General information
The organs of the lymphatic system play a protective role in the human body. They serve as a barrier to viruses, bacteria, and also filter out harmful substances. In total, there are more than 450 lymph nodes in the adult body, and their maximum number is formed by the age of 10.
Lymph nodes are connected by lymphatic vessels - lymph (a fluid with a high content of lymphocytes, or “white blood cells”) circulates through them. Produced in the bone marrow, lymphocytes circulate throughout the body, first passing through the spleen and then the lymph nodes. Thanks to this, they gain the ability to produce antibodies to destroy microbes. Source: A.G. Rumyantsev, professor, V.M. Chernov, professor, V.M. Delyagin, professor Enlarged lymph node syndrome as a pediatric problem Practical Medicine, 2007, No. 5 (24), pp. 12-15
When an infection enters , a kind of “attack” is carried out on it, as a result of which the lymph nodes can enlarge (during this period they more actively produce antibodies). After recovery, the nodes return to normal size. If their diameter and density do not return to their original state, the child must be shown to a doctor.
Prevention
To prevent the development of sublingual lymphadenitis, you should:
- dress warmly in winter and according to the weather in other seasons, so as not to overcool your throat;
- strengthen immunity;
- monitor oral health;
- treat colds until complete recovery.
For a strong immune system, you need to take vitamins, eat more fruits with vitamin C, and exercise. An untreated runny nose leads to sinusitis. Purulent inflammation of the nasal sinuses spreads to the gums, drawing the lymphatic system into the process. It is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations and complete the course of antibiotics. Interrupted treatment risks complications in the lymph nodes.
Indicators of normal lymph nodes:
- diameter up to approximately 5 mm;
- soft consistency;
- single location, that is, lack of connection with each other or with the skin;
- absence of pain upon palpation (palpation);
- mobility.
Reasons for enlargement and main groups of lymph nodes
| Group of lymph nodes | Typical reasons for the increase |
| Parotid | Pyoderma (inflammation of the scalp accompanied by pus), inflammation of the outer or middle ear, the presence of lice, atopic dermatitis, eczema. |
| Occipital | Various inflammations in the scalp, fungal diseases, rubella, etc. |
| Submental | Abscess of the jaw, inflammation of the lower lip, damage to the front teeth, stomatitis. |
| Submandibular | Gingivitis, stomatitis, dental damage. |
| Cervical (in the direction of the muscles at the back of the neck) | Sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, tuberculosis of the tonsils, adenoids, infectious form of mononucleosis. |
| Cervical (middle) | Scarlet fever, tonsillitis, “cat scratch disease”, Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma ( important - these are malignant oncological processes!), toxoplasmosis. |
| Cervical (lateral) | Tumors, lymph node tuberculosis, nasopharyngeal infections. |
| Elbow | Infections of the forearm or hand. |
| Axillary | Shoulder or arm infections, vaccine reactions, cat scratch disease. |
| Inguinal | Infections of the skin, bones and muscles of the lower extremities, inflammation of the joints, dermatitis, inflammatory processes in the genitals, reaction to a vaccine introduced into the femoral area. |
Survey
Most often, patients who have identified enlarged lymph nodes in the submandibular area without other noticeable clinical manifestations turn to hematologists. In case of obvious pathology on the part of the head organs or probable signs of an infectious process (fever, skin rash, enlarged spleen, liver), doctors of the relevant profile are involved in organizing their examination. The diagnostic search is aimed both at determining the root causes of lymphadenopathy and at assessing the condition of the affected nodes. The most informative ones are:
- Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound of lymph nodes is used to quickly determine the size, shape, location, and structure of lymphoid formations. The method makes it possible to clarify the involvement of surrounding tissues in the process, as well as to differentiate lymphadenopathy from lesions of the salivary glands. - Radiodiagnostics
. In order to determine the characteristics of lymph flow in the affected area, lymphography using X-ray contrast is prescribed. In more complex diagnostic cases, CT scan of the lymph nodes is indicated. A valuable non-invasive diagnostic method is MRI of lymph nodes. - Biopsy
. Sampling of lymphoid tissue for histological examination is an accurate way to detect inflammatory processes, fibrous degeneration of the lymph node, and the degree of its damage by the oncological process. Biopsy of the lymph nodes of the submandibular zone is performed by puncture and open method. - Lab tests
. The examination begins with a general blood test, which reveals inflammatory changes and possible neoplastic changes in the composition of cellular elements. To confirm the infectious nature of lymphadenopathy, culture of a throat smear, RIF, ELISA, and PCR diagnostics are performed. - Special instrumental diagnostics
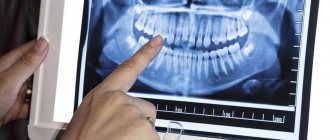
. To establish the cause of enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, pharyngoscopy, rhinoscopy, and otoscopy are performed. To exclude ophthalmological diseases, an examination of the eye structures is indicated. In case of possible dental pathology, radiography of teeth and jaws and other instrumental studies are used.
