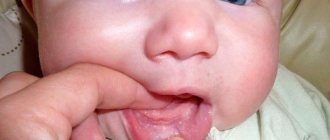
If the tongue in the throat is swollen and significantly increased in size, this may indicate the presence of a serious disease.
The uvula is the most important element of the soft palate; it consists of smooth muscle cells and many blood vessels. In its normal state, the organ is very small in size; a person does not even feel it.
The organ performs many important functions in the nasopharynx area, so if it is dysfunctional, a person may face dangerous ailments that pose a threat to life. By what signs can you identify uvulitis, and what to do if this deviation occurs?
No singer neglects to take care of his own voice. Some people drink exclusively warm water, others wear scarves even in summer, others prefer honey and raspberries as a tasty way to prevent throat diseases. However, they all use special exercises to strengthen and preserve their voice.
The essence of pathology
Most people don't know what the uvula is called. In medicine, the organ is called the “conical process” and takes part in a variety of functions:
- separates food ducts;
- distributes and directs air flows;
- activates the gag reflex if necessary;
- reduces the likelihood of infection through the throat;
- protects the throat from penetration of cold air;
- takes part in the speech.
If the uvula (throat) increases in size and becomes inflamed, a person develops uvulitis. The disease progresses rapidly, from the first days a person begins to experience pain and discomfort in the palate.
The disease entails disruption of most of the functions of the tongue, which can cause very serious complications. That is why experts warn that at the first signs of swelling, you must immediately seek qualified help.
When to see a doctor?
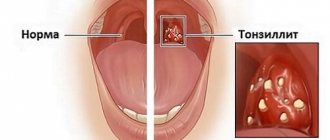
It is recommended to treat adult patients and children with swelling of the tonsils and other signs of oropharyngeal infections at home. The main emphasis of treatment is to eliminate inflammation in the pharynx, pain, swelling and reduce temperature. Urgent medical attention is needed for patients with the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the tonsils, making it impossible to swallow food, water and saliva;
- high temperature, slurred speech;
- excessive drooling, breathing problems;
- difficulty opening the mouth due to swelling of the lower jaw;
- lack of urination for 10-12 hours in a row.
The longer the swelling of the tonsils remains unattended and without the necessary treatment, the higher the chance of developing the dangerous consequences described above (they threaten not only children, but also adults).
What kind of doctor do you need?
First of all, to treat a swollen tonsil or inflamed tonsils on both sides, you need to consult a therapist. The doctor will first determine the nature of the disease, excluding or confirming an allergic predisposition.
If tonsillitis, pharyngitis or the formation of a peritonsillar abscess is suspected, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist (ENT).
Correction of the state of immunodeficiency is carried out with the participation of an immunologist, and complications that have developed in the heart or kidneys as a result of chronic tonsillitis are treated by a cardiologist and nephrologist.
On this topic:
Symptoms
If a person has an inflamed and swollen uvula on the soft palate, the signs of the disorder will be so pronounced that they cannot be confused with something else. Regardless of what causes uvulitis, the most common symptoms are:
- There is a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, which may indicate an increase in symptoms, and the swelling is very severe.
- Nausea and urge to vomit.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Pain and difficulty swallowing food.
- Speech dysfunction, the appearance of hoarseness.
- Increased salivation.
If swelling is caused by allergies, the pathology may be accompanied by the following disorders:
- appearance of cough;
- severe sneezing;
- the appearance of a rash in the oral cavity;
- tearing eyes;
- constant sore throat.
If uvulitis is a consequence of an infectious disease, a person will suffer from the following symptoms:
- excessive dryness of the throat mucosa;
- runny nose;
- pain when swallowing;
- the appearance of chills or fever;
- purulent neoplasms on the tongue;
- general weakness.
Experts warn that if the tongue in the throat is swollen and increases in size, the disease should alert the patient. To select the appropriate treatment, it is necessary to identify the causes of the pathology; only an experienced physician can do this.
The main causes of the pathological situation
Swelling of the uvula can develop under the influence of a fairly wide variety of factors.
