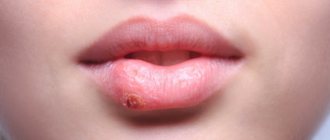
The term “diathesis” in domestic medicine refers to a feature of the body’s constitution, which is expressed in a predisposition to certain diseases. Usually, diathesis refers to allergic diathesis, the most common and easily diagnosed. According to various sources, diathesis occurs in 30-75% of children.
Unlike allergies themselves, diathesis is not associated with functional disorders of the immune system. An allergic reaction during diathesis in infants is usually explained by the characteristics of the child’s body. In children of the first year of life, the protective function of the intestine is reduced: the intestinal walls are thin, the amount of enzymes and antibodies produced is small. As a result, the child’s body may not be able to cope with a large number of highly allergenic foods and give an allergic reaction. By two to three years, the amount of enzymes becomes sufficient, and diathesis in most cases goes away.
Symptoms of diathesis
Inflammation of the skin during diathesis is the body's reaction to contact with an allergen. The main way an allergen enters a child’s body is food, but a reaction to contact with the skin of the allergen is also possible (the allergen, for example, can be components of washing powder that get on clothes during washing, plant pollen, dust, animal hair, etc.).
Diathesis in children under 3 months of age
The first manifestations of diathesis most often appear at the age of 2-3 months. This:
- diaper rash that does not disappear even with careful care;
- profuse prickly heat with mild overheating;
- sebaceous crusts of gray-yellow color on the head in the hairline area (seborrhea).
Diathesis in children aged 3 months and older
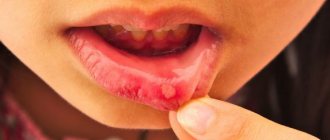
In older children, a typical manifestation of diathesis is red spots on the cheeks. As the condition worsens, the skin becomes crusty. The crusts become wet, the child experiences discomfort, itches, becomes excitable, sleep and appetite may be disturbed, and loose stools may appear.
Causes of congenital facial asymmetry in children
Congenital facial asymmetry in children is usually associated with developmental abnormalities of the skull bones and connective tissue. The cause may be intrauterine injuries, fetal presentation, torticollis, pathologies of the formation of bone and cartilage tissue caused by intrauterine infections. Sometimes congenital facial asymmetry is caused by rare genetic pathologies associated with chromosome mutations, for example, Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
Like any skeletal anomalies, facial asymmetry in all these cases is well corrected by osteopathic treatment in combination with therapeutic massage.
Methods of treating diathesis
When dealing with diathesis in a young child, the main thing is to choose the right diet, excluding foods that may cause an allergic reaction.
For a child in his first year of life, it is very important to receive breast milk.
The proteins of human milk are easily broken down by the baby's enzymes and are completely devoid of allergic properties. However, a nursing mother must also follow a diet excluding fish, poultry, tomatoes, chocolate, smoked meats, spices and other allergenic foods.
When mixed feeding, the child should not be given some juices: orange, carrot, tomato. Introduce any new product carefully - from a small amount. It is important to prevent an allergic exacerbation, and at the same time, to give the baby’s body everything it needs for its development.
Specialist consultation
The Family Doctor pediatric allergist-immunologist will help you deal with your child’s skin problems, determine the cause of allergies, and also build a rational diet that is suitable specifically for your child.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Hirschsprung's disease in children: no need to panic
Many genetically determined diseases are incurable, but there are lucky exceptions. For example, Hirschsprung's disease in children. Mikhail Yuryevich Kozlov, head of the surgical department of the Morozov Children’s Hospital, coloproctologist, pediatric surgeon of the highest qualification category, candidate of medical sciences, holder of the “Moscow Doctor” status, spoke about how this disease manifests itself, why it is dangerous and how it should be treated.
What do parents need to know about Hirschsprung's disease?
This is one of the most severe congenital defects of the colon, but it is curable. At certain stages of embryonic development, the wall of the colon does not receive a normal structure, that is, nerve ganglia (clusters of nerve cells) are not formed in it. As a result, the intestines do not perform their normal functions. The cause of the disease is a genetic failure. Changes in chromosomes can be either hereditary or spontaneous. Fortunately, the disease is quite rare: 1 case in 5,000 newborns. Today, the likelihood of having a child with Hirschsprung's disease can be determined using a genetic test. This is especially true if there has already been a case of this disease in the family.
