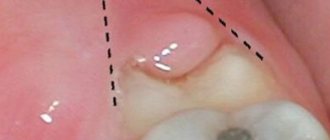
Preservation of the hole - a necessity or a new trend?
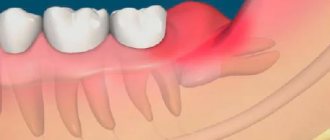
Preservation of the socket - filling the cavity formed after tooth extraction with osteogenic material - is a very important component of dental treatment after tooth extraction.
This technique completely prevents bone resorption, which is known to be 25% already in the first year, which means that within 3 years the loss of bone volume can be 60%.
Preservation of the socket not only stops this process, but also preserves the gingival contour without gaps and prepares the gingival bone for future unhindered implant installation.
It is important that conservation ensures the correct load on the bone tissue, which means that at the time of implantation the condition of the bone will be exactly what is necessary for installing the implant without prior bone grafting.
Thus, preserving the socket after tooth extraction will not only save the patient from additional bone-building surgery, but will also save a considerable amount, because bone grafting is not the cheapest dental operation.
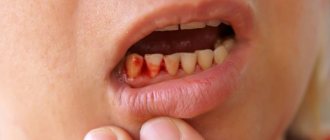
Inflammation of the socket
Inflammation of the tooth socket after its removal is called “Alveolitis”. It prevents the formation of a blood clot, or promotes its rapid destruction, which leads to the fall of food, infection and bacteria into the wound that has not yet healed. Inflammation is most often promoted by improper care after surgery, failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations, a complex course of the operation, and individual structural features of the dental tissue.
Alveolitis symptoms:
- prolonged pain felt throughout the jaw;
- the socket is dry, there is no clot;
- on the wound there is pus or a grayish-white coating with an unpleasant smell of rotting;
- malaise, poor health, elevated body temperature;
- swelling, like wounds and faces. Inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
Alveolitis will not go away on its own. It is imperative to consult a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
If implantation is not planned, is socket preservation necessary?
If implantation is not planned, preservation of the hole will still be the right decision. This simple procedure will, at a minimum, speed up the healing process of the hole and completely prevent all sorts of risks of complications and infection, and at most - taking into account the fact that you should never say “never” - it will be very useful when you need to install an implant. In other words, this is a real opportunity to give the patient choice.
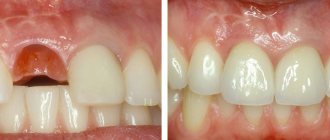
Preservation of the socket after tooth extraction is recommended for anyone who needs to install an implant in place of a missing tooth. This procedure will help preserve the volume of jaw bone and the natural contours of the alveolar process, and subsequently avoid alveolar bone augmentation for implantation.
There are practically no contraindications
except for acute pain. But even in this case, everything is individual, taking into account medical indications corresponding to the specific clinical situation.
Advantages of socket preservation after tooth extraction
- Minimum healing time for a socket after tooth extraction.
- Preventing infection from entering the socket.
- Preservation of bone tissue.
- The aesthetic appearance of the gingival contour is a guarantee of aesthetic prosthetics.
- Possibility to install an implant 1 month after tooth extraction.
- No need for augmentation.
The advantages of the procedure are obvious, which is why preservation of the socket after tooth extraction is very popular in dental dentistry.
100% guarantee of successful surgery - high-quality osteoplastic materials.
Materials for hole preservation Genoss (South Korea)
— the best bone replacement materials for socket preservation today.
Bleeding from a tooth socket and stopping it
The soft tissues of the gums have a good blood supply, therefore, after surgery, bleeding is inevitable. Normally, it should stop within 15-40 minutes, everything is individual. The hole will be filled with a blood clot, which will cover the wounded surface, stop the bleeding and promote its further recovery. Within 24 hours after surgery, discharge of ichor and minor hemorrhages may be observed, which is also normal. If there is not much bleeding:
- rinse your mouth with a cool decoction of chamomile, sage and just salted water. This will prevent infections, narrow blood vessels and promote speedy healing. This procedure must be done with extreme caution so as not to wash away the blood clot;
- Do not take painkillers with acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), because it has a blood thinning effect.
- apply a tampon to the hole for 15-20 minutes;
- Eat soft, not hot food.
- avoid physical activity and high temperatures (hot baths, saunas, etc.)
If there is heavy bleeding more than 1.5 days after surgery, you should immediately make an appointment with a dentist. He will identify the cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Genoss bone replacement materials
Genoss are bone substitutes of the highest quality, which have been successfully used in dentistry for a very long time.
When are Genoss osteoplastic materials used?
Genoss have proven themselves to be excellent in filling sockets at the site of an extracted tooth, dental implantation, bone ridge plastic surgery, filling cystic hilar cavities, in the case of post-osteotomy techniques, in restoring periodontal tissues, and filling cavities during sinus lifting.
Benefits of Genoss
- One hundred percent biocompatibility with tissues of the human body.
- High resorbability.
- Rapid tissue healing.
- Improvement of hemostasis.
- Easy to use.
this is the paradox...
