This article describes all the possible causes of the appearance of bubbles in the mouth on the mucous membrane and effective methods of treating the resulting pathology.
The first sign that allows you to suspect the occurrence of a formation in the mouth is the sensation of a foreign object.
Depending on its location, the bubble will cause various symptoms:
- Pain when chewing food if the bubble is located on the gums or tongue.
- Pain when talking or smiling occurs when a bubble appears on the inner surface of the lips.
- Pain and the sensation of a fish bone stuck in the throat occurs if the bubble is located at the root of the tongue, in the oropharynx or in the upper part of the larynx.
If you look at the neoplasm, you can see and evaluate the nature of the changes in the tissue:
- An elevation above the level of the mucosa in the form of a tubercle.
- Redness around the raised area.
- Swelling of the tissue around the elevation.
The 3 above signs are often signs of an inflammatory process and require careful monitoring of the course of the disease in order to promptly and correctly prescribe treatment.
It is worth noting that the bubble can be not only inflammatory in nature. If the formation of a vesicle and its presence are not accompanied by pain, redness, or swelling of the mucosal tissue, then the cause of the vesicle is not an inflammatory process, which narrows the range of possible causes and radically changes the direction of treatment.
In this case, you need to contact a dermatologist who will assess your health. In this case, treating yourself is dangerous to your health.
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
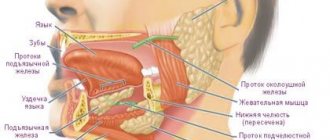
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration. If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action.
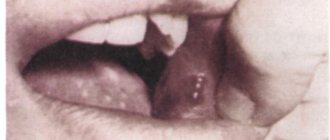
A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs due to trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
Complications and prevention
Formations in the oral cavity are a sign of a serious health problem.
Therefore, if the condition does not improve within 24-48 hours, you must urgently contact your local physician, who will determine the cause of this symptom and refer you to the right specialist. Delay in providing medical care can lead to the spread of the inflammatory process into the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the neck, lymph nodes of the oropharynx and lower jaw.
Prevention is the best treatment for any disease, so using only washed vegetables and fruits, cleaning the mouth from food debris after eating, brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth 2 times a day will significantly reduce the risk of inflammatory processes.
The main causes of a blood blister
The general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa usually indicates the level of health of the body. Often, by examining the appearance of the oral mucosa and blisters, the doctor makes a final diagnosis. After all, the symptoms of most infectious, bacterial, chronic, and acute processes that occur in the body are associated with changes in the integrity and color of the oral mucosa. Therefore, it is important to understand the main reasons that cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth.
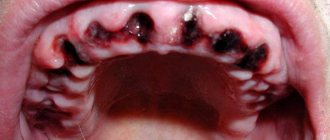
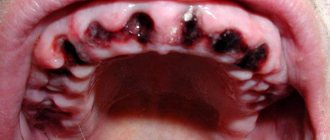
Blood blisters are distinguished by the place of their occurrence - on the tongue, under the tongue, on the cheek. They can occur as a result of injury or be a signal of the presence of a serious disease in the body. Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. The cause of the sudden appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth is damage to the mucous membrane.
There are the following types of injuries to the oral cavity:
- mechanical injury.
The cause may be various objects, solid food, biting the cheek; - chemical injury.
It occurs due to the consumption of spicy, salty foods, and exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane. This irritates the delicate oral mucosa and causes injury; - thermal injuries.
Their appearance is provoked by too cold or hot food or drinks.
Treatment
Usually a bloody blister does not require specific treatment. Since it is a natural response of the immune system to external stimuli, the formation goes away on its own within a few days.
Important! If the resulting blister did not appear due to injury, often recurs, or multiple growths are noted, a doctor’s consultation is required to rule out possible pathologies.
In some cases, therapy for hematoma is indicated. It is required for large bladder size, pain and discomfort. When treating, the dentist takes into account the following factors:
- size of education;
- time and factor of appearance;
- location of the bubble: on the cheek, tongue, lip, gums;
- whether there are other blisters or sores.
If the bubble does not go away, contact your dentist.
Treatment of a bloody ball consists of a puncture, ensuring the outflow of accumulated fluid and antiseptic treatment. Rarely, surgical excision of tissue is required to remove the lesion.
When blisters appear due to chipped teeth or incorrect dental work, the defects must be corrected. Otherwise, the cheek will be constantly injured.
Important! If the doctor suspects that the bubbles have formed not due to injuries, but as a consequence of systemic pathologies, the patient will be prescribed a comprehensive examination. Further therapy will be based on test results.
According to indications, multivitamin complexes with a high content of vitamins C, K, E, A, and group B can be prescribed. This will strengthen the walls of blood vessels and prevent hemorrhages.
After surgery, the patient is recommended to:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a while;
- do not eat food that irritates the mucous membranes: salty, smoked, spicy, pickled, rough;
- treat the oral cavity with medicinal solutions and herbal infusions with an antiseptic and wound-healing effect: chlorhexidine, miraministin, soda-saline solution, decoctions of chamomile, oak bark, sage.
To be safe from complications, rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution for several days.
What can and cannot be done if a blister appears on the cheek?
The formation of a blood globule is always a cause for concern. However, there is no need to panic. First of all, it is necessary to establish the reason why it could appear: whether there were injuries, whether hot or irritating food was consumed. Further actions are aimed at relieving inflammation and disinfection:
- The mouth is treated with antiseptic drugs.
- Rinsing with a solution of baking soda and salt will help relieve inflammation.
- Provoking factors are excluded: smoking, alcohol, consumption of salty, sour, spicy, pickled foods.
