Glossitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
Contents:
What is glossitis
Symptoms of glossitis
Causes of glossitis in adults
Types of glossitis in adults
How and with what to treat glossitis in adults
Prevention of glossitis
Doctor's advice
Answers on questions
There are many factors that lead to pathologies in the oral cavity. Glossitis - what is it? This is a term that combines various diseases of the tongue.
Treatment of glossitis
The treatment of glossitis is based on the correction of underlying diseases and the elimination of factors that provoke the occurrence of the inflammatory process. In addition, the therapy program includes:
- adherence to a diet that includes the inclusion of various purees, slimy porridges and pureed soups in the patient’s diet;
- rinsing the mouth with solutions of furatsilin or chlorhexidine;
- applications with solutions of pyromecaine, trimecaine, lidocaine and other anesthetics;
- relieving signs of dry tongue using a mixture of glycerin and anesthesin;
- accelerating the process of regeneration of affected tissues using drugs made on the basis of solcoseryl and vitamin A;
- surgical intervention (in the presence of pronounced hyperkeratic changes).
It is important to know that with timely and competent treatment, inflammatory lesions of the tongue can be easily corrected. An unfavorable outcome of the disease, characterized by the development of abscesses, cellulitis and cancer, is observed only in the absence of adequate therapy.
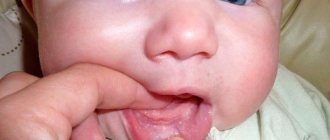
Symptoms of glossitis:
- pain when eating and moving the tongue;
- difficulty moving;
- color change, plaque appearance;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- deformation;
- loss of taste sensitivity (partial or complete);
- sensation of a lump in the throat, a foreign object in the oral cavity;
- the appearance of solid formations and compactions.
If these symptoms are detected, you should immediately contact dentistry in Moscow to avoid complications or the disease developing into chronic glossitis.
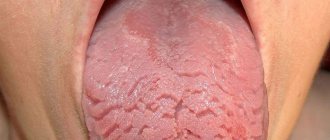
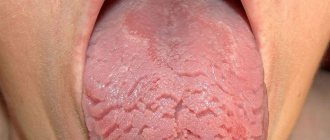
General symptoms of glossitis
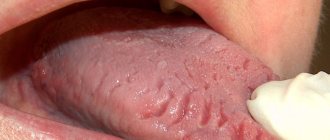
The first signs of inflammation of the tongue are discomfort, burning and the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. Subsequently, the tongue noticeably swells and acquires a burgundy or scarlet hue. The symptomatic picture of the disease may include:
- increased salivation;
- dullness or complete loss of taste;
- perversion of taste;
- pain and difficulty eating;
- slurred speech;
- the patient's desire not to use the tongue when creating sounds.
Symptoms of chronic glossitis
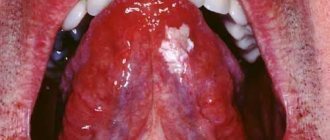
Chronic glossitis is characterized by persistent swelling and changes in the structure of the tissues of the tongue. With bacterial inflammation, hyperemia, soreness, swelling of the affected area and a local increase in temperature can be observed. The development of glossitis, which is of viral origin, is accompanied by the appearance of small blisters on the surface of the tongue, which eventually open and form painful erosions. The disease, which is of a fungal nature, is manifested by the appearance of a dense or loose white coating on the affected surface, as well as hyperplastic changes in tissue.
Causes of glossitis in adults
There are many factors that lead to the occurrence of this pathology:
- infectious factor (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- inflammatory gum diseases (periodontitis, gingivitis), carious teeth;
- poor oral hygiene;
- thermal, chemical burns;
- injury to the tongue with sharp objects, including sharp edges of fillings and dentures;
- smoking;
- reduced immunity.
Most often, patients have several factors that lead to
Types of glossitis in adults
- Interstitial glossitis - occurs with syphilis, often leads to cancerous tumors of the tongue
- Gunterovsky - the initial symptom of pernicious anemia, manifests itself in the form of smoothing of the surface.
- Diamond-shaped tongue is a developmental anomaly.
- Folded is a congenital developmental anomaly.
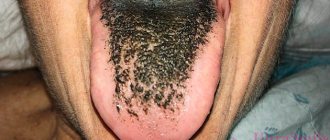
- Hairy tongue - severe keratinization of filiform papillae, resulting in a black coating.
- Geographic (folded) - noticeable red spots, furrows.
- Ulcerative – bleeding ulcers and bad breath are observed.
- Catarrhal - a white dense coating covers the entire surface of the muscle.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up
Types of glossitis
In modern dental practice, it is customary to distinguish the following forms of glossitis:
- deep;
- desquamative;
- diamond-shaped;
- villous;
- folded;
- Gunter's;
- interstitial.
