Herpes on the tongue (herpetic glossitis) - signs of the disease and methods of its treatment
There are a huge number of taste buds on the surface of the tongue. They allow us to enjoy the taste of our favorite dishes and drinks, recognize the temperature and consistency of food. In addition, language plays a very direct role in human communication, allowing us to communicate with each other. The appearance of an organ alone can tell a lot about a person’s state of health. Thick plaque, redness, swelling, pain - all these are signs of certain disorders in the functioning of internal organs and systems, and these problems require medical intervention. One of the common diseases of the organ is glossitis. Today we’ll talk about a separate type of this pathology, namely herpes on the tongue or herpetic glossitis. Read on to find out whether herpes occurs in the mouth, what this form of the disease is, what symptoms are typical for it and how to cure it.
Herpes virus type 8
Herpes virus type 8 can cause Kaposi's sarcoma and Castleman's disease. Kaposi's sarcoma is a serious pathology that is accompanied by the appearance of malignant skin tumors. It is quite difficult, especially with immune deficiency. May be complicated by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the palate and lymph nodes.
Castleman's disease is a rare disease in which fever, enlargement of the liver and spleen, anemia, and a sharp decrease in body weight are observed.
What is glossitis
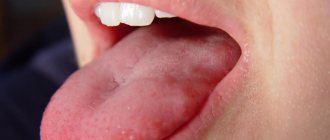
Glossitis is an inflammatory pathology of the tongue, which often begins due to banal injury to the organ and penetration of harmful microorganisms through an open wound. Hence the widespread prevalence of this disease, because all of us at least once in our lives accidentally bit our tongues while eating or talking. Another common prerequisite for the development of the disease is insufficient oral hygiene, which leads to the active proliferation of bacteria.
The photo shows glossitis of the tongue
Pathology can be either an independent phenomenon or a consequence of complex problems in the functioning of the body as a whole or a specific dental disease. If you ignore obvious symptoms for too long, things can end up with very serious complications.
Symptoms
The disease most often develops acutely. The patient's body temperature rises. He complains of weakness and decreased performance. Pain appears in the arms and legs. Your head may hurt a lot.
The skin of the tongue becomes very sensitive. Small lesions appear on its surface, and when touched, severe pain occurs. The ulcers are getting larger every day. It gets to the point where they merge with each other. Then the course of stomatitis worsens. The tissues swell.
A person cannot eat, smile, or talk normally. Bleeding gums may occur. The smell from the mouth becomes unpleasant and foul. No hygiene products intended for treating the oral cavity can help eliminate it. Salivation increases significantly.
Despite the fact that stomatitis affects only the tissues of the tongue and oral cavity, it negatively affects the well-being of a person as a whole. With a strong decrease in immunity, it often comes to the point that the patient develops severe intoxication.
How to treat
If the disease is not advanced, it is quite possible to cure it on your own by rinsing and using antiseptic pharmaceutical ointments. But if after two or three days of self-therapy the situation has not improved or, even worse, the disease has begun to progress even more actively, it is recommended to immediately consult a dentist. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, determine the true cause of the pathology and select an effective treatment.
to monitor oral hygiene during therapy After every meal you need to rinse your mouth. For this purpose, it is allowed to use self-prepared decoctions and infusions of herbs, special dental solutions, or at least warm water.
Causes
The main provoking factors leading to the development of the disease in question have already been mentioned above. Let's look at all the most common causes of glossitis in more detail:
- damage to organ tissue: people often injure their tongue while eating, for example, with sunflower seed shells or fish bones. Injury can also result from accidental biting, the use of a worn-out prosthetic device, improper installation or adjustment of an orthodontic system to correct the bite, or damage to the mucosa from the sharp edges of a crown or filling. In addition, the cause of scratches and ulcers on the organ can be a burn or aggressive effects of acids contained in certain foods,
Tongue injury can cause pathology - long-term use of powerful medications, including antibiotics,
- allergies to hygiene products - toothpaste or mouthwash,
- disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: in this case, glossitis becomes a kind of symptom of a specific disease of the stomach or intestines, and here the help of a gastroenterologist will be needed,
- spread of infection - active spread of fungus or harmful bacteria in the oral cavity and esophagus,
- addiction to cigarettes and alcohol - the aggressive effects of tobacco smoke and alcohol on the oral mucosa in combination with a weakened immune system often leads to the development of various pathologies of the mucous membrane,
- acute deficiency of vitamins A and E.
