Ointments for treatment
Flucinar An integrated approach is used to treat the edematous form of herpes.
Treatment is prescribed after diagnostic studies. Treat the inflamed area with gel or ointment. For example ''Acyclovir'' or its analogue ''Zovirax''. More effective ointment ''Flucinar''. Antiviral drugs, immunity boosters, and others are also used. They reduce swelling, quickly heal ulcers, reduce itching, and help wounds heal quickly. It is better to apply the ointment with cotton swabs so that the herpes does not transfer to another area of the skin. Continue treatment for a week. Along with the medications described above, it is good to take vitamins C, group B. Vitamin E accelerates healing and reduces pain. Zinc with vitamin C reduces the duration of the disease. Damaged cells are restored using the herbs ginseng, echinacea, as well as pantocrine and mumiyo, which have a good effect.
What is herpes?
Almost 90% of people are infected with the herpes virus. However, the disease manifests itself in only 17%. There are about 100 types of herpes, 8 of which can parasitize the human body.
When a person is healthy, his immune system copes with the virus, but as soon as he catches a little cold, herpes begins to attack the body. Sometimes signs of virus activation appear near the eyes, on the eyelids. How dangerous is this? Many people have encountered this disease. Some people don't even make any attempt to get rid of the signs of herpes. They often go away on their own as soon as a person recovers from a cold. However, herpes on the eye is a very dangerous disease, since if left untreated, the virus causes severe side effects and causes the development of serious ophthalmological diseases.
It is impossible to completely cure herpes. If it enters the body, which happens through airborne droplets, through contact with household objects, through food, it is no longer possible to get rid of it. The virus will remain dormant in the nerve ganglia until the person becomes ill and his immunity weakens. In this regard, therapy does not eliminate the virus itself, but its symptoms. So, why does herpes occur on the eye, how is it treated and can its occurrence be prevented? Let's take a closer look at these questions.
The journey of the virus in the body
The source of HSV infection is a patient or a virus carrier (there are no external manifestations of the disease, but the virus is excreted in saliva, urine, and discharge from the genitourinary system). The virus is transmitted by contact, airborne droplets, blood transfusions and organ transplants. During pregnancy, infection of the fetus can occur transplacentally (through the placenta) and during childbirth.
It has been established that in 40% of cases, primary HSV infection occurs by airborne droplets in early childhood, and the source of infection, as a rule, is family members who have active signs of herpes infection (usually recurrent herpes of the lips). The herpes simplex virus enters the body through injured skin or mucous membranes (red border of the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, conjunctiva) - where typical blistering rashes appear (the result of the activity of the virus), and penetrates the bloodstream and lymphatic system. Viral particles reach the nerve nodes (ganglia) of the central nervous system, where they remain inactive for life. For example, with herpes of the face, the virus is stored in the ganglia of the trigeminal nerve, and with herpes of the genitals - in the ganglia of the lumbosacral spine. From the nerve ganglia, viral particles begin to move to the periphery - the skin, mucous membranes, and a focus of infection develops during a relapse.
Under certain conditions, HSV multiplies in lymphocytes (blood cells), which leads to their damage and disruption of the genetic mechanisms that control immune responses. Clinically, this manifests itself in frequent colds, decreased performance, weakness, increased body temperature, and enlarged lymph nodes.
A recurrent course of the disease is observed in 17-50% of the population infected with HSV. Exacerbations of herpes occur after various provoking factors: hypothermia, mental or physical trauma (dental, gynecological medical procedures), alcohol intake, against the background of hormonal surges (“menstrual herpes”). “Solar herpes” is known, which appears under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
However, it is worth noting that the herpes virus may never manifest itself as a disease during a person’s life.
How to relieve swelling with herpes?
There are 8 forms of herpes infection. Of these, edema is most often provoked by the activity of the first type of pathogen. During the course of the disease, various clinical phenomena are possible, among which the most common are:
- itching;
- burning;
- pain.
Thus, the first type of disease manifests itself shortly before the formation of vesicles with serous contents.
Knowing the causes of pathology, you can take measures in advance to prevent exacerbation of the disease. The appearance of herpes is promoted by various factors that weaken the immune system:
- kidney diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- respiratory and other pathologies;
- mechanical damage to tissues and so on.
Under the influence of these factors, the herpes simplex virus is activated, which is why the patient may feel an unpleasant burning and tingling sensation in a place where watery formations may subsequently appear. As they form, the size of the bubbles gradually increases, which increases the swelling of the affected area, which is explained by the rapid development of the inflammatory process.
During this period, it is necessary to use a medicine whose action is directed directly against the virus. Otherwise, the inflammatory process will spread to healthy tissue, causing the affected area to increase.
Less commonly, when this disease recurs, no blistering rashes occur. The only sign of exacerbation is swelling.
Manifestations of infection can be controlled with antiviral medications and other medications
It is important that in the treatment of herpes, a complex of drugs is used that not only eliminates the symptoms, but also strengthens the immune system. It is optimal if treatment is started at the initial stage of the disease (when a burning sensation appears)
Isolation and identification of HSV
In specialized virology laboratories, HSV is isolated using the culture method. Its essence lies in the fact that the material for research (the contents of herpetic eruptions, human secretions) is placed on specially grown cells in which the virus begins to multiply. Then, after 5 days, the presence of HSV is determined by characteristic changes. Thus, we can say for sure that this disease is of a herpetic nature.
To identify the causative agent of HSV, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is widely used, which makes it possible to find out what type of herpes virus is present in the body. The material for research is taken with a special brush from the rash sites. The PNR method is highly sensitive and is performed within 24–48 hours.
Oral medications
Herpes is a viral infection. You can get rid of its symptoms with the help of medications taken orally. Oral medications block the activation of viral cells, due to which the external manifestations of herpes go away.
Most often, dermatologists prescribe drugs based on acyclovir - these are tablets of the same name, Zovirax, Ciclovir and others. The course of treatment depends on the course of the disease, usually it does not exceed 7 days. Symptoms such as swelling, burning and itching disappear after 1-2 days.
Immunomodulators are rarely prescribed as primary treatment and are usually combined with antiviral medications.
- Cycloferon, the full course of treatment lasts a month.
- Amiksin, course duration varies from 10 days to a month.
- Likopid, the course of treatment lasts 6-10 days, after which a break is taken for 3 days.
Immunomodulators relieve swelling by activating natural protective functions. The body begins to fight herpes on its own and after a few days the unpleasant symptoms of the disease begin to subside.
Before you start dealing with swelling, you should consult a dermatologist or therapist. The doctor will confirm the diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment regimen.
Author of the article
Dermatologist, doctor of the highest category, 31 years of experience.
What to do for warning?
The best preventative measures to prevent this disease and its manifestations will be regular measures to strengthen the immune system. These include:
- Hardening. Dousing with ice water, Russian bath and sauna with herbal teas, walking barefoot on the grass in the summer, contrast shower.
- Autohemotherapy. A method in which blood is taken from a vein and injected into the buttock according to a special scheme. First, increase the dose and then gradually decrease it.
- The use of well-known strengthening folk remedies: ginseng, echinacea, licorice root, rose hips, herbal teas.
