ointment is recommended is presented:
- genital candidiasis complicated by trichomoniasis;
- dermatomycosis;
- dermatophytosis;
- mycoses complicated by infection of pyogenic cocci.
- thrush;
- some types of lichen;
- paronychia;
- superficial candidiasis;
- stomatitis;
- erythrasma.
The drug is contraindicated:
- in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- for abrasions, wounds, skin erosions;
- intolerance to component components.
Use in the second and third semesters of pregnancy requires the permission of a doctor; during lactation, it is prohibited to apply the ointment to the breast. The medicine is prescribed to newborns with restrictions:
- A small area of skin is subjected to the procedure;
- Large lesions are treated in parts.
The medication in the form of powder is prescribed to infants with an infected type of diaper rash. Treatment of fungal infections is important for pathologies that cause drying of the dermis.
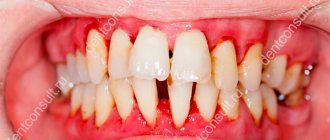
Oral candidiasis is divided into 3 types:
- Pseudomembranous. This is a classic thrush in the form of a superficial white film or white spots. Accompanied by a feeling of slight discomfort. In mild forms of the disease there may be only a few such plaques, and they can be easily removed. In severe cases, many large spots appear, they merge and gradually affect the entire mucous membrane, and can penetrate lower, affecting first the throat, and then the esophagus, up to the gastrointestinal tract. The spots may thicken, making them difficult to remove. Most often, ordinary acute candidiasis occurs in adults who have taken antibiotics, immunosuppressants or corticosteroids, as well as in infants.
- Atrophic. It can be acute or chronic. In the first case, there may be no plaque, but the mucous membrane becomes inflamed - it becomes bright red, the patient complains of a strong burning sensation in the mouth, increased dryness, and sometimes an unpleasant taste with a hint of bitterness or metal. Most often, acute candidiasis is a consequence of drug therapy. The chronic form usually occurs due to wearing orthodontic structures or dentures. The symptoms of the disease are more subtle.
- Hyperplastic. Candidiasis in the mouth affects the lips, corners of the mouth, cheeks, soft palate, and back of the tongue. White spots are usually large, merge with each other, and may acquire a yellow tint. Gradually they become rough and cannot be scraped off. The disease is chronic and is diagnosed only in adults.
pharmachologic effect
Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that inhibits the growth of pathogenic yeasts by altering the permeability of cell membranes. The action of clotrimazole is fungistatic at concentrations of the drug up to 20 μg/ml and can be fungicidal in vitro against Candida albicans and other species of the genus Candida at higher concentrations. Unfortunately, resistance to clotrimazole, which was rare in the past, is now common among various patient groups.
The drug Clotrimazole fights fungus well
Clotrimazole is generally considered a fungistatic rather than a fungicidal drug, although this difference is not absolute as clotrimazole exhibits fungicidal properties at higher concentrations.
The action of the drug is based primarily on damage to the permeability barrier in the cell membrane of fungi. Clotrimazole inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. If ergosterol synthesis is either completely or partially inhibited, the cell is no longer able to create an intact and functional cell membrane. Since ergosterol directly stimulates the growth of fungal cells in a hormone-like manner, the rapid onset of the above processes results in dose-dependent inhibition of fungal growth.
Although there is a decrease in ergosterol, due to the inhibition of lanosterol 14-demethylase (also known as CYP51), which is believed to be responsible for the antifungal properties of clotrimazole, this drug also exhibits other pharmacological effects. These include inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase, intracellular calcium depletion, and blockade of calcium-gated potassium channels and voltage-gated calcium channels. The action of clotrimazole on these complexes explains other effects of this drug that differ from its antifungal activity.
Treatment of candidiasis in the mouth
There are several types of candidiasis of the oral mucosa, but treatment tactics do not differ significantly.
The most commonly used drugs for oral candidiasis are local antimycotics in the form of aerosols, solutions, gels, for example, fenticonazole, miconazole or amphotericin B.
Additionally, antiseptics with antifungal activity are used in the form of solutions for rinsing or lubricating lesions. For rinsing, preparations based on hexetidine and chlorhexidine are often used. A good medicine for candidiasis in the mouth is Lugol's solution, it is used to lubricate plaques.
