Treatment of fibroids on the gum, lip and other soft tissues of the oral cavity, as a rule, involves surgical intervention - removal with a laser or radio wave method. However, in some cases it is possible to do without radical therapy, it depends on the causes of the formation and the ability to quickly eliminate provoking factors.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to undergo a dental examination, consult with a doctor and, if necessary, take a photo of the pathological area. Timely visit to the clinic minimizes the likelihood of complications. In addition, the patient should adhere to preventive measures to prevent the disease and its consequences.
What is fibroma
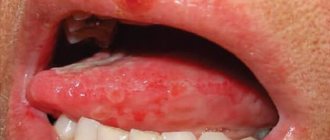
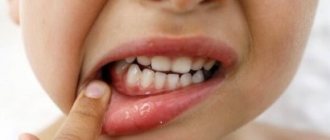
This is a benign neoplasm in the form of a small node on a stalk or broad base, which consists of fragments of connective tissue. In most cases, it is localized on the mucous membranes of the gums, lips, palate, on the inside of the cheeks, and a little less often on the tongue. The pathological process is more often encountered by primary schoolchildren and adolescents aged 6-15 years.
The patient is not in pain; at a very early stage he does not notice the pathology. As the thickening grows, it is easily felt and accidentally injured.
Can fibroids in the mouth resolve on their own, without medical intervention? In most cases, surgical excision of the tumor is required. However, do not worry about the complexity and duration of the operation. In less than an hour, an experienced doctor will eliminate the defect without subsequent complications and a long rehabilitation period. Currently, clinics use laser and radio wave techniques.
Despite the relative harmlessness of fibrous growths, they still need to be treated even in the absence of discomfort. If the seals increase in size and are constantly exposed to traumatic effects, it is highly likely that an infection will enter the wound. In this case, treatment will be very long, difficult and will not always lead to positive dynamics. In addition, the lack of therapy sometimes leads to the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant one.
Treatment
The most effective and most commonly used approach can be considered surgical intervention. Its essence is to excise the tumor using a laser or radio wave method. The tumor is completely removed, including the stem. If the oral fibroma was large enough, patch closure of the resulting defects is used to avoid deformation of the affected mucous membrane. A small “patch” is cut out from nearby tissue and the tumor removal site is covered with it.
Reasons for education
After conducting numerous studies, scientists have not been able to determine an exhaustive list of factors that provoke the development of pathology. However, some conditions and phenomena still occur most often when diagnosing this disease. For example, this is possible with a hereditary predisposition to fibroids on the gums (shown in the photo below), tongue, inside the cheeks and other areas of the mucous membranes. In this case, the disease develops in childhood in young patients from 1 to 10 years.
Often, in the presence of this diagnosis, a history of regular traumatic exposure is established. There may be constant biting of a certain area of soft tissue. They can also be injured by sharp edges of crowns, orthodontic structures, dentures, especially poorly fixed ones, and hard food.
Taking certain medications can also be a provoking factor. Some medications can cause the appearance of benign lumps in representatives of different age categories, not only in children and adolescents. Drugs that may cause fibromatosis after use:
- Cyclosporine. It is indicated to prevent organ rejection during transplantation.
- Valproate, used by epileptics.
- Verapamil and other calcium channel blockers.
- Estrogens of synthetic origin in oral contraceptives or other hormonal pills.
The culprits in the development of the disease may be inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. These include stomatitis, glossitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis, etc.
It is impossible to exclude a hereditary factor, but the risk of formations can be significantly reduced if you follow simple preventive rules:
- do not forget about hygiene;
- Carry out regular professional cleaning to remove thick plaque and tartar;
- protect soft tissues from traumatic effects (solid food, biting), and also avoid sudden temperature changes;
- treat dental diseases in a timely manner;
- consult with doctors before starting to take medications and avoid self-medication;
- visit the dentist for preventive maintenance at least once every six months.
