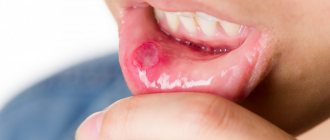
Many adults experience such a symptom as gum inflammation. It is characterized by bad breath, redness of the gums and bleeding. A good effect in the case of this disease is provided by complex treatment prescribed by a periodontist. The specialist may recommend topical medications and, if necessary, prescribe oral antibacterial agents or physical therapy.
As local therapy for gum inflammation, medications containing antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and analgesic substances are usually prescribed. They can be used in the form of rinses, irrigations, and applications. Let's talk about the most famous medications for gum inflammation.
Rating of the top 10 drugs for gum inflammation in adults according to KP
Angidak solution
Angidak.
Photo: Grotex A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that has an analgesic effect. It has antiseptic, specific antimicrobial and antifungal effects.
When applied topically, the drug quickly penetrates into inflamed tissues, so a few minutes are enough for the effect to occur. Available without a prescription. Indicated for inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, including gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease
Contraindicated in children under 12 years of age (for this dosage form), pregnant and lactating women. Made in Russia.
show more
Stomatidin solution
Stomatidin. Photo: Bosnalijek
The medicine has an antimicrobial and antibacterial effect, adheres well - it literally sticks to the mucous membrane and is practically not absorbed. After a single rinse, it is present on the oral mucosa for another 65 hours.
The drug has a disinfecting and hemostatic effect. Stomatidin helps cope with any infectious and inflammatory diseases of the mouth and pharynx. It is indicated for gingivitis and bleeding gums.
Contraindicated in children under 5 years of age and pregnant women from 1 to 3 months of pregnancy.
Country of origin: Bosnia and Herzegovina.
show more
Good to know
Gum inflammation: how to relieve it at home
Metrogil–Denta
Metrogil–Denta. Photo: Unique Pharmaceuticals
The gel contains the antibacterial agent metronidazole and chlorhexidine, an antiseptic. Metrogil-denta fights inflammation and pain in the gums, helps reduce the sensitivity of the affected areas of the gums.
The drug is used in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the periodontium and oral mucosa. Approved for use by adults and children over 6 years of age.
Made in India.
Cholisal gel
Holisal.
Photo: market.yandex.ru Local anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and analgesic agent. The main active ingredient is Choline salicylate, it inhibits the development of the inflammatory reaction and has a local antipyretic and antifungal effect.
Cholisal does not contain sugar, and the gel base allows it to remain on the mucous membrane for a long time. Cholisal is used for diseases accompanied by inflammation and pain.
Should be used with caution by pregnant, lactating women and children under 1 year of age. Made in Poland.
show more
Dentamet gel
Dentamet gel. Photo: Altaivitamins
Dental gel containing metronidazole and chlorhexidine. A combined antimicrobial, disinfectant and anti-inflammatory agent is used to treat acute and chronic diseases of the oral cavity. For therapeutic purposes, it is applied to the gums, and for prevention, a small amount of gel is added to toothpaste. Indicated for gingivitis, periodontitis and other diseases of the teeth and gums.
Contraindicated in children under 6 years of age and pregnant women in the first trimester.
Produced in Russia.
show more
Kamistad gel
Kamistad gel. Photo: STADA
Thanks to the included ingredients, lidocaine and chamomile flower extract, it has a local anesthetic effect for gum inflammation.
The gel is indicated for stomatitis, gingivitis and pain due to gum inflammation. Contraindicated in children under 12 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Kamistad gel is available without a doctor's prescription.
The product was made in Germany.
Dental adhesive paste Solcoseryl
Solcoseryl Dent dental adhesive paste. Photo: Legacy Pharmaceuticals
Stimulator of tissue regeneration. Solcoseryl improves the transport of oxygen and glucose to inflamed cells. Accelerates healing of wound surfaces, ulcers and erosions of the oral cavity. If the oral mucosa is infected, it is recommended to first treat the inflamed area with medication. It is prescribed for gingivitis, periodontal diseases, after removing tartar and more.
There are no contraindications for using the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding; the only contraindication is individual sensitivity to any of the components.
When prescribing Solcoseryl and medicinal rinses simultaneously, the paste should be applied after rinsing the mouth.
Made in Switzerland.
Spray Stomatofit expert
Stomatophyte. Photo: Fitofarm Klenka
The spray is a dark brown liquid that contains extracts of calamus, arnica, oak, mint, chamomile, thyme and sage. Combined drug with anti-inflammatory, astringent, antiseptic effect. Unlike other drugs in the line, the Stomatofit expert aerosol reduces bleeding gums; it is indicated for stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease. Contraindicated for children under 12 years of age.
Made in Poland.
Mestamidine aerosol
Mestamidine. Photo: Grotex
A product consisting of two antiseptics: octenisept and phenoxyethanol. These substances have antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and anesthetic effects. Mestamidine sanitizes and heals wound surfaces on mucous membranes and skin.
It has no toxic effect and is not addictive. Mestamidine is contraindicated in people with hypersensitivity to the ingredients.
