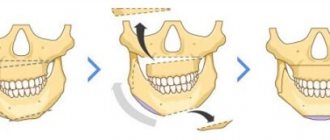
Facial swelling is not only a cosmetic defect; if it appears frequently or is accompanied by redness and pain, it is a sign of quite serious health problems that need to be identified and treated.
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ANDREY GRACHEV Leading cardiologist of the SM-Clinic holding, MD, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Facial edema is not a separate disease, but only a reflection of an imbalance between retention and excretion of fluid in the body. But what problems in the body can cause the face to swell and how serious is it?
Why does the face swell in adults?
Swelling on the face can occur at different times of the day - mainly in the morning or late afternoon, or they persist throughout the day, decreasing or increasing.
There are two types of reasons:
- physiological (or natural, not associated with diseases), they are usually not pronounced, not very strong, and disappear quickly;
- pathological, can be very strong, with changes in facial features, signs of inflammation, and are often quite persistent.
Each type of edema has the most typical causes; they occur mainly in the morning or evening hours, or do not depend in any way on the time of day. These characteristics are important for the doctor so that he can identify the leading causes and determine the tactics of examination and treatment.
Diagnostic stages
Consultation and examination by a therapist. After a detailed conversation and medical examination, the patient can be referred for consultation to other specialists depending on the etiology of the disease: cardiologist, allergist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, urologist, etc.
Laboratory research. First of all, the following are carried out:
- general (with leukocyte formula) and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis.
- Instrumental studies:
- ECG;
- echocardiography;
- Ultrasound of blood vessels of the lower extremities;
- X-ray of the chest organs.
Next, the doctor prescribes a set of studies on an individual basis in each individual case.
To effectively eliminate swelling, you need to know exactly what disease is causing it. Edema is not an independent disease, but a symptom. Diagnostics using modern equipment will allow us to determine the cause of the pathology. The information obtained allows the doctor to choose the most effective treatment. Don't put off taking care of your health until later. Schedule a consultation with your doctor today to stay energized for years to come.
sign up for a consultation
Is there swelling on the face due to heart disease?
Yes, these questions usually worry women, says cardiologist Andrei Grachev.
They run to see a cardiologist when they can’t put a ring on their finger in the morning because it’s swollen or put on makeup because their face is swollen. The patient wants to look great, regardless of age and health status. And this is commendable. Men, as a rule, do not contact a cardiologist with such questions. The peculiarity of this issue is due to the fact that in patients with cardiovascular diseases, as a rule, swelling on the face appears at the final stage of a complication such as heart failure. First, they appear on the legs (the lowest point in relation to the heart), then fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, the liver and spleen enlarge (as a blood depot). And only after the fluid reaches the pleural cavities and the heart sac, swelling may occur on the face or hands.
Swelling on the cheekbones: causes and consequences
Year after year goes by. The first signs of age appear as bags and puffiness under the eyes. After a few more years, a second fold begins to appear in the area of the cheek bones. These are “painting bags” (their second name is “sufa”).
Like bags under the eyes, they have similar unpleasant properties.
Firstly, fatty hernias on the cheekbones greatly spoil the appearance and make the face sad.
Secondly, these formations consist entirely of adipose tissue, so they tend to retain water, increase in size and form malar edema.
We often hear that the cause of swelling on the cheekbones is insufficient self-care. They say, take time for yourself, and miraculous creams, massages and vitamin complexes will remove all the bags under the eyes on the cheekbones in a month, and you will again shine with youth and beauty.
To be fair, it is worth saying that cheekbones are not a disease. This is an anatomical feature of the body: paint bags filled with adipose tissue. However, in youth, the good tone of young skin hides the problem.
With age, the skin becomes drier and thinner, the facial muscles lose their elasticity, the fatty tissue begins to sink down, sag, and... Everything secret becomes clear.
When do they occur most often?