Causes
Thanks to the tear fluid - it contains secretory immunoglobulins that reliably protect our eyes from various infections. Her strength, unfortunately, is not enough if the immune defense of the body as a whole weakens.
This happens for various reasons: after infectious diseases, surgery, stress, hypothermia.
In such circumstances, ophthalmoherpes quickly finds the “weak link” and manifests itself in all its “glory.”
The immediate impetus for the start of his hostilities is:
- eye injuries;
- contact with a sick person;
- using the same hygiene products with the patient;
- use of immunosuppressants.
An outbreak of the disease can occur in a pregnant woman, since during pregnancy the body undergoes dramatic changes and the immune system weakens.
Experts distinguish two methods of infection: endogenous (viral herpes, having entered the body, under favorable circumstances, manifests itself in various areas, including the cornea of the eye or the eyeball) and exogenous (the infection enters the mucous membrane of the eye from the outside).
The second option is more common in children than in adults, because children constantly violate the rules of hygiene, participate in general games and can easily catch some kind of infection.
According to medical statistics, 80 percent of infections in young patients occur through exogenous infection.
What to do for warning
The best preventative measures to prevent this disease and its manifestations will be regular measures to strengthen the immune system. These include:
- Hardening. Dousing with ice water, Russian bath and sauna with herbal teas, walking barefoot on the grass in the summer, contrast shower.
- Autohemotherapy. A method in which blood is taken from a vein and injected into the buttock according to a special scheme. First, increase the dose and then gradually decrease it.
- The use of well-known strengthening folk remedies: ginseng, echinacea, licorice root, rose hips, herbal teas.
If the lip is swollen, folk recipes or medications should be used in combination and regularly, then a quick and lasting effect is achieved. Thus, treating swelling with herpes will not be a problem at the very beginning of the disease and will help speed up healing. The main thing is to monitor your health and then herpes will not cause inconvenience.
When a tumor has formed on the lip, one can only assume that this is a consequence of herpes if the body is characterized by this disease. At the initial stage, before the bubbles appear, the lip is very swollen and painful.
Within a day, a bubble forms at the site of the swelling, containing a clear liquid inside. The bubble that appears cannot be broken or pressed. This should not be done because there is an infectious agent in the bladder.
Contact with healthy areas of the lip or skin nearby can lead to swelling of this area. It is best to use remedies at the swelling stage that will remove the swelling and avoid further development of the disease.
Very often lip swelling occurs:
- from hypothermia;
- weakened immune system;
- overwork;
- stress;
- headache;
- insomnia.
Swelling is characterized by sharp swelling of the tissues, which collides with fatty tissue on the skin. If herpes often appears in the same area of the lip, a lump may form on the skin.
External medications
You can get rid of swelling using acyclovir-based creams and ointments.
This substance not only removes swelling, but also has other properties:
- relieves itching and burning, these symptoms are characteristic of any stage of herpes;
- triggers regeneration processes in skin cells, promotes rapid healing of the source of infection;
- has an antiviral effect, blocks the activity of herpes.
The most famous drug based on this substance has the same name - Acyclovir. The product is available in the form of ointment and cream, they differ in their base. The ointment has a greasy texture due to lanolin in its composition.
Using the drug you can relieve swelling in a short period of time. If you use the product according to the instructions, apply it to the affected areas of the skin 4-5 times a day, then the swelling may disappear the very next morning.
Zovirax is a drug in ointment or cream format that contains acyclovir. To achieve the fastest effect, apply the product throughout the day with an interval of 3-4 hours. Complete relief from herpes occurs within 6-7 days of regular use of Zovirax, and swelling disappears after 24 hours.
If you notice the very first symptoms of herpes, then Panavir-gel can help avoid swelling altogether. The drug is based on organic raw materials extracted from potato shoots. Apply the gel to the affected areas in a thin layer up to 5 times a day. The main advantage of Panavir is the lack of addiction to the components of its composition.
Bepanten wound healing ointment is used as an additional remedy aimed at relieving the symptoms of herpetic infection. You need to apply the product 1-2 times a day in a thin layer, the swelling goes away after 1-2 days. The drug is approved for use by pregnant and lactating women.
Possible complications
Without timely and adequate treatment, herpes infection can cause severe complications:
- disruption of internal organs;
- eye diseases;
- deafness;
- sore throat;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- infertility.
Sources:
- A.G. Side. Herpesvirus infections in children - an urgent problem of modern clinical practice // Children's infections, 2010, No. 2, pp. 3-7.
- Taieb, N. Diris, F. Boralevu, C. Labreze. Herpes simplex in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnostic value of clinical signs, clinical course // Ann Dermatol Venerol, 2002, v.129, No. 4, p.603-608.
- M.N. Kankasova, O.G. Mokhova, O.S. Pozdeeva. Frequently ill children: the view of an infectious disease specialist // Practical Medicine, 2014, No. 9(85), pp. 67-71.
- I.F. Barinsky, L.M. Alimbarova, A.A. Lazarenko, F.R. Makhmudov, O.V. Sergeev. Vaccines as a means of specific immunocorrection for herpes infections // Questions of Virology, 2014, pp. 5-11.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Complex therapy, pain relief
A patient suffering from a neuralgic disorder must be treated with painkillers. Doctors do not recommend enduring pain steadfastly - this can provoke an increased reaction and the development of a chronic syndrome.
Painkillers should be taken until the discomfort disappears. To relieve the syndrome, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- NPS – “Ketorolac”, the drug “Aspirin”, the drug “Ketorolac”, “Ibuprofen”.
- Antidepressants (tricyclic) - Clomipramine, medication Imizin.
- Anticonvulsant medications - Pregabalin or Gabapentin.
- Blockades using novocaine, electrical stimulation of injured nerves.
- Potent analgesics that can reduce the intensity of the syndrome are Tramadol.
- Local medications that contain capsaicin - “Mataren Plus” ointment.
NPS are used at the height of the disease. To alleviate the painful syndrome, a neurologist may prescribe:
- "Nimesulide", simple "Aspirin";
- "Ibuprofen" or "Desketoprofen";
- "Ketoprofen".
NPS allow you to numb the problem area and relieve inflammation during the period when neuralgia begins to progress. The drugs are taken orally in the form of a suspension, capsules or syrup. To relieve herpetic syndrome, topical agents with hot pepper extract are prescribed along with medications of this group. Lidocaine-based gel provides effective pain relief.
After recovery, postherpetic neuralgia is treated with novocaine blockades, drugs of the NPS group, using other methods at the discretion of the doctor and taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Swelling due to herpes
Causes
The main reasons that provoke an exacerbation of the disease are:
- contact with a person with an active phase of the disease;
- significant hypothermia;
- severe stress;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- overwork and heavy loads;
- colds or other viral, bacterial diseases.
Symptoms and manifestations
Different forms of the virus have different types of external symptoms, but the most common are:
- with manifestations on the genitals;
- with manifestations on the skin of the face, mucous membranes and swelling on the lip.
The bubbles merge with each other, affecting more and more tissue.
