3D CT – what is this procedure and what is it for?
3D imaging of the jaw is one of the main dental procedures used in diagnosis. The data obtained allows us to assess the condition of a specific maxillofacial area and plan further treatment.
This diagnostic tool is universal; it is used by both therapists and orthopedists, periodontists and implantologists. Using a 3D image, the therapist assesses the condition of the roots and canals of the tooth, and clarifies the localization of the inflammatory process.
An orthopedist can examine the anatomical structure of the temporomandibular joints, an implantologist can examine the volume and density of bone tissue in the area of the upcoming operation, as well as the parameters of the maxillary sinuses (maxillary sinuses).
Sometimes a large part of the tooth remains, as they say, “behind the scenes”, and the dentist simply cannot see it. Then computed tomography comes to the rescue, which allows you to examine the hidden area and prevent unpleasant consequences for the patient.
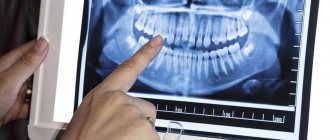
Until recently, the “gold standard” for instrumental diagnostics was a panoramic image. Today there is a more advanced method in which the maxillofacial area is scanned using computer technology.
Interpretation of results
After completing the scanning procedure, the radiologist deciphers and interprets the data obtained. The main task of the radiologist when interpreting tomograms is to describe the nature and density of detected tumors, tissue lesions and abnormalities in the development of the jaw. However, the diagnostician does not have the right to make a definitive diagnosis, recommend treatment or give advice on the use of medications. Therefore, after a CT scan of both jaws, the patient should always make an appointment with the attending physician. Based on the issued x-ray report, CT images of the jaw, examination and other studies, the specialist makes a diagnosis and makes decisions on the course of further treatment of the patient.
Study Details
- Doctor's referral: Required for CT scans for children
- Preparation: Yes in case of CT angiography, CT OMT, CT OBP
- Application of contrast: As prescribed by a doctor and with CT scan of blood vessels
- Time: 5-7 minutes
- Contraindications and restrictions: Pregnancy, allergy to iodine on CT with contrast, renal failure
- Results delivery time: 30-40 minutes
| List of studies | Price | Stock |
| CT scan of a large joint (knee, elbow, shoulder, hip, ankle) | from 2500 rub. | At night |
| CT scan of small joints (wrist joint, foot and toe joints, hand joints and fingers) | from 2500 rub. | At night |
| CT scan of the jaw joint and jaw | from 1300 rub. | At night |
| CT scan of bones (one zone) | from 2000 rub. | At night |
| CT scan of the skull | from 2000 rub. | At night |
Unique visualization method
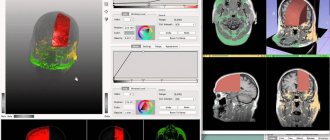
A computed tomograph produces a high-quality three-dimensional image of an individual tooth, maxillary sinuses, one or both jaws. Unlike standard panoramic images, a 3D tomogram allows the doctor to see the desired anatomical structures in a virtual section, from any angle.
During the procedure, the doctor can enlarge, rotate and study the maxillofacial area of interest at the required angle, which is unrealistic with conventional radiography.
Computed tomography is an integral and primary stage of examination before implantation. It allows you not only to assess the condition of bone tissue, but also to measure its height, width and density. Moreover, three-dimensional beams help to choose the optimal method for installing implants through preliminary virtual surgery.
3D CT is a multi-purpose and indispensable diagnostic tool that makes it possible to avoid many medical errors and complications. Thanks to this examination, the quality of treatment increases significantly and eliminates unnecessary traumatic operations.
Performing a CT scan with a radiopaque tray when planning a surgical template
Most patients who come for implants already have fillings, crowns, veneers or other dental restorations. All these materials can produce additional glare during CT scanning, so-called artifacts. To minimize them and ensure the accuracy of the CT examination, this procedure is performed using special radiopaque trays. They can be standard (if there are supporting teeth) or individual (when there are very few or no teeth and guidelines are needed for further work).