To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to take vitamins, especially C, P and group B.
Oral and even infusional antifungal antibiotics for oral candidiasis (sertaconazole, miconazole, isoconazole) are required for severe or chronic disease.
It is important that during the therapy period patients follow a diet that excludes fast carbohydrates (all types of sweets), since they are an excellent breeding ground for candida. Patients should refrain from eating sour and spicy foods.
When treating oral candidiasis in children, it is recommended to carry out “alkalinization” - treating pacifiers, bottles and toys that the baby may put in the mouth with a baking soda solution.
Clotrimazole
Clotrimazole
(Latin
Clotrimazolum
, English
clotrimazole
) is a broad-spectrum antifungal drug, an imidazole derivative. Acts mainly on microorganisms in the stage of division and growth. Clotrimazole is poorly absorbed when taken orally, it cannot be administered parenterally and is used almost exclusively for the local treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, skin and gynecological diseases.
Clotrimazole is a chemical compound
The chemical name of clotrimazole is 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-1H-imidazole.
The empirical formula of clotrimazole is C22H17ClN2. Molecular weight 345 g/mol. White crystalline substance, odorless. Almost insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ether, very soluble in ethanol and polyethylene glycol 400.
Microorganisms against which clotrimazole is active or inactive
Mushrooms:
- Clotrimazole is active against yeast fungi: Candida spp.
(including
Candida albicans
and
Candida glabrata
(
Torulopsis glabrata
) and excluding
Candida guillermondii
),
Rhodotorula spp., Malassezia furfur (Pityrosporum orbiculare), Blastomyces dermatitidis - active against dermatophytes: Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Arthroderma otae (Microsporum canis)
- Clotrimazole resistant: Candida guillermondii
Bacteria:
- clotrimazole has antibacterial activity in vitro against strains of gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp.
(including
Staphylococcus aureus), Streptococcus spp
.
(including Streptococcus pyogenes), Proteus vulgaris, Corynebacterium minutissimum, Salmonella spp. - clotrimazole is active against gram-negative (gram-variable) bacteria: Bacteroides spp., Gardnerella vaginalis
- resistant to clotrimazole: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis
and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Protists: Clotrimazole in high concentrations is active against Trichomonas vaginalis
.
Clotrimazole in ATC
Clotrimazole is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of the drug. In ATC, clotrimazole is included in a number of different groups, each of which has its own code, in particular:
- "A01 Dental preparations", "A01AB Antimicrobial preparations for local treatment of diseases of the oral cavity", code A01AB18
- "D01 Antifungal drugs for the treatment of skin diseases", "D01AC Imidazole and triazole derivatives", code D01AC01
- “G01 Antiseptics and antimicrobials for the treatment of gynecological diseases”, “G01AF Imidazole derivatives”, code G01AF02
Indications for use of clotrimazole
Clotrimazole is indicated for diseases of the skin, oral cavity, mucous membranes of the female and male genital organs with microorganisms sensitive to it:
- fungal infections of the skin and mucous membranes: dermatomycosis, dermatophytosis, trichophytosis, epidermophytosis, microsporia, candidiasis, stomatitis, interdigital fungal erosion, fungal paronychia
- candidiasis vulvitis, vulvovaginitis
- balanitis, balanoposthitis
- trichomoniasis
- lichen: pityriasis versicolor or versicolor
- erythrasma
- mycoses complicated by secondary pyoderma
Order of use of clotrimazole and dose
Fungal skin infections, erythrasma, lichen
. Clotrimazole ointment, cream or solution is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes 2-4 times a day and rubbed in gently. The duration of therapy is about 4 weeks, or until the clinical manifestations disappear and another 2 weeks (for fungal infections of the legs - 2-3 weeks).
In the treatment of oral
: 0.5–1 ml (10–20 drops) of clotrimazole solution, using, for example, a cotton swab, is applied to the affected areas of the oral mucosa 3-4 times a day.
At least 3-5 days of treatment; Duration of treatment: from 3 or more days until complete recovery.
