54079
Crooked, unhealthy teeth can ruin the appearance of an otherwise attractive person. Oral health is important not only for our attractiveness, because the main function of teeth is to grind food. The condition of the stomach and intestines depends on this, which directly affects health and life expectancy .
Correct bite: what is it like?
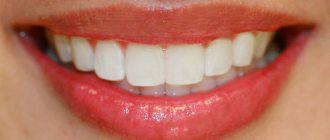
Bite is the way the teeth of both jaws interact when they are completely closed. If it is correct, there are no difficulties when chewing and pronouncing sounds, the aesthetics of the smile is not impaired, but minor defects are still possible. What does a bite that does not require orthodontic treatment look like? Its main characteristics:
- Presence of 28–32 teeth. Not all people develop “eights”, which is determined by genetic factors. Their presence (if they have grown correctly) or absence does not affect the closure of the jaws. Moreover, in some cases, wisdom teeth removal is indicated during orthodontic treatment. Then there is more free space in the mouth.
- Symmetry in the closure of the dentition.
- The incisors of the upper jaw overlap the lower ones by one third.
- No interdental gaps, cracks or chips.
- Correspondence of molars and premolars of both dentitions to each other. Their closure is tight.
- Ease of chewing food, even hard ones. Opening the mouth is easy and there is no pain.
Correct bite does not always look aesthetically ideal. But the face is harmonious.
Some terminology
The arrangement of the lower and upper teeth in relation to each other is called the bite. There is a similar concept - occlusion, which refers to the natural closure of the jaws. This is a process where the masticatory muscles, teeth, and temporomandibular joints take part. There are central, anterior and lateral clutches of the jaws. Central occlusion, in essence, is a bite. If it is correct, it is called physiological; if not, it is called abnormal or pathological. With normal occlusion, the functions of chewing and speech are not impaired. With pathology, it’s the opposite.
Types of correct bite
The above describes the orthognathic bite, which is the reference. It occurs in only 5% of people. But there are other types of teeth closure in which violations are not detected. What does each one look like? Experts identify the following bites:
- Biprognathic. Both jaws are slightly pushed forward, and the teeth are slightly directed towards the lips.
- Opisthognathic. The opposite of the previous type. The teeth are directed inward. Opisthognathic occlusion is rare. Its features are noticeable when viewed in profile.
- Progenic. The lower jaw protrudes slightly, but this feature is not pathological. The functioning of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and the functionality of the teeth are not impaired.
- Straight. The upper row of teeth is parallel to the lower one. The incisors touch their cutting edges. This feature is not a deviation, but it threatens rapid wear of the teeth due to increased load.
Sometimes, if you have one of these malocclusions, minor adjustments may be needed. But the treatment in this case will be easy.
When should the situation be corrected?
There are often cases when, with a normal physiological occlusion, it is necessary to carry out correction. Direct occlusion leads to tooth wear, and progenic and biprognathic bites can cause aesthetic discomfort, for example, when the upper lip is very short, exposing the front teeth, or when they are large and unsightly.
Abnormal types of closure with obvious defects require mandatory correction, since such pathologies interfere with the normal functioning of the jaws, have a negative effect on the body, and distort the proportions of the face.
There are several pathological levels:
- Violation of the shape, position and number of teeth.
- The size of the dentition is increased or decreased.
- Abnormal positions and sizes of the jaw bones.
The severity of the pathology is influenced by the area and degree of deformation of the constituent elements of the dental system. Therefore, when identifying an abnormal bite, it is important not only to identify the defect, but also to establish the reasons for its development.
Anomalies in the closure of teeth
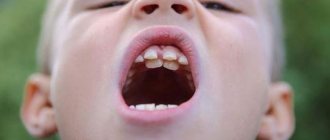
Dental rows are not always placed correctly. How do you know when treatment is required? Depending on the type of malocclusion, the following signs of violations are distinguished:
- Distal - the upper jaw is more developed when compared to the lower jaw. She comes forward significantly.
- Mesial. The situation is the opposite of the previous case - the lower jaw is more developed. It may bulge forward slightly or strongly.
- Cross. With this pathology, there are interdental gaps. Part of the upper front teeth is behind the lower ones, and the other part is in front of them. Such a smile looks unaesthetic. As a rule, teeth grow in different directions.
- Deep – the upper row of teeth almost completely overlaps the lower one. If even more than 30% of the teeth are blocked, this is considered a pathology. But visually such a violation may not be visible.
- Open. When the jaws close, only the chewing teeth come into contact; pronounced gaps are visible between the front teeth. In some cases, it looks like an open mouth.
Whatever the diagnosis, any pathology must be treated.
Self-diagnosis
The presence or absence of an anomaly can be determined independently. You need to stand in front of the mirror, swallow and naturally close your teeth. The jaw line normally looks like this:
- There is no gap between the rows - the teeth are in close contact with each other.
- The imaginary vertical lines between the lower and upper incisors coincide.
- The upper row overlaps the lower teeth by a maximum of a third of the height.
- The cutting edge of the lower incisors is in contact with the palatal cusps of the upper ones.
- During chewing movements, the molars do not lose contact with each other.
- The upper dental arch, similar to a semi-oval, is larger than the lower one and is inclined slightly towards the mouth. The lower one is similar to a parabola and is directed towards the larynx.
Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish between normal and pathological. An orthodontist can assess the state of the structure of the dental system.
How to find out what kind of bite you have
Patients are often interested in how to determine whether their bite is correct. Usually the presence of abnormalities can be identified by facial features. It is also worth taking into account the criteria for correct bite described above. Go to the mirror, open your mouth and clench your teeth. In some cases, violations are immediately visible. Just because your smile looks aesthetically pleasing does not guarantee that everything is fine.