What symptoms suggest Hirschsprung's disease?
The absence of nerve ganglia (or their deficiency) leads to the fact that the intestinal wall does not stop - it cannot push feces towards the exit. A condition arises that is popularly called constipation, and we, doctors, talk about stool retention. This is the main manifestation of Hirschsprung's disease. However, everything is individual: if for one child going to the toilet 3 times a day is considered the norm, then for another, stool 2 times a week will not be a deviation. Provided that such stool retention is not combined with other clinical manifestations. But progressive constipation, along with a lack of appetite, bloating and developmental delays in a child, is already a reason to immediately consult a doctor to rule out Hirschsprung’s disease at an early stage.
What does Hirschsprung's disease lead to if left untreated?
The consequences of the disease are extremely severe. If the child is not operated on in time, he will stop going to the toilet, a large amount of feces will accumulate and his colon will overstretch. As a result, chronic fecal intoxication will occur: the stomach will begin to swell, appetite will disappear, and vomiting will appear. If a child has been suffering from this problem for a long time, then, against the background of intoxication, by the age of 3–4 years of life he will develop encephalopathy with all the ensuing consequences: developmental delay, uncontrolled psycho-emotional behavior, problems with attention, etc.
Is Hirschsprung's disease currently curable?
Yes, 100%, but we are talking exclusively about surgical treatment. Hirschsprung's disease is not a case where some mythical drops will help; it can only be treated by surgeons. The operation is called "single-stage laparoscopic colon resection." For the first time in Russia, we performed this operation at the Izmailovo Children's Hospital back in 2004, and at the Morozov Hospital we have already continued to improve this technique. Since then, we have successfully operated on more than 700 children, and our hospital is one of the most advanced in terms of treating this disease.
The essence of the operation is extremely simple: laparoscopically, that is, through three small punctures on the anterior abdominal wall, the aganglionic (i.e. non-functional) section of the colon is excised, its healthy part is lowered down and sutured, roughly speaking, to the butt. Then a direct anastomosis is performed, without any stoma (an artificial opening between the intestinal cavity and the environment). The surgical intervention is performed under general anesthesia with the obligatory addition of epidural anesthesia in order to minimize the use of narcotic analgesics in the child in the immediate postoperative period. On average, a small patient stays in the hospital for no more than two weeks.
All parents are concerned about the question of how safe such an operation is for the child, since during it about 40 cm of the colon can be removed?
Theoretically, any operation, even banal removal of a wart, can have complications for the body. As for one-stage laparoscopic colon resection, over 16 years of experience in our clinic using modern equipment, we have perfected the surgical technique. Therefore, the risk of postoperative complications is 0.5-1%. Judge for yourself: if at the stage of mastering the technique the operation lasted 3–4 hours, today it takes no more than 40 minutes. In this case, two medical teams work simultaneously: one from the abdominal cavity performs the laparoscopic stage, the second from the perineum performs the perineal stage.
After laparoscopic surgery, is Hirschsprung's disease cured forever or will the child need some more treatment throughout his life?
Yes, after a competently performed laparoscopic resection of the colon in one stage, the child no longer needs any surgical intervention and leads a normal life. The only exceptions are secondary patients. Our colleagues in the regions are mastering this technique, but the level of equipment or experience does not always allow it to be performed flawlessly. Recently, we have had a sharp increase in the number of repeat operations: children are being admitted who have already been operated on 2-3 times. But repeated reconstructive surgical interventions are more dangerous in terms of the number of complications and the postoperative result is no longer so ideal.
Can you share the most interesting case from your practice related to Hirschsprung's disease in a patient?