Ultrasound examination of the submandibular lymph nodes
Oncological alertness
Lymph nodes are often enlarged due to lymphogranulomatosis (Hodgkin's lymphoma) or lymphosarcoma (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma). These are malignant processes that are manifested by increased density, painlessness and large diameter of the lymph nodes in the absence of other reasons for their deformation. Lymph nodes enlarge in groups, asymmetrically (for example, on one side of the neck). At the initial stage of the process, their mobility and separate arrangement are maintained. If the oncological process continues without treatment, the lymph nodes may become fused, and moderate pain rarely occurs. Source: N.V. Nagornaya, E.V. Vilchevskaya, A.P. Luachak, E.N. Marchenko, E.V. Bordyugova, A.P. Koval Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) in children // Child's Health, 2013, No. 1 (44), pp. 13-15
Symptoms that require consultation with a doctor are enlarged lymph nodes:
- more than 7 days;
- more than 1 group;
- accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- in a child under one year old;
- progressive over time;
- with changes in local skin.
Symptoms, photos and diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis
Submandibular lymphadenitis can be distinguished from the usual enlarged lymph nodes, which occurs with reduced immunity, by the presence of pain and compaction. If there is no pain when you touch the node and the lump is not palpable, its enlargement may be caused by decreased immunity. A compacted lymph node can signal the development of oncology, so if it is detected, it is necessary to urgently be examined by a doctor.
Submandibular lymphadenitis is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes, but it is not the main symptom. For a doctor to suspect lymphadenitis, at least one of the following signs must appear:
- Pain syndrome. In the early stages of the development of the disease, aching, nagging pain of high intensity is noted in the lower part of the head - under the lower jaw. Severe pain is felt when lightly pressing on the lymph node, during chewing, when yawning, or turning the head. As the disease progresses, pain during palpation increases, and then at rest. Patients are unable to relieve pain on their own.
- Significant enlargement of the lymph node and severe swelling, which makes swallowing difficult and provokes a feeling of fullness in the sublingual area. When swallowing, there is a feeling that a piece of food is too large. Speech becomes difficult.
- Labored breathing. It occurs gradually and is accompanied by cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and pallor of the skin of the face.
- Visually noticeable swelling under the cheek. The size of the compaction depends on the severity of the ongoing pathological process, the amount of serous fluid and pus.
- An increase in body temperature to 39–40 °C, which may be accompanied by severe headache and sweating. This temperature is difficult to reduce with conventional antipyretics.
- Redness of the skin above and around the node. If pus has accumulated in the node, the skin around it will acquire a pronounced purple tint.
An accumulation of pus can be detected by palpation; pus can be felt even through the texture of the skin and node.
If there are signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph node, you should seek help from a doctor. The treatment of lymphadenitis is carried out by therapists, otolaryngologists and surgeons.
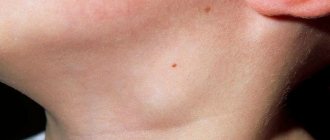
Photo: chronic inflammation of the lymph node
Photo: acute inflammation of the lymph node
In addition to visual inspection and palpation of the node, doctors use several other clinical diagnostic methods:
- General blood analysis. With the development of submandibular lymphadenitis, there is a significant increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood.
- Ultrasonography. Allows you to detect the presence of pus and serous fluid inside the lymph node.
- Bacteriological analysis of fluid from a lymph node. Allows you to determine the type of bacteria that caused the inflammation and select the most effective antibiotics.
- Carrying out a complete differential (excluding other diseases) diagnosis. It is necessary due to the similarity of the symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis with other diseases: inflammation of the salivary glands, adenoiditis.
To prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to identify the form of the disease and determine the severity of the pathological process.
Diagnostic methods
After examination and collection of complaints and medical history, the specialist sends the child for a general examination . It includes x-rays, blood and urine tests . Additionally, the following studies may be needed:
- blood serology;
- diagnosis of tuberculosis;
- lymph node biopsy followed by cytological examination in the laboratory;
- Ultrasound.
