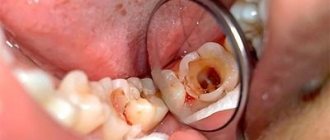
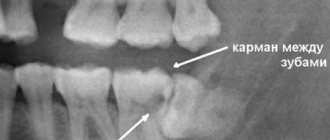
Problem: a woman came to the Family Dentistry for dental prosthetics. In addition to the main reason for the visit, the patient complained of pain in the lower jaw on the left, but could not indicate the exact location. Diagnostics showed that the wisdom tooth was destroyed by caries, and there was inflammation inside the tooth - pulpitis. The woman did not want to have the tooth removed.
Solution: pulpitis of the wisdom tooth (eighth tooth) was treated with a microscope, the tooth was restored with a composite.
What is special about wisdom teeth?
The maximum set of molars for an adult is 32. In this case, it is considered normal to have 28 teeth, since four teeth are the so-called eighth molars or wisdom teeth. For some, they do not erupt at all, for others, when “eights” appear, complications and pathologies arise, but in other cases, wisdom teeth occupy the correct position in the dentition and do not bother their owner. “Eights” usually appear between the ages of 17 and 27, that is, during the period when a person has already formed an attitude towards hygiene and his own dental health. Why is it important? Due to the remote position of wisdom teeth, it is quite difficult to carry out high-quality cleaning, so only very good hygiene can reduce the risk of dental damage. In reality, it is the third molars that are in the top in terms of the number of cases of caries and its common complication - pulpitis.
How to prevent the development of dental caries?
Good dental hygiene helps prevent the development of dental caries, and regular dental examinations detect caries at the very beginning and prevent complications. The distant teeth - wisdom teeth - can be difficult to access for self-cleaning. Maintaining a good level of hygiene requires professional teeth cleaning. Plaque removal using the Air Flow method cleans the most difficult to reach areas. Visiting a hygienist twice a year is a reliable prevention of caries and gum inflammation. Read more about caries prevention measures and dental hygiene here.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: symptoms and treatment
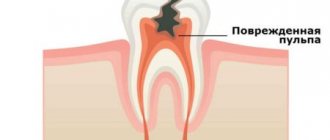
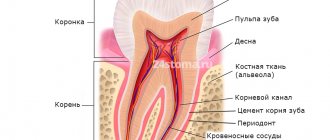
Pulpitis affects the connective tissue of the tooth - the pulp. It has a crown and a root part: depending on the shape and degree of the disease, one or both parts may be affected. The symptoms of wisdom tooth pulpitis are exactly the same as in the case of other teeth.
- Painful sensations.
In acute pulpitis, the pain is acute and paroxysmal, and can be felt in the temples, ears and other parts of the jaw. The pain intensifies at night and when exposed to irritants (temperature, chemical or mechanical). With chronic pulpitis, the pain is dull and less pronounced, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease, given the location of the wisdom tooth;
- Bleeding.
It appears only in chronic hypertrophic pulpitis, when granulation tissue grows;
- Change in tooth color.
Observed in the case of tissue necrosis with gangrenous pulpitis.
When a wisdom tooth hurts, pulpitis is just one of the options that could be the cause. To diagnose pulpitis, a visual examination, x-ray or EDI (electrodynamic diagnostics) is required. Of course, such procedures are carried out only by professionals, so if you suspect pulpitis, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor. Most patients who face a similar problem have two questions: is wisdom tooth pulpitis treated and is it worth treating wisdom tooth pulpitis. The answer to the first question is yes, but to answer the second, you need to consider each clinical case separately.
Causes of inflammation of the dental nerve
Infection in the pulp.
Most often this happens as a result of complications of untreated caries. The carious cavity expands, bacteria penetrate into the pulp and infect it. The infection can also enter the pulp through the apex of the tooth root from deep periodontal pockets with gum disease or through blood from other foci of infection.
Tooth trauma with damage to the pulp chamber, bruxism.
Even a small crack in the tooth enamel can allow bacteria from the oral cavity to penetrate into the pulp and cause inflammation. Therefore, any, even minor, tooth injury requires consultation with a dentist and subsequent observation if there is a suspicion of opening of the pulp chamber. If there is an open pulp, the tooth requires urgent endodontic treatment.
Doctor's mistakes.
Incorrect actions by the dentist can also damage the pulp and provoke inflammation. This may happen if:
- the tooth was treated with too aggressive alcohol or alkaline solutions during treatment,
- the pulp was overheated during the preparation of tooth tissue without sufficient cooling,
- the pulp chamber was damaged due to negligence during the treatment of caries,
- a filling material was used that caused an allergic reaction in the patient.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: treat or remove?
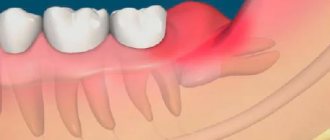
In most cases, a wisdom tooth with pulpitis is removed. The main indications for removing a diseased “eight” are developmental pathologies, as well as being outside the bite (in this case, the tooth has no function). We are talking, first of all, about retention and dystopia. An impacted wisdom tooth is completely or partially hidden in the jaw, and a dystopic wisdom tooth has an incorrect position relative to the rest of the dentition. These pathologies in themselves are a good reason for removing the “eight”, however, if pulpitis occurs due to the impossibility of full treatment, such teeth are definitely removed.