In these cases, special radiopaque trays are placed in the oral cavity, a CBCT (cone beam computed tomography of the jaws) is performed, then the trays are removed and sent to a dental laboratory. It is thanks to this type of research that it is possible to achieve accurate results and guarantee that the implant is installed in the area in which its location will be best. If implantation using surgical templates is planned, a CT scan with a radiopaque tray must be done. Before implantation with immediate loading, this study allows the fabrication of a temporary prosthesis to be worn before surgery.
Indications
Computed tomography is prescribed to identify:
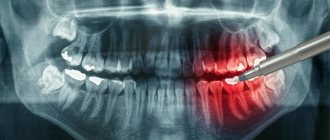
- hidden carious lesions;
- defects in the structure of the jaw and dentition;
- fully or partially unerupted teeth;
- dystopic dental units with incorrect location or direction of growth;
- supernumerary teeth;
- damage to the dentition due to jaw fractures and other injuries;
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint TMJ;
- tumors, cysts and other neoplasms in the jaws;
- condition of periodontal and periodontal tissues in case of gum disease, inflammation in the root area;
- number of roots, canals of teeth;
- cracks in the roots of teeth;
- features of the structure of bone tissue before jaw surgery (installation of implants, bone augmentation).
A 3D photo must be taken before dental implantation. The fact is that the jaw bone is clearly visible on a regular x-ray, but it does not allow assessing the soft tissues. On a three-dimensional tomogram, you can see in detail not only the bone, but also the nerve of the lower jaw, as well as blood vessels.
A 3D tomogram is much more informative than a panoramic image or targeted photographs of all teeth.
The procedure for performing CT scans of teeth in Moscow at Dental Guru clinics
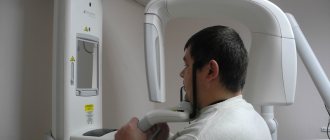
Computed tomography of the jaw, Moscow. Any Dental Guru clinic has a full range of X-ray diagnostics, including a computer tomography machine. No special preparation required. Before the examination, all metal jewelry and items of clothing (earrings, chains, piercings in the dentofacial area, hairpins) are removed. A lead vest or apron is worn to protect against X-ray radiation. To fix the head, the chin rests on the stand and the forehead on the bracket. During the examination, the sensor scans the dentofacial area. At this time, you should refrain from any movements, including swallowing. The patient sits or stands and the examination takes 30 seconds. At Dental Guru clinics, cone beam computed tomography is performed using a multifunctional Rayscan device.
CT scan before implantation
Diagnostics using a computed tomograph before installing implants allows, first of all, to determine whether implantation is necessary at all. The image will give a complete picture, and the doctor will see where the teeth are missing, whether there are problem units, and whether they can be cured.
The 3D tomogram will show:
- hidden carious cavities;
- unerupted and “extra” teeth, which may interfere with the installation of artificial pins;
- properties of roots, canals - curved, narrow and long canals require a special approach, which should be taken into account before implantation;
- bone dimensions in height and width, on the basis of which the type and size of the implant is selected;
- condition of bone beams, partitions, voids in the jaw bone;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the root area - cysts, granulomas, abscesses where implants are planned to be installed. All this needs to be treated or removed before surgery;
- inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and lacrimal ducts, which can become a temporary obstacle to implantation;
- density, size, inclination of the alveolar process, thickness of the cortical bone layer, taking into account which the optimal type of artificial pin is selected;
- the physiological structure of the maxillary sinuses, the mandibular canal to determine the angle of inclination of the implant rod;
- defects and anomalies in the structure of the dentofacial apparatus;
- quality of installation, strength of fixation of implants after surgery for their implantation;
- severity and nature of traumatic injuries in fractures.
Based on the results obtained, a virtual operation to install the rods is performed. The appropriate size of the titanium pin is selected, its inclination and the point of implantation are determined, bypassing the anatomical structures. Thus, the final outcome of implantation is modeled.