Mild balanoposthitis
Balanitis, vulvitis
. 2-3 times a day for 1-2 weeks - clotrimazole ointment, cream or solution.
Vaginitis, trichomoniasis
. Vaginal tablets are inserted deep into the vagina, once a day, in the evening: either 6-7 days, 100 mg of clotrimazole, or 3 days, 200 mg of clotrimazole, or 1 day, 500 mg of clotrimazole. The cream, a full applicator, is inserted into the vagina as deeply as possible once a day, before bedtime.
Candidal esophagitis
. Clotrimazole 10 mg tablets, sucked every 6 hours (Harrison's Handbook of Internal Medicine).
Sanitation of the birth canal
- 1 tablet of clotrimazole once.
In the absence of clinical effect
within 4 weeks, a repeated study is required to determine the infectious agent.
Use of clotrimazole in pregnant and nursing mothers
The FDA risk category for the use of clotrimazole in pregnant women is B (animal studies have not revealed a risk of adverse effects on the fetus; there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women).
It is not recommended to use clotrimazole in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the II-III trimesters, it is not recommended to use intravaginal applicators. Since there are no reliable studies confirming or refuting the excretion of clotrimazole into breast milk, therapy with clotrimazole for nursing mothers is not recommended.
Trade names of drugs with the active substance clotrimazole
The following drugs with the active substance clotrimazole are (have been) registered in Russia: Amyclone, Antifungol, Gine-Lotrimin, Imidil, Yenamazol 100, Candibene, Candid, Candid-B6, Candizol, Kanesten, Kanizon, Clotrimazole, Clotrimazole-Acri, Clotrimazole-Teva , Lotrimin, Faktodin.
See also (pdf): “Instructions for use of the drug for medical use Clotrimazole-Teva.”
Clotrimazole has contraindications and side effects; before use, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Back to section
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you should carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Every person is recommended to undergo a preventive examination at the dentist once a year and have their teeth treated on time. People who wear dentures should do so more often. Smoking is also one of the causes of thrush, so it is advisable to give up this bad habit.
During the period of antibiotic therapy, it is necessary to take eubiotics to correct the intestinal microflora.
Peculiarities
Clotrimazole should not be used during the first trimester of pregnancy unless the doctor considers its use necessary for the patient's health. The drug should not be used during menstrual periods in the treatment of candidiasis vulvitis (thrush). If breastfeeding, clotrimazole can be used only as prescribed by your doctor.
The drug weakens the effect of nystatin, natamycin, amphotericin B when used simultaneously. The cream is not used to treat nails or fungal diseases of the head.
For external use, Clotrimazole cream is rubbed into the affected areas of the skin. Do not apply the product to the area around the eyes.
Clotrimazole is not prescribed to infants and premature infants
To treat candidiasis vulvitis, the capsule is inserted into the vulva, and the perineal area and mucous tissues are treated with cream. During treatment of candidal vulvitis, unprotected sex should be avoided so as not to infect the partner. If infection does occur, treatment should also be carried out by the partner. When carrying out therapy with the drug, tampons, spermicides and other vaginal products should not be used.
Popular questions about candidiasis
How to determine candidiasis?
The disease has a specific symptom - white plaque in different parts of the oral cavity.
Which doctor treats oral candidiasis?
Dentist-therapist.
How is candidiasis treated?
Doctors usually prescribe the following medications to treat oral thrush: chlorhexidine or hexetidine solution, as well as nystatin, amphotericin B, or miconazole. They are available in different dosage forms (in the form of a gel, solution, aerosol), everyone will choose the one that is convenient for themselves.
Overdose
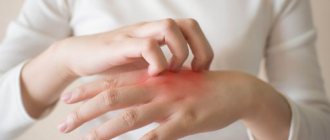
Symptoms of overdose include erythema, tingling, blistering, peeling, swelling, itching, urticaria, burning and general skin irritation, and cramps. As with all topical medications, skin sensitization may occur.
Clotrimazole does not pose a risk of acute toxicity as it is unlikely to occur after a single vaginal or cutaneous application. Overdose when applied is possible over a large area under conditions favorable for absorption, or accidental oral administration. There is no specific antidote.