Due to a number of circumstances, adds cardiologist Andrei Grachev, such as the flow of fluid to the upper half of the body in a lying position, changes in the biorhythms of hormone production (more often their active synthesis occurs at night or in the early morning hours), edema syndrome most often manifests itself in the early morning hours .
Morning
If we talk about physiological reasons, morning swelling is usually associated with constant lack of sleep, fasting or strict diets (limiting protein and fats). Sometimes swelling in the morning is caused by the wrong selection of skincare products (face cream, toner or cleanser). Also, morning swelling of the face can be caused by crying or stress in the evening or at night.
Possible swelling of the face in the morning due to an incorrectly selected pillow (it is too high, it provokes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck). Another physiological factor is an excess of fried, salty foods or liquids taken in the evening, before bed. In women, facial swelling in the morning can be caused by hormonal fluctuations, PMS or pregnancy. Some women report morning swelling during menopause.
Pathological causes of morning edema are mainly kidney damage. Such swelling is usually soft, mobile, appears on the face after sleep, and the skin acquires a waxy or yellowish tint. The most common causes of facial swelling are:
- glomerulonephritis - the acute form of the disease leads to edema, which lasts up to 2-3 weeks, if the process enters the chronic phase, edema is typical for periods of exacerbation of inflammation;
- Kidney amyloidosis - edema is typical of the second stage (proteinuria), when protein loss occurs and kidney function gradually deteriorates;
- membranous nephropathies - occur after taking certain medications, tumor therapy, acute infectious pathologies. Edema occurs in waves, with sharp or barely noticeable symptoms;
- chronic kidney disease (previously called renal failure) - swelling occurs gradually as renal damage progresses;
- kidney damage in severe systemic pathologies - edema is typical for nephropathy due to diabetes or systemic lupus erythematosus.
Evening
Sometimes facial swelling becomes noticeable in the evening, especially after an active day. Often this is one of the manifestations of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Often, swelling of the face is accompanied by severe swelling in the area of the extremities - hands and feet, legs. These swellings are denser, the skin has a lower temperature than on other parts of the body, and such swelling goes away slowly. Often occur against the background of the following pathologies:
- amyloidosis of the heart and blood vessels;
- cardiomyopathy;
- sclerotic heart disease (cardiosclerosis);
- certain types of arrhythmia;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- some heart defects;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiac lesions due to rheumatism.
Day
Sometimes facial swelling is most pronounced during the day or its appearance is not clearly related to the time of day. Among the main pathologies that lead to such edema are endocrine disorders - especially a lack of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism). Facial swelling is especially pronounced with congenital hypothyroidism, in pregnant women or with autoimmune thyroiditis, cytokine-induced thyroiditis.
Rapidly increasing swelling of the face during the day can be a sign of allergies - to food, insect bites, cosmetics, medications and even cold. Sometimes facial swelling occurs during an attack of bronchial asthma due to difficulty breathing and fluid retention in the veins.
Facial swelling is possible in people who smoke and drink alcohol. This is due to the increased work of the lymphatic system to remove toxins from tissues.
Severe swelling of the face during the day is possible with respiratory infections and their complications - sinusitis, tonsillitis, frontal sinusitis. Swelling of the face is possible with a deficiency or excess of vitamins (especially fat-soluble ones).
Swelling of the eyelid
The eyelids are folds of skin around the eyes, consisting of many organs, each of which plays an important role. The muscles help a person blink, the conjunctiva helps to moisturize the eyeball, and the meibomian glands retain moisture. Together they form a complex system, the main purpose of which is to protect the eyes from drying out, dirt, bright light and other negative environmental factors. Inflammation of one of the organs leads to the development of diseases, the main symptom of which is swelling of the eyelid.
Symptoms
Characteristic signs of developing pathology include:
- swelling of the area around the eyes;
- increased temperature (symptoms of barley, conjunctivitis, furunculosis);
- pallor of the skin – with a non-inflammatory nature of the disease;
- characteristic enlargement of lymph nodes - during the inflammatory process.