... that there are very few clear manuals, recommendations and described experience in the conservation of holes. The authors are content with either drawings or not entirely convincing “before” and “after” photographs, from which it is not clear whether the tooth socket healed “on its own” or such healing is a consequence of the conservation procedure.
In other words, in theory everyone knows how and why this is done. I am sure that most doctors are fine with their practice, but very few colleagues are able to clearly demonstrate their own experience. Therefore, in fact, I had to master everything on my own, simultaneously making mistakes and complicating my own work. But who said that implantology and surgery are easy?
Cost of surgical tooth extraction
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist | 500 rub. |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist using a CT scan and drawing up a treatment plan | 1,000 rub. |
| Simple tooth extraction surgery | 3,500 rub. |
| Tooth extraction surgery is complicated | 5,000 rub. |
| The operation of removing impacted (semi-retained), dystopic 8th tooth with root separation | 7,500 rub. |
| The operation of removing impacted (semi-retained), dystopic 8th tooth with cutting out a mucoperiosteal flap and partial resection of the cortical plate of the bone | 10,000 rub. |
Mucogingivoplasty - essence and meaning
This unpronounceable word refers to a group of surgical interventions to change the gum phenotype in the area of teeth and implants. By analogy with the classification of osteoplastic operations, we can divide them into two large groups:
Note: of course, there are also “pedicle flaps”, etc., they can be placed in the green sector.
The topic of today's article is collagen matrices, and therefore we will leave modifications alone, then we will only talk about transplantations - those operations when something is transplanted somewhere. And here we are very limited in our choice - we can carry out either autotransplantation, using our own mucous membrane (SDT) or one of its layers (SST) as a transplant (graft), or xenotransplantation - if we try to replace the body’s own tissues with some inert biomaterial.
The goal of all gingivoplastic operations without exception is to change the gum phenotype, or some of its parameters , L and D. In the context of our topic today, we can do this using, among other things, xenografts and collagen matrices.
How possible is it to replace autografts with xenografts? To answer this question, we need to understand what collagen matrices are and how they work.
Anatomy of the alveolar process
The alveolar, or dental, process (from Latin - processus alveolaris) is the part of the upper and lower jaws that extends from their bodies and contains teeth. The development and normal functioning of this structure is ensured by the roots of the teeth located in it. The alveolar process appears only after teeth erupt and almost completely disappears with their loss. After a tooth is removed, the corresponding area undergoes resorption (resorption). Dental alveoli, or sockets, are individual cells of the alveolar process in which teeth are located. They are separated from each other by bony interdental (interalveolar) partitions. Inside the alveoli of multi-rooted teeth there are also internal (intra-alveolar) interradicular septa, which extend from the bottom of the alveoli and divide the alveoli into chambers (according to the number of roots). The alveolar socket of the tooth has clear, defined boundaries, and it has all the conditions for bone regeneration; you just need to help it maintain its contour.
Geistlich Mucograft – what is it and how does it work?
Today, mucogingivoplasty is almost the main trend in modern oral surgery; the creation of appropriate xenografts was only a matter of time. Thus, in 2010, Geistlich Biomaterials released the world's first collagen matrix, a soft tissue graft called Mucograft, and in 2022, Fibro-Gide.
In 2011, I was invited to a meeting where very important and smart people from our Institute of Dentistry (TsNIIS) were present, and there the clinical trials of a new biomaterial necessary for registration in the Russian Federation were taking place. A famous lady doctoral student was present at the meeting; she showed an article ready for publication, in which she called Geisltich Mucograft a “barrier membrane” and for some reason compared it with barrier membranes. This type of error still occurs in the dental community.
Where does it all begin?
And it all starts with a low-traumatic tooth extraction.
And this is the real problem. Neither patients nor some doctors consider this an important procedure, although proper tooth extraction could save a lot of effort and money during further implantation.
Let's reformulate the problem of the delete operation. Let us designate it not as “ tooth removal at any cost ,” but as “ tooth removal with maximum preservation of surrounding tissue .” Even in case of acute pain. Because if a tooth is literally ripped out with half of the alveolar ridge, no subsequent preservation will help avoid osteoplasty.
Therefore, sometimes low-traumatic tooth extraction takes a long time and requires more than just working with forceps:
then
In general, friends, by spending a little more time and effort on tooth extraction, you can seriously make your future implant treatment easier.
Contraindications
Preservation surgery is subject to the same restrictions as any osteoplastic surgery. Separately, I would like to note that it is not recommended to preserve a hole after tooth extraction in a state of acute pain, since the risk of complications increases. But in each specific clinical case, the actions of a professional dentist are strictly individual. Sometimes situations arise when you have to take risks, but this is due solely to medical indications. In any case, it is necessary to understand that performing a tooth extraction operation and subsequent preservation on a planned basis is better than as part of emergency care.
Treatment quality criteria
The main criterion for the quality of an alveolar socket preservation operation is its independent complete healing and maximum preservation of bone tissue, preservation of the natural contour and volume of the alveolar ridge, improvement of the condition of soft tissues and simplification of further stages of treatment. If the operation is successful, there will be enough bone tissue in the socket to install a dental implant. Separately, it is worth highlighting the advantages of condomization for the doctor and the patient - this is improved long-term treatment results, more predictable aesthetics and, of course, saving time for the doctor and the patient.