Complications of pulpitis
If you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner, pulpitis can develop into a more serious disease - periodontitis, cyst or granuloma, periostitis. That is, the inflammation will go deeper and go beyond the tooth root. Such complications can lead to tooth extraction, after which neighboring teeth will begin to shift, leading to malocclusion. Since the disease causes some discomfort while chewing food, the patient may face serious gastrointestinal problems.
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis is carried out in the same way as on other teeth. In 90% of cases, the doctor performs complete removal of the pulp: only in the initial stages of chronic fibrous pulpitis is it possible to save part of the pulp. However, even if the wisdom tooth is positioned correctly and has completely erupted, very often the doctor suggests extraction rather than treatment. This is due to some features of wisdom teeth that reduce the likelihood of a successful treatment outcome.
- Location of position. Wisdom teeth are difficult to reach, and treatment of pulpitis requires almost pinpoint precision.
- Wisdom teeth have curved roots, which sometimes makes the depulpation procedure extremely difficult.
Despite the difficulty of treatment, sometimes preserving wisdom teeth is advisable. First of all, this applies to situations where, of all the molars, only “eights” remain (in the future, a prosthesis can be attached to them), as well as in the initial stages of the disease, when the chances of a successful and predictable result are higher.
Recommendations after manipulation of wisdom teeth
Treatment of wisdom teeth is the most unpredictable process in dentistry. The risk of developing secondary caries is one of the highest among other types of diseases. Even if nothing bothers you after dental procedures on your wisdom teeth, a preventive visit to the dentist is recommended after 6 months.
After tooth extraction or periocoronitis excision, it is recommended to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, as they are aimed at speedy healing. If pain persists for more than 5-7 days, contact the clinic for examination.
Pulpitis of the tooth due to poor quality of caries treatment
Poor treatment of caries can cause the development of pulpitis. In order to treat a carious tooth correctly, a specialist must remove all tissue damaged by the disease during work, and then check the quality of the manipulations performed with a special caries detector. If at least one area with destroyed tissues was missed, the drug will paint it a bright color. However, some specialists neglect the verification stage and treat the tooth without using detector drugs.
Such an unscrupulous approach is fraught with relapse of caries: the disease will continue to develop and destroy dentin, and ultimately bacteria will penetrate into the pulp chamber, causing tooth pulpitis.
Pulpitis in children
Unlike adults, children's dental pulpitis develops not due to improper oral care or caries, but due to the characteristics of milk teeth: the enamel of children's teeth is thin and poorly protected, the hard tissue of the tooth is poorly mineralized. Because of this, pulpitis occurs quite often in children.
The symptoms of childhood pulpitis do not differ from those of adults, but there are some nuances in the course of this disease: in children it is less painful; in the acute stage, there may be an increase in temperature and inflammation of the lymph nodes, the appearance of flux, and swelling of the soft tissues. Children's pulpitis is treated in the same way as adults: after examination and analysis of the clinical picture, the dentist decides how the treatment will proceed - with preservation of the pulp and nerve or not.
View clinical cases Before and After, make an appointment,
You can visit the VID clinic Instagram @denta_vid_rostov_ Also, registration is available by phone
8(863)2098902.
Second visit:
By the way, it is preferable to fill root canals without anesthesia, but this is not necessary. This is due to the fact that if a slight pain occurs when filling the canals, the doctor immediately understands that he has moved the gutta-percha pin beyond the apex of the root. Accordingly, the doctor can change the filling depth in time.
- Removing a temporary filling.
- Flushing the canals with antiseptics.
- Filling canals using gutta-percha and sealer - after the root canals have been washed and dried, it is necessary to seal them tightly.
This is done using gutta-percha pins of different sizes (Fig. 16) and a sealer (this is something like a paste). The pins are inserted into the root canals and compacted there. In Fig. 14-15 you can see the mouths of the root canals Before and After the canals were filled with gutta-percha. Read more about this stage in our article: → “Mechanical treatment and filling of canals for pulpitis”
- X-ray control of the filling ( required!!! ) if everything is OK on the x-ray, we proceed to the next stage.
But, if we see that the canal is not filled up to the apex, or the gutta-percha pins extend beyond the root into the surrounding tissues, it is necessary to remove all the gutta-percha pins and start filling the canals all over again. In Fig. 17-19 you can see well-sealed root canals (all root canals are sealed to the apex of the root). Unfortunately, it is worth noting that the vast majority of dentists, even if they see that the root canals are filled, do not redo the work. This is precisely what is connected with the percentage of poor-quality treatment of pulpitis that we announced at the beginning of the article (in 60-70% of cases). Type of high-quality filled root canals –
At the end of the visit, a temporary filling is placed, and the patient is warned that the tooth may begin to hurt after undergoing anesthesia. Good tablet analgesics will help relieve pain. A little pain is normal because... during instrumental work in canals, K-files slightly injure the tissue in the area of the root apex.
