High-quality restoration of contact chewing surfaces is the key to proper load on the teeth
When our teeth hurt or decay, all we want is to get rid of pain and discomfort, and also to protect them from removal. How the dentist will act in this case does not even matter to many patients. The main thing is that the work is done efficiently. But when it comes to the treatment and restoration of dental contact points, it is good to understand at least a little about the terminology and restoration methods that doctors use to carry out this incomprehensible procedure.
Reviews
Restoration of teeth, and in particular, the correct restoration of their contact points, is a very important topic in dentistry.
Are all professionals coping with such an urgent problem? You can share your experience of receiving or providing such treatment in the comments.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: tooth extension, tooth decay
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Basics of Root Canal Irrigation
Next article
Subtleties of specifying tooth color according to the Vita Scale to restore smile aesthetics
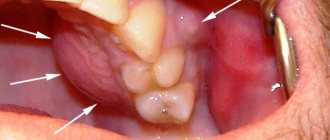
Let's understand the terminology: what is a tooth contact point?
For many people, it is a mystery what the contact point between the teeth is. Let's figure it out.
Our teeth are located in the mouth in such a way that their lateral surfaces touch each other and thereby create a continuous arch, which is a single whole and forms a beautiful smile. This is provided that the person does not have any pathologies of the maxillofacial system or there are no missing units.
On a note! The contact point is easy to detect if you pay attention to the interdental spaces - they have a triangular shape in the gingival region, and the tip or apex of the triangle is directly facing the point of contact of the teeth.
If you open your mouth and look at its contents in the mirror, you will see that each tooth has a vestibular, i.e. on the external, visible side, in addition to the most frontal coronal part, there is a cutting edge, a neck and two contact (they are also called “proximal”) surfaces on each side, i.e. these are vertical areas facing neighbors. In those places or points (as a rule, these are the convex parts of the lateral surfaces of the crowns) where the tooth comes into contact with neighboring units, a contact point is formed. Incisors, canines, premolars always have two adjacent contacts on both sides (medial and distal) and only the outer molars in the row have only one such contact point (we are talking about sevens or eights, i.e. wisdom teeth, if you have any There is).
It is important to understand that there are several contact surfaces - lateral (one or two), as well as chewing ones. But it is the contact point that is called the lateral surface in the area of the apex of the crown of a living tooth.
Prevention
Treatment of interdental caries is always more expensive than any preventive measures. Therefore, it is worth making a little effort to prevent this disease:
- Brush your teeth, moving the brush in the right direction, at least twice a day.
- Use enamel strengthening products recommended by your doctor.
- For hygienic treatment of interdental spaces, use floss and irrigators; carry out this procedure before bed.
- Eat fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, and do not overindulge in sweets.
- After eating carbohydrate-rich foods, rinse your mouth with special products or a soda solution.
- Once every 6-12 months, undergo a professional hygiene procedure at the dentist. The doctor will remove soft plaque and dense dental deposits and remove stone.
- Avoid overloading the maxillofacial system.
An important condition for the prevention of interdental caries is regular scheduled examinations by a dentist. They won't take much time, but they will bring great benefits. When carious lesions appear in hard-to-reach places, only a doctor can detect them. And, perhaps, he will carry out treatment without a drill or filling.
Types of contact points
Experts distinguish only two types, characterized by the peculiarities of the fit of the two proximal surfaces of neighboring units.
The first one is point. This type of contact is typical for children who have recently erupted teeth and for young adults. The crowns themselves in the area of contact have an almost ideal round or spherical shape, so they interact with each other only pointwise.
The second is planar. This type is typical for mature and elderly people, because... Over the course of life, the enamel gradually wears out and wears out, and the coronal part in the lateral areas gradually becomes flat as a result of friction and physiological mobility of the units. As a result, the lateral surfaces of neighboring teeth are no longer limited to point interaction, but have quite pronounced proximal areas or points.
About the head doctor
Hello, my name is Maxim Vladimirovich Arkashov. I am a practicing implantologist, orthopedist, founder and director of the KDM Center for Dental Medicine in Moscow. Because I now manage a team of smart and talented doctors and technicians, I have had to become an expert in many areas of dentistry. Currently, I am engaged in aesthetic rehabilitation on a functional platform - this complex vocabulary means that everything I do with patients is first precisely verified taking into account their functional characteristics (type of body growth, type of formed bone class of the jaws, stereotypes of neuromuscular activity of the maxillofacial system ). And it’s precisely in such huge system analyzes that digital dentistry comes to the rescue; we can create 3D virtual treatment plans and predict how the rehabilitation will end!
vote
Article rating
Why are contact points needed?
