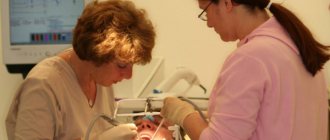
Dental surgery today is a popular area of medicine with a wide range of services. In the past, the specialty “dental surgeon” was associated only with the removal of problem teeth. Now its main goal is to preserve teeth - it helps solve problems in cases where conservative therapy is ineffective or impossible to carry out. The patients of a dental surgeon can be both adults and children; he performs not only operations, but also diagnoses diseases of the oral cavity.
Surgical dentistry - what is it?
This is one of the separate medical disciplines that studies surgical methods for treating pathologies and injuries:
- teeth;
- oral organs;
- faces;
- neck;
- skull and its joints.
Surgical interventions serve as the main methods, but contrary to popular belief, the main task is preservation, not removal, with the help of the latest technologies. Surgery is interconnected with other specialties:
- conservative therapy;
- orthopedics;
- pediatric dentistry.
Standard education for the profession of “surgeon” is not enough; additional practices are required - internship and residency.
Modern dental surgery
When hearing the word “surgeon”, almost every patient experiences fear and imagines some kind of painful, bloody procedures, so they are extremely reluctant to undergo treatment. In fact, modern medicine allows any intervention to be carried out absolutely painlessly, under anesthesia.
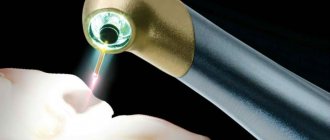
In addition, today there are a considerable number of minimally invasive atraumatic techniques that can speed up the healing process and reduce the discomfort caused to the patient during the rehabilitation period to a minimum. For example, a new branch of dentistry - laser medicine - makes it possible to carry out complex extractions and interventions almost bloodlessly, without injuring surrounding tissues and thereby significantly accelerating healing after surgery.
Therefore, patients need to be afraid not of the intervention itself, but of the consequences of not treating it: ignoring a problem that can and should be solved surgically will lead to the development of serious complications in the future and will have an extremely adverse effect on the overall health of the body.
The high level of development of modern dental surgery makes operations on teeth and jaws effective and safe for the patient.
Main activities
This multifunctional area of medicine covers not only tooth extraction, but also operations aimed at preserving dental units. Include:
- implantology;
- orthodontic therapy;
- plastic surgery on the jaws, their reconstruction;
- purulent and oncological surgery.
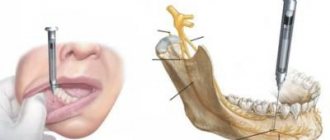
All treatment procedures are carried out under anesthesia, so it is not painful. General or local anesthesia is used:
- conductor;
- infiltration or intraligamentary;
- intraosseous.
Types of dental operations
Dental-preserving interventions include:
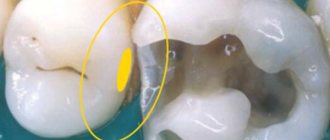
- Tooth root resection is the removal of part of the root affected by an infectious-inflammatory process.
- Hemisection – removal of the root and part of a tooth.
- Cystectomy - removal of cysts on the roots.
Such operations make it possible to do without complete removal and preserve a healthy part of the dental tissues with their subsequent restoration. Today, dentists perform tooth extractions only in extreme cases, when it is not possible to save them or they interfere with a normal bite (wisdom teeth). In all other cases, the doctor will try to save every tooth to the last, leaving prosthetics as a last resort.
In addition to tooth-preserving interventions, dental surgery also solves the following important problems:
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases of soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity (periodontitis, periodontitis, periostitis, etc.).
- Treatment of acquired and congenital defects of the dental system and face.
- Removal and treatment of tumors.
- Treatment of diseases of the salivary glands, TMJ, trigeminal nerve.
- Plastic and reconstructive surgeries.
- Preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics.
These operations affect the teeth only indirectly, but without them it is often impossible to achieve either oral health or normal functioning of the dental system.
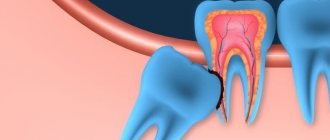
And of course, the duties of a dental surgeon include the removal of teeth, including complex teeth (eights) and milk teeth in children when the bite changes.
What functions does it perform and what tasks does it solve?
The range of surgical dentistry services is quite large. Today it includes: procedures to save the tooth. This is the extraction of roots (in whole or in part), parts of the dental crown. During operations, a dental surgeon, using special instruments, including a drill with various attachments, removes not only part of the tooth, but also the infectious source. The healthy tooth surface is completely preserved and the tooth can function fully in the future.
Elimination of purulent inflammations inside the mouth. Such clinical cases are abscesses, phlegmons, sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary sinuses), periodontitis. During the treatment, the purulent cavity is cleaned out, the inflamed tissues are disinfected with the help of antimicrobial drugs.