Associated symptoms are itching, tingling, burning and pain. Redness and swelling are observed in the affected area of the skin. When the lip is severely swollen, painful blisters soon appear. Such elements filled with liquid can be single or multiple, prone to fusion. They merge, and the tissue around them swells even more. As they develop, the blisters burst and change into ulcers or erosions. Lips with herpes become covered with a hard, dark crust that can crack and bleed.
Diagnostics
To give the patient an accurate diagnosis, the doctor conducts a series of studies that will help understand the problem and determine the stage of cancer and the presence of metastases.
What examinations will you have to go through:
- Having contacted the doctor with complaints, the patient will undergo a palpation examination of the lip, oral mucosa and cheeks.
- The doctor will also examine the lymph nodes for tenderness and mobility.
- To get an accurate picture of the patient’s condition, you will need to do an ultrasound of the lip, as well as undergo a series of tests.
- A biopsy and histological examination of tissues are performed. In rare cases, a blood test for tumor markers is prescribed, but it can be uninformative.
- In addition to biopsy and histology, MRI and CT of the organ are performed, and if necessary, ultrasound examination of the cervical lymph nodes is prescribed.
What to do for warning?
The best preventative measures to prevent this disease and its manifestations will be regular measures to strengthen the immune system. These include:
- Hardening. Dousing with ice water, Russian bath and sauna with herbal teas, walking barefoot on the grass in the summer, contrast shower.
- Autohemotherapy. A method in which blood is taken from a vein and injected into the buttock according to a special scheme. First, increase the dose and then gradually decrease it.
- The use of well-known strengthening folk remedies: ginseng, echinacea, licorice root, rose hips, herbal teas.
Acyclovir-based drugs
Acyclovir and derivatives of this drug (Zovirax, Virolex and others) are used in the treatment of all forms of herpes, including herpes zoster. The medicine affects only the virus, introducing itself into the DNA structure of the pathogen and preventing the spread of infection to healthy tissue. A drug with this effect is available in the form of tablets and ointments.
It is recommended to use Acyclovir when the pathology manifests itself in the form of itching and burning. Due to the fact that the drug suppresses the activity of the virus, the swelling quickly subsides.
"Acyclovir" in tablet form is used in severe cases when the disease becomes generalized. In case of local damage, ointments based on this substance are prescribed. Patients with immunodeficiency should consult a doctor before use. Frequent treatment of affected areas of the face reduces the effectiveness of Acyclovir.
Principles of treatment
Herpes can and should be treated. Currently, medicine has a whole arsenal of drugs that, in most cases, make it possible to obtain a lasting clinical effect in those who suffer from recurrent herpes and to successfully control periods of activation of the disease in asymptomatic forms. It is impossible to achieve complete removal of the virus from the body using currently existing treatment methods; it is possible to maintain the body in a state where the virus does not have a chance to activate. Currently, there are two main directions of treatment for herpes simplex:
- The use of antiviral drugs, the main place among which is occupied by acyclovir-containing (ACV) drugs. In case of exacerbation of herpes, the first aid remedy is medications containing acyclovir: ZOVIRAX, VAPTREX, ACICLOVIR-ACRI, VIROLEX. They are available in the form of tablets and creams. The same drugs are used locally in the form of cream and ointment. Taking these medications should begin in the first hours of an exacerbation.
- A complex treatment method that includes immunotherapy in combination with antiviral therapy. As a rule, the disease occurs against the background of suppressed immune reactions, so immunotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of herpes. If relapses of the disease are seasonal (autumn, spring) and they are accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, then to antiviral treatment with drugs containing acyclovir, it is advisable to add a course of drugs that stimulate the synthesis of interferon (a substance produced by the body and providing an antiviral effect): herbal immunostimulants (for example, IMMUNAL) and synthetic drugs such as ARBIDOL, AMEXIN, VIFERON, KIPFERON. Moreover, they can be used for preventive purposes about a month before the onset of autumn slush and spring hypovitaminosis). If relapses of herpes (at any location) occur more than 3-4 times a YEAR, this is a reason to consult a doctor. This means that the body's defenses (immunity) cannot cope with the infection. In such cases, after studying the immune status, the patient is prescribed complex treatment, including antiviral and immune drugs. In patients with recurrent herpes, the drugs TACTIVIN, TIMALIN, THIMOGEN, MYELOPID, etc. are successfully used (treatment must be carried out after an immunological study).
What to do for warning?
The best preventative measures to prevent this disease and its manifestations will be regular measures to strengthen the immune system. These include:
- Hardening. Dousing with ice water, Russian bath and sauna with herbal teas, walking barefoot on the grass in the summer, contrast shower.
- Autohemotherapy. A method in which blood is taken from a vein and injected into the buttock according to a special scheme. First, increase the dose and then gradually decrease it.
- The use of well-known strengthening folk remedies: ginseng, echinacea, licorice root, rose hips, herbal teas.
How to treat swelling?
When a person develops herpes, there are different ways to remove swelling from the lip. The use of ointments and creams based on acyclovir can help stop the process of relapse of the disease, bring you closer to a speedy recovery and get rid of lip swelling.
The composition contains zinc, l-lysine, hydroxytolene. These medications can quickly heal ulcers and blisters and reduce itching.
These drugs contain components that destroy the manifestations of herpes, relieve pain and heal. Use at least 5 times a day for a week. The ointment should be applied regularly until the blisters disappear completely and then used for another 2 days.
Your doctor may prescribe the drug valacyclovir, in tablet form. If you take 2 tablets of valacyclovir in the morning and evening, you will notice that the affected area heals quickly, and the symptoms of a cold and lip swelling are blocked.
If the affected area is small and does not cause severe pain, you can use antiviral ointments such as Herpevir, Zovirax. They will help the wounds heal quickly.
At the first symptoms of herpes, you should change your diet. It is not recommended to eat fatty and salty foods, drink beer, chocolate, peanuts, as these products favor the development of herpes infection. Also, you should not kiss during the period of illness, avoid kissing children. In childhood, the body is more susceptible to infection.
When the occurrence of herpes occurs very often, you should visit a doctor. This course of the disease may be due to problems in the lymphatic system.
Traditional methods
It is very rare to meet a patient with the disease herpes on the lip at a doctor’s appointment. Often people resort to self-medication, relying on traditional methods.
A universal folk remedy is garlic. It helps eliminate swelling and relieves symptoms. It is best to use it at the initial stage of development, when you feel a tingling, burning sensation on your lips.
Therefore, lubricate the swelling with garlic juice. Onions are also excellent for removing swelling; pieces of it are applied to the affected area.
Aloe juice is an excellent antibiotic. As soon as the first signs of the disease appear, you need to squeeze the juice out of the leaf. Take 1 teaspoon daily 2-3 times a day.
If the lip is very swollen, a piece of ice wrapped in a scarf can help and alleviate the patient’s condition. It must be applied to the inflamed area. By doing this procedure, the swelling will go away and the itching will decrease. In this case, taking medications is mandatory. If herpes appears on the lip, you should immediately replace your toothbrush, also after the disease has passed.
Using Kalanchoe juice will dry out the formation on the lip, and the wound will heal quickly. The plant contains substances that can suppress the virus in a short time.
You can do a procedure to get rid of colds using black tea. You should brew the tea, then lower the spoon into the hot tea leaves and hold it there for 2 seconds. Apply to the affected area. To get rid of the sore, perform manipulations at least 5 times a day.