Made in Russia.
show more
Propolis tincture
Propolis tincture. Photo: Bagrif
Propolis is a waste product of bees that contains wax, essential oils, a mixture of resins, cinnamic acid derivatives, flavones and other biogenic compounds.
Propolis has an anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect on gram-positive flora, enhances the regeneration of damaged tissues and normalizes metabolic processes in the body.
For damaged and inflamed gums, an aqueous solution of propolis tincture (15 ml of tincture per 1/2 cup of warm water) is used as a mouth rinse. The product is available without a doctor's prescription and is contraindicated for children under 18 years of age and pregnant and lactating women.
Made in Russia.
show more
When is antibiotic treatment necessary in dentistry?
Most often, antibiotic therapy is prescribed in maxillofacial surgery - as a prophylaxis before surgery and to minimize the risk of complications after it. In dental clinics in Moscow it is indicated for patients:
- with catarrhal gingivitis;
- with periodontitis, in which there is a need for treatment of a dental cyst;
- with advanced periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- with periostitis and osteomyelitis;
- after a complex tooth extraction.
Since the bacterial microflora of the oral cavity is mixed, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action are prescribed to treat inflammation.
How to choose medications for gum disease in adults
Medicines for gum inflammation and the duration of their use can only be recommended by a periodontist based on an examination of a particular patient.
In the early stages of the disease, professional cleaning and the use of topical antiseptics may be sufficient to relieve symptoms. Metronidazole tablets are also sometimes used. To improve regeneration, local use of Solcoseryl, a propolis solution, may be indicated.
If gum inflammation has spread throughout the oral cavity, the patient feels unwell, and a general blood test shows signs of inflammation, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Immunostimulants, vitamins and agents for restoring microflora are also used.
Popular questions and answers
dentist Venera Sultanova, answered popular questions about the treatment of gum inflammation .
Why does gum inflammation occur?
The most common reason is irregular oral hygiene.
Because of this, dental plaque thickens, conditions are created for the growth of pathological microflora, the active activity of which leads to inflammation of periodontal tissue. In some cases, it is enough not to perform oral hygiene for several days for the plaque to harden. Increasingly, the cause of gum inflammation is a weakened immune system, which suffers during cold and flu seasons and due to the current pandemic.
The most important thing is to prevent the inflammation process from becoming chronic, as this leads to the destruction of periodontal tissue, and the focus of chronic inflammation in the body can provoke:
● necrosis of periodontal tissues; ● high blood pressure; ● risk of cardiovascular complications; ● increased levels of glucose, cholesterol, C-reactive protein; ● indigestion.
Is it possible to treat gum disease with folk remedies?
It's possible, but not necessary.
Self-medication and the use of only folk remedies can aggravate the disease, after which the person will not only lose his teeth, but also his health in general. The inflammatory process deepens and is more difficult to treat. To prevent inflammation of the oral cavity, you can use decoctions of oak bark, sage and calendula herbs, aloe juice and salt rinses. But if you already have gum disease, then folk remedies as an auxiliary treatment must be combined with medication and mandatory professional cleaning.
When to see a doctor if you have gum disease?
Any feeling of discomfort, swelling, redness or bleeding of the gums is a reason to once again contact your dentist for advice. If you regularly visit the dentist, if your doctor listens to you carefully and carries out treatment carefully and conscientiously, then you will not face inflammation of the gums and other diseases of the oral cavity.
Inflammation of a wisdom tooth
The most problematic for most people are the third molars of the lower dentition, which are commonly called “wisdom teeth.” The upper “eights” relatively rarely become a source of serious problems, but the lower ones are a real headache not only for people, but also for dentists. Their correct treatment or removal requires the doctor to have a lot of experience, skill and, to some extent, wisdom, which once again confirms the accuracy of the popular name for eights.
Lower third molars: history of the problem
Why are the third lower molars so problematic, why does inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth occur in almost every second inhabitant of the planet? This is our payment for a comfortable lifestyle, in particular, for changed eating habits. Modern food is very different from what our ancestors ate even a few hundred years ago. Heat treatment made the food soft, making long chewing unnecessary. Children often swallow food without chewing it properly.
What is the result? As a result, the lower jaw does less work, and for the body this becomes a signal that its development can be slowed down, because there is no need for a massive mandibular bone. As a result, it becomes smaller than nature intended. The number eight, which is the last to erupt, has no room left for normal growth and development. Hence the typical problems - retention, dystopia, gum inflammation, almost inevitable pain during teething.
Alarming symptoms
The eruption of the figure eight is often accompanied by pain. But what exactly does a person hurt? Dental tissue, gums near the wisdom tooth, bone tissue of the lower jaw? Or do neighboring elements of the dentition hurt, on which the problematic third molar puts pressure?
The gums near the wisdom tooth hurt. The area of gum that covers the third molar has its own name. It is commonly called the gingival hood. Very often the molar cannot overcome the resistance of the hood and a problem arises. The wisdom tooth does not fully erupt (in this case it is called impacted), and the gums above it become inflamed. Inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth is called pericoronitis.