The functions of dental contact points cannot be underestimated, because the health of the oral cavity as a whole, the condition of the maxillofacial system, and the aesthetics of a smile depend on their correct structure and location.
So, let's take a closer look at what having an anatomically correct contact point gives:
- the teeth are able to lean on each other and provide each other with support,
- each unit occupies its designated place in the row and is protected from loosening and displacement,
- in the presence of a contact point, a correct redistribution of the chewing load occurs: when a load is applied to the tooth during chewing, its coronal part is deformed due to a reduction in height and expansion in different directions. As the crown expands, the load is transferred throughout the row through the contact surfaces,
- The gingival papillae that fill the interdental spaces remain protected from food particles and injury.
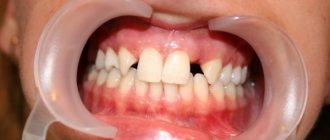
If you have caries or, due to various circumstances, damage to the contact point occurs, then any irritant can cause the development of an inflammatory process on the gingival papillae. The same food debris that gets into the interdental spaces can injure the delicate mucous membrane and provoke a disease such as gingivitis. If the problem is not given attention, gum inflammation will be complicated by periodontitis, mobility, displacement, loosening and even tooth loss.
Also, if the anatomically correct contact of the lateral surfaces of the teeth is disrupted, one of them may eventually receive excessive occlusal load or pressure during chewing food and quickly begin to collapse. A characteristic sign indicating functional overload is vertical cracks in the enamel. The same traumatic occlusal load on the maxillofacial apparatus is characteristic of people who have had part of their teeth removed or lost, but are in no hurry to restore them, get prosthetics, or do implantation.
Therapeutic dentistry
Dental treatment near Chistye Prudy metro station.
IMPORTANT: Dentist therapist
The orthopedist is the leading specialist in the treatment of the patient, and he coordinates the actions of specialist doctors: periodontist, orthodontist and implantologist. Involving highly specialized specialists in the work will allow you to correctly build a treatment plan and improve the quality of the service provided.
What diseases does therapeutic dentistry treat?
- Caries.
- Non-carious lesions: wedge-shaped defect
, enamel hypersthesia.
(sensitivity), abrasion
, enamel erosion (hypoplasia). - Aesthetic defects are abnormalities in the color and shape of the tooth.
- Canal treatment ( endodontics ).
The competence of an orthopedic therapist also includes not only the treatment of caries, non-carious lesions of teeth, root canal treatment, but also prosthetics. Particular attention is paid to the prevention of pathologies of the dental system.
Treatment methods and diagnostics.
Prices for dental treatment near Chistye Prudy metro station.
Cost of caries treatment
at the dental clinic "Dentist" is presented
on the Price website page. The price of
caries treatment
procedure depends on several factors: anesthesia, the number of teeth to be transformed and the material used.
The price of a filling
Enamel
and
Estet-X nanocomposites in Moscow
varies from 5,000 to 15,000 rubles, depending on the volume of the defect being restored.
IMPORTANT:
The shrinkage of the Enamel and Estet-X materials is so negligible that the risk of the filling falling out is simply minimal. Due to the unique nanocomposition of the filler, the Estet-X and Enamel composites ensure filling durability of up to 10 years, natural shine and ideal surface smoothness. However, in order to more fully assess all the costs, it is necessary to take into account the advantages that these innovative materials provide in the treatment of caries.
In the “Therapeutic Dentistry” section you can see current prices for fillings, restorations and other procedures. Also visit the “Hygiene”
to find out prices for preventive and aesthetic procedures.
Reviews of dental treatment near Chistye Prudy metro station.
The evaluation of patients treated in our clinic is very important. We provide high quality services and value our reputation. You can also leave your feedback about treatment at our clinic. Below we would like to provide several reviews that characterize the level and quality of the services provided.
“I see Valentina Vladimirovna in this dentistry. She always knows what to do to make her teeth look perfect! I went to see my son in Yekaterinburg for a year, where a unfortunate doctor tried to restore my chip with a filling. It was such a disgrace, it only made it worse, a crack appeared! Upon arrival in Moscow, immediately here. We covered this nightmare with veneer. Thank you, once again I am convinced that for me there is no better doctor than you!”