Fir oil will also help remove the infection. The oil has an analgesic and restorative effect in the fight against wounds. Apply to the affected area every 2 hours throughout the day.
You can get rid of the disease with the help of soda. You need to prepare a mushy paste by adding a little water. Apply the paste every 20-30 minutes without interruption. After 6 hours, the result will be noticeable, the herpes will begin to go away. Apply the paste for at least 2 days.
The occurrence of an infection on the lip signals a strengthening of the immune system. Having appeared once, the virus remains in the body forever and with each weakening of the immune system it constantly manifests itself.
How to treat swelling?
When a person develops herpes, there are different ways to remove swelling from the lip. The use of ointments and creams based on acyclovir can help stop the process of relapse of the disease, bring you closer to a speedy recovery and get rid of lip swelling.
The composition contains zinc, l-lysine, hydroxytolene. These medications can quickly heal ulcers and blisters and reduce itching.
These drugs contain components that destroy the manifestations of herpes, relieve pain and heal. Use at least 5 times a day for a week. The ointment should be applied regularly until the blisters disappear completely and then used for another 2 days.
Your doctor may prescribe the drug valacyclovir, in tablet form. If you take 2 tablets of valacyclovir in the morning and evening, you will notice that the affected area heals quickly, and the symptoms of a cold and lip swelling are blocked.
If the affected area is small and does not cause severe pain, you can use antiviral ointments such as Herpevir, Zovirax. They will help the wounds heal quickly.
At the first symptoms of herpes, you should change your diet. It is not recommended to eat fatty and salty foods, drink beer, chocolate, peanuts, as these products favor the development of herpes infection. Also, you should not kiss during the period of illness, avoid kissing children. In childhood, the body is more susceptible to infection.
When the occurrence of herpes occurs very often, you should visit a doctor. This course of the disease may be due to problems in the lymphatic system.
Traditional methods
It is very rare to meet a patient with the disease herpes on the lip at a doctor’s appointment. Often people resort to self-medication, relying on traditional methods.
A universal folk remedy is garlic. It helps eliminate swelling and relieves symptoms. It is best to use it at the initial stage of development, when you feel a tingling, burning sensation on your lips.
Therefore, lubricate the swelling with garlic juice. Onions are also excellent for removing swelling; pieces of it are applied to the affected area.
Aloe juice is an excellent antibiotic. As soon as the first signs of the disease appear, you need to squeeze the juice out of the leaf. Take 1 teaspoon daily 2-3 times a day.
If the lip is very swollen, a piece of ice wrapped in a scarf can help and alleviate the patient’s condition. It must be applied to the inflamed area. By doing this procedure, the swelling will go away and the itching will decrease. In this case, taking medications is mandatory. If herpes appears on the lip, you should immediately replace your toothbrush, also after the disease has passed.
Using Kalanchoe juice will dry out the formation on the lip, and the wound will heal quickly. The plant contains substances that can suppress the virus in a short time.
You can do a procedure to get rid of colds using black tea. You should brew the tea, then lower the spoon into the hot tea leaves and hold it there for 2 seconds. Apply to the affected area. To get rid of the sore, perform manipulations at least 5 times a day.
Fir oil will also help remove the infection. The oil has an analgesic and restorative effect in the fight against wounds. Apply to the affected area every 2 hours throughout the day.
You can get rid of the disease with the help of soda. You need to prepare a mushy paste by adding a little water. Apply the paste every 20-30 minutes without interruption. After 6 hours, the result will be noticeable, the herpes will begin to go away. Apply the paste for at least 2 days.
The occurrence of an infection on the lip signals a strengthening of the immune system. Having appeared once, the virus remains in the body forever and with each weakening of the immune system it constantly manifests itself.
How to relieve swelling with herpes
Currently, there are 2 types of this disease:
- A sign of the disease is swelling, which appears on the lips. This type of disease is the most common.
- Symptoms appear on the genitals.
Let's consider the first type of disease. Shortly before the appearance of swelling on the lips, where the rash should appear, you may feel slight pain, itching, and tingling.
If you look in the mirror, you can notice redness of the skin in this area. If you do not miss these symptoms, it is possible to prevent the appearance of swelling and rash on the lips.
For this purpose, medications that include acyclovir are used. For itchy skin, the patient should take 1 tablet of paracetamol or aspirin. Doctors consider this the first stage of this disease, when the patient is not yet a carrier of the virus and cannot infect others. At the second stage of the disease, a watery blister appears on the lips, during which the patient experiences pain. This rash appears as a watery blister and gradually increases in size. At this stage, swelling of the lips appears at the site of the rash.
How to relieve swelling? You can get rid of swelling with fir oil. Lubricate the bubble that appears with this product every 2 hours. At the third stage of the disease, the watery blister breaks and the colorless liquid filling it flows out.
At the fourth stage of the disease, a scab forms at the site of the ruptured vesicle.
Signs
Before a tumor appears in the intended area, tingling, pain, tingling, and itching are felt. The causative agent of herpes causes both swelling, inflammation, and ulcers, blisters that contribute to the formation of swelling
This area of skin becomes red and swollen, and small blisters appear. The contents are initially transparent, but then become cloudy. Further, after the bubbles rupture, erosions form and become covered with crusts.
The onset of the disease manifests itself in an acute form. There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, and the level of antibodies in the blood serum increases. Severe cases are characterized by fever, sweating, and general malaise.
To prevent the appearance of a tumor and the further maturation of blisters, appropriate medications should be used as early as possible. The tumor may become larger after some time. In this case, it is necessary to apply lotions, moisturizing the wound so that there are no cracks.
More: Herpes on the lips, main causes and methods of control
How to relieve swelling with herpes?
If your lip is swollen from herpes and causes discomfort, it is important to take measures to eliminate the negative symptoms. To do this, you can use folk remedies to prevent severe swelling and prevent further spread of herpes
If you do not fight herpes in the early stages, this can lead to a weakening of the body, general malaise, increased body temperature and complications of the condition.
What folk remedies are there?
- Garlic. Cut the clove and wipe the desired area. This product works as an antiseptic and actively kills the virus in the first stage.
- Black tea. High-quality black tea is brewed in boiled water and compresses are applied 6-7 times a day. This will help clean up the leak quickly.
- Essential oils. Coniferous oils and typical antiseptic oils (tea tree, chamomile, lavender) will be excellent antiviral agents. A couple of drops of essential oil should be mixed with any base oil (grape seeds, almonds, etc.) so that the disease goes away faster.
- Baking soda. It is diluted to the consistency of thick sour cream and applied 3-4 times a day if the lip is very swollen.
- Natural antibiotics - juices of aloe, Kalanchoe, celandine. Lubricate areas with rashes. Aloe juice can be taken orally at the same time for enhanced treatment of colds on the lips.
- Herbal tinctures. Tinctures of calendula, St. John's wort, plantain, and string have a high effect in the treatment of herpes.
- Propolis tincture. This remedy is very effective in the treatment of many diseases, including herpes and helps relieve swelling. It cauterizes the rash and kills the virus.
Medicines
The drug relieves swelling.