Pain is the first and main symptom of inflammation, but it is far from the only one. In many patients, the gums become swollen, and along with it, the nearby soft tissues of the cheek swell. As a result, the entire middle third of the face on the side of inflammation becomes swollen. Pain often occurs when swallowing and chewing food.
Redness of the gums is another clinical sign that unmistakably indicates the development of an inflammatory process. If you wait too long to seek help from a specialist, purulent inflammation develops, which indicates an infection. Discharge of pus from under the gingival hood and bad breath are symptoms of a purulent-inflammatory process. In the future, the infection can spread to neighboring tissues, including the jawbone.
Treatment Options
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, it is better to immediately contact the nearest dental clinic or medical center where you will receive the necessary assistance. The first step should be x-ray diagnosis. If your dentist plans to treat you without an x-ray, consult another specialist.
An x-ray will show exactly how the third molar is growing and erupting. If it grows at an angle in the direction of the second molar, if it “lies” and literally crashes into the adjacent element of the dentition, it needs to be removed. Otherwise, there is a high probability of developing malocclusion, destruction of enamel and carious lesions of the second molar, as well as other problems with the lower dentition and the dental system as a whole.
It should be said that the situation described above with dystopia (abnormal position and direction of growth) is not uncommon. Dystopia of the figure eight occurs very often. If left unattended, sooner or later it will lead to other more serious problems requiring expensive, lengthy and tedious dental treatment.
Is it possible to do without deletion? Certainly. If the molar is growing in the right direction and is not pressing on its neighbor, there is no need for extraction. In this case, the dentist will choose the following algorithm of actions:
- Prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers and antihistamines to reduce gum swelling.
- The area of gum above the figure eight is removed to facilitate its eruption. Important! Removal is possible only if there is no infection.
- With the development of a purulent-inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed.
- In case of infection, the gingival hood is not removed, but dissected to improve the outflow of pus. After suppressing the pathogenic flora, gum excision is performed.
The cost of therapeutic treatment of gum inflammation near a wisdom tooth is low - about 2,500 rubles. Hood dissection is a painless procedure performed using local anesthetics. After a visit to the dentist, it is enough to follow his recommendations: take medications prescribed by the doctor, regularly rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions, apply dental gels with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects to the inflamed area of the gums.
Wisdom tooth removal
If the position and direction of growth are abnormal, removal of the third molar is indicated. Since it is a vestigial organ, its absence will not in any way affect the function of the dental system, while abnormal growth can lead to malocclusion and other serious problems.
Removing a wisdom tooth is a complex procedure. The figure eight has a powerful root system and is firmly anchored in the jaw bone. The roots are often curved, making the extraction process more difficult. However, dentists have an expression that a good doctor turns a complex extraction into an easy procedure for the patient, but an inexperienced dentist makes a simple extraction difficult and painful. It is very important to contact a qualified specialist!
The presence of a well-developed root system requires special preparation for removal. It involves drilling or crushing the area of bone that holds the roots. A good tactic is sawing the crown; fragments are much easier to remove than the entire tooth.
The cost of complex extraction of impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth varies from 6 to 12 thousand rubles. This price includes anesthesia benefits. The procedure is performed under conduction or infiltration anesthesia; most often, local anesthetics based on articaine (Ultracaine, Ubistezin) are used for these purposes. The extraction lasts 15-20 minutes, but if the doctor does not have the proper experience, the process can even take a couple of hours.
Is it painful to have a third molar removed? According to most patients, it is a little scary, but not painful at all. Psychological discomfort, of course, is present, but there is no pain. Patients who are terrified of dental procedures may be offered sedation or anesthesia, but this is extremely rarely necessary.
After removal
After the procedure, you must follow a few simple rules. First, you should abstain from eating for three or four hours. Smokers must abstain from smoking during this time. You can drink water within an hour and a half after the operation.
In the future, you need to eat soft food for one or two days. Food should not be hot or cold, ideally its temperature should be close to body temperature. Chew food on the healthy side to avoid washing out the blood clot. Formation of a blood clot in the socket is an important part of the healing process. To speed up the healing dynamics, ask your dentist to place one or two sutures on the gum above the hole before extraction. It doesn't hurt, but it's very effective.
Pain after removal cannot be completely avoided; it will make itself felt after the anesthetic wears off. Fortunately, postoperative pain is not severe and can be easily relieved with conventional analgesics. Doctors often prescribe Ketanov or its analogues in injection form to patients. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection; this is especially true in the presence of a purulent-inflammatory process.
Regular rinsing with antiseptic solutions will help suppress the vital activity of pathogenic microflora. Chlorhexidine, which is sold in any pharmacy, is well suited for these purposes. Gels or creams with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects should also be applied to the surface of the gums. Please note that you need to rinse your mouth carefully so as not to provoke the blood clot to be washed out of the hole. The procedure is more similar to baths than to the usual rinses.
The body temperature remains elevated after removal. A normal reaction to surgery is weakness and general malaise. There is no need to worry about minor bleeding from the wound. After three to five days, the condition returns to normal, the bleeding stops, and the pain no longer bothers you.
You can learn more about the treatment of inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth by consulting a medical dentist.