Leukoplakia is an inflammatory process accompanied by keratinization of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and a white coating.
In some cases, the disease is not dangerous and goes away without a trace over time. In others, it may develop into a precancerous condition and later into oral cancer. This is why prevention of leukoplakia of the oral mucosa is so important: it is easier to prevent complications than to deal with the consequences.
The risk of the disease in men is much higher than in women: 80% of patients versus 20%
“The influence of cryodestruction and antioxidants on the activity of hydrolases in blood leukocytes of patients with leukoplakia” Dr. med. Mashkilleyson A. L.
Hairy leukoplakia of the mouth or tongue - symptoms and treatment
Content:
What is oral leukoplakia
Causes of leukoplakia in the oral cavity
Symptoms of hairy leukoplakia
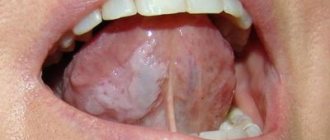
What does hairy leukoplakia look like?
What are the dangers of leukoplakia?
How to treat hairy leukoplakia
Various diseases occur on the oral mucosa, which are a manifestation of reduced immunity. A common condition is hairy leukoplakia of the tongue.
Symptoms of the disease
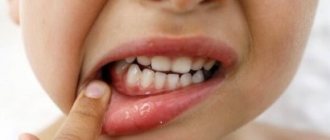
The main danger of hairy leukoplakia is that it may not manifest itself for a long time, and only a visit to the dentist can help identify this disease in time. The first and most typical symptom that should alert you is a strong white or gray coating covering the back and bottom of the tongue.
As a rule, those suffering from leukoplakia do not feel any particular discomfort - except in cases where the disease is accompanied by a fungus.
The following symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
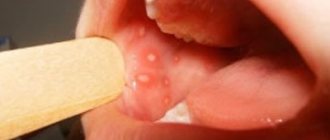
- The appearance of folds and plaques formed from plaque;
- Cracks in the tongue;
- Erosion in the advanced stage of the disease;
- General signs of immunodeficiency: diarrhea, sudden weight loss, night sweats, fever that occurs for no apparent reason, general pain and weakness.
What is oral leukoplakia
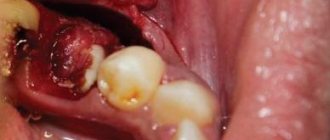
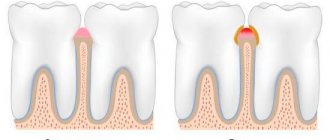
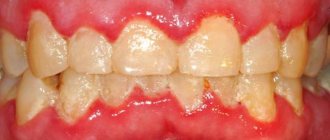
Leukoplakia is a lesion of the oral mucosa in which excessive keratinization is observed. Located on the cheeks, hard and soft palates, and tongue.
Types of leukoplakia:
- Flat is the most common form. Usually does not cause discomfort. Discovered by chance at a dental appointment.
- Verrucous - more pronounced keratinization than with the flat form. Patients note a feeling of roughness and tightness on the mucous membrane, a burning sensation.
- Erosive – is a complication of the previous two forms when exposed to a traumatic factor. Characterized by pain. which occurs when talking or eating.
- Hairy leukoplakia is a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Often observed in patients with HIV.
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia - it is found in long-term smokers. It is observed on the soft and hard palate.
Some forms of this disease are considered precancerous. If left untreated, they develop into malignant tumors. Therefore, it is important to contact a dental clinic in Moscow when you first detect pathological changes in the mucous membrane.
Nutrition
Since in most cases of disease the patient does not experience any complications or pain symptoms, there is no need to follow a diet for leukoplakia. However, most often the cause of the formation of plaques is a low level of immunity, and therefore, nutrition should be complete, healthy and rich in vitamins.
In advanced and severe forms of the disease, when it is difficult for the patient to open his mouth and chew food due to the formation of erosions and ulcers in places where the mucous membrane is damaged, it is recommended to switch to a porridge-like and puree-like consistency of food. It is also necessary to avoid eating too spicy and too hot foods.