Causes
The exact culprit behind the development of fibroids in children has not yet been determined. Experts have identified a number of factors contributing to the appearance of tumors. These include:
- unfavorable environmental living conditions (proximity to chemical and cement plants, landfills, contaminated areas);
- frequent injuries, bruises and falls;
- various infectious diseases of acute and chronic form;
- irrational use of potent drugs;
- endocrine pathologies;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Classification of fibroids
Pathology is divided into several types according to criteria. This includes the density of the benign neoplasm, the nature of its origin, as well as the severity of clinical manifestations.
Dense fibroma
Characterized by a solid consistency. This is due to the fact that the contents are quite hard fibers of connective tissue. They include a small number of cores. Formations of this type are most often found on the gingival surfaces and palate.
Soft fibroma
The fibrous structures are thin and freely located, so their clusters are characterized by a high degree of softness. This type is most often observed on the tongue and the inside of both cheeks. Benign neoplasms of a mixed type, combining the signs of all the varieties listed above, can be found on the sublingual part and on the mucous membranes of the floor of the oral cavity. For example it could be:
- Fibrolipoma. It is hard to the touch because it contains fibrous fibers. It can be eliminated surgically, with laser, or radio waves.
- Fibrohemangioma. As a rule, it is provoked by infectious processes occurring in the child’s body. It is extremely rare in adults. It never degenerates into malignant tumors. Most often it is treated surgically, in some cases it can resolve on its own.
Fibroma from irritation
This is not a tumor formation in its usual form, but the result of reactive hyperplasia. Chronic pathology is characterized by the development of focal lesions, which are caused by systematic mechanical action and subsequent injury.
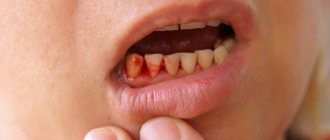
The most common cause is installed crowns, fillings, and dentures. In the latter case, the disease is called prosthetic granuloma. The orthopedic structure exerts continuous pressure on the alveolar process, leads to its resorption, moves forward and contributes to the formation of compactions, which are associated with the inflammatory process.
The risk group includes not only patients who have undergone prosthetics, but also people with untimely cured caries, in adulthood, with foreign objects in the oral cavity (for example, with piercings). Studies have shown that women are more prone to such hypertrophic transformations than men.
Symmetrical fibromas
Doctors diagnose such tumors in the area of the third molars in the areas between the gums and the roof of the mouth. The tumor is hard to the touch and resembles a bean in shape.
It should be noted that this type of compaction does not apply to true fibromatosis. These are just overgrown tissues in the gingival membranes, accompanied by the process of scarring and other changes of a similar nature.
Lobular fibroma
It occurs as a result of reactive hyperplasia with systematic trauma to delicate sensory fibers with prostheses or other orthopedic structures. The main distinguishing feature of such formations is their rough, textured surface. When palpated, tubercles are felt.
Fibrous epulis
This is a dense growth of pinkish tissue that does not cause pain or other discomfort. The edges are often hyperemic, have clear boundaries and irregular shape. The base is quite wide.
The vestibular part of the gums is usually affected. There are cases of neoplasms occurring in the interdental spaces in the form of a saddle with spread to the intraoral surface.
Quite often, a dental unit located in a pathological area has a poorly fitted metal crown, extensive carious lesions, or a prosthetic clasp. It is these structures that are the provoking factor in the occurrence of a chronic inflammatory process with the formation of granules, which over time are transformed into mature connective fibrous fibers.
In dentistry, there are also angiomatous epulis. They are brighter in color, somewhat softer to the touch and bleed. In this case, blood appears not only at those moments when the surface is affected mechanically, but regardless of the presence or absence of a traumatic factor. When conducting diagnostic studies, many vascular branches are detected in the pathological area.
What are fibroids?
The formations are divided into several types, differing in their density, nature of origin and how severe the clinical manifestations of the neoplasm are. Dense education. It is characterized by a thick consistency and is most often localized on the gums and palate. Consists of soft fibers of connective tissue. Typically found on the inside of the tongue and cheeks.
Formation arising from irritation. A chronic disease caused by constant trauma to one area of the mouth. The cause may be installed fillings or prostheses, as well as piercings.