We are always glad to see you at the Dentist dental clinic!
| Filling (simple restoration in the area of one tooth) Estet-X | 7500a |
| Filling (restoration in the area of one tooth is complex) Estet-X- Dentsply Germany | 4500a |
| Artistic restoration Estet-X | 15000a |
| Restoration of Estet-X | 15000a |
| Artistic restoration in the area of one tooth ENAMEL PLUS HRi | 18000 a |
| Restoration of a contact point with the PALODENT PLUS system | 4500a |
| Veneer, composite Estet-X | 13000a |
| Composite veneer ENAMEL PLUS HRi | 15000a |
| Non-contact method of caries treatment AIR-FLOW S1 Prep | 3500a |
The therapist and periodontist must work together as members of a team. Very often, the cause of discomfort (for example, food gets stuck between correctly placed fillings) is deep bone pockets and you cannot do without a periodontist. Both the therapist and the periodontist combine their expertise to develop the optimal treatment plan and keep each other informed about your health.
It is necessary to remove dental plaques twice a year; ultrasound will not cause harm.
Why do contact surfaces fail?
Most often, the integrity of contact points and their anatomically correct location are violated due to the occurrence of a carious process in the adjacent areas and interdental spaces, which develops here due to inaccessibility and poor or insufficient oral hygiene. As mentioned above, the smallest pieces of food easily get into the spaces between teeth and get stuck; it is not always possible to clean them out on your own, and sometimes it is easy to notice. Moreover, the carious process in these areas can be difficult to identify independently, so it can remain unnoticed for a long time and progress, affecting several units at once. How to avoid this? Undergo preventive examinations in a timely manner. This should be done at least once every six months for adults, and 3-4 times a year for children.
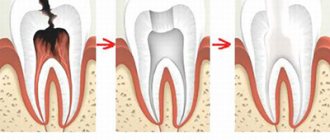
Doctors, when faced with such defects, must not only take care of removing carious lesions and stopping the inflammatory process, but also begin restoring the contact point of the teeth during filling and prosthetics.
Basically, in their medical practice, dentists are faced with defects of class II and III caries according to the system developed back in 1986 by Black. The second class includes caries of the contact surfaces of molars and premolars, the third class includes the carious process on the lateral surfaces of the canines and incisors without disturbing the cutting edge. Class IV defects are also less common in practice, when not only the contact surface of the fangs and incisors is damaged, but also the cutting edge is destroyed.
News
Seminar by Andrey Tikhonov “Miniscrews in orthodontics. Alloy of metal and intelligence"
April this year turned out to be very productive for our specialists!
Orthodontists from the Kremlin Dentistry attended Andrei Tikhonov’s seminar “Miniscrews in orthodontics. Alloy of metal and intelligence" in Moscow, during which the following topics were touched upon:
- Options and advantages of installing miniscrews.
- Indications and nuances of installing miniscrews. Causes of screw rejection, prevention.
- Distalization of molars using skeletal support. Tactic options. Features on the upper and lower dentition
- Mesialization of molars in edentulous cases.
- Insertion of lateral teeth. Popov-Godon phenomenon, open bite, tilt of the occlusal plane.
- Miniscrews as a support when extending impacted teeth.
- Preparation for prosthetics using skeletal support.
- Use of miniscrews for support during treatment with removal.
Signs of destruction of contact points
Visually, the destruction of the lateral surfaces of the teeth or the presence of a carious process on them may remain unnoticed until a large cavity or black “hole” forms on the side of the crown. However, it is better if the problem is identified much earlier. To avoid missing it, pay attention to the following signs:
- painful sensations when eating food, temperature changes,
- food easily penetrates the interdental spaces and gets firmly stuck there,
- discoloration on the lateral parts of the crown: this sign can be detected quite easily if the front incisors and canines are damaged. The enamel stops shining, may acquire a white chalky tint, turn yellow or brownish,
- gingival papillae are inflamed and swollen,
- Bleeding gums began to bother me.
