The appearance of ulcers in the mouth and inflammation of the mucous membrane are signs of stomatitis. The disease is inflammatory in nature. It occurs as a result of an immune response to external stimuli, often pathogenic microorganisms. It is important to carry out adequate treatment in a timely manner, identify and eliminate the causes. If the disease is not treated, it can become chronic and negatively affect the health of teeth and respiratory organs. A common complication after stomatitis is the addition of a secondary infection.
Reasons for development
Stomatitis often occurs in people with reduced immunity and impaired microflora. If these 2 conditions are observed simultaneously, then even opportunistic microorganisms can cause severe inflammatory processes. Many other factors also influence the development of the disease.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur in the following cases:
- mechanical, chemical, thermal injuries - hot burn, injury from solid food, cheek bite, etc. leads to tissue damage, penetration and spread of infection;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, especially C, group B, minerals - zinc, iron and others;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, eating unwashed fresh berries, vegetables, fruits, dirty hands while eating;
- treatment with medications that reduce salivation, antibiotics that destroy beneficial microflora, and a number of other medications;
- Frequent brushing of teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate leads to a decrease in saliva secretion and dry mucous membranes, which become more susceptible to aggressive substances;
- poor-quality prosthetics and dental treatment due to which the gums are constantly injured;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- dehydration with prolonged diarrhea, vomiting.
Stomatitis often occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal imbalance. At risk are patients with diseases of the heart, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, pathologies of the immune and endocrine systems, and those with helminthic infestation. In diabetes mellitus, the aphthous form is diagnosed. People who use hormone inhalers to relieve asthma attacks suffer from candidiasis.
To answer the question whether stomatitis is contagious or not, differential diagnosis is necessary. Bacteria, viruses, and Candida fungi can be transmitted from person to person. The most contagious is the viral form of the pathology. However, with good immunity, the infection will not necessarily develop. It is also important how stomatitis is transmitted. If this is direct contact, for example a kiss, then the risk of getting sick is higher.
Medicines for inflammation of gums and teeth
Antibacterial drugs are effective against inflammatory processes of tooth roots and gumboils. These are purulent diseases in the subnaosteal or subgingival part. They appear in the form of purulent sacs on the gums. Incorrect and untimely treatment leads to surgical intervention.
The main reasons for the appearance:
- jaw injury;
- complication after improper treatment of pulpitis and tooth extraction;
- consequences of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- mechanical damage to gingival tissue;
- advanced forms of caries;
- inflammation of gum pockets;
- hypothermia.
Fluxes come in different types: ossifying, ordinary, serous-albumic, purulent, fibrous. They are manifested by symptoms such as general weakness, fever, severe toothache radiating to the temple, swelling, pathological mobility of teeth, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, redness in the localized area.
An antibiotic for toothache that has developed as a result of gumboil helps at the initial stage of the disease. Medicines relieve symptoms. Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
The operation is prescribed in advanced cases. The abscess is opened under local anesthesia, cleansing is carried out, and drainage is installed to release residual purulent masses. After surgery, the patient will have to take antibacterial drugs prescribed by the dentist.
Therapeutic treatment with antibiotics has a cumulative effect, so it is important to follow the dosage and not stop taking it prematurely. The choice of means depends on the cause of inflammation, the age of the patient, the characteristics of the disease and the degree of its neglect.
You can use drugs such as Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Azithromycin, Citrolet, Clindamycin, Trichopolum, Biseptol.
The drugs are prescribed taking into account contraindications and individual tolerance. To avoid microbial resistance of the body, use for more than 10 days is contraindicated.
In childhood, flux is rare, but leads to serious consequences due to the accelerated spread of infection in the body. At the slightest sign of suppuration, you should immediately contact a specialist. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the source of the inflammatory process and generally strengthening the body and immune system.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms depend on the type of pathology, but there are common clinical manifestations. As a rule, the disease does not begin acutely. The mucous membranes become red, swelling, pain, and a burning sensation appear in the affected area. You can see what stomatitis looks like in the photo.
If it is a bacterial infection, then after a day an ulcer appears at the site of infection with a red halo radiating from the center. The ulcer is covered with a white coating. During this period, salivation increases and an unpleasant odor appears. Pain bothers the patient not only when eating, but also at rest.
Pimples and ulcers appear anywhere in the oral cavity; in severe cases, stomatitis develops in the throat. Stomatitis on the tongue is especially painful, since there are many nerve endings there. Some types are characterized by bleeding gums.
With further development of the pathology, the temperature may rise, the lymph nodes may enlarge, and symptoms of intoxication may appear - weakness, nausea, lack of appetite.
How to recognize the disease
It is not difficult to understand that discomfort in the mouth is associated with stomatitis. At first, mild swelling appears. In certain places, the mucous membranes become red and more shiny. Afterwards, zones covered with plaque form on their surface. Then the person begins to feel severe itching and burning.