Fibrous epulis. A dense pink formation that does not cause any discomfort to the patient. It has very clear boundaries and an asymmetrical shape. Localized on the vestibular region of the gums or in the interdental spaces.
Symptoms
The tumor grows and develops quite slowly, so for a long time the patient may not even be aware of its presence in the mouth. Fibroma of the oral mucosa looks like a hemispherical growth rising above the plane, covered with pinkish tissue. If you press it, pain or other discomfort does not appear. The surface is smooth, there are no irregularities or roughness on it.
The appearance of ulcers with such a diagnosis is very rare. In such cases, an infection is usually associated with the subsequent development of the inflammatory process. Swelling, redness, erosion occur, and pain is felt. The pain persists even if you do not touch the pathological area.
If you do not injure the formation, it may not change its size for quite a long time and remain in a stable state. If it is exposed to constant traumatic effects, there is a high risk of malignant degeneration, which is dangerous to the life and health of the patient.
Types of fibroids
There are two types of tumors: soft and hard.
Soft fibromas in a child are characterized by very slow growth, rather flabby consistency, mobility and clear localization. Such growths occur mainly in the genital area and anus, sometimes forming multiple clusters. Solid neoplasms are smooth or slightly rough pink and flesh-colored nodules with dense contents. Such fibromas are located on a wide base and, as a rule, do not exceed 1 cm in size.
Diagnosis of fibroids of the upper and lower jaw
The doctor will not prescribe treatment until he is sure that the diagnosis is correct. To do this, diagnostic procedures are carried out, the results of which will confirm or refute the fears of doctors.
First, the patient is asked to describe the symptoms. The dentist examines and palpates the tumor. However, this is not enough to develop therapeutic tactics, since it is extremely important to determine the depth of tumor growth into soft tissue. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination is performed.
In difficult cases (ulcers, development of an inflammatory process in a pathological area of the gum, etc.), a biopsy is indicated. After surgical removal of the tumor, fragments are necessarily sent for histological analysis.
The examination is necessary not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to identify the factors that provoked the disease. A full dental examination is carried out to confirm the presence of inflammation. In addition, one cannot do without radiography, orthopantomogram and other images in different projections.
If a person has dentures, a consultation with an orthopedic dentist may be necessary. This is necessary to eliminate the possible traumatic effects of artificial elements on the mucous membranes.
Differential diagnosis
Biopsy remains one of the most informative methods for distinguishing fibroids from other benign neoplasms. The study is indicated for suspected papilloma, lipoma, epulis of various structures, neurofibroma, cyst, squamous cell carcinoma, wart, etc.
If the growth is localized on the tongue or sublingual part, it is extremely important to differentiate it from all existing seals. Timely diagnostic measures make it possible to detect cancer at the earliest stages and provide high-quality therapy with a short recovery period.
Benign tumors in the mouth must be removed
Benign tumors of the oral cavity are neoplasms in the oral cavity of a benign nature, which are characterized by limited, slow growth. They can be localized on the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips, as well as in the thickness of the jaws and soft tissues.
The most common tumors are those whose origin is caused by glandular, flat, tooth-forming epithelial tissue, but formations from adipose, muscle tissue, connective tissue structures, blood vessels and nerve trunks are also found.
A person notices changes in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, inflammation and growths almost immediately. Discomfort intensifies when exposed to hot food or friction with dentures. This could be a papilloma in the mouth - a tumor-like formation on the mucous membrane. It is important to mitigate as much as possible the conditions that predispose to malignant degeneration of the inflamed and overgrown epithelium. By visiting a doctor, you can consult on complex treatment.
The proliferation of epithelial tissue in the oral mucosa is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Its particles are present in the bodies of 9 out of 10 adults on the planet. Some people have no idea about this and do not feel any changes at all. Others have to struggle with the unpleasant manifestations of papillomatosis for many years.
What symptoms of papillomatosis in the mouth should you pay attention to?
