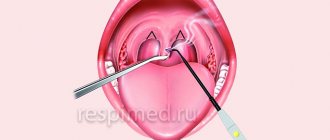
The uvula is an important component of the human body. This organ is located in the larynx. It is easy to notice - it is a small process, shaped like a pear. It is responsible for performing the barrier function, which includes protecting the respiratory tract from food entering it by redistributing air and food flows.
However, a serious pathology may be associated with this small organ - its adherence to the tonsil. This phenomenon is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and, in some cases, can only be cured with surgery.
Principle of operation
Human anatomy in the first stages of its formation forced scientists to ask the question: why does a person need this appendage?
Some believed that it was an underdeveloped second language that we inherited from reptiles. Others, on the contrary, were inclined to think that its presence was useless, and in some cases it even interfered. One way or another, with the evolution of medicine, the importance of this pyriform process has been scientifically proven.
The principle of its operation explains all its importance: when food enters the oral cavity and moves further, a spasm of the throat occurs, during which the mechanism of the hyoid muscle is triggered, closing the trachea from food entering them.
In addition, the tongue also takes part in the reverse process. That is, when the regurgitation process occurs, he completely controls it, not allowing food to rise into the oral cavity.
What symptoms are found in this pathology?
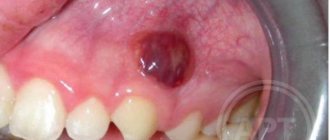
According to doctors, the first thing that should cause concern is a greatly enlarged tonsil, which, due to its size, can even partially block the pharynx. The palatine process adheres or grows between the tonsils, on which inflamed veins can be seen. With this pathology, the throat itself turns red, and the voice becomes hoarse. There is pain when swallowing food and a sore throat. In addition, the patient begins to cough, especially in the morning.
There are cases when doctors also noted an elevated temperature in sick people.
We recommend reading the article Food gets stuck in the tonsils
Functions
The tongue performs such important functions as:
- Separation and redistribution of air and food flow.
- Preventing foreign objects from entering the respiratory tract, causing a spasm of the throat, narrowing its lumen.
- Participates in the formation of the gag reflex and cough.
- It divides the pharynx conditionally into two symmetrical parts; by its presence, one can determine the anatomical state of the tonsils and compare their sizes.
- Actively participates in heating air masses during mouth breathing.
- Helps to give tone to the voice by regulating air flows and their strength.
The many functions of this important organ suggest that it is necessary in the human body.
Drug therapy for uvulitis
If you can see that the tongue in your throat has increased, then you should immediately go to the doctor.
The medical specialist will prescribe the optimal treatment after determining the cause of the pathological phenomenon. In most cases, drug therapy for uvulitis is carried out.
The patient is prescribed both antibiotics and some other medications.
Medicines are prescribed only by a medical specialist . The doctor knows which medications will effectively cope with the pathology without causing harm to the body. Some patients do not consult a doctor, but only spray their sore throat with antiseptic sprays chosen at their own discretion. You can't do that. If treated incorrectly, uvulitis can cause serious complications.
In case of an allergic reaction, therapeutic measures are taken to relieve inflammation of the throat and relieve swelling of the palatal area.
Antihistamines are prescribed to help relieve allergy symptoms.
Also, if necessary, the doctor can prescribe glucocorticoids and diuretics.
If the soft palate is inflamed due to damage to the mucous membrane, then simple treatment procedures are prescribed. To restore the mucous membranes, it is enough to maintain oral hygiene and properly care for your teeth and gums. Swelling of the uvula associated with injury usually goes away after 1 to 3 days.
If uvulitis is a consequence of damage to the body by a viral or bacterial infection, then the use of antiviral or antibiotic medications is required.
In what cases does pathology occur?
The tongue, like any other organ, may have pathologies in the process of its formation and functioning. There are several types of the most common pathologies that limit the full functioning of the organ.
Inflammatory process
As a result of microbes, mainly staphylococci and streptococci, getting on the surface of the tonsils, there is a possibility of inflammation on the surface of the uvula. This is mainly observed in advanced stages of the development of the disease, when the inflammatory process takes on an extensive form, penetrating and completely affecting the blood.
A long-term lack of proper treatment leads to the fact that the uvula becomes covered with ulcers and trophic lesions, completely disrupting the blood supply to the organ. In this case, its work is reduced to a minimum, limiting the throat capacity and also causing pain.
Sticking to the tonsils
Situations often occur in which the tongue sticks to the tonsil.
The reason for this may be either an inflammatory process (mainly of a chronic type) or a congenital pathology.
Temporary partial adhesion does not cause much discomfort, limited to the sensation of a lump in the throat and pain when swallowing. In this case, appropriate treatment is prescribed, which includes inhalations, rinsing and irrigation of the mucous membrane.
Adhesion may be temporary but may involve complete fusion of soft tissue. This pathology is quite dangerous, since with a strong cough it can provoke bleeding. The problem can only be solved surgically, so if you discover such a symptom, you should definitely consult a doctor.
No tongue
This diagnosis is congenital and is very rare. It is quite difficult for such people to control the eating process.
Quite often, food particles can enter the nasopharynx, causing significant discomfort. But, there are many ways to eliminate this defect, and get used to living fully in such conditions, following only the doctor’s recommendations regarding the pathology.
