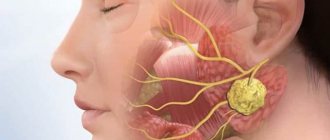
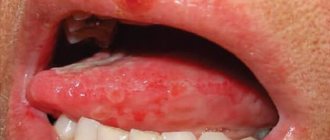
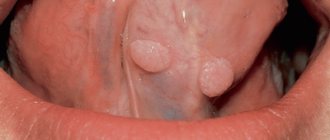
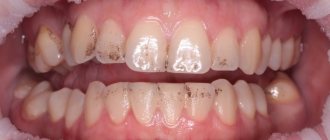
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
Classification and photo of stomatitis in the tongue
The classification of stomatitis in the tongue is based on the causes of the development of the pathological process in the oral cavity. The disease is divided into the following types:
- Bacterial. Glossitis develops due to the activation of staphylococcal or streptococcal microflora. A characteristic feature of this form of pathology is its rapid development. Symptoms of the disease appear in the form of small ulcers, which over time turn into ulcers. Stomatitis on the frenulum of the tongue occurs more often precisely because of the activity of bacterial microflora.
- Herpetic. Glossitis occurs due to activation of the herperovirus, which also occurs against the background of weakened immunity. A photo of herpetic stomatitis on the tongue shows the main signs of pathology: small blisters filled with clear liquid. The herpetic form appears in the form of small blisters.
- Candida. The causative agent of the pathology is fungi of the genus Candida. The latter are constantly present in the human body, localized mainly on the mucous membranes. More often, candidal glossitis develops against the background of decreased immunity caused by long-term use of antibacterial drugs or the course of pathologies of internal organs. In adults, stomatitis also occurs due to severe stress.
- Traumatic. The cause of the development of this form of glossitis is considered to be mechanical damage to the tissues of the tongue (bites, poor-quality dentures) and thermal burns.
- Allergic. Occurs when consuming food or due to orthodontic structures, the materials of which caused an allergic reaction in the patient. This form of stomatitis goes away immediately after the influence of the provoking factor is eliminated.
- Ray. Appears due to radiation therapy prescribed for the treatment of cancer. The peculiarity of pathology is the formation of small and large ulcers on the tongue.
- Catarrhal. It is the mildest form of stomatitis in terms of clinical features and duration.
- Ulcerative. Characterized by deep damage to soft tissues. The disease is accompanied by intense pain, which intensifies while talking or eating. Ulcerative stomatitis occurs as a complication of the catarrhal form of pathology.
- Aphthous. It manifests itself in the form of characteristic ulcers (ulcers) with smooth edges that penetrate deeply into the soft tissues. In the affected area, the mucous membrane becomes bright red. The plaque has a white or yellow color. Successful treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults is possible if its current form is diagnosed.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
Additional recommendations
For bacterial stomatitis, antibiotics are used. However, such medications must be used with extreme caution. Antibiotics negatively affect the immune system and digestive organs. Therefore, excessive use of antibacterial drugs leads to increased intensity of glossitis. In addition, antibiotics are not prescribed in cases where stomatitis occurs against the background of viral pathologies.
The allergic form of glossitis is treated with antihistamines:
Antihistamines suppress the intensity of pain and eliminate rashes on the mucous membrane.
Antiviral drugs are used in the treatment of herpetic stomatitis:
In addition to the above-mentioned drugs, medications are prescribed that accelerate tissue regeneration processes:
- "Solcoseryl";
- Shostakovsky balm and others.
In addition to vitamin complexes, immunomodulators are used to strengthen immunity (general and local).
If stomatitis occurs due to severe stress, the doctor prescribes sedatives.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Stomatitis on the tongue in adults photos
The human oral cavity contains many microorganisms, some of which are opportunistic in nature. If there are provoking factors (injuries, low immunity, and so on), the colony of bacteria actively grows, which leads to stomatitis. The disease manifests itself in the form of a characteristic plaque. In the photo of stomatitis on the tongue it has a white color.
If the pathology manifests itself only on the tongue, then in medical practice it is usually called glossitis. In the treatment of the disease, medications are mainly used, the action of which is aimed at relieving symptoms and eliminating the cause of the development of stomatitis.
Possible complications
Typically, glossitis occurs without complications, even if the patient has not undergone treatment for the pathology. However, under certain conditions, stomatitis acquires an ulcerative-necrotic form, characterized by the gradual death of tissues and cells. As this disease progresses, the affected area extends to the jaw bones. As a result, the ulcerative-necrotic form can cause periodontal disease and tooth loss.
If left untreated, chronic glossitis also occurs. It is dangerous because it causes the formation of ulcers in the oral cavity.
To avoid negative consequences, it is important to promptly treat stomatitis on the tongue and eliminate associated pathologies. In order to prevent glossitis, it is necessary to follow the rules of oral hygiene, replace orthodontic structures that injure the mucous membrane, and avoid contact with allergens. At the same time, the immune system should be strengthened.
Classification
Cysts, lipomas, papillomas, and lymphangiomas usually form under the tongue. The most common types of formations that form on the oral mucosa include:
- Sialadenitis.
- Salivary gland cyst.
- Lipoma.
- Papilloma.
- Hemangioma.
- Lymphangioma.
Each type of neoplasm is characterized by certain symptoms that appear as the lump grows. They also have different causes.
Sialadenitis
Appears against the background of inflammation of the salivary glands. The causes are usually viruses, infections and pathogenic microorganisms. They penetrate into the oral cavity not only with food, but also from inside the body.
In medicine, the disease is called salivary stone disease, in which a white lump forms. A stone formed in the cavity of the formation clogs the duct and causes stagnation.