For the operating surgeon, every case is interesting, and it cannot be otherwise. But the most memorable is, of course, the very first patient. For me, this was a boy named Ilya, who was successfully operated on in 2004. Now he is already an adult young man who is preparing to enter a university. He is absolutely healthy and leads a full life. Therefore, I want to give only one piece of advice to all parents: don’t panic! You just need to operate on the child as soon as this disease is detected. Diagnosed with Hirschsprung's disease in a month? This means that we need to operate within a month. If diagnosed in a year, it is necessary to operate in a year. Don't wait and don't be afraid.
Can only Muscovites undergo surgery at the Morozov Hospital in Moscow, or is it also available for children from other regions of Russia?
In our hospital, this operation is performed free of charge for all residents of Russia under the compulsory medical insurance policy! The main thing is to contact us for help in a timely manner.
Source: Moscow - the capital of health
Stages of development of facial asymmetry
- First stage. The functionality of the facial nerve is preserved, no significant changes are observed.
- Second. A slight curvature appears when a person closes their eyes or smiles. The patient has weakness of the facial muscle tissues.
- Third. Signs of asymmetry are more pronounced, difficulties appear in raising the eyebrows, muscle mobility is partially limited, and there may be spasms.
- Fourth. The face becomes asymmetrical even at rest, the eye does not cover completely, and the position of the mouth is disturbed.
- Fifth. The main sign is the absence of contracture; movements of the injured side are imperceptible.
- Sixth. Muscle tone decreases, the patient complains of the inability to move the muscles of the affected part of the face.
If any signs indicating a violation of the symmetry of the front sides appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
The main causes of asymmetry in infants
The scientific literature describes more than 20 reasons that cause dissymmetry of the baby’s head and face. All of them can be classified into one of 2 groups - congenital and acquired.
A congenital anomaly is caused by genetic disorders in the formation of connective and bone tissue. Deformation of the facial part of the skull is observed in some chromosomal aberrations - syndromes:
- Treacher Collins;
- Goldenhar – craniofacial microsomia;
- Wolf-Hirschhorn;
- Sotos;
- Setre-Chotzena;
Intrauterine infections, asphyxia, complications during the gestational period, abnormal position of the fetus (presentation, multiple births) are also a significant cause of facial asymmetry. Disruption of the formation of tissues and parts of the skull, uneven healing of sutures (plagiocephaly), curvature of the nasal septum due to pathology of the development of cartilage tissue lead to pronounced disproportions.
Acquired facial asymmetry in a child develops under the influence of internal and external factors:
- birth and other injuries;
- obstetric complications;
- infectious and viral diseases;
- pathologies of ENT organs;
- ophthalmological diseases;
- dental anomalies and pathologies;
- incorrect position in the crib/stroller;
- torticollis;
- rachiocampsis;
- tumors;
- abnormalities of the temporomandibular joint;
- malocclusion.
Birth trauma of a newborn occurs as a result of violation of the technique of forced extraction of the fetus - application of obstetric forceps, vacuum extraction. Noticeable facial asymmetry can be caused by injury:
- skull bones - fracture, crack of the temporal bone, orbit of the orbit, jaw;
- muscle tissue - the sternocleidomastoid muscle is most often damaged, which leads to torticollis;
- nervous tissue – paresis of the facial nerve.
Fig 2. Severe facial disproportion with muscular torticollis
Torticollis can also be caused by damage to the spinal column, nerves, muscles, skin and subcutaneous tissue (scarring). Prolonged positioning on one side in a crib or stroller can provoke the development of deformity. Also, the anomaly can be adaptive-compensatory, for example, with strabismus, hearing loss, scoliosis. With torticollis, the child’s head is tilted to the side of the soft tissue lesion, takes a forced position, the eyebrow, ear, and eye on the side of the tilt are located lower than on the healthy side. The eye is slightly closed, the corner of the mouth is slightly lowered, the body is curved, the shoulder is raised.
Muscular hypertonicity on one side of the head, neck (sternocleidomastoid, trapezius masticatory muscles) can also cause asymmetry. Muscular dystonia is caused by a developmental disorder of the temporomandibular joint, which leads to a crossbite. An attempt to fix the joint and keep the mouth closed causes muscle hypertonicity on one side and relaxation on the other.