GBOU "NIKIO im. L.I. Sverzhevsky" of the Moscow Department of Health
Hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil
The lymphadenoid tissue of the root of the tongue is presented in the form of two clusters of large follicles located in rows or in random groups. These clusters are separated by a central groove extending from the middle of the lingual epiglottis fold to the largest, final, circumvallate papilla on the root of the tongue. Therefore, it is more correct to talk about not one, but two lingual tonsils. The number of large follicles in a 1-year-old child is 10-12, and in a 5-year-old child it is 20-30. At the age of 35 to 40 years, the maximum number of follicles (35-40) is observed with a simultaneous increase in their size. After 45 years, the number of follicles decreases and the size of each of them decreases (A.I. Tseshinsky, 1951).
One must think that the main cause of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil in adulthood is inflammatory processes in the oropharynx. In some cases, hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil develops as a compensatory process in individuals who have had their palatine tonsils removed (B. S. Preobrazhensky).
Symptomatology and diagnosis of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil.
Severe enlargement of the lingual tonsil can cause mechanical difficulty in breathing and voice production. Such cases, however, are very rare. Typically, patients with hypertrophy of the lingual tonsils complain of a feeling of pressure projected into the area of the hyoid bone, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, cough, and sometimes laryngospasm . These complaints are not pathognomonic for hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil. Therefore, their assessment requires caution. Sometimes patients with hypertrophy of the lingual tonsils complain of coughing paroxysms. In such cases, mechanical irritation of the lingual tonsil using a probe can provide some assistance in diagnosis. If cough occurs only when the lingual tonsil is irritated, then it seems likely that it is the receptive field of the cough reflex.
When making a differential diagnosis, you need to keep in mind the following diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the area of the root of the tongue. They can be caused by a banal infection (abscesses and phlegmon of the root of the tongue), tuberculosis, syphilis and various fungi (actinomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, blastomycosis, moniliasis). These diseases differ from hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil by the asymmetry of the lesions, their greater density and more saturated color. Histological (biopsy), serological and bacteriological examination helps.
- Tongue root cysts. In this area, there are retention cysts of the mucous glands and very rarely - cysts formed from elements of the thyroglossal duct. They are distinguished by a smooth-stressed surface.
- Benign tumors - adenomas and mixed tumors of the salivary glands are more common. They are also distinguished by their smooth surface and significant density.
- Malignant tumors - cancer and lymphoepithelial tumors are usually observed. Diagnosis is simple for ulcerated tumors.
- The goiter of the tongue root is distinguished by a pink, smooth surface covered with a network of highly developed venous vessels. It has a significantly higher density than hypertrophied lymphadenoid tissue. In some cases, the thyroid gland is absent in its usual place, which can be confirmed by palpation of the neck in thin individuals. Research with radioactive iodine helps, which, after ingestion, is concentrated in the thyroid tissue, as a result of which strong gamma radiation is detected in the area of the root of the tongue.
Treatment of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil.
With moderate hypertrophy, patients are prohibited from smoking and eating spicy foods. Sometimes alkaline rinses and lubrication with iodine-glycerin are beneficial. Some authors recommend cauterization with lapis and galvanocauter. The use of radiation therapy has been proposed. With severe hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil, its surgical removal is indicated. It can be removed piece by piece by “biting” under the control of a laryngoscopic mirror. Some authors prefer to perform complete enucleation of the lingual tonsils along with the capsule. Such intervention is especially advisable in cases where there are significant inflammatory changes in the hypertrophied lingual tonsils or if these tonsils are the cause of repeated phlegmonous inflammation in the area of the root of the tongue, damage to the kidneys, joints and other organs. Before the operation, a detailed clinical examination of the patient is necessary, studying the blood picture, its coagulability, counting the number of platelets, etc.
We perform removal of the hypertrophied lingual tonsil using a holmium laser (Ho:YAG) with a radiation power of 4.8 W (energy - 0.6 J, frequency - 8.0 Hz).
Why can the tongue stick to the tonsil?
In fact, there can be a lot of reasons for this process: from anatomy to complex inflammatory processes. So, let's consider each of them, as well as the opportunity to avoid negative consequences.
Inflammation
The inflammatory process that occurs naturally on the tonsils, as a result of the virus entering the blood, makes the tonsils loose.
The amount of mucus produced increases several times. As a result of this, there is a possibility of the tongue sticking to the tonsil, which is eliminated on its own once the person has fully recovered.
Increased tongue size
There are cases when the tongue has an elongated shape, which makes it possible for it to constantly hit the tonsils in any order. When coughing or sharp sneezing, the tongue is able to independently change its location, relying not only on the outer walls of the tonsils, but also “falling” into the larynx.
This pathology causes a lot of discomfort, which can only be removed by surgery.
Therapeutic methods
If, as a result of sticking of the uvula, a sore throat appears during swallowing, the doctor will prescribe local treatment. Procedures related to rinsing, inhalation, and pharyngeal irrigation are carried out. Sprays are used that, when used, destroy bacteria and relieve inflammation.
If the sticking of the tongue was a consequence of tonsillitis, then local procedures must be combined with the use of antiviral drugs or even antibiotics. With proper treatment, improvement occurs quickly. To fix it, a good folk remedy is recommended - a warm drink of tea with honey and lemon. It is necessary to monitor your diet: during illness and treatment, do not eat spicy or salty foods, alcohol and smoking are prohibited.