Methods for diagnosing the problem
Diagnosing a carious lesion in the area of the lateral surface of two teeth in contact with each other can be quite difficult even for an experienced dentist, especially if the units are crowded or closely located. That is why doctors sometimes use not one, but several different methods for diagnosing pathology:
- X-ray: it is always done because... with its help you can determine the depth of the carious lesion and the condition of the tissues surrounding it. In the picture, the carious areas will be black, the tooth itself will be gray, that is, much lighter than the inflamed area,
- digital method: using a special high-resolution video system, the doctor can transfer the image to his computer monitor, where he then comprehensively assesses the situation,
- Electroodontometry or EDI for short: allows you to identify the pathological process at the earliest stages of development. To determine the condition of soft and hard tissues, the doctor uses a special Diagnodent device that produces light pulses, which are then returned or reflected back. Based on the length of the pulse waves, the specialist determines the state of the areas under study. And the wavelengths in healthy and affected areas are completely different,
- transillumination: a special apparatus is also used for this, which literally illuminates all the examined areas. In those areas where the enamel-dentin layer is damaged or demineralized, the light takes on a different shade,
- colorimetry: here the patient is given to rinse his mouth alternately with different liquids. First use a methylene red solution, then use a glucose solution. In damaged areas, the PH level is changed and the acid-base balance is disturbed, so they “give” themselves a bright range of shades (yellow-red),
- vital staining: this procedure can be carried out only immediately after professional oral hygiene, then it will be most effective. The doctor applies methylene blue dye to the patient's enamel. The composition is kept for about 5 minutes, after which it is washed off with plain water. The result is painting in bright colors the areas where the carious process takes place.
Important! Before dental treatment or during a preventative examination, an experienced doctor will advise you to undergo professional oral hygiene - do not refuse this useful procedure. The procedure will help remove soft bacterial and hard plaque, which can serve as an obstacle to the correct diagnosis of various dental diseases and especially the diagnosis of caries in the proximal areas.
It is mandatory for doctors to conduct a visual examination using modern instruments. For example, endoscopes with bright LED lighting that transmit the resulting image to a monitor screen. In this case, the lateral areas of the teeth should be subjected to a comprehensive assessment, not only from the vestibular side, but also from the lingual, buccal, and occlusal side. A study is also carried out using a probe - thus, hidden carious lesions are detected against the background of bleeding of periodontal tissue.
Licenses and certificates
- About company
- Story
- Licenses
- Partners
- Customer Reviews
- Employees
- Vacancies
- Requisites
Dental Certificates
Issued for medical activities. From March 4, 2014
Issued for medical activities. From March 04, 2014
Dubov Boleslav Arkadievich certificates
Certificate of completion of the course in prosthetics on implants, issued to the specialist of the Dent-Art clinic, Boleslav Arkadievich Dubov, June 04-05, 2015.
Issued to the specialist of the Dent-Art clinic, Dubov Boleslav Arkadievich, for participation in a seminar on Modern technologies of dental prosthetics, April 4, 2014.
Issued to the specialist of the Dent-Art clinic, Dubov Boleslav Arkadievich, for participation in the International Symposium on Dental Implantology, April 4-5, 2013.
Dubova Tatyana Anatolyevna certificates
Issued to the specialist of the Dent-Art clinic, Tatyana Anatolyevna Dubova, after completing a master class on teeth whitening, December 3, 2009.
Certificate “Modern dentistry without risks and threats”, 2016
Certificate of lecture session “Modern concepts of caries prevention in children and adults”, 2013
Certificate of practical seminar “Repeated endodontic treatment. Equipping the workplace during repeated endodontic treatment", 2013
Certificate "Periodontal diseases - effective clinical tactics, algorithms and choice of treatment regimen", 2011
Practical course “New opportunities in non-surgical endodontics”, 2010
“Creation of highly aesthetic composite restorations”, 2010
Certificate “Endodontic dental treatment”, information and practical seminar 2009.
Certificate for working with the Vector device, issued in 2009
The certificate was issued to Tatyana Anatolyevna Dubova for her participation in an international seminar on tooth restoration in 2009
Rysyanova Elena Anatolevna certificates
A certificate of participation in the seminar on the latest achievements in the field of instrumental treatment and obturation of the root canal system was issued to the specialist of the Dent-Art clinic, Tatyana Anatolyevna Rysyanova, October 01-02, 2011.
Tools used for restorations
Restoring a tooth that has a damaged contact point is not an easy task for a dentist from a technical point of view. Standard caries treatment and fillings are not enough here. In order to restore the complex anatomy of the contact surface, it is necessary to use a set of special tools and devices, the main of which are matrices and wedges. Let's look at them in more detail.
Matrices
What is a matrix? This is a device that performs a kind of protective or restrictive function and helps to apply filling material for restorations in the required quantity. Using a matrix, a specialist models the surface and contact point, avoiding excessive layering of material. This limiter also does not allow it to go beyond the anatomical contour of a particular tooth. The device also protects the gingival papilla during manipulations.
Modern matrices for modeling surfaces can be made of plastic, metal or metal-plastic, can have different lengths (short, medium, long) and shapes - straight, contour or conical, perforated (flat and curved) for molars and premolars, volumetric. There are separation, protective or contouring (for modeling) models.