Gradually, painful lesions turn into ulcers (aphthae) and oval or round wounds. Most often they are located on the palate, under the tongue, on the inner surface of the lips and cheeks. Due to aphthae, normal eating becomes impossible - when trying to eat something solid, a person experiences acute pain.
Types of stomatitis
The disease has a broad classification, which includes the nature of the course, the cause of its occurrence, and the features of the clinical picture.
Pathology can be acute or chronic. If the symptoms are pronounced, there is swelling, redness, pain, ulcers, bleeding - this is acute stomatitis. How long this phase lasts depends on the form of the disease. Usually the duration of the acute period does not exceed two weeks.
If the disease is not treated, remission occurs or the inflammatory process becomes chronic. In the chronic form, the symptoms are mild, and the disease can be detected only during periods of exacerbation.
Drug-induced stomatitis
With increased sensitivity and intolerance to drug components, characteristic symptoms of the disease appear: blisters, erosions, swelling, redness of the pharynx, tongue, palate, burning, dense white coating. The list of medications that cause inflammation of the mucous membranes often includes antibiotics, iodine, barbiturates, novocaine, and sulfonamides.
Traumatic stomatitis
Inflammatory processes develop against the background of tissue injury from objects, chemicals, hot food, etc. Stomatitis on the gums usually occurs due to injury from the uneven edge of a tooth or prosthesis. Bacteria penetrate the wound and it becomes inflamed. Symptoms of catarrhal form are characteristic.
Bacterial stomatitis
Occurs when mucous membranes are damaged by staphylococci and streptococci. It is characterized by the appearance of pustules, which, when opened, transform into erosive foci.
Aphthous stomatitis
It may manifest itself acutely or have mild symptoms. Small spots up to 5 mm of round shape appear - aphthae with clearly defined boundaries, covered with a grayish coating. The spots can be single or multiple. In acute cases, body temperature rises and lymph nodes enlarge. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, reduced immunity, autoimmune pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the large intestine. In the chronic form, it manifests itself asymptomatically; sluggish symptoms are observed during exacerbation.
Catarrhal stomatitis
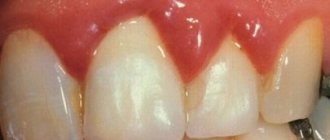
Diagnosed more often than other forms. It is characterized by mild symptoms: redness, swelling, bleeding gums. Occurs due to poor oral hygiene, decreased immunity, and injuries. It can be a complication of other diseases - influenza, pathologies of the digestive system, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, endocrine disorders.
Radiation stomatitis
It is the first symptom of radiation sickness. It is characterized by severe dry mouth, pinpoint hemorrhages on the mucous membranes and under the tissues, expansion of periodontal pockets, swelling of the tongue, gums, and palate. Advanced stomatitis of this form is manifested by necrotic foci, strong bad breath, dirty saliva with bloody streaks. Even after treatment, relapses may occur. Scars remain in place of the injured tissue.
Ulcerative stomatitis
It is the next stage after the catarrhal type. Symptoms intensify, ulcers appear, thick plaque, severe pain. Lymph nodes enlarge, and the concentration of leukocytes in the blood increases. At risk are patients with gastrointestinal diseases.
Candidal stomatitis
Fungal infections almost always have a long course. With thrush, a white dense coating appears on the cheeks, tongue, and lips, accompanied by hyperemia and cyanosis of the mucous membranes. In the fugonous form, severe swelling, erosion, and foamy plaque are observed. There is also angular stomatitis, in which fungi affect the corners of the lips (jams). Stomatitis on the lip can be fungal or viral.
Herpetic stomatitis
Develops due to the activity of the herpes virus. Blistering rashes with clear liquid can be seen in the mouth and lips. After the bubbles burst, erosions appear in their place.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/puti-sovershenstvovaniya-pervichnoy-profilaktiki-zabolevaniy-parodonta Acute herpetic stomatitis in children, Baranaeva E.A. Merkulova E.P. magazine "Medicine and Healthcare"
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/osobennosti-protivoretsidivnogo-lecheniya-allergicheskogo-stomatita Acute stomatitis in children, Drobotko L.N., Strakhova S.Yu.
How to treat the disease
Therapy involves the use of local and sometimes systemic drugs. The treatment regimen for the disease depends on what type of stomatitis is diagnosed. For this reason, you should not self-medicate, as it may turn out to be useless and the pathology will continue to develop into dangerous conditions.
The exception is mild catarrhal inflammation associated with poor hygiene. It is enough to exclude the cause and rinse your mouth with antiseptics for several days.
Treatment at home for other types should be discussed with your doctor. The use of folk remedies is not contraindicated, but they can only be used as a supplement to the main therapy. Only a dentist can evaluate the appropriateness and harmlessness of a particular prescription.
Effective drugs for adults
To relieve inflammatory processes, combat pathogenic microflora, and relieve pain, rinses, gels, sprays, lozenges, and ointments are prescribed. For severe pain, pain medications can be taken orally. Since treatment must be carried out regularly, it is important to choose a medicine for stomatitis that will be convenient to carry in your purse and use at work.