Regardless of the specific localization of growths on the oral mucosa, several general characteristics of tumors are distinguished. Usually papillomas on the gums and tongue are pink with a whitish tint, their size does not exceed 10 mm. The most characteristic feature is the presence of a narrow or wide base - the so-called “leg”. The upper part is lumpy, with uneven edges.
Feelings of a person who has become the “owner” of a small tumor in the mouth: it interferes with normal chewing of food and talking. Much depends on the specific location of the papilloma. Typically, the localization of formations is associated with the tongue, gums, lips, and lateral surfaces of the oral cavity. There are not only single papillomas, but also multiple growths. Some are soft and mobile to the touch, others have a keratinized surface.
Before removing growths with such characteristic signs, cytological and histological studies of the material obtained from the mouth must be carried out. Laboratory tests can distinguish papilloma from genital warts or epithelioma and determine the degree of oncogenicity of HPV.
Complex therapy of papilloma in the mouth
Specialists need to clearly limit the growth, identify hidden foci of papilloma in the mouth, the treatment of which is not started without consultation with an oncologist, dentist, or ENT doctor. The choice of therapeutic technique affects the final results, but it is difficult to achieve 100% results.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is carried out comprehensively. According to medical research and patient reviews, this approach reduces the number of relapses, that is, the appearance of new tumors in the oral cavity.
Removal of papillomas in the oral cavity
Treatment of small growths of the mucosal epithelium is fairly quick and almost painless. It is easier to get rid of small round formations on a thin stalk. Typically, oral papilloma has an uneven edge in the shape of a cockscomb or cauliflower. Its color is close to the tone of the mucous membranes, sometimes it is darker or lighter. Removal of such tumors is carried out by deep coagulation with radio waves, evaporation with a laser beam, or traditional surgical excision.
Oral fibroma is a benign neoplasm consisting of fibers of mature connective tissue. It is a clearly demarcated rounded nodule on a stalk or broad base, covered with unchanged mucosa. Characterized by slow exophytic growth. Oral fibroma can be located on the inner surface of the cheeks, mucous membrane of the lips, soft palate, gums, and tongue. Diagnosis of oral fibroma is made by inspection, palpation, ultrasound and histological examination. An orthopantomogram, radiography and periodontogram are used to identify inflammatory processes that provoke the formation of fibroids. Treatment of oral fibroma boils down to its excision. Along with papilloma, lipoma, myoma, nevus and myxoma, fibroma is a benign tumor of the oral cavity. It most often occurs in children aged 6 to 15 years. Clinical dentistry considers traumatic and inflammatory factors to be the causes of the formation of oral fibroma, and a hereditary predisposition can also be traced. Quite often, the history of patients with oral fibroma reveals regular biting of the same area of soft tissue of the oral cavity, which precedes its appearance. Factors that provoke the appearance of fibroma also include trauma to the mucous membrane with a sharp tooth edge, a poorly fixed prosthesis or crown; chronic inflammatory processes of the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis, glossitis, etc.) Signs of oral fibroma Oral fibroma has the appearance of a formation rising above the general surface of the mucous membrane with a wide base or stalk. It is painless, has a hemispherical shape and is covered with a mucous membrane of the usual pink color. The surface of oral fibroma is smooth and, unlike papilloma, has no outgrowths. No changes in the mucous membrane in the area of fibroma are usually observed. In rare cases, ulceration is observed over the tumor. In this case, an infection may occur with the development of inflammatory manifestations: redness, swelling, pain in the area of the fibroma. Oral fibroids typically exhibit a slow increase in size. If the fibroma is not traumatized, its size can remain stable for a long time. With constant trauma, malignant degeneration of the tumor is possible. Diagnosis of oral fibroma The characteristic clinical picture of oral fibroma in most cases allows the dentist to make a diagnosis based on examination and palpation of the formation. To determine the depth of growth of the base of the fibroma into the underlying tissue, ultrasound can be performed. In rare cases, usually when there is ulceration or inflammatory changes in the area of the fibroma, a biopsy of the formation is indicated. More often, histological examination of oral fibroma is carried out after its removal. An important point is the diagnosis of the causative factor in the formation of oral fibroma. For this purpose, a thorough dental examination is carried out aimed at identifying inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, radiography or radiovisiography, an orthopantomogram and a periodontogram are performed. Patients with dentures need to consult an orthopedic dentist to avoid the traumatic effect of the existing denture on the tissues of the oral cavity. Treatment of oral fibroids The most effective treatment for oral fibroids is surgical excision. Pedicled oral fibroids are removed along with the stem using two bordering incisions. The fibroma at the base is excised together with the base using a bordering or arcuate incision. Removal of fibroma on the red border of the lip is made with an incision perpendicular to the passage of the fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle. For large oral fibroids, to prevent deformation of the mucosa, patch closure of the defect remaining after tumor removal is performed. The flap is cut out using a V-shaped incision from adjacent tissues.