What complications can arise from eyelid swelling?
- When excessive internal pressure occurs, glaucoma occurs.
- Decreased visual acuity, complete blindness.
- Operable and inoperable cancer.
Description of the disease
Edema of the eyelid is a pathological accumulation of fluid in the area of loose connective tissue. The process results in visible swelling around the eyes.
Swelling in this area forms quite easily. This is due to the fact that the subcutaneous layer of fiber and muscles are poorly developed, and there are many blood vessels. Swelling of the area around the eyes is a common phenomenon that causes a lot of inconvenience. In addition, this is an alarming sign indicating a malfunction that has occurred in the body. Many people first of all think about the aesthetic component. But if a cosmetologist can get rid of the external manifestations of the disease, he will not solve internal problems.
Swelling is a symptom of many diseases, as well as a sign of an unhealthy lifestyle. Thus, swelling can occur due to a violation of the drinking regime or diet, alcohol abuse, or addiction to salty foods. Such swelling is physiological in nature, disappears within 24 hours and does not require medical intervention.
If the swelling is systematic and does not go away on its own, it cannot be considered as a cosmetic problem - you need to contact an ophthalmologist.
Classification of eyelid edema
Depending on the history, there are several types of edema of the paraorbital region:
- Inflammatory. The cause is bacterial damage. As a result of the negative impact, suppuration begins. Pus accumulates in the paraorbital area, the eyelids swell. Externally, the pathology is expressed in the form of hyperemia of the eyelids, a noticeable thickening at the site of the disease.
- Non-inflammatory. Unlike the inflammatory variety, this process rarely manifests itself visually. The main symptoms are pale skin and swelling in the morning. It usually appears on the lower eyelids and indicates a malfunction of some internal organs - liver, kidneys, thyroid gland. It can also occur due to incorrect head position during sleep.
- Allergic. In case of contact with an irritant, it begins to develop rapidly. After eating a food that causes an allergy, swelling appears after a couple of hours. The most aggressive form of the reaction is Quincke's edema, in which not only the eyelids, but also the tissues of the head, neck, and larynx swell. This leads to difficulty breathing and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
- Traumatic. In this case, it is not necessary to injure the area around the eyes: the eyelid swells when the soft tissues and muscles of the face are damaged. This could be a bruise, surgery, consequences of plastic surgery, microtrauma caused by wearing contact lenses.
- Reactive. The cause of its appearance is an inflammatory process near the paranasal sinuses.
Causes of edema
The main causes of paraorbital swelling, which causes discomfort and spoils external aesthetics, can be divided into two categories - pathological and non-pathological.
Non-pathological causes include:
- Fatigue caused by increased eye strain, prolonged sitting at the computer, and lack of sleep.
- Diet violation. For example, the abuse of pickles, which retain water in the body.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol displaces fluid from the body, which leads to a constant feeling of thirst. An unpleasant “bonus” is swelling of the paraorbital area.
- Incorrect head position during sleep. If you sleep on a low pillow or without one at all, you can provoke an abundant flow of blood to the head, which causes bilateral swelling. When sleeping on one side, fluid accumulates, resulting in unilateral swelling.
- Poor quality cosmetics, lack of habit of removing makeup.
- Eyelash extensions, tattooing, anti-aging procedures.
- Injuries. A bruise on the bridge of the nose provokes bilateral swelling. Trauma to the eye area is the cause of unilateral swelling. Various maxillofacial and plastic surgeries also lead to similar consequences.
- Predisposition. People with thin skin often experience swelling around the eyes in the morning after drinking an extra glass of water in the evening. Edema can also appear due to excessive physical exertion.
- Age. Over time, the tissue and muscles of the eyelids weaken, fat sag, and large amounts of fluid accumulate, causing “bags” to form.
