At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza you can:
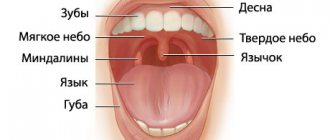
- quickly and efficiently examine the condition of the tonsils (perform pharyngoscopy, laboratory tests - bacteriological, immunological, etc.);
- decide on the choice of effective treatment for tonsillitis (inflammation of the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils): conservative - general and local, surgical.
We use the following methods of low-traumatic surgical treatment:
- tonsillotomy - partial removal of tonsils (tonsils) in children while maintaining their protective functions (all operations are performed under anesthesia);
- tonsillectomy - a low-traumatic operation to remove the tonsils;
- suturing wounds and using a bipolar coagulator to prevent blood loss;
- the use of innovations that accelerate and facilitate the healing process.
Timely diagnosed tonsillitis has a positive prognosis with conservative treatment without transition to the chronic stage. Radical treatment of chronic tonsillitis - tonsillectomy - prevents the development of systemic complications, often leading to disability.
Causes and complications
Tonsillitis occurs for many reasons, the main of which are bacteria and viruses that tend to infect the tonsils: Epstein-Barr virus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, less often - pneumococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, herpes virus, etc. or mixed microflora. Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- hypothermia due to a depressed immune system;
- avitaminosis;
- tonsil injury;
- chronic inflammation of the sinuses and oral cavity: sinusitis, caries, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- allergies.
Tonsillitis occurs in acute (angina) and chronic forms. The chronic form of the disease, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to serious complications from various systems and organs - joints, heart, blood vessels, kidneys, etc. This occurs due to an autoimmune reaction, which can be triggered by bacterial residues in the tonsils after acute tonsillitis that is not treated at home. The remaining bacteria support the inflammatory process, which becomes chronic. At the stage of decompensation of the disease, there is a threat of serious complications:
- paratonsillitis and paratonsillar abscess;
- systemic damage to blood vessels and connective tissues with the formation of rheumatic arthritis, etc.;
- glomerulonephritis;
- inflammatory processes in the myocardium, endocardium, which form heart defects;
- eye diseases with blurred vision;
- exacerbation of chronic pneumonia and other chronic diseases;
- complications on the liver and biliary system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- thyroid diseases.
Do not self-medicate to prevent the disease from becoming chronic and causing complications that are difficult to treat. Contact the ENT doctors of the Yauza Clinical Hospital if symptoms of acute tonsillitis appear.
Complications
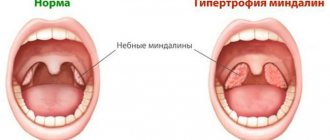
If inflammation of the tonsils becomes chronic, then exacerbations of the disease occur; 6-7 times a year. The presence of frequent exacerbations indicates a weakened immune response of the child’s body to the presence of infection in the tonsils. Inflammation of the tonsils often leads to the development of complications in the ears, lungs and other organs of the child. In the case of chronic inflammation, the tissue of the tonsils becomes scarred, lacunar plugs appear, and the lacunae themselves become foci for the spread of staphylococcal and streptococcal infections.
.
Symptoms of acute and chronic tonsillitis
Signs of acute tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, are characteristic and pronounced:
- sore throat when swallowing;
- redness and enlargement of the tonsils;
- enlargement of the submandibular and/or cervical lymph nodes;
- temperature rise above 38 degrees;
- the appearance of plaque on the tonsils, the accumulation of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- headache;
- general weakness.
A characteristic sign of chronic tonsillitis is a constant low-grade body temperature (37.1-38.0 °C) with an increase in the evening. Sometimes small ulcers appear on the tonsils and spread to the oral cavity.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils in the throat of a child is characterized by the appearance of the following clinical symptoms:
- discomfort in the throat: pain, soreness, rawness;
- increased body temperature (up to 37-38° C);
- appearance of cough;
- sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat (due to plugs formed on the tonsils);
- general weakness and fatigue, headache;
- white plaque on the tonsils.
Depending on the type and stage of inflammation of the tonsils, the clinical picture may be supplemented by enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, redness and swelling of the palatine arches, and the appearance of purulent plugs on the tonsils with a specific unpleasant odor.
.
Survey
In the department of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) of the hospital, patients with a chronic form of the disease are examined using:
- pharyngoscopy (visual method);
- PCR diagnostics - a high-precision method of molecular genetic diagnosis of infectious diseases;
- bacteriological tests - diagnosis of the main agent of infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- antigen tests - diagnosis of immune system activity;
- general blood tests.
conclusions
1. The vessels of adenoid vegetations have clear age-related characteristics, which are most clearly manifested from the age of 18 and are characterized by the development of sclerosis and hyalinosis with the formation of cavernous dilated full-blooded veins with thickened rigid walls.
2. In patients over 18 years of age, there is a morphological restructuring of the connective tissue (basal) layer, namely the newly discovered phenomenon of “immersion” of lymphoid tissue with a well-developed microvasculature, which may increase the risk of intraoperative bleeding during adenotomy in this age group.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Conservative therapy
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor draws up an individual treatment plan. Acute tonsillitis is treated by a therapist on an outpatient basis using conservative methods, using antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets, rinsing, washing, and irrigation of tonsil lacunae.
Therapy of chronic tonsillitis is the responsibility of an otolaryngologist, who acts together with an immunologist.
A good result in the treatment of the disease is achieved by affecting the tonsils themselves. The hospital's otolaryngologists conduct courses of medical manipulations, during which:
- caseous plugs are removed;
- The folds of the tonsils (lacunae), which hide foci of infection, are cleaned.
