Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
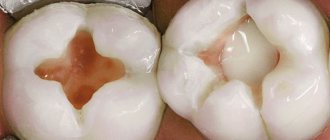
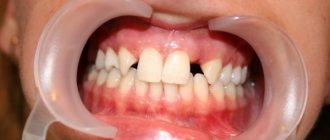
Periodontal disease is one of the most dangerous and insidious dental diseases, which can lead to the complete loss of not only single teeth, but also entire dentitions. Periodontal disease practically does not affect the teeth themselves, however, under its influence, periodontal tissue is destroyed - that part of the gum and jaw that is in direct contact with the root of the tooth and ensures its fixation. Not only the soft tissue of the gums weakens and collapses, but also the bone tissue, as a result of which the teeth become loose and there is a threat of their complete loss.
Degenerative processes in gum tissue that occur during periodontal disease develop under the influence of a number of factors, none of which researchers single out as the main and only one. Patients suffering from periodontal disease almost always exhibit certain trophic and circulatory disorders in the gum tissue, in particular of an atherosclerotic nature. However, such disorders can arise as a consequence of a wide variety of pathologies. Among the reasons that can provoke the occurrence of periodontal disease, experts name various dysfunctions of the endocrine and digestive systems, vascular diseases, neurological diseases and occlusion pathologies, single or regularly recurring injuries. Bad habits (alcohol and tobacco consumption), poor nutrition, which causes a lack of vitamins and minerals, and a persistent decrease in immunity, leading to increased activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms in the oral cavity, play a role in this process.
Unfortunately, today there is not a single drug that could completely restore destroyed tissue and reverse the process of development of periodontal disease. However, the use of a complex of physiotherapy and medications makes it possible to stop the progression of the disease, stabilize the patient’s condition and help the body regenerate damaged periodontal tissue. The leading role in achieving this result belongs to medications. You will learn about how to treat periodontal disease with medication from our material.
Antibiotics and antiseptics
Pathogenic microorganisms are not the main cause of periodontal disease, but their vital activity indirectly contributes to its development - it is no coincidence that a significant proportion of patients suffering from this disease exhibit one or another degree of decreased immunity. Accumulating in enlarged periodontal pockets and interdental spaces, the bacterial mass can cause inflammation, which in normal cases is not characteristic of this disease. That is why, in case of periodontal disease, it is often recommended to use various agents that can destroy pathogenic microflora and reduce the risk of secondary infection.
In the most severe cases, antibiotics in the form of capsules or tablets are used for this purpose, such as doxycycline and metronidazole, trichopolum, lincomycin. Broad-spectrum antibiotics effectively suppress the activity of microflora and contribute to the rapid elimination of inflammatory and infectious manifestations that complicate the course of the disease. However, long-term use of antibiotics is undesirable due to side effects and suppressive effects on the natural microflora of the body. They can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
For a more gentle disinfecting effect, it is recommended to use rinses, gels, sprays and other external products containing antiseptics. In particular, the antibacterial rinse ASEPTA, which contains benzydamine and chlorhexidine. The adhesive balm ASEPTA, which contains metronidazole and chlorhexidine, thanks to its sticky base, is retained on the gums for a long time and has a long-term healing effect. Extracts of sage, witch hazel, chamomile, as well as xylitol, which are part of the ASEPTA Fresh mouthwash, also have a mild antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Content:
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Why do you need an orthodontic consultation?
- Treatment
- Other recovery methods
Dentistry is one of the branches of official medicine, whose services in Russia are traditionally resorted to in extreme cases. In theory, everyone knows about the need for regular examinations and professional cleaning twice a year, but in practice they turn to a doctor when severe pain bothers them. One of the serious dental problems is receding gums with exposed teeth. Home methods and antibiotics will not help; only in severe forms with an inflammatory process, lincomycin is used for periodontitis.
Remedies for reducing tooth sensitivity
Due to the exposure of the necks and roots, the teeth of patients with periodontal disease become much more sensitive to the effects of various irritants - thermal, chemical, mechanical. Patients experience significant discomfort when eating spicy or sour foods, drinking hot or cold foods and drinks. To eliminate this unpleasant symptom, various means are used, including calcium gluconate, which is administered by electrophoresis (medicine applications combined with a weak electric current).
To combat hyperesthesia and eliminate other symptoms, you can also use special toothpastes. In particular, the minerals potassium citrate and hydroxyapatite, as well as thermal mud, which are contained in ASEPTA Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth, help reduce tooth sensitivity and strengthen enamel. It also contains extracts of medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
Other recovery methods
The most expensive, but also the most effective surgical method is the use of special membranes that are planted under the gums to reattach bone tissue. During treatment, an alveolar process is created that secures the mobile tooth.
Stem cells, fibroblasts and growth factors - protein structures that strengthen and restore blood and lymphatic vessels - will also help restore bone.
Medicines that reduce sensitivity have proven themselves well; they also alleviate the patient’s condition and improve his quality of life.
A strict diet is aimed at treating a disease that causes a lack of blood circulation to the mucous membrane. In case of systemic atherosclerosis, food products should contain a reduced intake of carbohydrates and animal fats, with the addition of statins. For diabetes mellitus, methods are used to reduce blood sugar concentrations. The presence of systemic pathologies requires their compensation to the stage of remission.
Regenerating drugs
The main problem in the treatment of periodontal disease is the restoration of tissues damaged or destroyed during the development of the disease. For this purpose, a variety of drugs are used, including stem cells and other biogenic stimulators of regenerative processes. They are most often administered by injection directly into the affected areas of the gums. Modern methods of treating periodontal disease include the use of the following drugs:
- Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts are connective tissue cells that play an extremely important role in the healing process of wounds and injuries, and also participate in the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers, which make the soft tissues of the body more elastic. The introduction of fibroblasts helps restore the elasticity and firmness of sagging gum tissue, and also increases the protective properties of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The strength of fabrics and their resistance to destructive influences of various natures also increases significantly.