There are a number of medications based on acyclovir. They have antiviral, wound healing and regenerating effects, and effectively relieve swelling. It comes in the form of an ointment or gel, applied to the affected areas of the skin several times a day (4-5 times). You can choose "Acyclovir", "Zovirax", "Panavir". Pharmacy medications will help remove the symptoms of the virus in a short period of time and avoid further spread.
How to remove swelling?
The most common herpes disease is a cold on the lips with the manifestation of the main first sign - swelling.
Shortly before the lip becomes very swollen and a rash appears on it, itching and tingling may be felt. Redness of the area is noticeable. To prevent swelling and rash, you need to use acyclovir-based drug in a timely manner. When the patient feels itchy lips, paracetamol or aspirin should be taken.
At the stage of the appearance of a watery blister, pain is felt. The bubble gradually becomes larger in size. A lip swelling appears at the site of the rash. What needs to be done to relieve swelling? Swelling can be removed by fir oil. The bubble that appears should be lubricated every 2 hours.
Swelling due to herpes
Causes
The main reasons that provoke an exacerbation of the disease are:
- contact with a person with an active phase of the disease;
- significant hypothermia;
- severe stress;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- overwork and heavy loads;
- colds or other viral, bacterial diseases.
Symptoms and manifestations
Different forms of the virus have different types of external symptoms, but the most common are:
- with manifestations on the genitals;
- with manifestations on the skin of the face, mucous membranes and swelling on the lip.
The bubbles merge with each other, affecting more and more tissue.
Associated symptoms are itching, tingling, burning and pain. Redness and swelling are observed in the affected area of the skin. When the lip is severely swollen, painful blisters soon appear. Such elements filled with liquid can be single or multiple, prone to fusion. They merge, and the tissue around them swells even more. As they develop, the blisters burst and change into ulcers or erosions. Lips with herpes become covered with a hard, dark crust that can crack and bleed.
Symptoms of different types of herpes
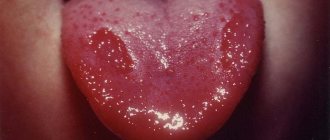
A “sleeping” virus may not bother its host for years. But if for some reason the virus enters the active phase, it is easy to recognize - by its characteristic rashes. The “classic” visual sign of herpes is itchy, watery blisters that can appear in different places - on the face and on the body.
There are several types of herpes virus - they differ in their manifestations. Most often in medical practice, diagnoses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2 are encountered - this is the abbreviated name for herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2.
Cold sores and chicken pox are related diseases caused by herpes. Several types of the virus can “coexist” in one person.
| Many people call this pathology a “cold on the lips,” although the “classic” cold and herpes are different things. We are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1, which usually “attacks” the lips and nasolabial triangle. Externally, the disease manifests itself in the form of rashes. They represent one or a whole cluster of bubbles with liquid contents. When asked whether there can be a fever with herpes, the answer is positive: many patients complain of fever, headaches and general weakness. Among doctors, there is another name for pathology: when you see a diagnosis such as oral or labial herpes in your medical record, know that we are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1. Herpes on the lip is usually very itchy |
| The second type of herpes simplex is accompanied by the development of genital (genital) infections. The disease in most cases is asymptomatic or, as with labial herpes, is accompanied by the appearance of blisters (ulcers), but only in the area of the external genitalia. Other signs of HSV-2 are fever, body aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes in the genitals. Most often, the disease is transmitted sexually, but infection can also occur from a person with labial herpes. |
| Virus type 3, also known as the herpes zoster virus, is the culprit of chickenpox. To become infected, it is enough to enter into a conversation with a sick person (transmission occurs through airborne droplets). Having had chickenpox, a person remains a carrier of this virus for the rest of his life. In case of relapse, there is a risk of developing herpes zoster. This disease is characterized by the appearance of itchy rashes throughout the body, as well as fever. Chicken pox |
| Herpes type 4 causes such a serious infectious disease as mononucleosis. This disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes and fever; the patient complains of a sore throat and general weakness. The liver and spleen are also affected. |
| Herpes type 5 provokes the development of cytomegalovirus. The disease manifests itself differently, depending on which organ is affected. A runny nose, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs - all this can be a sign of pathology. |
| In addition to those described above, there are also types 6, 7 and 8 herpes. Scientists are now studying these viruses. |
Herpes facial swelling
(Greek herpes - lichen, from herpo - crawling, stretching)
Herpes
- a group of viral diseases characterized by a rash of grouped blisters and manifested as herpes infection and herpes zoster.
The typical form of herpes simplex of the skin is characterized by the formation of grouped papules on edematous-hyperemic skin, turning into vesicles with serous contents. The number of elements varies from single to several dozen. The size of the vesicles is from 1 to 4 mm; in rare cases, when they merge, multi-chamber bubbles are formed. After a few days, the contents of the vesicles become cloudy and when they are opened, erosions form, which within 3-5 days are covered with yellow-brown crusts, under which epithelization occurs. Regional lymphadenitis may be observed 3-5 days from the onset of the disease. In addition to local manifestations, especially in children, with skin herpes there may be signs of general intoxication: general weakness, increased body temperature, headache, etc. After 6-9 days from the onset of the disease, the crusts fall off, and gradually disappearing pigmentation remains in their place. In typical cases, the entire process lasts 1-2 weeks.
Abortive form of herpes
characterized by limitation of the inflammatory process by the development of erythema and edema without the formation of vesicles. This form of infection includes cases of the appearance of subjective sensations characteristic of herpes in places where it is usually localized in the form of pain and burning, but without the appearance of a rash.
Edema form of herpes
differs from typical severe swelling of the subcutaneous tissue and hyperemia of the skin (usually on the scrotum, lips, eyelids), vesicles may be completely absent.
Hemorrhagic form of herpes
characterized by hemorrhagic vesicular contents instead of serous ones, often followed by the development of ulcerations.
Ulcerative-necrotic form of herpes
develops with severe immune deficiency. Ulcers form on the skin, extensive ulcerative surfaces with a necrotic bottom and serous-hemorrhagic or purulent discharge, sometimes covered with crusts. The reverse development of the pathological process with the rejection of crusts, epithelization and scarring of ulcers occurs very slowly.
Symptoms of genital herpes include burning or tingling in the genital area and the appearance of painful rashes on them that turn into superficial sores.
