Types Causes Treatment methods Diagnostics Prevention
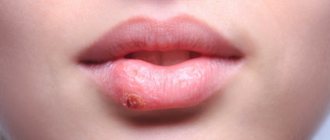
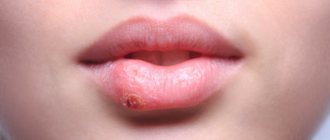
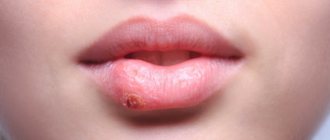
Toothache does not always bring us to the dentist. Quite often, problems are caused not by teeth, but by unpleasant sensations in the mouth, red spots on the tongue, and a burning sensation. These signs are characteristic of a variety of diseases, often systemic, but can serve as symptoms of glossitis - inflammation of the tongue.
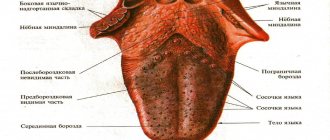
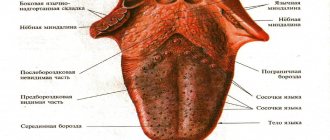
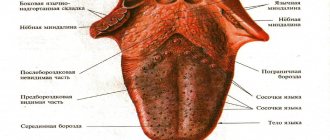
What does a healthy tongue look like?
First, let's remind parents what a healthy tongue looks like. The following signs indicate the state of normality:
- the size is not increased;
- humidity is moderate;
- the color of the tongue is pale pink, without spots or grooves;
- sensitivity is normal, papillae are not enlarged;
- allow for a light coating that is easy to clean;
- There is no bad breath.
If, upon examination of the child, the condition of his tongue corresponds to the signs described above, there is no reason to worry and see a doctor.
White
In a baby, the appearance of white spots on the tongue most often indicates thrush - a fungal infection of the mucous membranes due to a decrease in immune defense in the body or when taking antibiotics. Such spots are located asymmetrically, can have a variety of sizes, and are often covered with a cheesy coating.
If a child shows signs of thrush on his tongue, then it is necessary to visit a pediatrician who will find out the reasons for its appearance. Delay in treatment can cause progression of the disease and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which will cause pain and discomfort in the child. You cannot try to remove the plaque on your own; this can lead to additional trauma. To eliminate such white spots, it is most often recommended to treat the child’s oral cavity with a weak solution of baking soda or ordinary brilliant green. In more severe cases and with relapse of the disease, it may be necessary to take antifungal drugs.
Changes that should alert parents
In addition to changes in the color of the taste organ, parents should be wary of other accompanying symptoms, including:
- swelling, against which the imprints of teeth can be seen;
- insufficient moisture or obvious dryness of the surface of the tongue;
- enlarged papillae, especially pronounced in the root part;
- formation of persistent plaque on the surface of the tongue;
- burning sensation and impaired taste perception;
- the appearance of a specific odor from the mouth.
Parents can notice these changes during a visual inspection, which is best done in the morning in natural light. If the situation continues for a long time, the plaque thickens and the color of the tongue does not return to normal, there is every reason to consult a doctor to find out the reasons and identify hidden pathology.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Patients are advised to stop smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking foods that cause tongue tingling. Food should be steamed, stewed or boiled. Food should be soft, not traumatic to the tongue and oral mucosa. You can reduce the severity of the symptom by regularly rinsing with clean water. It is not recommended to use elixirs and other liquids that irritate mucous membranes.
Conservative therapy
At the initial stage, professional hygiene is carried out and the oral cavity is sanitized. If crowns or dentures are the cause of your symptoms, they may need to be replaced. When pinching another etiology, the following measures are taken:
- Glossalgia.
Psychological factors play a significant role in this disease, so patients are recommended to undergo a course of psychotherapy or hypnosis sessions. Light tranquilizers, sedatives of plant origin, and iron supplements are effective. To eliminate discomfort, oral baths with anesthetics are prescribed. It is possible to carry out therapeutic blockades and reflexology. - Glossodynia.
Local treatment does not bring the desired result; therapy for the causative disease, a special diet, and pathogenetic measures are necessary to normalize the functioning of the vagosympathetic part of the nervous system. The list of medications includes B vitamins, antispasmodics, and antihypertensives. To reduce the severity of paresthesia, neuroleptics and sedatives are prescribed, and blockades are performed. - Xerostomia.