To firmly fix the device, the doctor uses matrix holders designed for this purpose: rings and clamps, couplings and clamps.
Wedges
Wedges perfectly complement the matrices. They have several main goals:
- protect the gingival papilla and the adjacent tooth from damage during manipulations and contact with filling material,
- separate the unit being restored from its neighbor,
- increase interdental space for high-quality subsequent procedures,
- allow for a higher degree of fixation of the matrix,
- allows you to recreate a triangular hole in the gingival area during the restoration process.
Wedges are made of wood and plastic, just like the matrices have different lengths and widths. When installed, they adapt to the anatomical features of the tooth.
Experts consider the most optimal option to use wooden wedges made from maple, because They are hypoallergenic, do not injure the mucous membranes and, in addition, perfectly absorb excess moisture. However, plastic is more flexible and pliable than wood, so when the patient’s teeth are very closely spaced and crowded, doctors prefer to use plastic wedges.
To facilitate work with proximal surfaces and for reliable and complete polymerization of filling materials in such difficult-to-reach areas, doctors also use the latest generation equipment. For example, a light-conducting cone that helps ensure polymerization of the composite. Tools and light-conducting attachments with built-in light sensors - with their help you can easily see the deepest cavities.
Classification of matrices and fixation systems
Matrices and systems for their fixation are widely used for dental reconstruction.
In the manufacture of matrices, 2 types of materials are used: metal and plastic. When working with light-curing filling materials, it is more convenient to use plastic ones.
According to the shape of the matrix, they are produced in several types. They are made straight, they can be contoured or perforated.
Contour models are different for the outer and inner walls of the tooth. They vary in length and may have bulges and specialized shapes for different defects.
As for fixing systems, there are two main groups: matrix holders and wedges.
Matrix holders:
- For perforated matrices, a perforated holder is used;
- Sectional matrix system “3M” - fixes with spring rings;
- M. Tofflemeyer - a retainer for working with large defects, used both on the right and on the left. The matrix is put on the tooth and tightened with a coupling;
- Also for two- and three-channel teeth there are ready-made matrices equipped with a retainer; they are tightened with a clamp.
Wedges placed between the teeth can be of different sizes. They are made either from plastic or wood. They are needed to:
- create a triangular space between the teeth;
- wedge the teeth so that there is no gap left after removing the matrix;
- It is enough to secure the matrix tightly on the tooth.
A detailed review of the Glassix fiberglass pin set and quality characteristics of the products.
Come here to learn more about the features and purpose of gutta-percha points.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/krasota-i-uxod/narashhivanie/shtiftyi/parapulparnyie-kak-sposobov-vosstanovleniya.html we will consider the stages of placing parapulpar pins.
What types of matrices are better for modeling contact points?
It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously, because... the matrix must be selected based on many different factors. Depending on the clinical situation, the amount of work (macro- or micro-restoration is required), the stage of the procedure, the shape of the tooth and the anatomical features of the maxillofacial system, the doctor chooses one or another type of auxiliary instrument.
In the late eighties and nineties, doctors in their practice used cutout matrices to model contact points. But this device has shown its inconsistency over the years and is almost never used today, because such a matrix did not provide sufficient protection of the tooth neck and subgingival space from penetration of the composite there. And this situation often later became the cause of the development of chronic gingivitis. Today, this type of matrix is rarely used and only on the condition that the neck of the tooth is first coated with sealant.
In medical practice, there are also known methods according to which doctors completely refused to use auxiliary tools, namely, did not use wedges and matrices, or even rubber dams or rubber dams in their work. For example, the modeling method with sawing of contact surfaces implied the application of a composite material with a transition to the proximal surfaces. After this, the teeth in contact with each other were separated using an abrasive strip that resembled a hacksaw. This method also showed its inconsistency.
Today, some doctors prefer to use volumetric matrix modeling, because... they most accurately allow you to recreate the shape and anatomy of natural contact points.
Matrix installation
At this stage, we install the matrix simultaneously, orienting them to each other with their convex sides. This strategy gives us the advantage of matrix self-stabilization even in the most extreme cases. One matrix supports another and vice versa. There are very few clinical situations where it is not possible to install both matrices at the same time.
We will describe how to achieve a tight contact point with this strategy, using concepts from all ages.
FIG. 7 We select one cavity and fill it. We can add as many portions of material as we need. Typically, if the cavity is small, we make one injection of material into the proximal wall and into the center of the cavity.