At the first exacerbation of herpes:
swollen lymph nodes;
HERPES SIMPLE (HERPESIS SIMPLE)
This paper outlines the present-day concepts of the pathogenesis of herpes simplex, describes its main clinical manifestations, and considers its therapy. V.N. Grebenyuk, doctor med. Sciences, prof., head. Department of Pediatric Dermatology of the Central Research Institute of Dermatovenerology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. VN Grebenyuk, professor, MD, Head, Department of Pediatric Dermatology, Central Research of Dermatovenereologic Institute, Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. P
Herpes growth is a serious medical and social problem. This is one of the most common human viral infections, often characterized by a persistent chronic course, affecting various organs, systems and tissues. According to WHO, about 70% of the population of our planet is infected with the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and approximately 10 - 20% of those infected have some clinical manifestations of herpes infection. HSV is a predominantly dermatoneurotropic DNA-containing virus; it also has tropism for other tissues, its size is 150 - 300 nm. The virion, in addition to DNA, consists of an icosahedral capsid and an outer shell containing lipids. It reproduces intracellularly (in the nucleus and cytoplasm) with a 14-hour reproduction cycle. During an acute infectious process, daughter virions are released from decaying cells. HSV infection can cause spontaneous abortions, fetal death and congenital deformities. The herpes virus is associated with the possibility of developing cervical cancer and some cardiovascular diseases. There are two antigenic types HSV-I and HSV-II, which cause lesions of the skin and mucous membranes of various localizations, which is determined by the place of introduction of the virus, usually through contact (coitus, kissing, through household objects). The source of infection can be not only patients with herpes, but also virus carriers who do not have symptoms of herpes.
| Rice. 1. Herpetic lesions of the face. a - forehead, eyelids, bridge of the nose; b - cheeks; c - lips and chin. |
3-4 weeks after infection, antibodies to HSV are formed in the body, the level of which remains relatively constant throughout a person’s life, regardless of the form of infection - manifest or latent. In the vast majority of people, the infection is asymptomatic or subclinical, and only in some infected people does it manifest clinically. Having penetrated the body, the herpes virus reaches a certain regional sensory ganglion (spinal or cranial) through lymphogenous, hematogenous or neurogenic routes, where it constantly persists. The latent state of the virus is based on the biological balance between micro- and macroorganisms. Under the influence of various provoking factors (psycho-emotional arousal, intoxication, overheating, etc.), a relapse of the disease occurs due to the reactivation of latent HSV, which leads to the formation of a recurrent disease. The range of clinical manifestations of the disease - from virus carriage to generalized forms - is determined both by the biological properties of the pathogen and the reactivity of the host. In most people, immune mechanisms, mainly cellular, maintain HSV latency. But in some infected people, antiviral resistance turns out to be untenable and relapses occur. There are two hypotheses that allow for the development of relapses based on both the static and dynamic state of the virus. According to the first hypothesis, the virus is located in the cells of the paravertebral sensory ganglion in an integrated or free non-productive state. Under the influence of the “trigger factor,” the virus, when activated, moves from the ganglion along the axon of the peripheral nerve to the epithelial cells, where it replicates. Cell susceptibility and weakened immune control are thought to contribute to this. According to the dynamic state hypothesis, replication and release of small amounts of virus from the ganglion occur continuously. Reaching the skin nerve, HSV causes microfoci of infection, which are restrained by defense mechanisms, which prevents relapses or weakens their manifestations. The development of relapses is also influenced by the state of local immunity. Its inhibition creates conditions for the replication of the virus that has reached the skin. The immune system plays an important role in containing the spread of herpes infection in the body. Immune protection is determined by the interaction and complex participation of specific and nonspecific factors. The main place in this system belongs to T-cell mechanisms of immunity. Mononuclear phagocytes and neutrophils play a significant role in maintaining local immunity and preventing the dissemination of infection. The protective functions of the body and the preservation of its homeostasis are also greatly influenced by the ability of cells to produce interferon.
Rice. 2. Herpetic felon.
| Rice. 3. Manifestations of herpes. a - on the palmar surface of the hand; b - on the thigh; c - on the buttocks |
Diseases caused by HSV are distinguished by a wide clinical variety of localization, severity, and characteristics of clinical manifestations. Primary herpes usually occurs after the first contact with HSV. More often it is observed in childhood against the background of a reduced immune status, in particular in the absence or low content of specific humoral antibodies. It is distinguished by the high intensity of clinical symptoms. The incubation period lasts several days. Primary herpes in newborns due to hematogenous dissemination becomes systemic, affecting the central nervous system and internal organs. The disease is characterized by herpetic lesions of the oral cavity, eyes, liver, bronchi, lungs, and brain. Usually the disease occurs acutely in the first days after birth and is manifested by anorexia, dyspeptic disorders, convulsions, septic condition, body temperature (39 - 40 ° C), disseminated herpetic rash on the skin and mucous membranes; Deaths are common in the first 2 weeks of illness. Children who have had generalized herpes experience neuropsychic complications. Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis is another severe type of herpes. Occurs mainly in children. It usually occurs in patients with atopic dermatitis, eczema, and other dermatoses in which there are skin lesions. The source of the disease can be patients with herpes in the acute stage. In adults, the disease may be associated with a recurrence of herpes labialis or another clinical form. Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis is characterized by a sudden onset (chills, malaise, body temperature up to 39 - 40 ° C for 1 - 1.5 weeks), a profuse vesicular rash on large areas of the skin, and painful regional lymphadenitis. The rashes appear in paroxysms over 2-3 weeks at intervals of several days. Often, along with skin lesions, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, pharynx, trachea, and eyes are involved in the infectious process. Grouped and disseminated vesicles soon turn into pustules. In the center of the rash elements there are often umbilical recesses. After the crusts are rejected, secondary erythema remains on the vesiculopustules. Subjectively, the rash is accompanied by itching, burning, and soreness of the skin. Regional lymphadenitis is not uncommon. Patients are subject to hospitalization in an infectious diseases hospital or clinical hospital wards. In severe forms, the pathological process may involve the nervous system, eyes and internal organs. Relapses of Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis are rare, characterized by shorter duration and weakened clinical manifestations.
| Rice. 4. Genital herpes. a — bubble manifestations; b — erosive and ulcerative manifestations. |
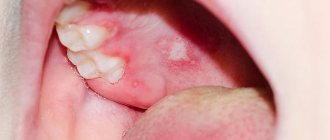
The most common clinical form of primary infection is acute herpetic stomatitis.