If we talk about pathological edema of the paraorbital region, they can be provoked by both eye and general diseases:
- Barley. Characterized by pain, hardness, and swelling. The swelling gradually increases, the skin turns red, but the site of inflammation is localized. After opening the abscess, the swelling subsides.
- Conjunctivitis. The causes of pathology are often streptococci and staphylococci. In severe cases of the disease, swelling of the eyelids gradually begins to develop.
- Blepharoconjunctivitis. Symptoms: inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye and eyelids.
- Trachoma. Pathology caused by chlamydia.
- Chalazion. A disease involving the edges of the eyelid, meibomian gland, cartilage. In some cases it is chronic.
- Blepharitis. Inflammation of the edge of the eyelids, accompanied by hyperemia, peeling, swelling, itching, and loss of eyelashes. The cause of the pathology is an allergic reaction to external irritants.
- Ophthalmoherpes. Symptoms: swelling around the eye, pain, itching, redness of the conjunctiva.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms in the eye area.
- Tuberculosis of the eye.
- Graves' disease. Caused by an increased amount of hormones produced by the thyroid gland. It manifests itself as protrusion of the eyeball, swelling of the periorbital region.
- Demodecosis. Damage by the parasite, accompanied by loss of eyelashes, discharge of pus, redness, itching, swelling.
- Fatty hernia, sinusitis. Often provoke swelling of the lower eyelid.
- Diseases from the ENT system.
- Kidney diseases. Characterized by bilateral, pale, soft-to-touch swelling.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Changes in hormonal levels. Sometimes small swellings are observed on certain days of the menstrual cycle. Swelling can also occur during pregnancy.
Not all pathologies indicated in the list have a real threat to human health and life.
Doctors are especially monitoring people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and endocrine glands.
Prevention
To prevent swelling of the paraorbital area, experts recommend adhering to certain rules:
- Do not drink large amounts of liquid. In the evening, you should refrain from salty foods, as they provoke a feeling of thirst. Before going to bed, just drink a glass of herbal infusion and warm milk. This will quench your thirst and help avoid morning puffiness. Fans of soda, strong tea, and coffee should limit the amount of these drinks.
- Maintain personal hygiene. The eyelids need to be cleaned daily - morning and evening before going to bed. This is especially true for women who use decorative cosmetics. It is also important that each household member has a personal towel that needs to be changed regularly.
- Using quality products. Facial care products and cosmetics should be purchased from trusted manufacturers - this will help avoid purchasing low-quality or counterfeit products. You should also consult with a specialist before the tattoo procedure.
- Compliance with safety regulations. Some professions involve processes and tools that can damage the mucous membranes and skin around the eyes. To avoid this and maintain your health, you must wear special glasses while working.
- Eye protection in the summer. Direct ultraviolet rays have a negative effect on the eyes in particular and the body in general. To protect the delicate mucous membrane of the sun, you need to wear glasses, use an umbrella or a hat with a wide brim.
- Maintaining distance when communicating with people. If the interlocutor is coughing, sneezing, or has visual signs of eye diseases, such as stye, it is better to postpone communication until he recovers.
- Regular cleaning of premises. Doctors note that the number of patients with allergies to dust, mold and other household contaminants is growing every year. This is why it is so important to carry out thorough and regular cleaning of premises. It is also worth going through old things and getting rid of those that are no longer useful, because they are an excellent accumulator of dust in a living environment.
- Pet care. Animal fur is a powerful allergen to which a large number of people are sensitive. To prevent your furry pet from becoming the cause of illness, you must regularly vacuum carpets, rugs, treat upholstered furniture and textiles, and comb your pets thoroughly, especially during seasonal molting.
If paraorbital edema has already appeared or often “pleases” you in the morning, you need to contact a specialist who will help you find out the cause, adjust your daily routine, diet and drinking regimen.
How to treat eyelid swelling
- If the cause of swelling is a bruise, the eyelid usually immediately begins to increase in volume. In this case, it is necessary to wash your hands with unscented soap, since scented options can cause an allergic reaction. Then treat the injury site with an antiseptic and apply a cold compress - it will help stop the growth of swelling. Then cover the affected area with a sterile cloth and go to the emergency room.