Next, the tomographic data is loaded into the computer, and the program creates a three-dimensional model. The patient’s personal surgical template is printed on a 3D printer - an overlay with guide holes for inserting rods.
During implantation, the template is placed tightly on the gums, and the placement of the pins is carried out with extreme precision.
Computed tomography of the upper jaw
To diagnose the condition of the maxillary sinuses before implantation, it is important to do a CT scan of the upper jaw. After tooth extraction, thickening of the mucous membrane in the maxillary sinuses often occurs; there may also be manifestations of sinusitis, a tumor process, the presence of a cyst or polyp. A CT scan of the jaw will show whether there is perforation of the maxillary sinus due to the protrusion of the root or crown of the tooth. The term “odontogenic sinusitis” means that the cause of the disease is in the tooth. The bony septum between the oral cavity and the maxillary sinus is quite thin, so infection from dental tissue can cause sinusitis. Therefore, for implantation to be successful, it is necessary to promptly identify and treat possible diseases and eliminate the inflammatory process.
Multispiral or cone beam?
A multispiral tomograph performs layer-by-layer scanning of an object along a spiral trajectory caused by the continuous movement of the table and the X-ray tube relative to each other.
Most often, MSCT - multislice computed tomography - is used in maxillofacial surgery for facial injuries and pathologies of the temporomandibular joint.
In dental practice, especially when planning implantation, this method is not widely used due to insufficient data accuracy. Since the patient lies down during the examination, the jaw connection is distorted.
In addition, the radiation level of MSCT can reach 1000 μSv, which is unacceptable, since implantological treatment involves more than one procedure over several months.
Cone beam CBCT is a more modern, accurate and safe method compared to MSCT. Its radiation exposure is less, about 25-50 μSv, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure several times a year.
Contraindications
A CT scan of the jaw can be performed on an adult patient if there is a referral from a doctor or on personal initiative. For children, due to the presence of radiation exposure to the body, computed tomography is performed strictly on the direction of a doctor and exclusively for strict medical reasons.
When scheduling a CT scan, patients should consider the following contraindications:
- the patient is pregnant at any stage;
- The age of the subject is up to 3 years.
3D CT or panoramic image?
An orthopantomogram allows the doctor to assess the condition of the teeth, root canals, and soft tissues. With its help, hidden inflammations, abscesses and abnormally located teeth are revealed.
However, a panoramic photo does not give a 100% accurate picture; the error is about 20%. Even a slight shift causes the focal spot to shift, and the image is compressed or stretched.
Due to the difference in the refraction of X-rays by tissues of different densities, it is impossible to assess the properties of the cancellous bone layer, since it is simply not visible behind the denser periodontium.
A two-dimensional orthopantomogram is, in fact, an auxiliary technique that gives a general idea of the condition of the oral cavity and identifies mainly obvious pathologies. It does not show the configuration and structure of the alveolar process at the desired level.
The advantage of a three-dimensional 3D tomogram is that it produces not one flat photo, but several consecutive images from different angles.
The doctor sees and evaluates all necessary objects located at any depth, from all sides and at different angles.
How to make a 3D tomogram
Usually the procedure is performed standing, the patient bites a small flat plate with his teeth and stands without moving for 15 to 30 seconds. The device makes several rotations around the head, managing to take about two hundred pictures in various projections.
In 10-15 minutes, the information is processed and transferred to electronic media.
We invite you to make a three-dimensional tomogram in our clinic using the latest generation dental tomograph. Sign up for the procedure online or by phone at a time convenient for you.
Preparatory stage
CT scan of the upper and lower jaw according to the basic (native) protocol does not require special preparation. If a CT scan of the jaw with contrast is prescribed, the diagnosis is usually carried out with a break in food for 2 hours. If the patient suffers from renal failure, tests to determine the level of creatinine in the blood are preliminarily prescribed before contrast tomography. This way, the doctor can assess the possible risks of developing nephropathy after administration of a contrast agent. Before entering the CT room, it is better to change into comfortable clothes and remove all jewelry.