Deep glossitis
Deep glossitis is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process at the bottom of the mouth and its gradual spread to the neck and chin. In most cases, the clinical picture of the disease is complemented by the formation of abscesses.
Desquamative glossitis
Desquamative glossitis is detected in pregnant women and people suffering from chronic gastrointestinal diseases, parasitic pathologies, liver diseases, blood diseases and metabolic disorders. The development of the inflammatory process is based on focal destruction of epithelial tissue, so its main symptoms are bright red spots, lines and furrows on the surface of the tongue.
Diamond-shaped glossitis
Diamond-shaped glossitis occurs against the background of gastritis with low acidity and other gastrointestinal diseases. Clinically, this form of the disease is manifested by the formation of bright red or bluish diamond-shaped areas in the root zone of the tongue. In some cases, the affected surface may atrophy, become covered with dense bumpy growths or hyperplastic growths.
Villous glossitis
Villous glossitis is characterized by elongation and keratinization of the papillae of the tongue. The risk group for this pathology includes smokers, as well as people suffering from candidiasis and using medications for a long time.
Folded glossitis
Folded glossitis is manifested by the appearance of painless folds on the back of the tongue. This form of pathology is congenital and requires treatment only for aesthetic reasons.
Gunter's glossitis
Gunter's glossitis occurs against the background of anemia caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12 in the body. In this case, the surface of the tongue acquires a bright crimson color, becomes smooth and shiny.
Interstitial glossitis
Interstitial glossitis is characterized by the replacement of part of the muscle tissue of the tongue with connective tissue and is one of the signs of syphilis of the tertiary period. This form of the disease is considered a precancerous condition in the patient and requires urgent treatment.
Answers on questions
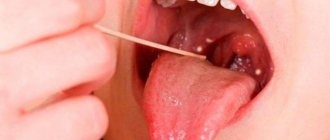
What diagnostics are carried out before treatment?
The dentist examines the patient, collects medical history data: complaints, data on the patient’s general health (presence of chronic diseases). If necessary, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed: a smear (culture) from the oral cavity for microflora.
How to treat hairy tongue in adults?
The doctor prescribes complete sanitation of the oral cavity: removal of stone, plaque, and carious teeth. Selects individual home hygiene products. Prescribes a diet that includes plenty of fluids and solid vegetables. Smoking is prohibited. If necessary, the dentist prescribes rinsing solutions and antibacterial agents.
Table - diseases that manifest as a sore on the tongue
Below is a table with a detailed description of tongue diseases.
| Disease | Symptoms | Treatment | Forecast |
| Stomatitis | Main signs of the disease:
| Depending on the type of disease, the doctor may prescribe:
| The prognosis for people suffering from stomatitis is favorable, especially if the person receives appropriate treatment. Complications, as a rule, are not observed, except for the chronic form of the pathology. Therefore, it is important to treat stomatitis in a timely manner, as well as follow the doctor’s preventive recommendations. |
| Injury | Main features:
| Treatment involves treating the wound with iodine tincture or brilliant green. In some cases, antiseptic medications are used. The doctor may prescribe rinsing the mouth with disinfectants. In addition, it is necessary to maintain oral hygiene and take vitamins B and C. In case of severe injuries that result in bleeding, sutures are allowed. | With timely treatment of this phenomenon, the prognosis is considered favorable. |
| Syphilis | At the initial stage of development of the disease, general malaise, loss of strength, depression, and depression appear. Next, painless round chancres (red bumps) form on the tongue. In advanced cases, enlarged lymph nodes, destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, tooth loss, and collapse of the nose are possible. | Therapy for this disease involves the use of penicillin medications. If an allergic reaction occurs, these drugs are replaced with Erythromycin, Tetracycline or Cephalosporin. In some cases, aminoglycosides are prescribed to inhibit the growth of syphilis pathogens. | The primary and secondary stages of this disease can be completely cured. However, after completing the course of therapy, it is necessary every 3 months. take control tests within two years. The tertiary stage of syphilis is now also being treated, but the deformations of the tongue that have begun cannot be restored. Also, the deep star-shaped scars left after gummas do not disappear. |
| Cyst | Cystic neoplasms (ranulas) affect the mucous membrane, as a result of which salivation worsens and the oral cavity dries out. As the disease progresses, the patient develops speech impairments and problems chewing food. | In case of infection of the affected area, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and antibacterial medications are prescribed. The optimal method of treating ranulas is to remove them in several ways:
| In most cases of cystic neoplasms, the prognosis is considered favorable. The disease does not pose a serious threat to the health and life of the patient. |
| Cancer | The disease manifests itself by:
| The following methods are used to treat this disease:
| With timely detection and radical combination therapy for tongue cancer, the prognosis is considered favorable in 65–80%, in some cases up to 95%. When starting treatment for advanced stage cancer with metastases to the lymph nodes, patient survival is no more than 35%. |