It is precisely the accurate identification of the cause of the inflammatory process that is the main thing in establishing the correct diagnosis and subsequent therapy. Swelling of this structure is formed both due to certain diseases and for reasons not related to illnesses. The uvula ensures safety when consuming food and drinks
Diseases that cause swelling
Doctors identify the following, the most common culprits of this pathology:
- Diseases of an infectious nature of the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
- Some chronic diseases of the nasopharynx (tonsillitis, asthma, pharyngitis, otitis media).
- Paramygdaloid abscess. This is an acute purulent disease of the peri-almond tissue.
- Long-term dental problems (untreated caries, inflammatory processes, purulent infections).
- Injury to this area. Inflammation and subsequent swelling can result from an alcohol burn to the throat as a result of consuming too strong alcoholic beverages.
- Allergic manifestations. Increased sensitivity of the immune system and allergies arising against this background lead to swelling of sensitive mucous membranes. The delicate tissue of the uvula may also be damaged.
Situations not related to diseases
The development of uvulitis does not occur in all cases due to existing pathologies. If the uvula begins to swell, but there are no pathological reasons for this development of events, it is worth looking for the reason among other provocateurs. Experts advise analyzing the possible presence of factors such as:
- passion for smoking (uvulitis is a frequent companion of an avid cigarette addict);
- injury to the uvula mucosa from too hot/cold food or drink;
- chronic snoring (usually in this case, swelling forms in the morning, and by the evening everything returns to normal);
- the need for long-term use of certain aggressive medications that irritate the delicate mucosal tissue;
- Sometimes the throat hurts after drinking alcohol (especially if there is damage to the mucous membrane and when drinking too strong alcohol), such soreness is often accompanied by swelling.
The most dangerous culprit of swelling is the development of the oncological process. It can be suspected if, apart from the swollen tongue, the patient does not have all irritating factors or any diseases.
Alcohol often acts as a strong irritant to the oral mucosa, which leads to swelling and inflammation of the uvula
Allergic uvulitis
If the throat uvula swells due to an allergic manifestation, antihistamines (Loratadine, Suprastin, Diazolin) are usually prescribed. To make the recovery of the swollen organ faster, you can use diuretics (Trifas, Veroshripon).
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Loratadine | From 35 rub. | |
| Suprastin | From 132 rub. | |
| Diazolin | From 57 rub. | |
| Trifas | Check | |
| Veroshripon | From 93 rub. |
If the conical process is so swollen that the patient's life is in danger, it is necessary to use corticosteroids - medications that are prescribed as first aid for allergies to prevent complications. If after taking medications from this pharmaceutical. group, the patient’s condition will not improve, the only solution will be surgical intervention.
You can speed up the recovery process using traditional medicine methods. The patient needs to gargle several times a day with decoctions based on medicinal herbs (raspberry, St. John's wort), an infusion of garlic has also proven itself to be good (100 grams of peeled vegetable, pour 100 ml of water and leave the medicine to infuse for five hours).
Experts warn that if the uvula located on the roof of the mouth constantly swells due to allergies, it is necessary to identify what is the primary source of such a reaction in the body, otherwise the pathology may recur with a certain periodicity and significantly complicate the patient’s life.
What medications are used to treat an inflamed uvula?
When an inflamed tongue swells in the throat, the choice of medications is approached with great caution due to the high risk of complications of the respiratory system. All medicinal tactics are aimed at reducing swelling and relieving inflammation of the uvula.
Complex therapeutic tactics include the use of:
- antiallergic drugs - antihistamines (Lordestin) and glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Triamcinolone);
- decongestant diuretics – Torasemide SZ, Hypothiazide, Furosemide. These medications are considered first aid and prevent the development of asphyxia.
- If the upper uvula is swollen after drinking alcohol, in order to stabilize the condition, Diazolin, Zyrtec or Aleron are prescribed and subsequent alcohol intake is completely avoided.