During the treatment process - washing, lubricating and irrigating the tonsils with medicinal solutions, inflammation is stopped, the compensatory stage of the disease is prolonged, which makes it possible to delay or avoid tonsillectomy. Additionally, complex treatment at home is prescribed.
How to treat inflamed tonsils?
The presence of a simple sore throat is not an indication for tonsil removal! There are many treatment methods that avoid invasive intervention:
- Antibiotics. It would not be amiss to remind you that the course of antibiotics must be taken completely in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, without skipping a single dose of medication and without abandoning treatment at any stage.
- Washing with various agents with an antibacterial effect. You may even be prescribed a simple solution of chlorhexidine, which will definitely not cause harm, but may well be a good medicine.
- Application of special solutions. This could be Lugol's solution or propolis - the doctor prescribes one or the other based on your individual characteristics.
- Physiotherapy. Ultrasound, magnets, electrophoresis - all this can be a completely sufficient method of treatment without any surgery.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system and avoiding hypothermia, although not a treatment method, is an excellent method of preventive intervention in the development of severe pathologies.
You can also read our article on the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Surgery
If no conservative treatment methods lead to a lasting therapeutic effect, the doctor recommends surgical treatment: tonsillotomy or tonsillectomy.
The hospital practices both of these types of tonsil removal:
- tonsillotomy - partial removal of the tonsils in children aged 3-12 years while preserving the protective functions of the lymphoid tissue that make up the tonsils;
- Tonsillectomy - complete removal of the tonsils, is used when the tonsils are pathologically changed and are a source of chronic infection, or when complications arise from the organs, blood vessels, and joints of the body.
At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, all types of operations to remove tonsils are performed under anesthesia. In the process of tonsillectomy, a bipolar coagulator is used, which minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues and allows almost completely to avoid blood loss due to coagulation of the vessels feeding the tissue.
The Clinical Hospital on Yauza uses modern technology for tonsillectomy with suturing of the wound surface. The innovative tonsillectomy technique allows:
- minimize the risk of bleeding in the postoperative period;
- significantly speed up the postoperative healing period;
- reduce the rehabilitation period: hospital stay - up to a day; restoration of working capacity - after 7-10 days.
The cost of tonsillectomy is calculated for each patient separately and depends on the diagnostic examination, surgical method, and length of hospital stay.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza you are guaranteed:
- strict adherence to the treatment protocol;
- examination in a laboratory equipped with the latest advances in medical science;
- conservative treatment and tonsillectomy using the most effective technologies and using innovative equipment;
- stay in a comfortable room;
- constant supervision of experienced practitioners.
For any manifestations of tonsillitis, contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza through the website by filling out the online appointment form.
You can see prices for services
Patients and methods
We examined and treated 46 patients (29 males, 17 females, aged from 7 to 42 years) with grade II-III adenoid vegetations who underwent planned surgical treatment at the NIKIO n.a. L.I. Sverzhevsky and Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 9 named after. G.N. Speransky. Inclusion criteria: presence of adenoid vegetations with clinically significant symptoms. Exclusion criteria: history of adenotomy, adenoiditis, diabetes mellitus, blood diseases, taking medications that affect the hemostasis system, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, exacerbation of chronic sinusitis, allergic rhinosinusitis.
Before surgical treatment, complaints, anamnesis, and examination of ENT organs were collected according to generally accepted methods. In pediatric patients from 7 to 12 years of age, the diagnosis was made on the basis of an X-ray examination of the nasopharynx in the lateral projection; in adult patients, computed tomography of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses was performed (spiral computed tomograph Brilliance ST 40, Philips, Germany) with a slice thickness of 0.5 mm. Before surgical treatment, an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx was performed. Karl Storz 0° and 30° rigid optics with a diameter of 2.7 mm were used in patients from 18 years of age. The children had their nasopharynx examined with a Karl Storz 2.5×270 mm rhinofibroscope.
All patients were combined into two groups: group 1 - 25 patients aged 7 to 12 years; Group 2 - 21 patients from 18 to 42 years old.
Patients of both age groups underwent adenotomy with a Beckmann instrument under endotracheal anesthesia. Visual control of the operation was carried out through endoscopy of the nasopharynx with 0° and 30° optics.
Histological examination was carried out at the Department of Pathological Anatomy of Moscow State Medical University named after. A.I. Evdokimov. Biopsy specimens were fixed in 10% neutral formalin and, according to the standard procedure, embedded in paraffin blocks, from which histological sections 3-4 μm thick were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Subsequent research was carried out using light microscopy with magnifications of 100, 200, 400.
In our work, we adhered to the division of adenoid tissue into three zones: peripheral, middle and basal.
Histological examination examined the state of the stroma and vascular bed of adenoid tissue. In group 2, a histological examination was carried out not only of the adenoids themselves, but also of the underlying tissues.
Reviews
Andrey
For most of my life I was tormented by constant exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. Every spring and autumn I consistently lost two weeks for treatment. Surgery to remove tonsils has bothered me since childhood. My wife almost forcibly brought me to the clinic. I didn’t even imagine that new techniques can eliminate the problem absolutely painlessly. I have been living without constant exacerbations for a year now, and I am very grateful to the hospital specialists for this.
Natalia
Not long ago I had to bring my child to have his tonsils removed. From my own experience I remember how unpleasant and painful this procedure is. I was more worried than my son. However, the clinic doctors were able to find an approach to the child and calm him down. The operation was performed without pain or blood. Now I know for sure that your clinic employs super specialists and kind, sympathetic people.