If after a few days the ball does not shrink and signs of healing are not visible, you should consult a doctor: dentist or therapist.
It is strictly forbidden to pierce the formation yourself. This can lead to infection or even greater injury.
Bloody blisters in the mouth most often appear as a result of injuries: biting, burns, chemical injuries. Less common factors are diseases of the oral cavity and systemic pathologies. As a rule, no special treatment is required. If the formation interferes, the dentist pierces it and prescribes antiseptic treatment.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die. This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin.
- These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered. After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Features of the pathology
A hematoma is a hemorrhage in the submucosal layer, so it will look like a bloody bubble, a burgundy or bright red ball. The blood inside it may be liquid or clotted. Hematomas that appear in the submucosal layer of the oral cavity are called superficial submucosal.
In addition, the hematoma cavity may be filled with colorless serum fluid secreted by the serous membranes. Such a neoplasm forms without damage to blood vessels, as evidenced by the absence of blood in the hematoma cavity. The healing period of the hematoma in this case will be shorter.
A hematoma in the mouth, due to the sensitivity of the soft tissues, can cause significant discomfort. But as a rule, the pain goes away 1-3 days after the bloody blister appears.
Hematomas can be localized on the palate, tongue, cheeks and gums.
Dental diseases
At an advanced stage of periodontitis, a fistula forms near the tooth involved in the painful process. If periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) develops, flux may appear. At first the lump is hard, but over time it becomes softer and filled with pus.
In case of periodontitis, the tooth is unfilled and the root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths are prescribed using special solutions. In case of periostitis, the dentist opens the tooth, places medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If this treatment does not help, the tooth is removed.
What other diseases can cause the appearance of red spots on the palate in children and adults?
If red spots appear on the palate of yourself or your child, be sure to consult a doctor.
A person can encounter the problem of redness of the palate only once during his life or periodically, which is due to the nature of the disease that has these symptoms. Relapses include herpes, thrush, and enterovirus infections.
Once the body has been affected, it is impossible to get rid of them.
When conditions are favorable for viruses and bacteria, the disease worsens, so it is important to take preventive measures to suppress the pathogen
The characteristic red rash in the mouth is one of the symptoms of other diseases.
- One of the symptoms of tuberculosis is flat red spots on the oral mucosa. Over time, the reddish or red-yellow inclusions merge to form plaques. The surface of the formations is heterogeneous, the color becomes red-bloody.
- ARVI is recognized in particular by red spots on the soft palate and tongue. Associated symptoms are characteristic of acute respiratory diseases.
- Oncology, among a large number of signs, has one more, which is related to the oral mucosa. A small ulcer forms on the palate, increasing in size over time. However, at first it does not cause discomfort, there are no painful sensations. Reaching large volumes, the ulcer begins to interfere, and difficulty is experienced when swallowing.
- Vitamin deficiency is characterized by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals important for all body systems. Their deficiency weakens protective functions and increases vulnerability to bacteria, fungi, viruses and infections. Red spots with vitamin deficiency are located locally on the skin and mucous membranes, without spreading intensively to neighboring areas.
- Herpes is a viral infection that once it enters the body, does not disappear. The disease worsens against the background of weakened immunity. A characteristic sign: small red spots on the mucous membrane, increasing in size, transforming into small bubbles with liquid inside.
- Chickenpox is diagnosed mainly in children under 14 years of age, but this does not exclude the risk of infection in adults. Not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes are covered with spots. In the mouth you can first find small red dots, which turn into bubbles and very soon burst. This results in gray or yellow ulcers with redness around the circumference.
- Measles is characterized by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, high fever, general physical weakness, and lack of appetite. The affected area even extends to the mucous membrane of the eyes. Initially, white spots form in the mouth behind the cheeks, and as it moves to other areas, the rash acquires a bright red tint.
- Infectious mononucleosis is recognized by its extensive affected area; spots cover not only the palate, but the entire oral mucosa. There is a soreness in the larynx, and the tonsils increase in size. Breathing becomes difficult due to nasal congestion. Characteristics of the spots: the color is bright, the parameters are impressive, they appear more often along the palate, and quickly spread to other areas.
- Scarlet fever is recognized by red spots that are localized on the soft palate. Other signs of the disease: headache, fever, nausea, pain when swallowing. The tongue becomes crimson in color, the mucous membrane is inflamed, and the rash on the skin is very itchy.
A similar mechanism for the appearance of spots in each individual case still has characteristic features and accompanying signs by which the diagnosis is made. But sometimes even the experience and colossal knowledge of a specialist do not make it possible to diagnose the problem without laboratory tests. Therefore, you should not postpone going to the clinic so that the situation does not get out of control.
Medicines
Drug treatment is prescribed based on the diagnosis. For aphthous stomatitis or pemphigus of the oral mucosa, the basis of treatment procedures is symptomatic therapy aimed at relieving pain - in particular, gels and ointments containing lidocaine (they can also be used for other pathologies).
Drug Indications Note Acyclovir (gel, ointment)
herpes simplex, shingles, chicken pox
Cholisal (ointment) is indicated for children under 3 months of age as injections.
cheilitis, stomatitis, candidiasis, mucosal injuries, teething in children
Not recommended for children under 3 years of age Prednisolone Dermatological diseases Children of any age under medical supervision Cyclosporine
atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pemphigus
Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of Stomatidin
pathologies of the pharynx and mouth, candidiasis, hygienic use
Contraindicated in children under 5 years of age Chlorhexidine Bigluconate 0.5% Treatment of damage to the mucous membranes Contraindicated in dermatitis; use Solcoseryl with caution in children Helps accelerate tissue regeneration In case of surgical removal of the blood bladder