The effectiveness of treatment largely depends on the cause of the pathology. Dry mucous membranes caused by medications, diseases of the teeth and salivary glands can be easily eliminated after treatment of the underlying disease. As part of symptomatic treatment, the mucous membrane is lubricated with various solutions, blockades are performed, vibration massage, electrophoresis, and galvanotherapy are performed. - Candidiasis.
If possible, discontinue corticosteroids and hormonal drugs. Antimycotic agents, alkaline applications and rinses are used locally. The oral cavity is first treated with antiseptics, and subsequently with keratoplasty preparations. General antimycotics, antihistamines, laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, and electrophoresis are prescribed.
A red or pale tongue is not the norm!
Both options indicate pathological changes occurring in the child’s body:
- A crimson-red tongue always indicates the presence of an infection (viral, bacterial or fungal). Most often it is tonsillitis, scarlet fever, stomatitis or glossitis.
- A red and shiny tongue is a sign of anemia, exhaustion and severe stomach disease;
- A cherry tint is a sign of influenza and measles, as well as general intoxication or kidney dysfunction;
- A bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen; there is reason to suspect disorders in the cardiovascular system or lungs;
- Purple color may indicate blood and lung diseases, heart failure.
- A too pale tongue, being penetrated by blood vessels, a priori cannot be lighter than blood. In most cases, this sign indicates exhaustion, deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B 12.
Let us remind parents that very often there may be a coating on the surface of the tongue, the color of which also has its own characteristics.
Taking antibiotics
If a person often uses antibiotics, and also does so without the supervision of a doctor, he may subsequently find redness on the surface of his tongue. The muscular organ is not completely stained, but only along the edges and in the center.
If such problems arise, you should immediately consult a specialist, since unlimited use of drugs can cause pathological changes in internal organs, and a red spot in the middle can signal damage to the stomach.
If a person actually uses antibiotics often and a lot and this method of treatment is the only one for him, then the drug should be replaced with another drug that also belongs to the group of antibiotics. A reddened tongue may indicate an allergic reaction.
Causes of tongue redness
All existing causes of external changes in the language, including its color, can be divided into two groups. The first group of factors are easily solvable problems that do not signal internal disorders and are not a cause for concern on the part of parents. These include:
- consumption of coloring foods and drinks,
- eating too hot (cold) food;
- mechanical trauma from a brush, teeth, lollipop, etc.
The second one combines negative causes that are inextricably linked with pathological processes that are hidden or obvious in the child’s body:
- inflammation of the taste buds;
- any inflammatory processes caused by viruses or infection;
- intoxication of the body due to poisoning;
- taking medications (antibiotics);
- allergic reaction to food, medications.
- lack of vitamins and microelements.
Only a doctor can identify the true cause of changes in the color and texture of the tongue. Parents should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication; this will only mask the problem and complicate the doctor’s work.
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of tongue tingling is the responsibility of a dentist. If the presence of provoking diseases is suspected, patients are referred to therapists, gastroenterologists, neurologists, and other specialists. The survey program includes activities such as:
- Dental examination.
Depending on the etiology of the symptom, tartar, poorly fitting dentures, carious teeth, dry mucous membranes, focal or diffuse changes in the tongue, cheeks and gums may be detected. Additionally, the acidity of saliva is determined and the potential difference is measured. - Neurological examination.
Informative for glossodynia. The results reveal the absence of curtain and pharyngeal reflexes, rhythmic trembling of the tongue. The submandibular and upper cervical vegetative nodes are painful when touched. According to electromyography, the prevalence and duration of paresthesia is determined. - Examination of the salivary glands.
Recommended to clarify the causes of xerostomia. Based on the results of ultrasound of the salivary glands, congenital anomalies, cysts, tumors, stones, and inflammatory processes are detected. During sialography using a contrast agent, neoplasms and signs of inflammation are detected. - Lab tests.
A general and biochemical blood test is performed to exclude B12-deficiency anemia and hypovitaminosis. If candidiasis is suspected, microscopy of the scraping is indicated. Identification of pseudomycelium is a reason for conducting a microbiological study. - Other techniques.
For secondary diseases that cause tongue tingling, fibrogastroscopy, colonoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, electrocardiography, echocardiography, and tests for specific markers to determine autoimmune pathologies may be prescribed.
Oral examination
What diseases does a red tongue hide?