Epulis, popularly called supragingival, refers to benign tumors of the maxillofacial region. Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm with a diameter of 0.5 to 6-7 centimeters, which is located on the alveolar process of the jaw. The predominant localization of the supragingival is the area of small molars, although in some cases it can occur at the level of any teeth of the upper or lower jaws.
The cause of the occurrence has not been definitively established, but in the vast majority of cases it occurs as a result of prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane of the alveolar process, for example, by the sharp edge of a decayed tooth or from irritation of the mucous membrane by dentures. It occurs quite often in pregnant women; they are often diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. Epulis grows slowly, although pregnant women often experience accelerated growth, apparently caused by hormonal changes in the body. As a rule, patients do not experience any pain, except in cases of injury to the teeth of the opposite jaw. The supragingival partly or completely covers the coronal part of one tooth, and more often than not several teeth at once from the vestibular and sometimes from the lingual surface.
Most often, the tumor has a wide stalk and is covered with ordinary mucosa, without any pathological changes; if the epulis is injured, then areas of erosion and hemorrhage appear. It differs from malignant tumors in that there are no areas of tumor decay. Prolonged growth of the supragingival can lead to destruction of the alveolar process and its spongy substance. In this case, osteoporosis of the bone will be visible on the x-ray.
The color of epulid is slightly different from the color of the oral mucosa - sometimes it has a red-brown or even bluish tint.
Treatment for epulide is only surgical. Considering that epulis has a growth zone in the periosteum and in the bone, after removing the tumor within the visible healthy mucosa, you need to do a thorough curettage around the tumor and remove the softened bone. Sometimes the tooth itself is also removed if it is located in the area of tumor growth and the alveolar process is destroyed by the tumor process. After removal, in some cases, the supragingival tissue may reappear in the same or other areas of the jaws.
Treatment of oral fibroids
Surgery remains the most effective and most common therapeutic method. The seal is excised using a laser or radio waves. This procedure lasts about half an hour. If the tumor is very large, after its removal the wound is covered with a flap, which is formed by the doctor from the surrounding tissue.
When pathology is caused by taking certain medications, they should be completely eliminated and replaced with alternatives with similar properties. After discontinuation of drugs in such cases, the appearance of the mucous membranes is often restored without outside help, and the likelihood of relapse approaches zero. However, this does not apply to situations where the disease is advanced.
Surgery can also be avoided in case of traumatic effects of orthopedic structures. For example, when a crown, filling, or prosthesis puts pressure on the tissue. Elimination of the provoking factor often leads to a decrease or complete disappearance of a benign formation. Most likely, it will be necessary to dismantle the old structures and replace them with new ones.
On the Internet you can find stories of healing using home remedies. It is worth remembering that the disease cannot be treated with the help of folk recipes. Herbal decoctions and infusions, and other compositions are used only as an auxiliary element of complex therapy.
Clinical case
A 12-year-old boy was examined at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry at the University Federico II of Naples in November 2016. The patient was referred to us by a private dentist due to the presence of an area of reduced radiopacity on the orthopantomogram located under the left angle of the mandible. The anamnesis was not burdensome. External clinical examination did not reveal any skin damage or edema. Examination of the oral cavity revealed the absence of tooth 37 and slight swelling in the same area of the lower jaw. Orthopantomography and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) revealed a large area of bone loss in the left corner of the mandible (Fig. 1, 2) extending from the first molar to the ramus of the mandible. The injury likely displaced tooth 38. In addition, complete agenesis of tooth 37 was revealed. Analysis of sagittal CBCT sections showed thin residual cortical bone, allowing planning of a conservative surgical approach.