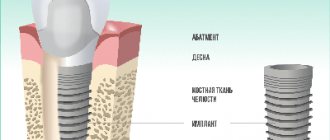
Dental implantation. After extraction of dental units, the natural bone tissue located in their place atrophies due to lack of loads. To prevent this phenomenon, the dental surgeon builds up the area in which the extracted tooth was located with artificial bone tissue. After its engraftment, a titanium implant with a crown is installed. The patient can receive an artificial, fully functional tooth.
Tooth extraction (complex, simple, emergency). Complete removal of teeth is used in extreme cases, if other treatment measures are ineffective or cannot be carried out. Impacted, dystopic teeth, destroyed by caries and mechanical injuries that threaten the health of neighboring teeth, are removed.
Primary preparation before prosthetics. If a removable denture cannot be fixed in the oral cavity due to lack of space, the dental surgeon will expand the distance between the gum and cheek. After such a relatively simple plastic surgery of the alveolar ridge, the prosthesis can be securely mounted on the jaw. Preparatory procedures before orthodontic treatment. These are plastic surgical interventions on the lips and lingual frenulum, removal of supernumerary and incorrectly located teeth from the jaw.
Treatment of facial trigeminal neuralgia. Inflammation cannot always be eliminated using conservative methods. In such situations, the dental surgeon will surgically free the nerve trunk from the blood vessel that is compressing it. In some cases, the nerve or its nodes are destroyed. Therapy of pathologies of the salivary glands. Inflammation can cause suppuration, which is eliminated by a dental surgeon by excision and drainage of the salivary gland.
Elimination of pathologies of the temporomandibular joint. Such diseases include dislocations, sprains, more serious injuries, as well as diseases - arthritis, arthrosis. A dental surgeon treats inflammation with the help of fixing bandages, splints (splinting), which are applied to the affected area, and also, if necessary, performs surgery.
Removal of tumors inside the oral cavity (benign and malignant). In the first option, they are simply removed (it is better to do this right away), in the second, combination therapy is used, consisting of surgery, radiation, and medication. Surgeries on periodontal tissues include opening the gum hood over an impacted tooth, treating gums for inflammation, curettage, flap operations, and excision of excess gum tissue.
The range of dental surgery services includes diagnostic measures from which the surgeon’s appointment begins, including the diagnosis of systemic diseases: syphilis, tuberculosis, etc. For diagnostics the following are used:
- basic blood tests for coagulation, red blood cells, hemoglobin, glucose;
- analyzes of purulent exudate from the inflammatory focus for pathological microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- blood test for group and Rh factor;
- facial radiography;
- CT - computed tomography and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- bone tissue scintigraphy to determine the presence or absence of neoplasms.
Surgery in dentistry
Surgery in dentistry
22.12.2017
Surgical dentistry
– this is a direction that includes the whole complex of manipulations and surgical interventions not only in the area of the dentition, but also in adjacent tissues. Most people have the impression that dental surgery only deals with tooth extraction. This opinion is erroneous, although a larger percentage of operations involve tooth extraction. A dental surgeon deals with all surgical interventions in the mouth, face and neck. The scope of competence of surgical dentistry is quite large: from tooth extraction to plastic surgery.
Areas of surgical dentistry
Surgical dentistry deals with the following areas
- Tooth extraction. Full or partial (aimed at preserving part of the tooth). Partial extractions remove diseased portions of the crown and/or root while maintaining the overall vitality of the tooth.
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases of the teeth and maxillofacial area, abscesses, periodontitis, periostitis and other diseases.
- Implantation. Includes tooth extraction, preparation of the bed for implant installation, the process of installing the abutment, and monitoring the healing process.
- Preparation of the oral cavity for further prosthetics. Operations to remove teeth and roots, excessively protruding bone and soft tissues, plastic surgery of alveolar processes and gingival papillae.
- Tooth-preserving procedures - removal of individual tissues affected by infection. Resection of the apex of the tooth root with foci of inflammation in the form of granulomas or cysts. Cutting off one tooth root, followed by its extraction and filling the hole with a drug that stimulates the formation of bone tissue.
- Treatment of oral tumors. Includes tumors of the tongue, buccal mucosa, floor of the mouth, tumors of the hard and soft palate of various etymologies.
- Treatment of diseases of the temporomandibular joint (dislocation, arthrosis, arthritis, neoplasms) and trigeminal nerve caused by various factors.
- Treatment of diseases of the salivary glands, such as chronic or acute inflammation of the salivary glands (sialadenitis), changes of a reactive-dystrophic nature (sialosis), tumors of the salivary glands.
- Removal of benign and malignant neoplasms on the face, papillomas, keratomas, dermatofibromas, lipomas (wen).
- Periodontal operations. Elimination of pathology of periodontal pockets using curettage, cryocuretage, gingivotomy and other methods. Flap operations for cleaning gum pockets and forming the vestibule of the oral cavity using vestibuloplasty.
- Reconstructive and plastic surgeries on the jaws. For defects of the upper and/or lower jaws (often complicated by defects of the tongue and adjacent soft tissues), tumors of various origins.
Tooth extraction operations remain the most popular and numerous.
If the tooth could not be saved with the help of therapeutic treatment, you should consult a dentist. A wide selection of anesthetic substances will allow you to perform the operation painlessly. Back