FIGURE 8. After polymerization, we remove the matrix from the completed restoration using forceps and immediately take a very important step, which is to firmly press the wedge between the teeth. This manipulation will create additional space to compensate for the thickness of the second matrix.
FIGURE 9. After completion of the restoration of the second cavity, thanks to the pressure of the wedge, a very tight contact is created. Please note that the contours are very rounded and will likely become more natural after finishing.
FIGURE 10. After removing the wedge, the contact is checked using dental floss. Finishing is done using the Finishing Style burs: a low-speed diamond bur, discs and spiral discs with paste, and finally a felt felt.
FIGURE 11 Final view of the restoration a year later. The shine, shape and adjustment prove the durability and success of these restorations.
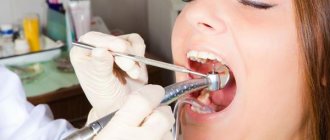
Preparation for the contact surface restoration procedure
First, the doctor carries out professional hygiene and antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity, puts the patient under anesthesia, and installs a rubber dam. Next, the specialist selects the necessary types of wedges and wedges two adjacent units. The wedge is always inserted from the tongue side, and the second end after installation should become noticeable from the vestibular side. After installing the wedge, you need to wait about 5-10 minutes so that the interdental space becomes clearly visible and nothing interferes with high-quality work.
Then the doctor opens and disinfects the carious cavity and removes the affected tissue. It is especially important to remove damaged tissue in the gingival area, because If this procedure is not carried out carefully enough, then there may subsequently be a risk of developing recurrent caries. Often in such cases, it is necessary to treat not just one, but several adjacent teeth, whose contact surfaces are in contact, for caries.
Next, depending on the clinical picture and indications, the doctor selects and fixes the matrix system, conditions the prepared cavity using special gels and applies an adhesive composition, after which he selects a technique for restoring or restoring both the tooth itself and its contact point with the neighboring unit.
Preparation
After diagnostic measures, the patient is given an allergy test for sensitivity to anesthesia, and, if everything is in order, a dose of the drug is administered. Next, you should wedge the teeth and check the occlusal contacts.
The wedge size is selected by correlating it with the parameters of the interdental triangle. Installation should not require any effort.
The best material for wedges is wood (maple), because it absorbs moisture and the wedges increase in size. Thus, in a short time, the required distance appears between the teeth.
There are several options for accessing the damaged area of the tooth. Let's look at the main methods.
From the chewing plane
When the dentist approaches the problem from the chewing plane, when removing the affected fragment, the entire protective layer, devoid of bone tissue, is removed. Then the enamel and edges are smoothed.
It is important that the enamel is in contact with the opposing tooth. An isthmus with the width of a quarter of the distance from one tubercle to another on the crown of the jaw arch element is required.
If the tubercle is severely damaged, you need to shorten it by 2 mm or more in order to further cover it with filling material. This will help reduce the risk of chipping in the future.
A cavity is formed; the side walls should not come into contact with the growing tooth next door.
It is very important to remove all areas of damaged enamel from the gum area. They can subsequently cause recurrence of caries.
Access for over-inflated clinical crown
If the patient has a high crown, or the problem area is located below the contact of the vestibular or palatolingual surface, in the presence of periodontitis, the technique described below should be used.
Tunnel preparation
This version of turning, performed from the chewing surface, is characterized by the lack of a full view of the cavity, and there is a high risk of injury when opening the pulp.
In addition, there are many possible complications and an increased likelihood of reoccurrence of caries.
Materials for restorations
To recreate contact surfaces, doctors use different materials: hybrids, nanocomposites and composites of increased fluidity, compomers, glass ionomers, amalgam. A combination of composite and GIC is often used.
Flowable composites are characterized by a high degree of wear resistance, are well suited for surface modeling and can be polished, are elastic, easy to mix and conveniently applied using special dispensers.
As for compomers, they contain fluorine, which helps strengthen and regenerate hard tissues. This material is very resistant to moisture and has a high degree of adhesion.
So, a dental microscope makes it possible to:
- conduct high-quality diagnostics of any dental disease;
- ensure super-precise fit of restorations;
- conduct microinvasive treatment;
- accurately determine the number, location and branching of channels;
- identify the features of the atypical structure of the canals;
- determine the degree of cleaning of the canal cavity;
- targeted action in the treatment of cysts and granulomas;
- remove fragments of instruments from tooth canals in the most gentle way;
- remove worn filling material;
- identify microcracks, perforations, sources of secondary infection and eliminate them.