Even if you know what a correct bite should look like, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis on your own. Only a specialist can do this. In addition to a visual examination and medical history, the doctor diagnoses the problem based on the results of a CT scan (computed tomography). Such an examination allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the oral cavity. Disturbances in the placement of teeth are also identified by an impression made from an alginate mass. The orthodontist also needs photographs of the person’s face taken from several angles. Using them, you can evaluate the occlusal relationships of the dentition.
Prevention
In order for people to be able to boast of their smile and perfectly positioned teeth as adults, they need to start taking preventive measures in infancy:
- Every woman during pregnancy should protect herself from all kinds of infections. It is necessary to take vitamin and mineral complexes and eat right.
- Mothers should ensure their children receive constant breastfeeding. In this case, children will have much less problems with teeth.
- Babies need to choose the right pacifier. If he is bottle-fed or is given juices from a bottle, then you should not make too large a hole in the nipple.
- Mothers should ensure that the child does not suck his finger, as this habit can lead to the development of deformation processes.
- If your baby is already teething, he should be introduced to solid food.
- It is recommended to carry out myogymnastics with children, which involves performing a number of exercises that contribute to the formation of an ideal bite.
Possible consequences of malocclusion
Anomalies in the location of the dentition relative to each other are fraught with the following problems:
- Increased stress on teeth, causing them to quickly wear out and break down. There is a risk of developing periodontal disease. If measures are not taken, a person may be left without teeth.
- Intensive formation of tartar. Sometimes bite pathologies do not allow you to properly brush your teeth.
- Increased gum sensitivity. Sometimes even ulcers form on them.
- Injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth, cheeks, gums, tongue, tissue inflammation.
- Development of TMJ diseases. They are provoked by increased load. These joints compensate for missing teeth. First, a person feels discomfort in the facial muscles, an unpleasant clicking in the TMJ, and pain appears. After some time, the headache begins to hurt, changes in appearance are visible.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. With malocclusion, it is difficult to chew food normally. Insufficiently crushed food ends up in the stomach, which leads to excessive stress on it. Over time, this can provoke some kind of disease.
- Disorders of respiratory, chewing and swallowing functions. If teeth are not positioned correctly, ENT diseases develop. Headaches and discomfort in the facial muscles appear.
In addition to problems with the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole, malocclusion can provoke psychological problems. Because of an ugly smile, a person becomes insecure and complexes appear. Difficulties may arise with the pronunciation of sibilants.
Knowing how to determine whether your bite is correct, you can eliminate the problem in a timely manner before your health is damaged.
What causes malocclusion to form?
Defects appear for various reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. In most cases, mesial and distal bites are inherited. Therefore, parents who have this problem should take their child to an orthodontist in early childhood.
- Anomalies of fetal development. A child’s teeth are formed while still in the womb. During a complicated pregnancy or the influence of negative factors on its course, anomalies of the dental system can form.
- Birth injury. Mesial bite in some cases is a consequence of dislocation of the baby’s lower jaw during childbirth.
- Bad habits. Constant thumb or pacifier sucking, improper latching of the nipple, incorrect sucking during artificial feeding - all this provokes the development of malocclusion pathologies.
- Inferiority of the dentition. You can resort to removing baby teeth if there is less than a year left before the change. Otherwise, the dentition becomes asymmetrical, the midline shifts, and the chewing movements of the jaw are blocked. The formation of a permanent bite ends at approximately 15 years of age. For adults, after tooth loss, it is important to undergo prosthetics in a timely manner.
- Displacement of the jaws as a result of hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, which can be observed due to stress.
Jaw injuries, as well as improper prosthetics, can provoke the development of malocclusions.
Features of treatment
About thirty years ago, only children and teenagers under 16 years old could count on correction of pathology.
Thanks to the active introduction of new technologies in the dental field, today people of different age groups can have an ideal smile.
To correct defects, innovative brace systems are used, which exert physical pressure on the deformed jaw over a fairly long period of time.
In the most difficult situations, dentists resort to prosthetics, as well as various types of surgical interventions.
How to correct an overbite
Orthodontic treatment is carried out at different ages, but it is easier and faster in children. For adults, it takes longer to correct abnormal teeth alignment. The milk bite is also subject to correction. Although it will be replaced over time, permanent teeth grow in the place of their predecessors. Modern methods of bite correction are safe. They cause the patient only minor discomfort.
The doctor carefully studies the problem, assesses the condition of the oral cavity (if necessary, it is sanitized) and develops a treatment regimen. One of the following designs can be used in the process:
- Bracket systems. There are different types. They differ in aesthetic qualities, installation methods and prices. Such orthodontic structures will help correct almost any disorder.
- A mouthguard is a polymer product made from an individual impression. Easily removable, which is necessary for eating and brushing teeth.
- Records. The most effective designs for correcting primary malocclusion. They can also be given to adults, but this will not be the main treatment.
In complex cases (congenital pathologies), surgical intervention is required. Sometimes auxiliary techniques are used. Treatment of tooth wear in a “reducing bite,” in which dental tissue wears down with age, is carried out through prosthetics with crowns or veneers.
Remember! Correcting your bite is not only about getting a beautiful smile, but also a significant contribution to your health. Entrust the solution to your problem to a specialist. He knows how to check the bite for abnormalities. If they are identified, the correction will be carried out competently.
Importance
It is extremely important for every person to have the correct bite, as it is not only pleasant, but also useful:
- The first advantage is the correct facial contour and a beautiful smile, which will greatly facilitate the process of meeting and further communication with people.
- The second advantage is the absence of speech defects, thanks to which a person will become a pleasant interlocutor whom others will listen to with pleasure.
- The third advantage is the normal functioning of all related systems of the body, in particular the digestive tract.