Symptoms of the disease include:
- Painful sensations in the area of the salivary glands.
- Decreased salivation and constant dry mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Enlarged gland.
You may also feel pressure and tension in the area of the duct. Treatment for salivary stone disease occurs surgically.
Cyst
A cyst under the tongue is rare. The disease is characterized by the formation of a tumor in the maxillofacial area. The cavity of the neoplasm is filled with secretion. There are several types of cysts:
- Dermoid. This is a small cone of white or gray color. At the initial stage, there are no symptoms other than mild discomfort. Over time, difficulty swallowing and chewing food appears. This type is a congenital disease and is removed surgically.
- Mucous. The cone does not reach 1 cm in diameter and has a bluish tint. It disappears upon spontaneous rupture.
- Ranula. It looks like a mucous cyst and is considered a type of cyst. It has the ability to grow up to five centimeters. After the break it appears again. The tumor can be completely removed surgically.
A ranula is a white lump with liquid inside. The reason for its appearance is the inability of the secretion to pass through the duct due to its blockage or inflammatory process.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the type of cyst. Some of them may go away on their own, while others require surgical removal. Only a doctor can diagnose the type of tumor.
Lipoma
It is formed from adipose tissue located under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The tumor has a benign course. Rarely diagnosed. The cone itself is always located towards the capsule and is separated by bridges.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Removal of the tumor is carried out in cases where it has reached a large size and becomes a cause of discomfort.
Papilloma
Formed from the epithelium of the mucous membrane. The cone is round or oval in shape and has a pale pink color. Papilloma can be single or multiple. In some cases it develops into a malignant formation. In medical practice, cases of spontaneous resorption are known.
Hemangioma
The lump begins to form from blood vessels as a result of embryogenesis pathology. Tissue changes are already noticeable in newborns. Has two types:
- Capillary. In appearance it resembles a small pink spot. It differs in shape, size and shade. Does not rise above the surface of the mucous membrane.
- Cavernous. When pressed, it decreases, but once again takes its previous shape. The tumor is convex and has a blue or purple tint.
Hemangioma is a congenital disease characterized by benignity and rapid growth. It may be located under the mucosa or have a part formed on the surface of the membrane.
Lymphangioma
Looks like a wart with blisters. Characterized by frequent inflammation after mechanical damage during eating. Appears more often in children of the first year of life.
In adults, according to experts, lymphangioma is formed against the background of bad habits or inflammation in harmful conditions. May have a malignant course.
When diagnosing, it is important to establish what type of neoplasm the formed lump belongs to. In certain cases, special research methods are required to establish the nature of the flow. Only after an accurate diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed.
Causes, risk factors
Possible causes of tongue cancer look like this:
- The influence of carcinogens in tobacco and other smoking mixtures.
- Constant exposure to alcohol on the tongue. Interesting fact: recent studies show that alcohol can enhance the effects of carcinogens found in tobacco.
- Contact with harmful substances: salts of heavy metals, asbestos, petroleum products - for example, when working in hazardous industries.
- Regular mechanical injuries to the tongue - biting, exposure to dentures, rubbing the tongue with a splintered tooth or poorly chosen filling, etc.
- The effect on the body of HPV - specifically strains that have a high oncogenic risk. People with HIV and other viruses are also at risk.
- Precancerous conditions of the tongue, which can later develop into cancer. These are chronic ulcers, papillomas, lichen planus, Bowen's disease, etc.
Obviously, not all reasons can cause tongue cancer (and not always) - we are only talking about a significant increase in risks.
Stages
Cancer of the root of the tongue or its body is divided into four stages:
- 1st (initial). At this stage, oncology is often confused with glossitis, stomatitis and other diseases. The person himself may mistake unwanted stains for plaque. There are few symptoms.
- 2nd. Clinical manifestations begin: compactions, tumors, pain. The pain often radiates to neighboring organs (neck, ears). Suppuration and infection of the tumor may occur. The tongue often swells and becomes numb. Already at this stage, metastases from tongue cancer are possible - usually to nearby lymph nodes.
- 3rd. If you ignore the symptoms of the second stage, aggressive penetration of cancer into the thickness of the tongue and neighboring tissues begins. Tissue breakdown also begins.
- 4th. At this stage, metastases are observed in various organs: lungs, liver, bones. Treatment at the fourth stage, as a rule, is limited to palliative care; patients rarely survive more than a year.
It is important not to let the situation get worse and pay attention to the signs of tongue cancer in time - then there will be a much greater chance of recovery.
Papillomas
A benign tumor of the tongue is caused by the human papillomavirus. Favorable conditions intensify and activate the disease. Such conditions include: stress, weak immunity, lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. The shoots are formed mainly in places prone to injury.
Most often they are located:
- under the tongue;
- on the side of the tongue;
- at the root of the tongue.
There are two types of papillomas: flat and pointed.
Flat
Pronounced round growths with clear boundaries. They do not cause any particular problems to humans.
Pointed
The nipple-shaped tubercles at the base of the tongue are pinkish in color. They cause some inconvenience, especially during eating and talking.
In cases of the appearance and growth of papillomas, their removal is prescribed, as well as treatment with antiviral drugs, since the presence of infection can cause re-formation of growths. Therapy at home with folk remedies is excluded.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, the disease is difficult to detect, since the lump is small and does not show symptoms. A preliminary diagnosis is established based on the patient's complaints and visible signs. The doctor carefully examines the tumor to determine its characteristics.
For confirmation, a histological examination is prescribed. To do this, cells from the tissue of the cone are collected with a special instrument, and then the sample is sent to the laboratory.
In some cases, consultation with other specialists, such as an oncologist, may be necessary.