The most difficult to correct is damage to the facial nerve. It is caused by the following reasons:
- birth injuries;
- neuroinfections with mumps, herpes, measles;
- Bell's palsy;
- inflammatory processes in the ear (otogenic);
- complications during the operation.
The facial nerve does not recover and causes paralysis of facial muscles, dysfunction of sucking, swallowing, chewing, and speech. The child has difficulty closing the eyelids, and there is lacrimation on the injured side. With age, the disease will progress, causing increased asymmetry. The child’s face on the affected side resembles a mask:
- smoothed nasolabial and frontal folds;
- drooping corner of the mouth;
- the palpebral fissure is widened.
The asymmetrical appearance of the facial part is accompanied by pain along the nerve. New growths in the nasal cavity, salivary gland, and paranasal sinuses can deform the face.
Reasons why one half of the face is larger than the other
Many people complain that one side of their face is different from the other. This becomes noticeable when carefully examining yourself in the mirror or in unsuccessful photographs. Some, noticing that their cheeks are different, begin to “sound the alarm” fearing that they are sick.
In fact, slight asymmetry is present in absolutely every person. This is what makes our face alive, unique and inimitable.
To make sure that each person is not symmetrical, you can take several photos of your friends and cut them into two equal parts along the line of the nose in a photo editor. Now one of the right halves is “mirrored” and connected to the other, and we do the same with the left parts. Take such photographs of several people, and you will see that the faces of the right and left halves of the same person are very different.
However, different halves of the face are not always the norm. Let's look at what factors can lead to pathological changes.
Reasons why one side of the face looks very different from the other:
- Improper development of bones and joints, as well as connective or muscle tissue. Such problems can be more or less pronounced, they can only be corrected with proper makeup or plastic surgery.
- Inflammation of the cheek can also lead to its enlargement. After eliminating the problem, the face acquires normal contours.
- Severe strabismus can also develop facial asymmetry. The same applies to torticollis.
- Facial muscles can become severely distorted when nerves become pinched or die. This problem often occurs with strokes and heart attacks.
- An incorrect bite or missing teeth on one side can lead to facial asymmetry. Flux can also cause a similar problem.
- A fracture of the facial bones that did not heal properly.
- The habit of chewing, sleeping or squinting to one side is the most common cause of facial asymmetry.
There are many reasons. Some of them can be avoided by taking timely treatment and controlling your facial expressions.
One side of the face is larger than the other: normal or pathological
If you notice that the sides of your face are different, first of all, you need to determine whether it is pathological or normal. To do this, you need to know the symptoms of the pathology.
If there is facial asymmetry, parchment skin may be present. This symptom is associated with a genetic disease.
Asymmetry, which is considered normal, should not be too obvious. If this is a normal facial structure, then the difference is noticeable only upon careful examination.
Symptoms of abnormal facial asymmetry:
- The affected side is swollen and the tissue may be hard;
- The corners of the mouth and cheek on the affected side are drooping and drooping;
- The affected half of the face loses mobility;
- The folds on the forehead and nose suddenly smooth out sharply;
- The eye on the affected side becomes narrower, or, conversely, larger;
- The eyes, nose and lips on the affected side lose mobility;
- There are speech disorders;
- The affected part is painful.
Even one of these signs suggests that asymmetry is the result of a serious problem. In this case, it needs to be treated.
Gymnastics to restore symmetry or how facial muscles work
Facial muscles are constantly working. However, if this occurs unevenly, asymmetry may occur. This problem also often appears with age. If this is not associated with the presence of serious diseases, then the problem can be eliminated with the help of gymnastics.
Exercises to eliminate facial asymmetry:
- The palms hold the muscles and skin of the forehead, while the eyebrows rise as much as possible up and down;
- We open our eyes as wide as possible and hold this for three counts, relaxing our eyes;
- We inflate our cheeks as much as possible, count to three and retract them, again counting to three;
- We inflate and deflate the cheeks one by one;
- Smile from the top of your mouth without showing your teeth, and then form your lips into a tube;
- We move the jaw forward, left and right.
We perform each exercise ten times. If done regularly, exercise will give the first results within a month.