Rice. 1. Orthopantomogram before treatment.
Rice. 2. CBCT of the lower jaw.
Surgical excision was performed under general anesthesia, using an approach through the alveolar process (Fig. 3 a-e), without removing large areas of the vestibular cortical bone, using a fiberscope connected to a monitor (video-rhinolaryngeal model CCD 11101 VP with a diameter of 3.7 mm , Karl Storz, Switzerland) (Fig. 4). The intraosseous cavity was visualized to inspect the peripheral lesions and clarify the position of the 38th molar, allowing for a more conservative removal of the bone and tooth. Then the final curettage of the bone area was performed through a fiberscope.
Rice. 3 a. Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 3 b. Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 3rd century Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 3 g. Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 3 d. Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 3 f. Surgical stage and tumor measurement.
Rice. 4. Video rhino-laringo model CCD 11101 VP, diameter 3.7 mm, Karl Storz (Switzerland).
Macroscopic examination of a tumor sample measuring 60x40x40 mm revealed a heterogeneous surface and fibroelastic consistency (Fig. 5). The affected tissue was then subjected to histopathological examination, which showed a picture of ameloblastic fibroma: a stroma of poorly differentiated mesenchymal tissue, in which the epithelial cellular component is immersed, located in the form of threads and inclusions (Fig. 6). In peripheral areas, undifferentiated bone tissue with scant epithelial cells was observed (Fig. 7).
Rice. 5. Macroscopic examination of the tumor.
Rice. 6. Histological examination (20x) showed a characteristic picture of ameloblastic fibroma.
Rice. 7. Histological examination of peripheral areas (10x), where undifferentiated tissue similar to bone tissue was observed, with small inclusions of epithelial cells.
Rice. 8. Control orthopantomography after 6 months.
No clinical complications were identified in the postoperative period. The patient was followed monthly for 6 months and no clinical or radiological signs of recurrence were observed. After 6 months, orthopantomography showed the formation of new bone in the left distal part of the body of the mandible.
Let's sum it up
Mucous fibroids on the inside of the cheeks, gums, lips, and tongue grow very slowly and do not cause severe discomfort. They do not pose a danger to the patient, but the problem must be eliminated as early as possible. The fact is that a benign seal in the oral cavity with regular trauma can degenerate into a malignant one, and the oncological process requires serious therapy and is extremely dangerous to life and health.
It is impossible to get rid of the disease using traditional methods. It is important to undergo high-quality dental diagnostics and consult with specialists. In most cases, surgical excision is indicated, but with small growths, the absence of severe symptoms and the elimination of provoking factors, there is a possibility of rapid tissue restoration without external influence.
There is no need to worry if the doctor has decided to undergo surgery. Modern clinics practice laser or radio wave removal on an outpatient basis. These are the most gentle and highly effective methods. An extremely important point in a positive prognosis for the treatment of dental fibroids is an early visit to a doctor and proper excision by an experienced physician.
Prognosis and prevention
When patients seek medical help in a timely manner, doctors can formulate a favorable prognosis in 75–80% of cases. The likelihood of a complete recovery of a child or adult is reduced when fibromatosis is advanced or secondary pathologies are attached to the disease.
Preventive measures are simple - patients are advised to avoid repetitive trauma to the skin, soft tissue and bones. Persons working in hazardous industries must undergo regular preventive examinations. Children and adults should eat a healthy diet and include adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Diagnostics
The examination begins with a visual examination: the doctor listens to the complaints of children and parents, carefully palpates the formation, and collects a detailed medical history. To determine the nature of the lesion, a number of instrumental studies are carried out:
- ultrasound examination of soft tissues;
- radiography;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
A biopsy and cytological examination of biological material help to identify the nature of the pathology and clarify the diagnosis.