Types of material and types of stitches
In dental practice, the removal of a permanent tooth is a fairly serious procedure, which in some cases is equal in complexity to surgical operations. The only difference is that it is performed in a dental chair.
Often the teeth have a fairly wide crown and a deep root part. To remove such an organ, the doctor has to make additional incisions in the gum, which must be sutured at the end of the procedure. The material for these purposes must be of high quality.
The main objectives of the performed operation are to achieve rapid healing of the empty area in the jaw arch, provide a good aesthetic effect, and prevent the occurrence of undesirable consequences.
During operations, suture material is a foreign body that remains in living tissue until complete healing. Therefore, it is important that the thread is of high quality and has an optimal chemical composition and structure.
Absorbable and non-absorbable sutures are used in dentistry. Below we will consider both types in more detail.
Absorbable sutures
Surgical sutures that dissolve are characterized by sterility, strength along the entire length, resistance to infections and ease of handling. They are divided into natural and synthetic. During tissue regeneration, no procedure is required to remove the tissue.
Depending on the type of raw material, the threads may decompose without leaving any residual components. These include:
- Dexon. Braided suture thread made of synthetic material.
The raw material used is glycolic acid hypopolymer. It does not contain collagen. Dexon is contraindicated in clinical cases where constant tension of the tissues being connected is expected. The resorption process starts hydrolysis. On the 20th day, the thread retains its strength by 35%. Complete resorption occurs approximately 2 months after application. - Catgut. Material made from natural collagen thread. The resorption process is triggered by the action of proteolytic enzymes.
Strength lasts up to 20 days. It is eliminated from the body by an enzymatic effect within 55-65 days. The thread is characterized by elasticity, smooth surface, good handling properties, high breaking load, and knot reliability.Among the disadvantages, dentists point out the ability to cause mild aseptic inflammation of surrounding tissues.
- Vicryl. Polyfilament absorbable sterile suture material. It features reliable knot fixation and good handling properties.
May cause minimal initial inflammatory response in tissue. Tensile strength is lost 20 days after application. Complete dissolution occurs after 3 months.Compared to Catgut, Vicryl is much easier to work with, despite its synthetic origin. It does not have a slipping effect, is more durable and has a predictable time frame for complete resorption. The suture thread decomposes gradually, transforming into acids.
Intestinal sutures (absorbable stitches) have the advantage that they do not need to be removed. They disappear on their own, without damaging the wound and surrounding soft tissues.
Non-absorbable sutures
Modern non-absorbable suture materials used in surgical dentistry today are polymer threads and silk. They have high strength, good handling properties, are distinguished by manufacturability, affordable cost, and are able to remain in tissues for a long time without adverse reactions of the body.
The following surgical threads are widely used by doctors:
- Polyester. Non-absorbable suture material of synthetic origin.
It is distinguished by its ductility and resistance to tearing. The basis of the multifilament thread is terephthalate (a thermoplastic polymer) with or without a sheath. Living tissues show minimal reaction to a synthetic base. - Nylon. The material is a synthetic insoluble monofilament.
Made from polyamide by extrusion (pressing a melt of material through a forming device). It has a uniform diameter along its entire length and easily passes through damaged structures without injuring them. Among the advantages, it is worth highlighting the high and constant strength of the node, resistance to infections, and excellent visibility in the surgical field. - Silk. The material is made from a protein of organic origin – fibroin.
The thread can be twisted or braided, coated or uncoated. Dentists often prefer it for its strength, flexibility, ease of manipulation, and ability to securely hold knots. Negative properties are expressed in terms of hygroscopicity and the ability to provoke pronounced inflammatory reactions in surrounding tissues.
When suturing the gum, the dentist selects a suture that is appropriate for a particular clinical case. These can be interrupted or continuous stitches.
The first type is most often used in surgery. Characterized by the presence of stitches independent of each other. Each of them is fixed by a separate unit.
This method of suturing a wound allows you to maintain the integrity of the tissue even if one of the stitches breaks.
Continuous suturing is the tightening of the edges of the wound area with a suture thread, which is fixed at the end of the suture with one knot. For the doctor, manipulation in this way is faster, but leaves the risk of damage to one of the stitches and failure of the entire thread structure.
All the pros and cons of laser removal of a dental cyst, the procedure for carrying out the procedure.
In this publication we will talk about the reality of removing teeth at home for disabled people.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/molochnyih-u-detey.html we’ll talk about the indications for removing a baby tooth in a child and the cost of the issue.
Our doctors
Clinic director, implant surgeon, orthopedist
Berezin Pavel Nikolaevich
Chief physician, therapist, periodontist
Sakhnova Galina Leonidovna
all Doctors
Restrictions
It is logical to perform a preservation operation after the removal of permanent molars, within the so-called sevens, second molars (except for wisdom teeth, eights), since when baby teeth fall out, bone tissue does not resorption. There is no upper age limit for performing an operation aimed at preserving the natural contours of the alveolar process.