- When diagnosing a viral or bacterial infection that provoked inflammation of the uvula, antibiotics (Azithromycin, Amoxiclav) or antiviral drugs (Cycloferon, Remantadine, Arbidol) are prescribed.
Complex therapy also includes:
- treatment of the larynx with antiseptic sprays - Hexoral, Kameton;
- taking vitamin complexes (Vitrum, Multi-Tabs and immunomodulators (Immunity, Zdorov).
All medications are taken in a course, in accordance with the doctor’s prescription and under his supervision.
Pathogenic microbes
If the organ is swollen and taking antihistamines does not bring relief, most likely the illness is caused by mucous infections.
If the disease is of viral origin, you need to take antiviral drugs (Viferon or Arbidol), but when the pathology is caused by pathogenic microbes, you need to take antibiotics.
Often, with infectious uvulitis, various anti-inflammatory sprays are prescribed that fight the causative agents of the inflammatory process and reduce pain.
How to treat swollen tonsils?
To quickly cure an oropharyngeal infection, you need a high-quality diagnosis. To determine the type of pathogen, the doctor takes a swab from the throat; for a viral infection, PCR diagnostics is required, especially for an unspecified type of virus.
If chronic infections (sinusitis, sinusitis) and the onset of abscess formation are suspected, radiography is performed. Therapy can be either conservative or using traditional methods and surgical (according to indications).
Conservative treatment
To remove swelling of the tonsils, it is necessary to establish the type of pathogen and select medications in accordance with its sensitivity to the drugs. Treatment is carried out using several measures:
1
The use of antibiotics is justified for bacterial throat infections. The drugs used are penicillins (Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Flemoxin Solutab), macrolides (Azithromycin, Sumamed, Erythromycin) and cephalosporins (Cefalexin, Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin). 2
Antiviral and immunostimulating - prescribed for infections of the throat by viruses. The drugs used are Interferon, Cycloferon, Viferon, Immunal, tincture of Echinacea and Eleutherococcus, Bronchomunal.
3
Gargling - use solutions that have antiseptic and healing properties, these are Miramistin, Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine, propolis or calendula tincture, Rotokan, Furacilin. 4
Treatment of the mucous membrane with sprays - drugs help relieve swelling, eliminate pain, and reduce the level of inflammation. These are Ingalipt, Hexoral, Lugolit, Tantum Verde, Yox. 5
Dissolving tablets with antiseptic and analgesic properties are indicated for sore throat, white coating of the tonsils, and dry cough. Recommended products are Strepsils, Doctor Mom, Lizobakt, Grammidin, Septolete, Hexoral Tabs.
If the pain is so severe that it radiates into the ear, and the infection is caused by bacteria, the course of antibiotics must be completed to avoid relapse of the disease and the development of complications.
The use of folk methods and remedies
Traditional medicine can be used at home while taking medications, or during the recovery stage. Among these methods, inhalations are distinguished - they are carried out in the absence of high temperature, so as not to provoke the spread of infection deep into the respiratory tract.
Inhalations are carried out with oils of eucalyptus, sea buckthorn, mint, tea tree, fir or pine. The steam should not be scalding (no higher than 40-45o), after 10-15 minutes of the procedure you need to lie down without going out into the open air.
Gargling is another way to reduce inflammation, cleanse the mucous membrane and relieve swelling of the tonsils. You can use saline solution, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, coltsfoot, sage, and plantain.
A good way to heal the damaged epithelium of the larynx and relieve pain is to dissolve a piece of propolis in the mouth until completely dissolved.
Natural honey has a pronounced antiseptic and analgesic effect - it can be added to tea and milk, mixed with lemon juice and drunk as an elixir, dissolved in water.
Compliance with drinking regime
– the third condition for the treatment of inflammation of the tonsils. Among the folk remedies, decoctions of rose hips, viburnum and rowan fruits, chamomile, sage, and mint are suitable. Warm milk with a pinch of soda and butter helps with pharyngitis.
When is surgery needed?