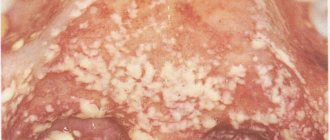
This is what a fungal infection looks like on the tongue
. It is worth noting that glossitis quite rarely appears against the background of only one of the reasons described above. Typically, the development of pathology is facilitated by a whole range of problems associated with the condition of the oral cavity and the digestive tract, and injury to the organ becomes only a “trigger”. At risk are people whose professional activities involve constant contact with chemicals, as well as those who neglect to comply with hygiene rules.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
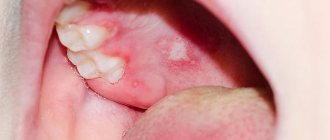
Herpetic form - features
One of the most common forms of the pathology in question is the so-called herpetic or herpetic glossitis. In this case, the development of the disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus. A distinctive symptom of this type of disease is the appearance of rashes in the form of watery blisters that appear on the surface of the organ - they can appear at the tip, directly at the root, under the tongue and even on the frenulum.
Herpetic form of glossitis
The tumors are very painful and cause a burning sensation, especially when eating. Herpetic glossitis is a serious disease that requires timely treatment. Like the herpes virus, this disease is extremely contagious, so during treatment it is better to isolate the patient, if possible, from contact with other people.
Methods of infection with viruses
Infection with viruses can occur through airborne droplets, household contact, sexual contact and blood contact. Infection is possible both from patients and from carriers of the virus. The infection persists for a long time in a dried state and can be easily transmitted through household items: cups, towels, toys. The virus also spreads through saliva, blood, vesicle contents, semen, vaginal secretions and other body media.
Infection often occurs in the form of autoinoculation, which involves mechanical transfer of viral particles from one site to another. For example, the virus can spread through the skin and mucous membranes when scratching.
Susceptibility upon contact is quite high. It is believed that about 90% of the adult population are carriers of one type or another of herpes and up to 25% suffer from recurrent forms. As a rule, when examining frequently ill children and adults, several herpes viruses are detected at the same time.
Appearance in children
The risk of developing herpes on a child’s tongue is increased by the fact that young children constantly put various objects in their mouths. Unfortunately, very often this disease manifests itself in children. In this case, the herpetic form of pathology is not the most common, because more often children have to deal with catarrhal inflammation, which is caused by injury to soft tissues due to constant biting, wearing an orthodontic plate and burns from eating too hot food.
“We had glossitis last winter. I noticed purple ulcers on the tip of my daughter’s tongue, I grabbed her and ran to the doctor. The child admitted to the dentist that her tongue began to tingle, but just the other day, that is, we managed to contact her at a very early stage. The doctor prescribed us pills and rinses with chamomile solution. We recovered in about a week.”
Oksana N., Omsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Stomatitis is common in infants.
An open wound on the oral mucosa opens a direct path for the penetration of harmful microorganisms. As a result of the development of the disease, the child may experience pain and burning in the organ. Another common type of glossitis in children is the candidal form - it occurs most often in the youngest.
Stomatitis: how to overcome the “language barrier”?
Stomatitis on the tongue is just one of the manifestations of this “popular” disease. There are a huge number of reasons for its appearance, as well as ways to treat it.
There are several types of stomatitis, when it manifests itself specifically on the tongue: glossitis, viral stomatitis, vesicular stomatitis, enteroviral vesicular stomatitis, catarrhal stomatitis, fungal stomatitis, etc.
In general, stomatitis on the tongue is most common. Its notable feature is small ulcers, from which the patient suffers greatly. If inflammation is observed only on the tongue, and, for example, there are no signs of stomatitis on the palate, cheek or gum, then this disease is called glossitis.
During pregnancy
Glossitis in a pregnant woman usually develops against the background of weakened immune defenses of the body. The lack of a balanced diet coupled with a lack of vital vitamins and microelements often provokes vitamin deficiency, and glossitis becomes one of the associated pathologies. Other provoking factors during this period may be exacerbations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as damage to the oral mucosa due to frequent vomiting against the background of toxicosis.
Treatment of the disease during pregnancy is carried out in such a way that the negative impact on the body of the mother and child is minimal. To do this, the specialist selects effective and at the same time safe medications, usually of local action - lozenges and lozenges, all kinds of rinsing solutions.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The appearance of neoplasms on the tongue of an adult or child should at least alert you. If redness, pain and swelling are added to everything else, it’s most likely glossitis. However, to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the appropriate treatment method, you must consult a doctor. Already as part of the initial visual examination, the specialist will be able to draw certain conclusions regarding the clinical picture, and to identify the specific cause of inflammation, it may be necessary to undergo the following types of examination:
- general blood analysis,
- blood chemistry,
- scraping from the damaged area.