Treatment price
Prices for treatment of pulpitis in Moscow at the InWhite Medical clinic are calculated individually in accordance with the complexity of the disease and the scale of the lesion. On this page you can see a sign with approximate prices for the treatment of pulpitis. In each specific case, we develop a plan of therapeutic measures, optimally selecting the necessary materials and methods.
| Service | Price |
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist | 2 000 ₽ |
| Orthopantomography (OPTG) | 1 900 ₽ |
| Teleradiography (TRG) | 1 900 ₽ |
Pulpitis: what kind of disease is this?
With dental pulpitis, the internal tissues of the tooth become inflamed, which in medicine are referred to as “pulp”. The pulp is located partly in the coronal part of the tooth and partly in the dental canal and consists of nerve, connective tissue cells and microvessels. The pulp performs an important function: it provides nutrition to the dentin of the tooth with substances necessary for its health. The process of inflammation in the pulp begins with the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the tooth and most often this happens due to untreated caries.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Caries destroys the hard tissues of the tooth, resulting in the formation of deep cavities, from which infection easily enters the pulp chamber and dental canals. This is how pulpitis occurs, the onset of which can be indicated to a person by increased sensitivity of the tooth to cold and hot, and throbbing pain. Less commonly, pulpitis occurs for other reasons, including: periodontitis, poor-quality tooth treatment for caries, poor-quality tooth grinding during prosthetics.
Forms of acute pulpitis
The cause of acute pulpitis is caries, the treatment of which was not carried out in a timely manner. This form is characterized by pronounced symptoms: the patient is bothered by unbearable throbbing pain, the intensity of which is especially high at night. Acute pulpitis can occur in two different forms: focal or diffuse.
Focal pulpitis of the tooth
It is the initial phase of the disease, lasting an average of 2 days. A person with focal pulpitis may experience severe shooting pains, which manifest themselves both under the influence of external factors and without impact on the tooth. The average duration of one attack is from ten minutes to half an hour. Afterwards the pain may stop, but after a while it will return. With focal pulpitis, the pain has a clear localization, that is, a person can always tell the doctor which specific tooth is bothering him.
Diffuse form of acute pulpitis
If you ignore the symptoms of focal pulpitis and do not go to the dentist for its treatment, after two days the pain will lose its clear localization and will begin to radiate to the cheekbones, occipital or temporal zone. The duration of painful attacks will increase - up to forty minutes, and the intervals between them, on the contrary, will be significantly reduced.
With this form of pulpitis, the inflammatory process moves from the coronal part of the pulp bundle to the root. If at the same time purulent fluid begins to be produced, the pain will be severe and incessant. A cold compress can help reduce the intensity of pain, but consuming hot food and drinks and heating the area of the diseased tooth should be avoided in every possible way - this is fraught with the active development of inflammation. With a diffuse form of pulpitis, body temperature may even rise.
If diffuse pulpitis is not treated, after some time it will become chronic.
Fibrous form of chronic pulpitis
Fibrous pulpitis often does not show itself in any way for a long time. The person does not complain of pain or other discomfort. However, at the same time, there is significant carious destruction in the tooth, during which a cavity of great depth is formed. If you press on its bottom, a sharp pain impulse occurs. Pain does not appear during the development of the disease precisely because of the presence of a large cavity through which the outflow occurs, which accumulates during inflammation of the fluid. However, there is no point in hoping that in this case you can wait to treat pulpitis. Over time, the pulp tissue will begin to die, and inflammation will spread to the roots of the tooth, which will ultimately lead to the need for its removal.
Gangrenous form of pulpitis
The reason for the appearance of this form of the disease is pathogenic microflora, which causes the gradual death of nerve fibers in the pulp. The pulp bundle changes its color, becomes grayish, and a rotten smell appears in the mouth.
Hypertrophic form of acute pulpitis
With this form of pulpitis, the carious cavity connects with the tooth cavity, in which connective tissue begins to actively grow. This process leads to the formation of a polyp, which will fill the entire space; if you press on this formation, it will begin to bleed. However, patients rarely complain of pain. USEFUL TO KNOW: an exacerbation of chronic pulpitis can occur at any time. At this phase, the pain does not stop for a minute and does not subside after taking painkillers. Only a visit to the dentist’s office can help for high-quality and effective treatment of pulpitis.
Tooth nerve removal
Removing tooth pulpitis includes several stages:
- Removal of tooth enamel and the subsequent hard layer of dentin.
- Removal of the tooth nerve, which is performed using a special instrument.
- Preparing dental canals for filling. To do this, the canals are expanded using a drill. Treatment of pulpitis may be accompanied by one-, two-, or three-channel filling.
- After removing and filling the canals, the dentist installs a photopolymer filling and restores the damaged coronal part.
Removal of tooth pulpitis is carried out with mandatory local anesthesia, which makes it possible to minimize the patient’s discomfort and discomfort during medical procedures.