Inflammation of the lymph nodes near the ear is a common phenomenon, the causes of which can be very different. Lymph nodes are an integral part of the immune system and play the role of a biofilter. They take part in metabolic processes and protect the human body from microbes, thereby forming immunity. If the lymph nodes near the ears have changed in structure and density, pain is felt along with swelling, then this is a reason to seek medical help.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes
This phenomenon is very unpleasant. Inflammation of the lymph nodes near the ear appears, as a rule, as a result of the following reasons:
- In the presence of viral infectious diseases such as rubella, herpes, mumps or measles.
- The presence of a bacterial infection in the mouth and nasopharynx, for example, with bacterial pharyngitis, tonsillitis, periodontal disease, otitis media, and so on.
- Against the background of a fungal disease, for example, candidiasis, stomatitis.
- With neuritis of the auditory nerve.
- In the presence of cancer.
- In case of infection of the body with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Against the background of parasitic infections.
- For head or neck injuries.
Next, we will find out what symptoms accompany the pathology when the lymph nodes in the neck near the ear become inflamed.
The main symptoms of this unpleasant disease
The most common symptoms include the following:
- Lymph nodes behind the ear change density and structure.
- Presence of pain behind the ear.
- A “bump” is felt behind the ear upon palpation.
- The appearance of cyanosis in the area of the auricle, with severe pain in the points behind the ears.
- The lymph nodes under the ears are hyperemic and inflamed.
- Lymph nodes near the ears have a purple tint.
- The development of several pustules or a single abscess, while behind the ear it swells and is very painful.
- Temperature increase.
- Significant deterioration in general health.
- The presence of intoxication phenomena in the form of nausea, weakness, pale skin, etc.
So, the lymph node near the ear is inflamed, what should you do?
Causes and symptoms
Most often, a lump behind the ear is a symptom of a cyst, inflammation of the lymph nodes due to an advanced form of otitis media, fistula, lipoma or mumps. In children, neoplasms in the ear area appear during teething, oral diseases, and hypothermia. In adults, a lump behind the ear appears when the immune system is weakened, hyperhidrosis, hormonal imbalance, or furunculosis.
Induration associated with inflammation of the lymph nodes
If the lump has grown due to inflammation of the lymph nodes, then it is motionless, hard on the inside, and hyperemic on the outside. Children develop general weakness, lack of appetite, and fever. The clinical picture is complemented by a runny nose and stuffy ears due to inflammation of the postauricular lymph node as a result of otitis media.
Induration associated with tumor formation
Volumetric inflammation up to two centimeters in size, localized on the bone - most likely a fistula. It occurs in newborn babies and does not hurt when touched. Most often, atheroma or lipoma is formed. The seal is soft to the touch, does not move when palpated and gradually grows up to five centimeters. You can distinguish a cyst by the redness of the skin around it, mobility upon palpation, and the presence of free fluid inside.
Induration associated with ENT diseases
Sometimes an ENT doctor diagnoses lumps behind the ear that are caused by mastoiditis, an infection of the mastoid process. It occurs when there is inflammation of the middle ear or throat. The skin above the ear swells, the ear hurts, swells, headaches and tinnitus appear. This condition requires immediate medical attention, otherwise there is a risk of developing intracranial complications and hearing loss.
If the lump grows near or under the lobe, then it probably appears as a result of a sore throat, and the tonsillar lymph nodes become inflamed.
Induration associated with inflammation of the sebaceous glands
With heavy sweating, the sebaceous ducts behind the ear become inflamed. A lump forms and can be identified by strong redness and a white dot in the center of the lump. It is hot, and pain occurs as its size increases.
Treatment of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes
It is necessary to begin treatment for inflammation of the lymph nodes near the ear immediately from the moment the true causes are accurately established. In cases where the viral nature of the inflammation is confirmed, in the presence of acute respiratory diseases or in epidemic infections, patients are prescribed antiviral, and at the same time immunostimulating drugs in the form of “Immunoflazide”, “Anaferon”, “Amiksin”, “Novirin” and others. Therapy is supplemented with restorative medications of plant and synthetic origin, as well as vitamin complexes and dietary supplements.