Popular medicines:
- Chlorophyllipt, Inhalipt, which have an antiseptic effect. Available in the form of sprays. Apply up to 5 times a day for one week. Sprays are convenient to use if there is stomatitis in the palate or throat.
- Solcoseryl accelerates tissue regeneration, restores mucous membranes, and protects against the development of ulcers. The gel is applied several times a day. The course is from 7 to 14 days.
- Cholisal has a detrimental effect on bacteria, relieves inflammation, and improves tissue healing. The gel is used three times a day for at least a week. An analogue of the drug is Kamistad. Excellent help with aphthous, bacterial form of the disease.
- Viferon, Acyclovir are prescribed to patients with a viral infection. Ointment for stomatitis in the mouth is applied to areas of inflammation several times a day. The course of therapy is up to 2 weeks.
- Lidocaine Asept, Lidochlor are used for any form of pathology, since the main purpose is to relieve acute pain. Available in spray form. Can be used up to four times a day, no more than 1 week.
- Lugol kills bacteria, treats ulcers, and relieves inflammatory processes. The oral cavity is treated with a spray 2 - 3 times a day.
- Miconazole and Nystatin are prescribed for fungal infections. In severe cases of the disease, the ointment is used in combination with systemic medications. Apply to affected areas 2 to 4 times a day.
Any medication for stomatitis must be prescribed by a doctor. The symptoms of the varieties of the disease are similar and it is impossible to independently understand the cause of the inflammatory reactions.
What can you rinse your mouth with?
To treat pathology, you can use pharmaceutical drugs aimed at destroying bacteria, reducing inflammation and healing tissue.
Medicinal solutions that can be bought at the pharmacy:
- Aqualor with sea salt;
- Stomatofit, Dr. Theiss Sage based on sage;
- Romazulan with chamomile extract;
- Chlorhexidine (pre-diluted with water).
Decoctions and infusions for rinsing are easy to prepare at home from chamomile, calendula, aloe juice, sea buckthorn, linden flowers and other medicinal plants. A solution of salt and soda helps a lot.
Commonly used drugs for inflammation
In dentistry, several types of antibiotics are used for toothache and inflammation.
- Penicillin group. Prescribed at any age, with minimal side effects and easy tolerability. The main use is for periodontal inflammation. Effective against anaerobic bacteria.
- Cephalospoirins. They are used when it is necessary to perform dental manipulation with the risk of injury, as well as during periodontal and odontogenic inflammatory processes.
- Tetracyclines. Relieves swelling in the area of bone and soft tissue.
- Imidazole and derivatives. They have a depressing effect on pathogenic microorganisms and quickly penetrate bone tissue. Recommended for extensive inflammatory lesions.
- Macrolides. Used during pregnancy and allergies to drugs of the penicillin group. Eliminates gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
- Lincosamides. Do not cause allergies. Used for severe bone tissue infections.
The prescription of osteotropic antibiotics is combined if the tests reveal different types of pathogenic microbes.
Prevention
In the oral cavity of any person there is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, which can be activated when immunity decreases. For this reason, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, and treat illnesses.
Hygiene rules must be observed. Do not eat dirty vegetables, wash your hands before eating, and replace your toothbrushes regularly.
For persons predisposed to the disease, any trauma to the oral mucosa should be excluded. Do not eat scalding, hard foods or spicy seasonings. If a wound appears, you should immediately treat it with an antiseptic.
It is imperative to carry out timely treatment of dental and ENT diseases. Chronic diseases and advanced caries are sources of infection.
Side effects and contraindications
Despite the fact that the antibiotic has proven itself well for toothache and inflammation, its use is contraindicated in case of kidney and liver pathologies, diabetes mellitus, and taking certain medications. Prescribed with caution to children, elderly patients, and pregnant women.
Possible side effects:
- dermatitis, urticaria, skin rashes and other allergic reactions;
- diarrhea, nausea;
- kidney and liver damage;
- headache;
- anemia;
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes.
Dental antibiotics are an irreplaceable thing. The drugs prevent a serious complication, but subject to the right choice and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
Author: Zhukov M.A.
Diagnostic methods
The treatment is carried out by a dentist-therapist. Diagnosis begins with an examination and a detailed survey: the doctor will find out what medications you have taken recently, and whether there are any chronic or infectious diseases. A cytological examination of plaque taken from the mucosa is mandatory. This is important because a buildup of non-fungal flora can easily be confused with a fungal infection.
The scraping is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach; there is no need to brush your teeth before the procedure. The day before, it is important to avoid eating foods rich in carbohydrates so as not to provoke the growth of pathogenic flora. Research allows not only to accurately determine the causative agent and type of Candida fungus, but also to find out the sensitivity of fungi to the main antifungal drugs. Based on the test results, the doctor will determine the fungus in the oral cavity and prescribe medication.