The dental system performs the functions of breathing, swallowing, chewing and speech. It is a part of the body that changes dynamically throughout a person’s life. Its structure and functions reflect the development of the human psyche, the characteristics of his character, and behavior in society.
As the cultural level rises, people attach increasing importance to the shape of the face and the harmony of its structure.
Disorders in the maxillofacial area can be prevented by applying preventive measures and using the patterns of growth and development of the dental system.
II PERIOD - from birth to 6-9 months (before the eruption of the first milk teeth)
Prevention of dental anomalies:
- identification of congenital anomalies (cleft palate, lip) and development of a treatment plan
- rational regimen and balanced nutrition of mother and child
- breastfeeding baby
- correct artificial feeding of the child: correct positioning during feeding, preventing pressure from the neck of the bottle on the alveolar process, regulating the child’s efforts when sucking by squeezing the mother’s breast with the fingers, correct selection of the hole in the nipple, the length of the nipple and the degree of its insertion into the oral cavity, monitoring regularity swallowing
- identifying prematurely erupted teeth and deciding on their removal
III PERIOD - from 9 months to 3 years (formation of temporary bite)
Prevention of dental anomalies:
- massage of the alveolar processes of the jaws for difficult eruption of baby teeth
- monitoring the sequence of eruption of primary teeth and their establishment in the dentition
- the use of medicated nipples that apply pressure to an overdeveloped area of the jaw
- preventing the development of bad habits: thumb sucking, constant sucking on pacifiers, placing a fist under the cheek while sleeping, etc.
- identification of habitual incorrect posture (standing, sitting, lying), postural disorders and flat feet
- therapeutic exercises, massage, orthopedic consultation
- normalization of lip closure, nasal breathing, correct positioning of the lower jaw with the help of therapeutic exercises and vestibular plates
- detection of dental anomalies. Orthodontist consultation. Dispensary observation
Correction Methods
There are several methods for correcting malocclusion in childhood. At the initial stages of the problem, children may be shown myogymnastics, nutrition correction, or wearing removable devices.
For children under 3 years of age, soft elastic structures are recommended to prevent damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth, for example, lip bumpers.
The device helps correct pathologies of the maxillofacial apparatus and is shaped like a silicone pacifier.
It is possible to prevent the development of an abnormal bite due to the rapid loss of primary teeth with the help of removable orthodontic structures.
After 4 years, the fight against pathology is carried out according to a different scheme. To correct a pathological bite, the following are used:
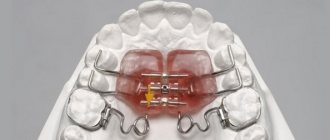
Orthodontic plates
The devices are intended for children from 4 to 10 years old; they are manufactured individually depending on the parameters of the patient’s jaw.
The shape of the plate resembles an overlay covering units of both jaws and a system of fastenings. Due to the fixing element, the force of pressure on the teeth changes.
Orthodontic plates perform a number of important functions:
- prevent further development of existing defects;
- move incorrectly located units to their normal position;
- adjust the parameters of the palatal wall.
The effect of the structures can only be achieved with continuous wear , so parents need to ensure that the child does not remove the plates from the mouth. At night, the device should also be in the child’s mouth.
Trainers
Most often they are installed from the age of 7. Trainers are made of dense silicone using computer modeling.
The following types of trainers are used in pediatric dentistry:
- periodontal – redistribute the chewing load between all teeth;
- for braces – prescribed to older children and used to correct deficiencies in the masticatory apparatus;
- retainers – prescribed after the main course of treatment with braces to consolidate the results obtained.
In 90% of cases, treatment with trainers gives positive results. In addition, after wearing the devices, no additional installation of corrective structures is required.
The success of therapy largely depends on the child’s ability to wear the device for the prescribed time.
Let's figure out together how the pacifier affects the bite, and how to avoid problems.
In this article we will tell you how to correct a crooked jaw.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/lechenie-rezko-vyirazhennyih-kompaktosteotomii.html read what compactosteotomy is and to whom the operation is indicated.
Mouthguards
The structures are made from hypoallergenic materials . Mouth guards can be standard or custom-made to fit the patient's jaw. In the latter case, the effect of using the devices will be more noticeable.
The devices are sold in sets. Each of them is designed to last several weeks of wear. During this time, the teeth have time to change their position to install the next aligner.
Thus, the dentition gradually returns to its normal anatomical position. The treatment period ranges from six months to 2 years.
You should know! Orthodontic plates and aligners are removed during meals and when brushing teeth.
Structures require regular hygienic care. They are washed under running water and treated with antiseptic solutions.
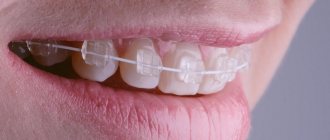
Braces
The optimal time for installing structures is 9-10 years. Braces are a thin arch attached to clasps, which, in turn, are fixed to the teeth. The arc controls the force of pressure on the elements.
Depending on the material, braces are divided into ceramic, metal, sapphire, plastic, and combined.
Teenagers may be offered lingual systems, which are installed on the inside of the dentition.
These braces are less noticeable, but require longer basic correction times and more careful maintenance.