In the case when the lymph node near the ear hurts and tests show the presence of bacteria and specific pathogens (based on the results of bacteriological culture), antibacterial therapy begins. Preference is given mainly to cephalosporin or penicillin antibiotics, for example, Amoxiclav, Ofloxacin, Ospamox, Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime, Zatsefu, Suprax and others. If the lymph node near the child’s ear becomes inflamed, then you can take the drug “Doccef”. This antibacterial agent can be taken orally (directly with food). Thanks to its use, you can avoid unpleasant injections.
Against the background of an allergy to this type of antibiotic, the lymph nodes near the ear (pictured) are treated with fluoroquinols, for example, Ciprofloxacin, Ciprolet, Norfloxacin, and so on. Such drugs are very effective in treating inflammation. But therapy begins only after consulting a doctor.
When it comes to sick lymph nodes near a child's ear, it is important to be especially careful.
If for some reason fluoroquinols cannot be used for the patient, then macrolides are prescribed. Natural macrolides include erythromycin, on the basis of which today drugs are produced in the form of “Spiramycin”, “Josamycin” and “Midecamycin”. Among the semi-synthetic drugs it is worth mentioning Azithromycin and Roxithromycin. Each macrolide affects a specific type of bacteria. The doctor decides which medication will be effective. The advantage of this group is the short-term use of drugs, due to the accumulation function in the body.
Tuberculosis infection and inflammation of the lymph nodes near the ear are treated with anti-tuberculosis drugs, which include Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol. Depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition, the doctor may prescribe the patient a combination of drugs with selective biochemical activity.
Therapy of the disease (treatment)
If inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear is a complication of diseases such as colds, flu, ear inflammation and the like, then eliminating the cause will quickly lead to the disappearance of the effect. The cured primary source of infection also normalizes the inflamed lymph node. It is also necessary to take into account: in order to reduce pain and eliminate other symptoms of inflammation of the lymph node, the use of thermal procedures is under no circumstances permissible. In order not to cause harm to health or have more serious consequences, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
When treating an acute form of inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes, broad-spectrum antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs, antiallergic drugs and means for general strengthening of the body are prescribed. Anesthetics and analgesics are used to reduce pain. To reduce the degree of swelling, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated.
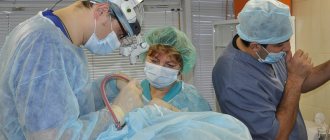
If a doctor identifies a case of acute purulent lymphadenitis, which is complicated by phlegmonous or necrotic processes, antibiotics are also prescribed and the abscesses are opened. Then drug treatment of inflammation is carried out.
Homeopathy for inflammation in the lymph nodes
In uncomplicated cases, when pain and swelling appear behind the ear, homeopathic preparations, which are made from plants with therapeutic characteristics, can also come to the rescue. The advantage of these drugs is their mild effect. It is important to understand here that antibiotic therapy is considered the basis for the treatment of inflamed lymph nodes behind the ears, homeopathy is only a component of it.
When the lymph nodes behind the ears become inflamed, you can take a homeopathic remedy called Guna Lympho. The detoxifying property of this drug eliminates inflammation of the lymph nodes near the ears, soothes, heals the epithelium, and enhances the outflow of toxic components from the intercellular environment. This medicine relieves muscle spasms.
An equally popular homeopathic remedy for the treatment of lymph nodes near the ears is Lymphomyosot. This phytotherapeutic composition produces a detoxification, decongestant and lymphatic drainage effect. Thanks to its intake, lymphatic drainage improves, metabolism is stimulated, and the barrier functions of the lymph nodes are strengthened.