A red tongue can be a symptom of diseases of various etiologies, including:
- angina;
- flu;
- chickenpox,
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- pneumonia;
- Kawasaki disease;
- gastritis;
- severe poisoning;
- renal failure;
- vitamin deficiency (vitamin B deficiency).
As you can see, the list of diseases is quite wide and requires visiting not only an otolaryngologist, but also, if necessary, other specialized specialists: dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Higher medical education
- Abdominal surgery
- obstetrics and gynecology
- Allergology and immunology
- Angiosurgery
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology and resuscitation
- Bacteriology
- Biochemistry
- Valeology
- Laboratory doctor
- Gastroenterology
- Hematology
- Geriatrics
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Hirudotherapy
- Homeopathy
- Dermatovenereology
- Dermatocosmetology
- Pediatric abdominal surgery
- Pediatric allergology and immunology
- Pediatric anesthesiology and resuscitation
- Pediatric gastroenterology
- Pediatric hematology
- Pediatric gynecology
- Pediatric dermatology
- Pediatric cardiology
- Pediatric cardiology interventional
- Pediatric cardiac surgery
- Pediatric combustiology
- Children's physical therapy
- Children's drug addiction
- Pediatric neuropathology
- Pediatric neurosurgery
- Pediatric nephrology
- Pediatric general surgery
- Pediatric oncology
- Pediatric otorhinolaryngology
- Pediatric ophthalmology
- Pediatric pathological anatomy
- Pediatric plastic surgery
- Child psychiatry
- Child psychology
- Child psychotherapy
- Pediatric pulmonology
- Pediatric rheumatology
- Pediatric X-ray surgery
- Pediatric LUTS
- Children's dentistry
- Pediatric dentistry therapy
- Pediatric dentistry-surgery
- Children's forensic drug testing
- Child forensic psychiatric examination
- Pediatric audiology
- Pediatric toxicology
- Pediatric thoracic surgery
- Pediatric traumatology-orthopedics
- Pediatric transplantology
- Pediatric urology and andrology
- Pediatric physiotherapy
- Pediatric phthisiology
- Pediatric maxillofacial surgery
- Children's extracorporeal detoxification
- Pediatric endocrinology
- Pediatric endoscopy
- Pediatric infectious diseases
- Dietetics
- Immunology
- Infectious diseases
- Cardiology
- Interventional cardiology
- Cardiac surgery
- Clinical laboratory diagnostics
- Clinical pharmacology
- Combustiology
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging
- Resortology
- Physiotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Mammalogy
- Manual therapy
- Emergency and disaster medicine
- Medical biology
- Medical genetics
- Medical psychology
- Medical physics
- Medicinal chemistry
- Healthcare management
- Methodology
- Narcology
- Neuropathology
- Neurosurgery
- Neonatological surgery
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- General practice
- general surgery
- Oncologist-gynecologist
- Oncology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Pathological anatomy
- Pediatrics
- Perfusionology
- Plastic surgery
- Proctology
- Occupational pathology
- Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Radiology
- X-ray surgery
- Reflexology
- Sexopathology
- Ambulance and emergency medical care
- Social hygiene and health care organization
- Sports medicine
- Statistics
- Dentistry
- Dentistry-orthodontics
- Dentistry-orthopedics
- Dentistry-therapy
- Dentistry-surgery
- Sujok therapy
- Forensic drug testing
- Forensic psychological and psychiatric examination
- Audiology
- Therapy
- Therapy for teenagers
- Toxicology
- Thoracic surgery
- Traumatology-orthopedics
- Transplantology
- Transfusiology
- Urology
- Physiotherapy
- Phytotherapy
- Phthisiology
- Functional diagnostics
- Cytology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Expert histologist
- Expert thanatologist
- Extracorporeal detoxification
- Electrocardiography
- Endocrinology
- Endoscopy
Geographical
If red spots and a white coating along their edges appear on the tongue, then this is a sign of a geographic tongue - desquamative glossitis. The disease is not inflammatory in nature and may indicate some hormonal disorders, worms and problems in the digestive system. Such spots do not have smooth outlines, they quickly change their location and do not bother the child in any way. They can be oval, round or have fancy shapes.
This disease lasts a long time and often goes away on its own after some time, even without specific therapy. Sometimes antiseptics, vitamins and drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration processes are used to treat geographic tongue. But most experts (for example, Dr. Komarovsky) believe that there is no need to treat geographic spots.