- Cold compresses or ice cubes. Moreover, these can be cubes from herbal decoctions, such as calendula, mint or parsley. If necessary, the pieces are removed from the mold, wrapped in gauze, and carefully wiped over the eyelids.
- Tea lotions. It is especially convenient to use tea in bags, which must first be brewed and cooled to room temperature.
- Eye drops. In this case, it is important to consider the cause of the tumor. So, Oftalmoferon will help in case of eye damage from viruses. Tetracycline is indispensable when swelling is caused by bacteria.
- Decongestants. They are usually prescribed in case of blockage of the sebaceous gland. In a hospital setting, Tavegil will help cope with extensive swelling.
- Analgesics. The inflammatory process is often accompanied by painful sensations. To alleviate the condition, you need to take Analgin.
- Ointments. Hydrocortisone ointment has a pronounced antibacterial effect and helps eliminate swelling.
- Absorbents. You can use activated carbon, which will remove the substance that causes the swelling from the body.
- Antihistamines. You should take allergy medications only after seeing a doctor. Suprastin, Claritin, Zodak, Diazolin and others are usually prescribed.
- Use of liquid nitrogen. In the absence of metastases, the substance can help destroy the focus of a malignant neoplasm.
- Operation. Surgery will allow you to remove the cancer with excision of a small area of tissue surrounding the tumor. If further tests are within normal limits, the patient undergoes plastic surgery to correct the defect.
- Application of drops. Drugs from the vasoconstrictor group are used. Vizin and Octilia have proven themselves especially well.
In the case of malignant neoplasms in the later stages, the prognosis does not look very optimistic. If a small area is affected, all tissue from the area is removed during surgery. If manipulation is not practical, the patient is prescribed radiation and chemotherapy.
Lifestyle
You can help avoid swelling by following simple recommendations:
- Do not come into contact with substances that cause an allergic reaction.
- If itching occurs, it is important not to scratch it.
- Regularly visit doctors of various specialties.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Controlling the amount of liquid you drink.
When contacting our center, the patient can be sure that he will receive the most modern, effective treatment, selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Timely consultation with a doctor, competent therapy, a healthy lifestyle, and following the doctor’s instructions are the key to a positive result with minimal financial costs.
Author
Danilova Elena Fedorovna
ophthalmologist
18 years of experience
+7
How to quickly relieve facial swelling in adults
If this is physiological swelling of the face, not associated with serious pathologies that require medical supervision and the use of selected medications, excess fluid can be eliminated through certain simple measures and actions.
Taking a contrast shower or washing with cold/hot water. This method refreshes, increases tissue tone, enhances the outflow of fluid from the skin and reduces swelling.
Using ice – a couple of pieces of ice will help deal with swelling on the face quickly and effectively. In addition, you can prepare herbal decoctions with a tonic effect in advance and freeze them, using them for washing.
Facial massage is an effective remedy that helps improve microcirculation and swelling. Manual massage, the use of rollers, ice cubes, and cold spoons help. Sometimes you can first wipe your face with green tea and apply compresses with it to your face and eye area.
Features of swelling under the eyes
Swelling under the eyes is always clearly visible to the naked eye, even to a non-specialist, especially since such a disorder is seen by the person himself in the mirror.
Note! Sometimes the swelling may not be as noticeable, and it can be difficult to determine whether it is actually swelling or slight skin deformities that occur after sleep.
Pathological swelling that requires action is always characterized by the following symptoms :
- change in skin color under the eyes;
- slight or strong feeling of skin tension in the area of edema;
- the tissues in the area of edema become slightly denser.
In some cases, such formations may be accompanied by painful sensations.
But this does not happen due to the development of subcutaneous pathological processes, but due to strong tension of the skin and the creation of pressure under it due to the accumulation of fluid.