Taking homeopathic medicines helps to increase the degree of penetration of medications from other groups into the affected areas, which makes it possible to adjust their dosage and thereby reduce the toxicity of treatment. The choice of a particular medical drug should be approached with special responsibility; its advantages and disadvantages must be taken into account. The latter may include nephrotoxicity, a tendency to provoke allergies, the individual characteristics of the body to take a particular drug, and so on.
How else to treat lymph nodes near the ear?
Causes of the inflammatory process in the parotid lymph node
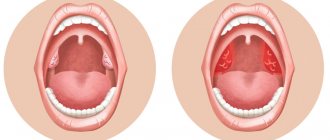
There are about six hundred lymph nodes in the human body. Each of them is a rounded formation 0.5-50 mm. In most cases they form groups. Lymph from there is sent to regional nodes.
The parotid lymph nodes are located along the posterior auricular vein. When a person is healthy, they are soft and cannot be felt. But when a focus of inflammation appears, they become larger, denser, and are easy to palpate. Most often, this is how lymph nodes react to a disease of a nearby organ. First of all, it is provoked by inflammation of the ear, a boil in the external auditory canal, congestion in the ear, and neuritis of the auditory nerve. Secondly, the area of inflammation is the mouth and throat: caries, periostitis, sore throat, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat, salivary glands and tonsils. In some cases, the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ear is ARVI with rhinitis, mumps and rubella. In the case when the lymph node has enlarged due to the action of one of the listed factors, but does not hurt or fester, doctors diagnose “local lymphadenopathy” - this is the reaction of the lymph system to an infection in a certain disease.
When there is excessive inflammation of the lymph node, swelling and pain, the diagnosis is “lymphadenitis”. And this is inflammation of the lymph node itself, the cause of which is its damage by infected cells from other foci. In this case, there may be a significant increase in body temperature and suppuration in the lymph node area.
The system of human lymph nodes in the neck and head (including behind the ear)
Treatment with topical anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease include heparin ointment and Dimexide. Heparin ointment is used when the lymph node behind the ear becomes inflamed. It relieves any inflammation very well, eliminating swelling, improving lymphatic drainage and accelerating the metabolic process in the affected tissues. Thanks to the use of this remedy, the formation of blood clots is prevented, and, in addition, superficial vessels dilate. If the lymph node behind the ear cannot be cured for a long period, then the use of this ointment will speed up the regeneration processes. It should be borne in mind that heparin ointment is not used in case of reduced blood clotting, and, in addition, in case of tissue necrosis.
"Dimexide", which is used in complex therapy in the form of an aqueous solution, can accelerate regeneration, removing swelling of the lymph node on the cheek near the ear. Its pronounced anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anesthetic properties allow it to be successfully used in this pathology.
How to use Dimexide? A napkin soaked in the solution is applied to the affected area. This procedure must be performed at room temperature. The same applies to the temperature of the solution. Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures related to warming up and wrapping the affected area is strictly prohibited.
Manifestations (symptoms)
The most important manifestation of inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear is an increased size and painful palpation, which radiates to the ear and to the area under the jaw. In many cases, there is hyperemia and swelling slightly above the node.
But in the case of lymphadenitis, which enters the stage of suppuration, the patient complains of a painful “bump” behind the ear, general weakness, severe headache, body temperature from +37°C to +38°C, decreased appetite, and sleep disturbances. In some cases, pustular rashes appear in the area of the lymph node.
If there is a purulent process that affects the lymph node, the patient experiences continuous and very severe shooting or throbbing pain. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor for consultation, diagnosis and appropriate therapy.
According to doctors, any inflammation in the head area can cause death. In this case, one should not hesitate, because if treatment for purulent lymphadenitis is not started on time, it can lead to general blood infection or (in a less dangerous situation) to purulent melting of the lymph node tissue with transfer to the surrounding fatty tissue.