It is more often observed in children in the first years of life; it is rare in adults. In weakened children, dissemination of the virus can lead to visceral pathology (in particular, hepatitis) and death. Acute herpetic stomatitis, occurring after about a week's incubation period, is characterized by a violent clinical picture. Chills, high body temperature (up to 39° C), painful vesicular-erosive rashes in the oral cavity, headache, general malaise, drowsiness - this is a list of the main symptoms of this disease. The rashes are most often located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, gums, palate, lips, tongue, less often - on the soft and hard palate, palatine arches and tonsils, and spread to the skin around the mouth. The rash initially looks like grouped vesicles against a background of erythematous-edematous islands of the mucous membrane. The transparent contents of the elements become cloudy after 1 - 2 days, the covers of the vesicles are destroyed, and erosions form. In this case, regional lymph nodes are almost always enlarged and painful. Regression of the process usually occurs after 2 - 3 weeks. Recurrences of herpetic stomatitis, as a rule, are milder and resolve earlier. Herpes simplex is more common as a recurrent form. Clinical manifestations compared to primary herpes are less pronounced and not as long lasting. Most often, rashes are located on the face (lips, cheeks, nose), conjunctiva and cornea of the eyes, on the genitals and buttocks. The disease can last for many years and recur with varying frequencies - from several times a year to several times a month. In rare cases, the process becomes permanent when new rashes appear against the background of previous lesions that have not yet resolved. Frequent relapses of genital herpes are especially painful. The localization of herpetic lesions is determined by the site of virus introduction. The appearance of the rash is preceded by prodromal symptoms (burning, itching, tingling and other sensations). Grouped vesicles with a diameter of about 2 mm occur against a background of erythema. The transparent contents soon become cloudy and shrink into lumpy-yellowish crusts. When the vesicles rupture, scalloped erosions form. Their bottom is soft, reddish, the surface is smooth and moist. Regional, slightly painful lymphadenitis with a pasty consistency often occurs. The rash resolves within 1 to 2 weeks, leaving reddish-brown spots. When a microbial infection is added, the duration of relapses increases. Atypical forms of herpes simplex are known: abortive, zosteriform, disseminated, hemorrhagic-necrotic, migratory, elephantiasis-like, ulcerative, rupioid. The abortive form occurs in areas of the skin with a thickened stratum corneum and manifests itself as barely noticeable papules. Abortive manifestations of the disease also include erythematous and pruriginous-neurotic forms, characterized by local subjective disorders without typical rashes. The edematous form is usually located in areas of the skin with loose subcutaneous tissue (eyelids, lips) and is characterized by pronounced tissue swelling. Zosteriform herpes simplex is localized along the course of a nerve on the limbs, trunk, face and is accompanied by neuralgia, headache and general weakness. In the disseminated form of the disease, the rash simultaneously appears on areas of the skin that are distant from each other. The migratory form of recurrent herpes is characterized by a change in the localization of lesions. In hemorrhagic and hemorrhagic-necrotic forms, an admixture of blood is detected in the contents of the vesicles and necrosis develops. The elephantiasis-like form of the disease is characterized by severe swelling followed by the development of persistent elephantiasis in the affected area. Chronic cutaneous herpes simplex is an extremely rare clinical form. It is observed in patients with immunodeficiency and is characterized by permanent active manifestations of infection. Persistent ulcerative lesions up to 2 cm in diameter appear. The ulcerative form of herpes simplex is characterized by the development of ulcerative lesions, which is associated with a weakening of the patient’s immunobiological defense mechanisms and the increased virulence of the virus strain. This clinical type of herpes is characterized by the formation of ulcers at the site of weeping vesicles and fused erosions. The bottom of the ulcers is soft, pink-red in color, sometimes with a grayish-yellowish coating. In the first days of the disease, local pain and burning are expressed. Sometimes the rash is accompanied by inguinal lymphadenitis. The rupoid form of herpes simplex is usually localized on the face. It is caused by pyogenic infection with the development of cracks and layered crusts. Relapses occur several times a year. The rash is often accompanied by tenderness and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. With herpes of the hands, the process is often located on the distal parts of the hands. Limited lesions are represented by single dense blisters, accompanied by severe pain. The most common type of herpes simplex is facial herpes. In most people, these are sporadic focal vesicular eruptions, often resolving within 1 week. In severe cases, the process involves large surfaces of the face - nose, cheeks, forehead, skin and red border of the lips. Genital herpes occupies a significant place in the structure of herpetic diseases. Etiologically, its occurrence is equally often associated with types of HSV-I and/or HSV-II. Infection with one type of virus does not prevent the occurrence of HSV infection of another type, which leads to the formation of intermediate (“double”) antibodies. Mixed infection with HSV-I and HSV-II is quite common. The frequent isolation of HSV-I, which was previously considered the causative agent of non-genital forms of herpes, in genital lesions is due to the prevalence of orogenital contacts. Genital herpes is distinguished by the variability of its clinical picture and its tendency to have a chronic, relapsing course. In men, limited herpetic eruptions are often localized on the inner layer of the foreskin, in the head groove, and less often on the head and shaft of the penis. In women, the labia minora, clitoris, cervix, perineum and thighs are most often affected. Rashes (vesicles, erosions, ulcers, cracks) against a background of erythema and swelling are usually painful and are also accompanied by itching, a feeling of tension and heaviness in the perineum. About a third of patients have inguinal lymphadenitis. When the urethral mucosa is involved in the pathological process, serous discharge from the urethra and pain when urinating appear. The source of infection in the case of genital herpes is usually a patient in the acute stage of the disease; it can also be a virus carrier, given the possibility of asymptomatic persistence of HSV in the genitourinary tract in men and in the cervical canal. The incubation period for primary genital herpes lasts from one to several days. Clinically, primary genital herpes has a more severe and prolonged course. The localization of rashes on the genitals and adjacent areas is determined by the gates of the viral infection. A recurrent course of genital herpes is observed in the majority of infected people. Provoking factors are a variety of influences - psycho-emotional experiences, hypothermia, menstruation, weather and climate fluctuations, and other factors that disrupt the state of biological balance of the body, contributing to a decrease in the immune response and activation of HSV. The clinical picture, the amount of virus secreted by the patient and the associated infectivity are more pronounced with primary herpes than with a recurrent disease. Possible complications of herpes simplex: the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, reinfection with the released virus of other epithelial integuments, neurological manifestations (aseptic meningitis, transverse myelitis), encephalitis, disseminated infection of internal organs, psychosocial consequences (psychological instability). The risk of developing cervical cancer is 2 times higher in women who are seropositive for human papillomavirus types 16/18 and infected with HSV-II.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of herpes simplex, especially its genital form, in most cases is based on the clinical picture. Difficulties arise with atypical manifestations of herpes. In this case, it is important to carefully collect anamnesis, paying attention to relapses accompanied by itching, burning, and ineffectiveness of antibiotic therapy. In addition, the patient may have a tendency to colds, general weakness, malaise, low-grade fever, and depression. Recurrent herpes is characterized by a wave-like course of the disease - an alternation of relapses and remissions. In women, relapses of herpes may be associated with certain phases of the menstrual cycle. The occurrence of erosions and ulcers on the genitals simulates syphilitic lesions. This similarity is most pronounced when a secondary microbial infection is attached, as well as during irrational therapy. The diagnosis of genital herpes is complicated by the fact that HSV is often associated with some resident autoflora microorganisms: chlamydia, streptococci and staphylococci, gardnerella and others, which can determine the occurrence of mixed infections. In addition, because herpes can be transmitted sexually, the patient must be tested to rule out other sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis and AIDS. In complex cases, when clinical data is insufficient, laboratory diagnosis is possible. There are a number of specific laboratory tests to recognize HSV infection: isolation of HSV in cell culture, including HSV-I and HSV-II typing, tests to determine HSV antigen or DNA using polymerase chain reaction; serological tests - complement fixation test, ELISA, indirect immunofluorescence reaction, reverse passive hemagglutination reaction, protein-specific immune tests (immunoblotting), cytological examination (detection of multinucleated giant cells in scrapings from the lesion).