Only tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Only with the results of the studies in hand, the doctor will be able to make a final verdict and prescribe the necessary therapy. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances - such arrogance can lead to a worsening of the situation.
Diagnosis of herpes virus infections
The most informative laboratory tests for diagnosing herpesvirus infections are the PCR method and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Depending on the location of the infectious process, blood, saliva, scrapings from the urethra, cervical canal, and vesicles can be examined.
During the diagnosis, the qualitative and quantitative content of immunoglobulins M and G is determined, as well as avidity, an indicator that can be used to assess how efficiently the immune system copes with the virus.
For more successful treatment, a general examination of the body is additionally performed to identify chronic infections. Sluggish chronic pathologies of the genitourinary, respiratory, digestive and other systems can support and cause exacerbation of herpesvirus infections.
How is the disease treated?
Treatment of herpes on the tongue can be quickly and effectively provided only by a doctor after making an accurate diagnosis and identifying a specific form of pathology. And in each individual case, the treatment method will largely depend on the individual clinical picture. Below are several general principles for combating the disease:
- elimination of all accompanying pathologies of the oral cavity - treatment of carious cavities, removal of plaque and dental deposits,
- rinsing with antiseptic solutions - Miramistin, Laripront, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin. If there is an advanced stage, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics,
- compresses - it is recommended to smear the affected areas with products that promote wound healing and eliminate pain. Among such ointments are “Kamistad”, “Vinizol”, “Malavit”, “Solcoseryl” and others1,
- treatment with oils: experts advise treating the affected areas with oil, for example, rosehip or sea buckthorn - they perfectly help in normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity,
- multivitamin complexes: taking healthy vitamins and minerals is necessary to restore the body's defenses.
The recommendations described above are relevant for most forms of glossitis, however, targeted therapy is necessary to effectively eliminate the disease.
Dietary recommendations
During treatment, experts advise following a certain diet. You should avoid foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Here are some important recommendations:
- give up too solid foods,
- food should be at room temperature,
- eat only fresh fruits and vegetables,
- It is better to exclude hot spices and acidic foods,
- limit the number of cigarettes you smoke and give up alcohol,
- exclude pickles and smoked products.
You should also avoid sweets if possible. Excessive sugar consumption during this period can lead to intensive proliferation of microbes in the oral cavity.
Possible complications
If no attempts are made to cure the disease, over time the lesion will spread further to the mucous membrane and will inevitably lead to serious health problems in general. In the worst case scenario, there may be a threat of an abscess, and it will have to be removed surgically. In this case, the person will experience throbbing painful sensations, and the tongue will increase in size, unevenly.
The photo shows a tongue abscess
How to treat a disease with folk remedies
Treatment of herpetic glossitis at home can only be as a concomitant therapy. To put an end to the problem once and for all, you need competent diagnosis and the help of a specialist. Let us remind you: only a doctor has the right to prescribe medications, and without his consent, you should under no circumstances make any attempts to cure the disease yourself. All this can end not only in vain, but also very disastrously.
If the specialist has given the go-ahead for the use of traditional methods, you should pay attention to medicinal herbs. For example, tea tree oil effectively promotes the restoration of mucosal tissue. Also, in the fight against glossitis, rinsing with a decoction of chamomile and a light solution of hydrogen peroxide have proven themselves to be excellent.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy 1 element | 700 rub. |
| Setting up functional tests | 190 rub. |
| Excision/removal of cutaneous/subcutaneous elements and formations (1 element) | 2550 rub. |
| Removal of milia of one unit using electrocoagulation | 350 rub. |
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of such an unpleasant and even dangerous disease as herpetic glossitis, you should adhere to the following tips and recommendations:
- you need to carefully care for your oral cavity, brush your teeth and tongue twice a day, rinse your mouth every time after eating,
- It’s better to stop smoking and drinking alcohol at least for a while,
- it is necessary to carefully control your diet, avoid too salty, spicy and sour foods, cold and hot dishes and drinks,
- it is important to regularly undergo preventive examinations not only with a dentist, but also with a gastroenterologist and immunologist,
- At the first symptoms of pathology, you should immediately seek medical help.
Regular brushing of teeth and tongue will help reduce the risk of disease.
Any form of glossitis, including herpetic, in the vast majority of cases develops against a background of weakened immunity. Therefore, an equally important condition for maintaining complete disease prevention is a healthy lifestyle. Walk outdoors more often, play sports, eat right, and don’t forget to take a responsible approach to oral hygiene.
- Borovsky A.L. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips, 2001.