- Stem cells
The anti-aging properties of stem cells are widely known in modern medicine and, especially, cosmetology. Stem cell preparations can stimulate regenerative processes and promote accelerated restoration of cellular structures. Under their influence, the healing process of damage is accelerated, which is extremely important in the treatment of periodontal disease and related diseases.
- Platelet-derived growth factor
Platelet growth factor is a special protein synthesized by the body and involved in the processes of tissue growth and repair. In addition, the growth factor promotes accelerated synthesis of collagen, glycosaminoglycans and other components of connective tissue.
The use of biogenic drugs is an extremely promising direction in modern medicine, but these methods are not widely used today due to technological complexity and high cost. To stimulate recovery processes, you can use more accessible means, in particular propolis. This substance is included in a wide variety of hygiene, therapeutic and prophylactic products; in particular, it is the main active component of the antimicrobial gel for gums ASEPTA. In addition to stimulating tissue restoration, propolis also has a pronounced antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the sensitivity of damaged gums, and eliminates bleeding.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively with the involvement of specialists in the field of dentistry, immunology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and therapy. The essence of treatment is to eliminate symptoms, strengthen teeth and prevent relapses. Additionally, restoration of lost tissue is carried out.
It is problematic to cure periodontal disease in the last stage, but contacting competent doctors will help get rid of unpleasant sensations and stop the further development of the disease, preserving your teeth.
Splinting
A treatment method used to strengthen loose teeth. Splinting involves combining individual teeth into a single orthopedic structure in the form of a block to reduce their mobility.
Prosthetics
Prosthetics for periodontal disease are carried out in combination with other treatment methods; it is possible to install several types of dentures, depending on the condition of the gums. Removable prosthetics helps reduce the load on areas affected by periodontal disease: installing clasp, nylon dentures that do not rub the mucous membranes and have a fastening system that does not damage the supporting teeth.
In some cases, permanent bridge structures are used to strengthen a number of teeth located one behind the other.
Prosthetics does not eliminate the cause of the disease. Without an integrated approach, tissue reduction will continue, and after 3-5 years the patient will need replacement prostheses.
Vitamins and minerals
To restore damaged tissues, the body needs a wide variety of nutrients, which are not always contained in the required quantities in the daily diet. That is why the drug treatment regimen for periodontal disease often includes taking vitamin complexes. The best effect can be achieved by taking special complexes, for example, the vitamin-mineral complex for teeth ASEPTA.
The ASEPTA complex includes a whole range of substances necessary to strengthen gums and teeth. Vitamin C strengthens the walls of capillaries and blood vessels, helping to improve blood circulation in the gums, disruption of which is one of the main causes of periodontal disease. Vitamins B3 and B6 help reduce gum sensitivity, strengthen bone tissue and promote healthy mucous membranes. Vitamin A is involved in all metabolic processes occurring inside the body and increases protection against inflammatory and infectious diseases that often accompany periodontal disease.
In addition to vitamins, the complex also contains green tea extract - a natural component that has an antimicrobial effect, eliminates unpleasant odors, and slows down the aging process of tissues. An equally important component of the complex is coenzyme Q10, a substance that is a rich source of energy for the growth and restoration of cellular structures. Taking coenzyme promotes accelerated regeneration of damaged gums.
The complex also includes substances intended to strengthen the hard parts of the tooth, which are subject to increased stress during periodontal disease - coral calcium, which is well absorbed by the body, and vitamin D3, necessary for the proper absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
Treatment
The treatment procedure depends on the stage of the disease and includes the following steps:
- Diagnostics at the dentist, making a diagnosis and taking an x-ray of the jaw;
- In-office dental cleaning to remove hard deposits, antibacterial therapy of the oral cavity;
- Orthopedic treatment of loose teeth to strengthen them. Splinting and prosthetic techniques are used to reduce the load on damaged teeth;
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - procedures to restore blood circulation to the gums and prevent relapses of the disease;
- Gum tissue augmentation is carried out when the necks of the teeth are severely exposed.
Self-treatment is impossible. Home remedies are not able to get rid of the causes of the disease. If you notice the first symptoms, contact your dentist.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of ASEPTA products has been repeatedly proven clinically. For example, clinical trials of ASEPTA gum gel have proven that using ASEPTA gum gel with propolis for a week can reduce gum inflammation by 31%.
Repeated clinical studies have also proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
Causes
In the age of the Internet, any ordinary person can find answers to all questions. Unfortunately, the professionalism of some dentists is also based on knowledge gleaned from the World Wide Web. Confusion in concepts arises, and as a result, incorrect treatment is prescribed, which aggravates the pathology, but does not eliminate it.
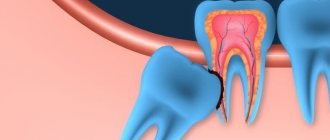
Periodontium is a set of tissues around the tooth responsible for its retention in the alveolus : gums, cementum, periodontium, periosteum and alveolar processes. When the functions of this complex are impaired, the dental units become loose and fall out; it is this pathology that is called periodontal disease.
The inflammatory process is periodontitis; it does not always accompany bone dystrophy, which has a chronic course and varies in severity.
Most often, receding gums develop in chronic pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2;
- malignant neoplasms and liver pathologies;
- atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease;
- endocrine disorders, increased stomach acidity;
- kidney damage, deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- psychical deviations.
The risk of developing periodontal disease is increased in smokers. Tobacco smoke negatively affects the immune system and directly affects the oral mucosa. A noticeable influence of the genetic factor, caries, and significant deposits of tartar was noted.