Treatment
Treatment of recurrent herpes remains a difficult task, which is not always solved effectively. It is possible to achieve some success if complex etiological and pathogenetic treatment is carried out at different stages of the disease, aimed, on the one hand, at suppressing the infectious agent, and on the other, at increasing the body’s immune reactivity. When choosing treatment, the stage of the disease should be taken into account. For relapses, interferon, antiviral chemotherapy, measles immunoglobulin, human normal immunoglobulin, levamisole, ascorbic acid, deoxyribonuclease, applications of 0.05% zinc sulfite solution are indicated; in the inter-relapse period - herpetic and polio vaccines, pyrogenal. The etiological focus is on antiviral chemotherapy drugs, which are more effective when used in the first hours and days of the appearance of rashes. Among them is the domestic drug Bonafton, which is used orally at 50–150 mg/day for 5–7 days for relapses. Simultaneously with the tablet form, 0.5% bonaftone ointment can be prescribed. It is applied to the lesions in an open manner when signs of relapse appear and is easily rubbed into the skin 2 - 3 times a day for 5 - 7 days. Side effects observed in some patients include malaise, loose stools, and dermatitis. Acyclovar (Zovirax) is effective, characterized by low toxicity and selectivity against HSV. The drug is used intravenously, orally and topically. It gives a pronounced therapeutic effect for Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis. Acyclovir is administered intravenously at the rate of 20 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day. However, the drug does not prevent herpes from recurring, infecting newborns, or infecting other people. Treatment of patients with recurrent herpes with acyclovir 0.1 - 0.2 g 5 times a day for 5 days during relapses shortens the time for resolution of rashes, reduces the severity of subjective sensations, smoothes out clinical manifestations and reduces the degree of virus shedding. Prophylactic administration of the drug 0.1 - 0.2 g 4 times a day for 6 - 12 weeks reduces the duration of relapses and weakens clinical manifestations. Other chemotherapy drugs: famciclovir, alpizarin (2 and 5% liniment), Viru Merz Serol, 1% oxolinic ointment, hevisos, ribavirin (virazol). A certain therapeutic effect is provided by immunocorrective drugs (myelopid, poludanum, arbidol), used both as monotherapy and in complex treatment. Myelopid (0.003 g in 2 ml of saline) is administered intramuscularly once every 3 days (5 injections per course). Treatment is carried out in two courses with an interval of 7 - 10 days. Poludan is administered subcutaneously into the forearm every other day, 100 mcg, for a course of 1000 mcg. Arbidol is prescribed 0.2 (2 tablets) 3 times a day - 5 days with a 2-day break, and then 0.1 g (1 tablet) 1 time per week for 3 weeks. Sodium nucleinate is also used orally at 0.5 - 1 g / day in 2 - 3 doses daily for 2 - 4 weeks. Taktivin is used to stop relapses and for prophylactic purposes. The drug is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 100 mcg every other day, 8 - 10 injections. During the inter-relapse period, 50 mcg is prescribed every other day, a course of 5 injections is repeated every 3-6 months. A course (4 - 5 injections) of treatment with timoptin is also carried out, which is administered subcutaneously at 100 mcg every 3 - 4 days. The courses are repeated after six months.
External treatment
Antiviral ointments, creams, lipsticks accelerate the epithelization of erosions, reduce or reduce subjective sensations in the affected areas. Local use of one or another antiviral drug in the treatment of herpetic lesions for 5 - 7 days shortens the time of regression; use 2 - 3 times a week during the inter-relapse period allows to prolong remission. Interferon has an inhibitory effect on HSV, which is applied to the skin and easily rubbed in for 4 to 7 days. During treatment, it is advisable to alternate antiviral drugs during relapses. Human interferons are effective in the treatment of recurrent herpes in the prodromal period and when the first signs of relapse appear. The ointment is applied to the lesions 2-4 times a day and rubbed in lightly; treatment is continued for a week. The use of interferon ointment during the inter-relapse period prolongs remissions and interrupts the development of relapses. In order to prevent relapses in frequently recurrent forms of herpes, patients for whom treatment is ineffective are prescribed a herpetic vaccine. Contraindications to its administration are lesions of parenchymal organs, diabetes mellitus, stage II and III hypertension, decompensated heart failure, acute infections and allergic diseases. The drug is administered intradermally during the period between relapses, 0.2 - 0.3 ml into the area of the flexor surface of one of the forearms. The first 5 injections are given after 3 - 4 days, the next 5 doses are administered after a 2-week break (once every 5 - 7 days). These 10 injections constitute the main course of treatment, 3–6 months after the end of which 1–2 cycles of revaccination are carried out, each of 5 injections with an interval between injections of 7–14 days and between cycles of 6–8 months. Over the next 2 years, an additional revaccination cycle of 5 injections is carried out every 8 - 12 months. At the injection site, after 18-24 hours, a local reaction develops, manifested by the development of erythema with a diameter of 2-5 cm with a papule in the center and accompanied by a burning sensation. During vaccination, a focal reaction such as abortive relapses may be observed. In this case, a break is taken in the treatment for 2 - 3 days, then it is continued. Specific vaccine therapy leads to an increase in the duration of remissions, a reduction in relapse periods, and the disappearance of subjective sensations. For the purpose of secondary prevention of relapse of herpes, the factors that provoke the disease are controlled. Great importance is attached to the sanitation of the body and health-improving measures in the process of medical examination.
Literature:
1. Barinsky I.F., Shubladze A.K., Kasparov A.A., Grebenyuk V.N.M.: Medicine. 1986, 269 p. 2. Masyukova S. A., Rezaikina A. V., Grebenyuk V. N., Fedorov S. M., Mkhitaryan A. G., Kolieva M. Kh. Immunotherapy of recurrent herpes simplex. Sexually transmitted diseases. Information analytical newsletter. Sanam Association 1995, 3, 27-30. 3. Minde CA. Genital Herpes. A guide to pharmacological therapy. Drugs 1994;47(2):297-304. 4. Whatley JD, Thin RN. Episodic acyclovir therapy to abort recurrent attacks of genital herpes simplex infection. J Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1991;27:677-81.
Swelling due to herpes
Causes
The main reasons that provoke an exacerbation of the disease are:
- contact with a person with an active phase of the disease;
- significant hypothermia;
- severe stress;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- overwork and heavy loads;
- colds or other viral, bacterial diseases.
Symptoms and manifestations
Different forms of the virus have different types of external symptoms, but the most common are:
- with manifestations on the genitals;
- with manifestations on the skin of the face, mucous membranes and swelling on the lip.
The bubbles merge with each other, affecting more and more tissue.
Associated symptoms are itching, tingling, burning and pain. Redness and swelling are observed in the affected area of the skin. When the lip is severely swollen, painful blisters soon appear. Such elements filled with liquid can be single or multiple, prone to fusion. They merge, and the tissue around them swells even more. As they develop, the blisters burst and change into ulcers or erosions. Lips with herpes become covered with a hard, dark crust that can crack and bleed.
Symptoms of herpes simplex infection
There are few signs of herpes, but they are all very characteristic. Therefore, difficulties in differential diagnosis almost never arise.
The main symptoms of infection with herpes simplex, which is the most common form of herpetic lesions, are as follows:
- painful tissue swelling appears in the affected area;
- after 1-2 days it transforms into a denser infiltrate;
- the infiltrate turns into a bubble with liquid;
- the blister bursts and a painful ulcer forms in its place;
- the ulceration dries out and is covered with a new layer of epithelium - the wound heals.
The way lips look after herpes is the same as after any other skin disease: the swelling disappears, but the ulcer cannot heal for some time. It is covered with a yellowish film that constantly “peels off” from the wound surface, thereby exposing the wound and delaying the process of epithelial regeneration at the site of the lesion.