Treatment of this pathology with traditional methods
Medicinal herbs help speed up the regeneration of diseased lymph nodes near the ear. With this pathology, pine shoots are very effective. People use them to prepare a healing and very tasty medicine. To do this, take light-colored pine shoots and place them to the top in a liter jar, and then pour in 0.5 liters of water and 0.5 tbsp. Sahara. Boil the product for two hours. After this, the broth is filtered. When the medicinal drug is ready, it should be taken daily, twice a day after meals, one spoon. Treatment should be long-term, up to six to eight weeks. You can conduct courses of therapy with a break of ten days.
Common hazel has general strengthening and anti-inflammatory properties. The leaves with the bark of the plant are usually brewed as tea and consumed three times a day, 100 milliliters before meals.
St. John's wort, yarrow, walnut leaves and mistletoe have similar properties. In order to prepare a decoction, take one spoon of dry herb (any of the above plants) and fill it with water, bringing to a boil and boiling for five minutes. The cooled broth is filtered and used to soak medicinal compresses. The compress can be applied at night for two weeks, while avoiding overheating.
A decoction for compresses made from onion and tar is a powerful decongestant. This combination improves the epithelization process, restoring metabolic processes in the lymph. To make it you will need onions and pharmaceutical tar. The onion, baked for twenty minutes, is crushed until smooth, after which a tablespoon of tar is added. The resulting mass is applied to the area of the inflamed lymph node overnight. For compresses, you should choose natural and breathable fabrics or use medical cotton wool; a bandage is also suitable. An alcoholic tincture of Echinacea can also be included in the therapy complex as a general tonic. It can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes always require special attention and the selection of an effective treatment option. An advanced disease threatens the development of sepsis, lymphadenitis and other dangerous manifestations. A person’s caring attitude towards himself and his health will make it possible to avoid possible complications.
Diagnosis
As was said, the lymph nodes behind the ear and in the neck tend to enlarge in the case of any acute respiratory viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, as well as inflammation of the organs of the ear, nose and throat. This explains the importance of medical history data (details of the disease, previous diagnoses, etc.).
Lymph nodes may not enlarge very much - reaching the size of a pea. And there are also such as walnuts. But in all cases, when making a diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully examine the lymph node and palpate it to determine not only the size, but also the degree of pain. It is also necessary to examine the lymph nodes in the back of the head and neck. In addition, the glands located nearby are subject to examination: salivary, tonsils, lacrimal, thyroid. In some cases of inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes, data from a patient interview and examination by a doctor are sufficient to make a diagnosis and determine treatment methods.
In such cases, therapy for the underlying disease that caused the lymphadenopathy ensures normalization of the size of the lymph node. But if the antibacterial agents prescribed by the doctor did not give the desired effect, and the inflammatory process behind the ear did not stop, the node increased to 3-4 centimeters, hardened, the inflammation spread to the tissues in the immediate vicinity of it, a general blood test is necessary. The degree of damage is determined by the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the level of leukocytes.
When the results of a blood test are unsatisfactory, the treating physician will order an x-ray, ultrasound, or computed tomography. This is important because inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes can be a manifestation of lymphoma (primary malignant tumor) or metastases to the nodes. Therefore, the doctor may refer you for additional consultation to oncologists and prescribe a biopsy.
Carrying out prevention
After successful treatment of the lymph nodes in the neck near the ear, it is necessary to treat the wounds with care and avoid infection. If an infection occurs, it must be treated immediately. Any ulcers that appear must be opened and disinfected. But one should not think that abscesses can be opened independently. This should only be done in medical institutions. Even squeezing out acne is prohibited, as there is a danger of causing an infection that can spread throughout the body and cause inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Personal hygiene as a means of preventing this pathology
We also must not forget that we must maintain personal hygiene, which largely protects the human body from infection. You should not come into contact with infectious patients, and if this happens, then measures should be taken to stop the disease, for example, taking antiviral medications. If wounds or scratches appear on the skin, they must be treated promptly with antiseptics. This will be the best prevention of lymphadenitis.
Among other things, you shouldn’t get too cold and walk around in the cold season without a hat and scarf. It is hypothermia that can provoke a condition in which the lymph node near the ear becomes inflamed. We have considered what to do in this case.