Causes of leukoplakia in the oral cavity
To date, scientists have not reached a consensus on why the disease occurs. There are factors that can lead to the development of excess keratinization:
- Constant exposure to irritating factors: smoking, regular burns from hot food, strong alcohol, etc.
- Work in industries where there are chemicals, alkalis, acids.
- Living in a hot, dry climate.
- Taking drugs that reduce immunity.
- Local traumatic factors: failed fillings, sharp edges of dentures and damaged teeth, poor-quality braces.
- Endocrine pathologies: diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism.
- Reduced immunity: HIV, AIDS, immunosuppressive state. Oral hairy leukoplakia is often observed in patients with HIV and AIDS.
Prevention of leukoplakia
The key measures for the prevention of leukoplakia are basic rules of personal hygiene and strengthening the immune system:
- regular hardening;
- sufficient physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of any disorders;
- regular preventive examinations;
- giving up bad habits, heavy and spicy foods that irritate the esophagus;
- careful intimate hygiene and visiting a gynecologist;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations during a preventive examination.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
How to treat hairy leukoplakia
Before starting treatment, you need to conduct a number of studies. The patient is referred to a therapist at the clinic. There, the doctor can prescribe laboratory tests: biochemical blood test, testing for sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
If a person is diagnosed with HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy is administered. With long-term use of drugs, the patient’s well-being improves, and the disease in the mouth goes away.
The dental clinic provides oral examinations, dental diagnostics, and professional hygiene. If sharp edges of fillings or failed prostheses are detected, they are replaced. Treatment of caries and its complications is carried out. Recommendations are given for home dental care: personal hygiene products (brushes, pastes, dental floss, rinses) are selected.
Keratolytic drugs are suitable for local treatment. In advanced cases, they resort to surgical manipulations: excision of the affected areas with a laser.
Treatment methods
Treatment of leukoplakia may require a collegial approach: the participation of the oncologist in developing an action plan. The basis of therapy is the elimination of provoking factors: quitting smoking, changing jobs due to occupational hazards, following a soft diet with no spices, etc. According to indications, correction of dentures, replacement of fillings, treatment of caries, removal of teeth that cannot be restored and other measures are carried out .
As part of complex treatment, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Preparations for restoring the normal structure of the oral epithelium. It is usually used in the form of applications to the affected areas.
- Antiseptics. Used for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory complications of the disease.
- Painkillers and symptomatic therapy. Systemic medications or applications of local anesthetics used in dentistry may be used.
Self-medication for leukoplakia in the mouth is strictly not recommended. Many drugs, including some anti-inflammatory drugs, are irritating and increase the risk of developing malignant tumors.
If the disease is severe, hospitalization may be required. The presence of ulcers and erosions is an indication for the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, proteolytic enzymes, etc. Surgery is indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective. Cryodestruction and excision with a scalpel are usually used.
General treatment for hypertrophy of the tongue papillae
- Antihistamines
- Vitamin therapy (oil solution of vitamins A, E)
- Normalization of keratinization processes of the tongue epithelium
- Vitamin C (increases the activity of the body’s immune system, activates metabolic processes in the body, accelerates wound healing processes)
- Vitamin B2 (strengthening the body’s defenses and the functions of vital organs)
- Antifungal drugs (they affect the growth and reproduction of spores of fungi of the genus Candida)
- Treatment of identified common diseases (referring to medical specialists to conduct a course of treatment and eliminate the causative factors of the disease)
Answers to popular questions about “black hairy tongue”
Why do the papillae of the tongue turn black?
The brown or black coloration of hypertrophied tongue papillae is caused by waste products of chromogenic bacteria that live in the oral cavity. Coloring can also occur due to pigments contained in the food consumed.
How long does it take to cure a hairy tongue?
Often, a hairy tongue is one of the symptoms of a general disease and goes away on its own after treatment. As a rule, improvements should appear within 5-14 days, provided that the patient maintains careful oral hygiene, uses antiseptic solutions, and stops consuming coloring products (tea, coffee, carbonated drinks).
Is it possible to remove black plaque on the tongue on your own?
No, because you can injure your tongue and aggravate the disease. It is recommended to consult medical specialists who will help you understand the cause of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment.
Which doctors should you contact if you have a black hairy tongue?
Tongue pathologies are dealt with by such specialists as a general practitioner (he will try to determine the causes, prescribe tests and refer to more specialized specialists), a dentist (surgeon), an ENT doctor, a gastroenterologist, and an endocrinologist.
I was diagnosed with hypertrophy of the tongue papillae, is this permanent?
No, not forever. First of all, you need to find out the cause of hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue, as well as the nature of the disease, the depth and size of the lesion. Based on these criteria, treatment is selected. If a black hairy tongue is a symptom of a general disease, then after treatment the pathology may go away on its own within 7-14 days, since everything is individual.
Can I use a tongue scraper if my tongue is black?
Can. With hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue, complete hygienic care for the oral cavity is necessary, which allows you to cope with symptoms and possible complications. A tongue scraper helps reduce the rate of proliferation of papillae, reduces the number of bacteria living in the affected area, and eliminates unpleasant odor in the mouth.
Is it possible to remove hypertrophied papillae surgically?
Do not forget that the treatment of black hairy tongue is complex.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the causative factors and treat common diseases. Surgical treatment methods are resorted to if the growth of filiform papillae does not decrease after simply cleaning the tongue with a scraper. One of the methods is cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen (freezing and destruction of tissue) - surgical removal of hypertrophied papillae through irrigation with liquid nitrogen for 15-20 seconds, after which the altered filiform papillae are rejected.
Diagnostics
Even with the current high level of medicine, it is impossible to determine leukoplakia by eye with one hundred percent accuracy. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a biopsy under local anesthesia. After a histological examination of the damaged mucosa and determination of the type of leukoplakia, the diagnosis is considered successfully completed.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment, which may include removing the source of irritation, local treatment of the damaged areas with retinol acetate or other oil solutions, and taking immunostimulating and vitamin-mineral preparations. Or, in case of a serious precancerous form and the presence of cellular atypia, the doctor will recommend cryodisruption of the lesion.
Why does a hairy tongue appear?
The true cause of the pathology has not yet been established. Often, a black tongue appears in diseases of the digestive system, liver, and also after infectious diseases. The appearance of a hairy tongue in this case is associated with long-term use of antibiotics, which disrupts the microbial balance of the oral cavity and suppresses the development of beneficial forms of microorganisms. Because of this, the amount of yeast-like fungi in the oral cavity increases.
The following factors play a major role in the occurrence of this pathology:
- trophic factor, when the nutritional processes of the mucous membrane of the tongue are disrupted
- physico-chemical factor: the use of tobacco, alcohol and medications reduce the acidity of oral fluid and saliva
- avitaminosis, that is, insufficient intake of vitamins in the body or their complete absence (it is worth noting that avitaminosis and hypovitaminosis are observed with hepatitis C)
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV infection, AIDS)
- dysbacteriosis (disturbance of intestinal microflora)
- poor oral hygiene
- chronic tongue injury
Diagnosis for suspected HIV infection
For differentiated diagnosis of HIV infection from similar dental diseases, the following tests are used:
- Blood test for PCR reaction (aimed at detecting HIV).
- Immunoblotting technique.
- Linked immunosorbent assay.
- Checking immune status.
If the results are unclear, additional blood tests, as well as bacteriological studies, may be prescribed. Early diagnosis of the root cause of diseases can significantly alleviate the course of the disease.
What is HIV? What is HIV infection
The human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, was identified and described relatively recently. Invading the human body, it primarily affects macrophage cells and T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and destroying hostile bacteria. Thus, the body's immune barrier loses its ability to resist both external bacterial attacks and internal opportunistic flora.
The immunodeficiency virus is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact or through direct contact of a healthy body with infected blood. Transmission of the virus through household or food contact is impossible.
HIV infection is a slow-onset disease caused by a virus and occurs against a background of suppressed immunity. It can take years from the introduction of the virus to the clinical manifestations of the disease. During this entire period, the virus does not manifest itself in any way, and its presence can only be diagnosed using a laboratory method.