IV PERIOD - from 3 to 6 years (the period of formed temporary occlusion)
Prevention of dental anomalies:
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the tongue
- complexes of therapeutic exercises to normalize lip closure, position of the lower jaw and tongue at rest and during functions
- combating sluggish chewing, avoiding eating hard foods, learning to swallow correctly
- learning the correct pronunciation of individual sounds (“r”, “l”, hissing)
- planned sanitation and hygiene of the oral cavity using special-purpose products
- monitoring the depth of the incisal overlap and the shape of the dental arches
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, teaching correct body position while standing, sitting, lying, walking
- introduction to outdoor games
V PERIOD - from 6 to 9 years (initial period of mixed dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- detection of malocclusions and their orthodontic treatment
- planned sanitation of the oral cavity and regular hygiene using special-purpose products
- observation of the sequence of eruption of the first permanent molars, incisors and massage of the alveolar process
- selective grinding of unworn cusps of temporary teeth (usually canines)
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the tongue
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the upper or lower lip (if there is a diastema, three)
- removal of retained primary incisors and erupted supernumerary teeth
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, therapeutic exercises and orthopedic consultation
- fighting bad habits of sucking and biting fingers, lips, cheeks, tongue, various objects, with habitual incorrect posture
- detection of nasal breathing disorders. Consultation with an ENT doctor. Sanitation of ENT organs. Removal of adenoids and velopharyngeal tonsils for orthodontic indications in cases of severe malocclusion
- the use of therapeutic exercises to normalize nasal breathing, swallowing, and posture
- training from a speech therapist in the correct pronunciation of individual sound phonemes
- early removal of the buds of 3 molars (wisdom teeth) at the age of 7 years
Role of parents
In most cases, changing primary teeth does not cause any particular difficulties. But if a child complains of discomfort in the gums, you can use gels that have an analgesic effect, for example, Dentinox or Kalgel.
If instead of a baby tooth there is a wound on the gum that is bleeding, you can apply a ball of sterile cotton wool to it and hold it for about 5 minutes. After a temporary tooth falls out, it is forbidden to eat food for 2 hours. On that day, it is better not to give your child spicy, salty or sour foods.
If a molar has already broken through, but the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, it is better to use the help of a dentist rather than remove it yourself.
VI PERIOD - from 9 to 12 years (the final period of the mixed dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- planned sanitation and training in oral hygiene using special-purpose products
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- selective grinding of unworn cusps of temporary canines and molars
- plastic surgery of the shortened frenulum of the tongue, lips (according to indications)
- removal of erupted or impacted supernumerary teeth
- identification of impaired posture, flat feet, torticollis. Therapeutic exercises and consultation with an orthopedist
- combating bad habits and incorrect postures, including during sleep
- therapeutic orthodontic gymnastics to normalize lip closure, nasal breathing, posture
- teaching proper chewing, swallowing, speech
- monitoring the sequence of eruption of premolars, canines, second molars, finger massage in this area
- rehabilitation of ENT organs
Development of primary occlusion
The primary occlusion is one of the most important periods in the formation of the dentofacial system. The fact is that even the slightest deviation that occurs at this time can lead to the development of serious violations in the future.
To assess the correct development of the primary occlusion, the following characteristics are used:
- timing of eruption: normally, the first milk tooth erupts at 6 months, and the last at 30 months. The norm is also a deviation of 3-5 months. Violation of eruption juices is the main sign of the presence of anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus;
- pairing: during the period of primary occlusion, simultaneous eruption of antagonist teeth occurs on both sides of the jaw. Growth retardation of one of them for a period of no more than 1 month is the norm. A more significant violation of pairing may signal disturbances in the development of the jaw, for example, slow growth of bone tissue.
VII PERIOD - from 12 to 15 years (period of formation of permanent dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- planned sanitation of the oral cavity, mandatory consultation with a periodontist to identify periodontal diseases and their treatment
- oral hygiene training, individual selection of hygiene and prevention products
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, torticollis, therapeutic exercises and consultation with an orthopedist. Swimming, fitness classes
- identification of gastrointestinal dysfunctions, introduction to food hygiene, consultation with a therapist
- identification and elimination of calcium deficiency
- determination of skeletal ossification disorders and consultation with an endocrinologist
- introduction to risk factors
Price
The cost of correcting a bite is not limited to the installation of orthodontic structures. The therapy consists of successive stages, for each of which the patient is forced to pay:
- consulting a doctor and choosing the appropriate treatment method;
- diagnostic measures to identify contraindications to the procedure and measure jaw parameters;
- installation of devices selected in advance by the orthodontist;
- adjustment of orthodontic systems and their replacement;
- removal of fixed structures.
The cost of installing each orthodontic system should be considered separately:
- plates – 6,000–7,000 rubles;
- trainers – 7,000–10,000 rubles;
- mouthguards – from 15,000 rubles per set;
- braces from 16,000.
VIII PERIOD - from 15 to 21 years (completion of the formation of permanent dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- sanitation of the oral cavity, hygiene, use of individual care and prevention products
- mandatory professional hygiene
- observation by a periodontist, consultation and treatment of periodontal diseases
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- introduction to food hygiene
- elimination of calcium deficiency
- restoration of crowns of damaged teeth
- restoration of bite height, alignment of occlusion, selective grinding of teeth
- timely prosthetics
- monitoring the eruption of 3 molars (wisdom teeth) and their timely removal
- identification of incorrect habitual postures, posture disorders,
- prevention and treatment of osteochondrosis
- sports, fitness, swimming
- eliminating risk factors
- formation of useful habits and skills
- surgical treatment of severe deformities of the maxillofacial area
PERIOD IX - from 21 to 40 years (active functions of the dental system)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- regular sanitation of the oral cavity, compliance with hygiene rules using special-purpose products
- observation by a periodontist, treatment of periodontal diseases
- professional oral hygiene
- restoration of crowns of damaged teeth
- replacement of missing teeth using implantation and prosthetics
- removal of 3 molars
- selective grinding of teeth and elimination of traumatic occlusion
- achieving multiple contacts between teeth with various types of articulation and occlusion of the dentition
- prevention of diseases of the temporomandibular joints
- food hygiene
- elimination of calcium deficiency
- sports, fitness, swimming
- identification and elimination of risk factors
- fighting bad habits
- prevention of secondary dentofacial deformations
no images were found