Sometimes children are prescribed antibacterial drugs as part of the diagnosis. Based on their effectiveness, they confirm or refute the bacterial nature of the disease.
How to treat submandibular lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes can be completely cured only with an integrated approach
. The doctor determines the treatment regimen for submandibular lymphadenitis in a child or adult after studying all the symptoms and medical history of the patient.
The first stage of treatment is carried out by dentists and surgeons and may include medical and surgical therapies. At this stage, two main tasks must be solved - sanitation of the source of infection and relief of pain. The main groups of prescribed drugs are:
- Antibiotics. In the vast majority of cases, the disease is bacterial in nature, so treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis requires antibiotics
. Penicillin antibiotics are usually used, since the typical causative agents of the disease are streptococci or staphylococci. To select the most effective drug, the doctor may prescribe the patient to take a puncture to determine the resistance of bacteria to a particular drug. Ampicillin, Ampiox, Oxacillin, Bicillin, Amoxicillin or Ticarcillin are usually prescribed. - Anti-inflammatory drugs. Used to relieve inflammation. The medicine should be selected by the attending physician, taking into account the course of the disease and medical history.
- Analgesics. Necessary solely to eliminate acute pain syndrome. Analgesics are a concomitant medication; the main medicine for submandibular lymphadenitis in adults is antibiotics.
In parallel with drug therapy, the doctor sanitizes the foci of infection. If the cause of the disease is inflammation of the oral mucosa, then it will be treated by a dental surgeon.
To quickly relieve inflammation and speed up the recovery process in the purulent form of lymphadenitis, the node is surgically opened, after which the accumulated pus is removed from it.
When the original source of inflammation has been eliminated and the acute period of the disease has passed, the doctor will prescribe physiotherapy to the patient. Electrophoresis is especially effective. At this stage of treatment, you can use folk remedies for a speedy recovery.
Treatment methods
Enlarged lymph nodes are not an independent disease, but a symptom of some other disease. Therefore, therapy in this case comes down to eliminating the root cause of this reaction. The rate at which nodes return to normal size varies, depending on the severity and type of underlying disease.
If a child gets sick very often, then immunomodulators are recommended to strengthen the body's defenses. The choice of drug should be made only by a doctor.
Important! Enlarged lymph nodes should not be heated - this can lead to the development of suppuration and blood poisoning! Any self-medication is prohibited - the reason and type of therapy is determined by a specialist.
What not to do if the chin lymph nodes are enlarged
Having discovered a pathology, you need to consult a specialist. Self-medication can only aggravate the situation or blur the true picture of the disease. This is especially true for the use of antibiotics at your own discretion. In some cases, drugs may be useless and even harmful. In addition, it is prohibited:
- warm the affected formations;
- apply cold compresses;
- unauthorized use of painkillers.
Most often, enlarged lymph nodes under the chin are observed in diseases of the oral cavity and ENT organs. The pathology disappears after the cause of its appearance is eliminated. If this does not happen, then additional consultation with a doctor is required.
Sizes, location and main disorders of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes
Previous post
Normal size and function of the submandibular lymph nodes
Next entry
Advantages of contacting SM-Clinic
“SM-Clinic” is a team of some of the best specialists in St. Petersburg, advanced diagnostic equipment and comfortable conditions. We have no queues, all examinations are carried out quickly, appointments are conducted by highly qualified doctors.
If your child has enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or in any other area, you should urgently contact a specialist for diagnosis and treatment. Delay in some cases is very dangerous!
To make an appointment with a pediatrician, immunologist or other pediatric specialist, call us.
Sources:
- A.G. Rumyantsev, professor, V.M. Chernov, professor, V.M. Delyagin, professor. Syndrome of enlarged lymph nodes as a pediatric problem // Practical Medicine, 2007, No. 5 (24), pp. 12-15.
- N.V. Nagornaya, E.V. Vilchevskaya, A.P. Luachak, E.N. Marchenko, E.V. Bordyugova, A.P. Koval. Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) in children // Child's Health, 2013, No. 1 (44), pp. 13-15.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: immunologist
Experience: 24 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Features of pathology in pediatrics
Often in children, the sublingual lymph nodes are enlarged, but do not hurt. This is due to the fact that the child’s immunity develops and learns to resist the bacteria that it encounters every day. To make sure there are no pathologies, you need to take a general blood test.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes causes pain and is accompanied by an acute reaction of the child’s body - high fever. Swelling and redness of the skin in the lymph node area occur.
Mumps occurs as the area under the jaw increases. In this case, the swelling also covers the adjacent neck area. Lymph nodes become hard to the touch.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |