What are the reasons for the violation
The most likely cause of the acetone odor is diabetes. With this disease, there is a lack of insulin as a result of metabolic disorders. The smell will be the first sign of this disease, as will lethargy, apathy, fatigue and other manifestations of intoxication.
Another factor is disruption of the hepatobiliary system and kidneys. They remove toxic substances from the body. In various diseases, organ function is disrupted and harmful components, including acetone, accumulate in tissues.
An acetone odor is noted in renal failure. This phenomenon is also present during fasting.
One of the most dangerous signs will be the appearance of odor against the background of thyroid pathologies. With hyperthyroidism, increased hormone synthesis occurs, which, with the right approach, can be eliminated with medications. In some cases, there is a critical deviation from the norm, which causes increased metabolism.
The infectious process can also be manifested by an acetone odor. This is the result of protein decompositions. Therefore, during infections, it is recommended to drink more to remove acetone from the body.
Other reasons may be:
- poor oral hygiene;
- smoking;
- dry mouth;
- binge eating;
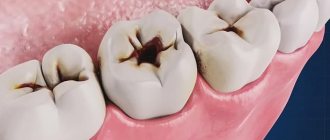
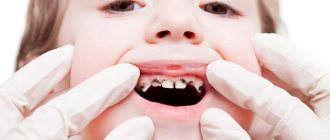
- dental diseases.
A childhood disease called "acetone"
August 18, 2017
In recent years, pediatricians have increasingly encountered complaints from mothers about the smell of acetone in children. Often the smell is accompanied by other symptoms – vomiting and fever. What to do in such cases and is this condition dangerous? Helping your child with the smell of acetone on their breath First, make your child sweet, warm tea. And to determine acetone, there are special test strips that are sold in a regular pharmacy. It is better to always have such a test system if you have a child at home.
You should read the instructions for the system and do testing. Depending on the results obtained, a set of measures is taken. Learn reliable information on acetone syndrome. This is what doctors call this condition.
Why does children smell of acetone on their breath?
Attention!
A smell reminiscent of acetone is not a disease or diabetes, as many people think. This is a sign that the baby's glycogen stores are depleted. Glycogen is necessary for energy production; its deficiency occurs when metabolism is disturbed and precisely when there is little glycogen in the baby’s body.
Features of a child’s body compared to adults:
- Glycogen, which is contained in the liver and muscle tissue, is much less - from 45 to 70 grams. An adult has about 650 grams.
- Metabolism in children is more intense.
- Blood glucose (sugar) levels fluctuate frequently.
- Pancreatic enzymes are less active.
Smell of acetone.
Reasons for appearance. Acetonemic syndrome and ketone bodies In some cases, the child has a high need for additional energy. For example, in case of overexcitation, overwork, after an illness, hunger, etc. The body takes energy from glucose in the blood, but this is enough for a short period of time (just a few minutes). To make up for the energy deficit, you have to use another source - glycogen (located in the liver and muscles). It lasts for several hours, but this is still not enough. Then fats are consumed. But in order to be converted into energy, fats (lipids) first need to go through certain stages with the formation of intermediate substances. Experts call these substances ketone bodies. When the amount of ketone bodies is small, the body is able to quickly utilize them, and when there are too many of them, they begin to be excreted through the kidneys, intestines and lungs. Hence the specific smell. When should you call an ambulance? You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- prolonged crying (no tears);
- dry tongue in a child;
- no urination for more than six hours;
- refusal to drink.
There is no need to try to stabilize the child’s condition on your own or use questionable methods!
Here you only need qualified help. For other, non-serious conditions, there are a number of simple measures that mom and dad should study. Why does a child vomit when using acetone? Mothers are most frightened by vomiting in children. The urge to vomit and loss of appetite appears due to an excess of ketone bodies, which: 1. Act directly on the vomiting center in the brain. 2. Suppress the hunger center. 3. They irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract as they pass through the intestines. Because of this, the child may not only have nausea and vomiting, but also have a stomach ache.
Conclusions. Acetone in children is not a pathology (that is, a disease), but a specific reaction of the body to a deficiency of glucose in the blood. Acetone appears when fats are broken down in the body with the formation of ketone bodies in quantities that are difficult for the body to remove. Parents must know how to help their child in such cases. If you find similar symptoms, it is still better to immediately make an appointment with a pediatrician. by phone
In what diseases is it observed?
It has been established that the smell of acetone can occur in the following diseases:
- poisoning;
- coma;
- kidney inflammation;
- kidney failure;
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- dehydration due to intestinal infections;
- diabetes;
- liver injuries.
When an unpleasant odor begins to bother you, you should make an appointment with a therapist. After examination, questioning and studying the test results, the doctor will be able to refer you to a specialized doctor - gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, nephrologist.
If such a symptom appears, the doctor will definitely prescribe a blood and urine test for diagnostic purposes. Additionally, nasopharyngeal culture and CT may be required. The research results will help identify the cause and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Acetone syndrome in children
When a large number of ketone bodies (acetone and acetoacetic acid) accumulate in the child’s blood, the child develops an acetonemic crisis.
Recurrence of crises indicates the presence of acetonemic syndrome in the child.
Acetonemic syndrome is not a disease, but an extreme manifestation of the characteristics of a child’s body, which occurs as an inadequate reaction to ordinary external stimuli. There are primary and secondary acetonemic syndrome.
Secondary syndrome accompanies a number of diseases: diabetes mellitus, infectious toxicosis, traumatic brain injury, brain tumors and others.
Primary acetonemic syndrome
Develops in children from the first year of life and can be accompanied until 10-12 years of age.
As a rule, such children experience neuro-arthritic diathesis (NAD).
NAD is based on a violation of purine metabolism as a result of liver enzyme deficiency. Excess uric acid increases the excitability of the nervous system. Children with NAD immediately after birth are characterized by sleep disturbances, excitability, fearfulness, and do not gain enough weight. Neuropsychic development, on the contrary, is ahead of age norms: children begin to talk early, are inquisitive, remember and retell stories well. From 2-3 years of age, they experience night pain in the joints, abdominal pain, biliary dyskinesia, odor intolerance, low temperature, enuresis, skin allergies, and the appearance of urate salts in the urine. Older children develop neuroses, asthenia, and vegetative-vascular dysfunction.
The most pronounced manifestation of metabolic disorders in children with NAD is an acetonemic crisis.
Many factors can contribute to its development: fear, pain, conflict, excess emotions, overheating, physical stress, nutritional errors (excess proteins and fats).
The crisis occurs suddenly or after warning signs: headache, nausea, abdominal pain, lethargy or agitation, poor appetite, smell of acetone from the mouth.
Manifestations of acetone crisis
– repeated or uncontrollable vomiting for 1-5 days;
– dehydration and intoxication;
– anxiety and excitement at the beginning of the crisis are replaced by lethargy and drowsiness;
– cramping abdominal pain, nausea;
– increase in body temperature to 37.5-38.5;
– presence of acetone in urine, vomit, and exhaled air.
Actions of parents during an acetonemic crisis
At the first bouts of vomiting, the child is shown to be hungry. Do not give large amounts of water, as this will cause more rounds of vomiting. It is necessary to do a cleansing enema with cool water at 25-26 degrees. Start feeding your child sweet tea with lemon, alkaline non-carbonated mineral waters such as Borjomi, Polyana Kvasova, complex solutions such as Rehydron, Humana Electrolyte, fructose solution (absorbed faster than glucose), and a decoction of dried fruits. Drink in small doses: 1 teaspoon every 5 minutes, alternating types of drinks. The child should drink a volume of liquid of at least 100 ml/kg of body weight per day. In addition to drinking, you can make microenemas with a warm 35-36 degrees soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per 200 ml of water).
Monitor the level of acetone in urine using an acid test.
If it is impossible to give the child something to drink or his condition worsens, he must be hospitalized for infusion therapy.
Diet of the first days of crisis
Day one: drink only. Once the vomiting stops, you can give a cracker.
Day two: drink, crackers, rice water (to loosen stool), baked apple.
Day three: drink, crackers, liquid pureed porridge, baked apple.
Day four: drink, biscuits, porridge with water, vegetable soup.
Further expansion of the diet includes pureed water, porridge - buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, sea fish, soup with beef meatballs, turkey, omelet, kefir, steamed dishes.
Drug therapy is determined by the doctor.
Prevention of acetone syndrome
Children with acetone syndrome should not be overfed or force-fed. Meals should be frequent, 5-6 times a day. The basic principle is a hypoketogenic diet, i.e. exclusion (limitation) of foods containing purines, reducing the fat content of the diet.
From the diet, exclude soups with meat broth, veal, young poultry, offal, smoked meat, marinades, soups with fish broth, river fish (except pike perch and pike), tomatoes, champignons, baked goods, chips, chocolate, sour fruits (cherries, oranges), yogurt, full-fat cottage cheese and cheese, black tea, coffee, carbonated drinks, concentrated juices.
Often drink dried fruit compote, green tea with lemon.
For any illness, stress, stress, give glucose tablets - "ASKANOVA" from 4 years of age 4-6 tablets per day, at 7-10 years old - 6-8 tablets, from 10 years old - 10 tablets per day.
Due to the restriction of the diet in the winter-spring period, conduct courses of vitamin therapy and medicinal prophylaxis 2 times a year.
Walking often, dosing physical activity, a swimming pool is useful.
Although acetonemic crises in most children stop after 10-12 years, there remains a high probability of developing hypertension, urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus, and gout in adulthood.
In this regard, children with NAD are considered a risk group and are subject to dispensary observation.
Pediatrician of the highest category V.I. Cooper.
Discolored stool
Hepatitis
54288 August 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. The color of stool depends on the amount of bile pigments (products of the breakdown of hemoglobin), coloring substances contained in food and medications, admixtures of fresh or clotted blood, and metabolic products of microorganisms living in the intestines.
In the absence of strongly coloring food pigments, the color of stool is normally light to dark brown.
Stercobilin, a breakdown product of bilirubin, gives stool its brown color. A change in the color of stool from light green to yellowish-gray can occur with various diseases.
If bilirubin does not enter the gastrointestinal tract for any reason, the stool will become discolored. Such feces are called acholic. Discolored stool can have a different consistency, which is determined by the amount of water consumed, plant fiber, intestinal tone and other factors. These factors are taken into account when diagnosing liver diseases.
Possible reasons
Damage to the hepatic and bile ducts
.
If the patency of the hepatic ducts is impaired cholestasis
, which is characterized by acholic feces. Cholestasis can be caused by blockage of the ducts with small stones (cholelithiasis), blood clots, parasites (with opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis, clonorchiasis), and can also be a consequence of congenital anomalies, cicatricial stenosis, and the presence of tumors of the bile ducts. The lumen of the common bile duct may be narrowed due to tumor growth, due to inflammation and cysts of the pancreas, recurrent cholangitis, lymphadenitis due to tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, or be a consequence of surgical treatment and adhesions. In all cases, the flow of bile from the liver is impaired.
Symptoms of cholestasis are: skin itching, jaundice, discoloration of stool and dark urine; severe cases are manifested by a flu-like condition (chills and fever).
Sclerosing cholangitis
is a pathology that is also accompanied by discoloration of stool due to a violation of the outflow of bile. With this disease, sclerosis of the bile ducts occurs (replacement of healthy organ tissue with scar connective fibers) due to inflammatory processes.
Sclerosing cholangitis in most cases is accompanied by inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease).
Patients develop jaundice of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera, itching, weakness and fatigue, weight loss, impaired motor activity due to limited mobility of the limbs (symptoms of osteoporosis).
Functional disorders of the biliary tract
. Functional dysmotility of the biliary tract - biliary dyskinesia - is one of the most common causes of changes in the color of stool. This is due to a narrowing (muscle spasm) of the lumen of the bile ducts and duodenal papilla, which regulates the flow of bile into the intestine.
Spasm can occur due to hormonal disorders, systemic diseases, pain, or after surgical interventions. In this case, the stool discoloration will not be permanent. The stool becomes light only after spastic attacks, and during the period of resumption of motility of the biliary tract, its color returns to normal.
Considering that the brown tint of stool is caused by bile pigments, any process of disruption of their synthesis or entry into the gastrointestinal tract is accompanied by a change in the color of the stool. Discolored feces do not always indicate illness: with excessive consumption of fatty foods
the usual amount of bile is not enough to process all the absorbed fats, and the feces become light in color.
In some infectious diseases
(cholera, salmonellosis, dysentery),
digestive disorders
(inadequate absorption of nutrients, irritable bowel syndrome), increased intestinal motility leads to the rapid movement of feces, which do not have time to change color.
If discolored feces persistently form, diseases of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gallbladder, hepatic and bile ducts, sphincter of Oddi) should be suspected.
Degenerative-inflammatory liver diseases (hepatitis of various etiologies, cirrhosis) affect the synthesis and metabolism of bile pigments and bilirubin, which is often manifested by uncolored feces.
Damage to liver cells (hepatocytes)
. Hepatocytes that produce bile can die under the influence of many factors.
The infectious nature of liver diseases should be considered first.
hepatitis
viruses enter the blood, an acute infectious disease develops, which is manifested by high fever, nausea, vomiting, heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, a yellow coloration of the sclera appears (icterus), urine darkens, and feces become discolored.
When infected with hepatitis B and C viruses,
the process often becomes chronic. The incubation period for hepatitis C can be up to six months, and in the acute period of the disease, symptoms resemble a respiratory infection. Chronic viral hepatitis B and C, if left untreated, can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis can be accompanied by cytomegalovirus infection, diseases of herpes viral etiology, infectious mononucleosis (caused by the Epstein-Barr virus).
Currently, alcoholic hepatitis
.
Ethyl alcohol products and its metabolites have a direct damaging effect on liver cells.
The chronic course of alcoholic liver disease ends with massive replacement of hepatocytes by connective tissue with complete loss of their functions. In the clinical picture, the main complaints are heaviness and characteristic pain in the right hypochondrium, which can radiate to the arm, shoulder blade, and lumbar region. Yellowness of the skin develops, the sclera develops, feces become discolored, urine darkens, and signs of encephalopathy appear. In the last stages of alcoholic illness, cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus, etc. develop.
Among the toxins that have a destructive effect on liver cells
, include plant poisons (some mushrooms, bittersweet and groundsel juice) and industrial chemicals (phosphorus, arsenic, organochlorines, phenols, pesticides). Many drugs (anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antituberculosis, anticonvulsants) change the functional activity of hepatocytes, which affects the color of stool.
Liver cells die due to oxygen starvation caused by circulatory failure and oxygen deficiency in the blood. With hepatic cell failure syndrome, a dysfunction of hepatocytes occurs, which is accompanied by general intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics and examination
For complaints of discolored, acholic stools, diagnosis includes physical and laboratory tests.
Information about the functioning of the liver and gallbladder is provided by general blood and urine tests; biochemical blood test (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, glucose, amylase and lipase).