Surgical removal of the tonsils is carried out when the lumen of the larynx is completely blocked, with existing complications in the heart and joints, after the formation of a peritonsillar abscess, as well as in the chronic form of tonsillitis with regular relapses. Main methods of surgical treatment:
- classic method using a scalpel, scissors and a loop;
- cauterization with high-frequency current;
- ultrasonic scalpel;
- radiofrequency ablation;
- laser therapy using thermal welding;
- laser treatment using a carbon dioxide laser.
The appropriate intervention method is selected by the doctor and agreed with the patient. Indications, contraindications and possible complications that may arise in a particular patient are taken into account.
Abuse of bad habits
As surprising as it may be, excessive alcohol consumption and frequent smoking can also lead to swelling of the uvula mucosa. What measures to take in such a situation?
Doctors advise drinking as much warm liquid as possible. Why do this? If the kidneys and urinary system work at an accelerated rate, the body will quickly cleanse itself of toxins. If a person drinks little fluid, intoxication may last several days.
The following will also help speed up the recovery process:
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- complete cessation of alcohol and smoking (at least for the duration of treatment).
Uvulitis is a dangerous pathology that, in the absence of competent and timely treatment, can cause various complications. That is why, in order to maintain your health, when the first symptoms of a disorder occur, you must immediately visit a doctor.
If discomfort in the throat occurs, which turns into painful sensations, treatment must be carried out immediately. The tongue tends to increase in size; it is necessary to monitor its condition.
Prevention measures
Uvulitis can be prevented if:
- stop smoking and minimize alcohol consumption;
- brush your teeth and tongue daily;
- undergo regular dental examinations and promptly treat caries and gum disease;
- do not eat too hot or cold food;
- Chew any food thoroughly so that you don’t have to swallow huge pieces;
- treat infections of the nasopharynx and oropharynx, based on the recommendations of a doctor.
Uvulitis causes discomfort and anxiety, but responds well to therapy. As long as it doesn't bother you too much, you can treat it at home. But if there is no effect, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Features of the course in children
Untreated diseases accompanied by swollen tonsils in childhood become chronic. And constant advanced inflammation is fraught with problems with digestion, heart, kidneys and joints.
The most common causes of tonsil swelling in children are chronic and acute tonsillitis. They say about the development of sore throat:
- sore throat, especially when trying to swallow something;
- temperature above 38 degrees, accompanied by fever;
- enlarged tonsils;
- labored breathing;
- in the chronic form, pus may be discharged.
Kids refuse to eat. Due to decreased immunity, children become lethargic and avoid active games and entertainment. Schoolchildren's performance is falling.
It happens that the tonsils become enlarged when a child joins a new group: he goes to kindergarten or school for the first time. This is not a dangerous condition, but a natural reaction of the body. The load on the immune system increases, and the tonsils, as part of it, work in enhanced mode.
Can an untreated tooth hurt your throat?
Yes, such a situation is possible. Patients do not always notice a sore throat only after tooth extraction. Some people experience an unpleasant symptom even when there is a unit in the mouth affected by caries or other dental disease. You need to understand that the same untreated caries is a source of infection for the whole body. The carious cavity contains pathogenic microorganisms, which are activated during a period of weakened immunity and can affect any nearby organ, causing sinusitis, otitis media, inflammation of the tonsils and throat. People with untreated carious lesions are more likely than others to suffer from acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
Is it worth removing a tooth if your throat hurts?
You cannot undergo surgery if you have not been cured of diseases such as acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, influenza, sore throat, pharyngitis. The procedure cannot be performed if you have a runny nose or sinusitis. It is not recommended to perform extraction if there is nasal congestion and otitis media. All these diseases belong to the ear-nose-throat area. Viruses and bacteria move freely from one organ to another, causing complications. Thus, even the mucus that drains from the nose during a runny nose easily enters the mouth, from where bacteria can penetrate the wound of a newly extracted tooth and contribute to the development of alveolitis.
If you have ENT diseases, then it is better to postpone tooth extraction until you are cured and your immunity is stronger. On average, the state of the immune system returns to normal within two weeks after any illness, but everything again depends on its severity.