Oral anatomy
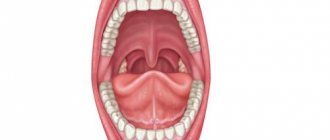
The oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive apparatus. The oral cavity is divided into two sections by the alveolar processes of the jaws and teeth: the vestibule of the mouth and the oral cavity itself.
The vestibule of the mouth is the space located between the lips and cheeks on the outside and the teeth and gums on the inside. The vestibule of the mouth opens outward through the oral opening. The transverse oral fissure is limited by the lips, which are muscle folds, the outer surface of which is covered with skin, and the inner surface is lined with mucous membrane.
The oral cavity is located on the inner side of the alveolar processes, limited above by the hard palate and the anterior portion of the soft palate; the bottom is formed by the diaphragm of the mouth and is occupied by the tongue.
The oral cavity is lined by the oral mucosa, covered with stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium. It contains a large number of glands. The area of the mucous membrane attached around the neck of the teeth on the periosteum of the alveolar processes of the jaws is called the gum. The oral cavity communicates with the pharynx through the isthmus of the pharynx.
The cheeks are covered on the outside with skin, and on the inside with the oral mucosa, which contains the ducts of the buccal glands and is formed by the buccal muscle. Subcutaneous tissue is especially developed in the central part of the cheek. Between the masseter and buccal muscles is the fatty body of the cheek.
The upper wall of the mouth (palate) is divided into two parts. The hard palate is located in the anterior part of the oral cavity, formed by the palatine processes of the maxillary bones and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones. The palatine bones are covered with a mucous membrane, along the midline of which there is a suture of the palate, and on the sides there are several transverse palatine folds.
The hard palate passes into the soft palate, formed mainly by muscles and aponeurosis of tendon bundles. In the posterior part of the soft palate there is a small conical protrusion, called the uvula, which is part of the so-called velum palatine. Along the edges, the soft palate passes into the anterior palatoglossal arch and the posterior palatopharyngeal arch. Between the arches on each side, in the recesses lie the palatine tonsils. The lower palate and arches are formed mainly by muscles that help swallowing.
The muscle that lifts the velum palatine of the soft palate and narrows the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube begins on the lower surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone and attaches to the middle section of the aponeurosis of the palate, intertwining with bundles of the muscle of the same name on the other side.
The palatoglossus muscle narrows the pharynx, bringing the anterior arches closer to the root of the tongue. Its beginning is located on the lateral edge of the tongue root, and its attachment point is on the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The triangle of the velopharyngeal muscle brings the velopharyngeal arches closer together, pulling the lower part of the pharynx and larynx upward. The muscle begins on the back wall of the lower part of the pharynx and attaches to the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The tongue is a mobile muscular organ located in the oral cavity and facilitates the processes of chewing food, swallowing, sucking and speech production. The tongue is divided into the body of the tongue, the apex of the tongue, the root of the tongue and the dorsum of the tongue.
From above, from the sides and partially from below, the tongue is covered with a mucous membrane, which fuses with its muscle fibers, contains glands, lymphoid formations and nerve endings - receptors. On the back and body of the tongue, the mucous membrane is rough due to the large number of papillae of the tongue, which are divided into four groups:
- Filiform papillae are located throughout the body of the tongue and represent a conical body with racemose appendages at the apexes.
- Fungiform papillae are located on the back of the tongue closer to its edges and have the shape of pineal growths.
- Leaf-shaped papillae are concentrated in the lateral sections of the tongue and represent 5-8 folds separated by grooves. They are unequal in size and are most pronounced in the posterior parts of the tongue.
- Cylindrical papillae, surrounded by a ridge of mucous membrane, the largest, but weakly protruding above the surface, are located on the border between the root and body of the tongue.
The muscles of the tongue are represented by skeletal muscles and the actual muscles of the tongue. Skeletal muscles connect the root of the tongue to the bones of the skull. The actual muscles of the tongue have points of origin and attachment points in the thickness of the tongue, located in three mutually perpendicular directions: the lower longitudinal muscle shortens the tongue; the superior longitudinal muscle flexes the tongue, shortening it, and raises the tip of the tongue; the vertical muscle of the tongue makes it flat; The transverse muscle of the tongue reduces its diameter and makes it transversely convex upward.
When the mouth is closed, the tongue with its upper surface comes into contact with the palate. The mucous membrane, passing to the lower surface of the tip of the tongue, forms the so-called frenulum along the midline. On either side of it, at the bottom of the mouth, on the sublingual fold, the ducts of the submandibular gland and sublingual gland open, which secrete saliva and are therefore called salivary glands.
The submandibular gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located in the lower part of the neck in the submandibular fossa, below the mylohyoid muscle.
The sublingual gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located under the mucous membrane of the mouth on the mylohyoid muscle under the tongue.
The excretory duct of the third, the parotid salivary gland, opens in the vestibule of the mouth on the mucous membrane of the cheek, at the level of the upper second molar.
Teeth, depending on their structure and functions, are divided into large molars, small molars, canines and incisors. All of them are strengthened in the sockets of the alveolar processes of the lower and upper jaws.
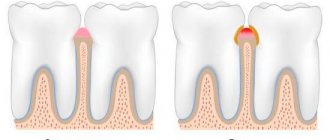
Each tooth consists of a part that protrudes above the gum - the crown of the tooth, a part covered by the gum - the neck of the tooth and an internal part - the root of the tooth. Moreover, some teeth have two or more roots.
The bulk of the tooth is dentin, which is covered with enamel in the crown area, and with cement in the neck and root area.
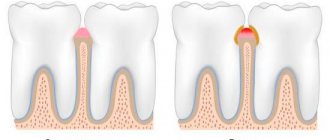
The root of the tooth is surrounded by a root membrane - the periodontium, which, with the help of tooth ligaments, attaches it to the dental alveolus. Inside the crown of the tooth there is a tooth cavity, which continues into a narrow canal of the tooth root. Vessels and nerves pass through a small hole in the apex of the tooth root into the tooth cavity containing the pulp, or pulp.
According to data from dental reference books
A full range of dental services in Istra for adults and children: from consultation to complex operations within one clinic “Doctor Nebolit”
Consultation and appointments daily from 9:00 to 19:00
- +7 (49831) 4-42-12
- Contacts
Symptoms and their manifestation
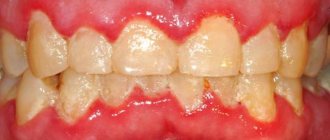
Oral diseases can be diagnosed independently at home. It is only necessary to notice changes that have characteristic signs of a pathological process:
- The appearance of itching, burning or pain;
- Swelling;
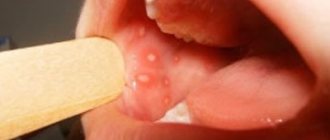
- Formation of ulcers and pustules;
- Bleeding gums;
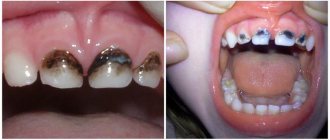
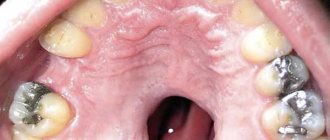
- Damage to tooth enamel;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- Weakness and sickness.
The need to maintain hygiene
More than 15 thousand bacteria and microbes live in the mouth. By feeding on food particles, they secrete acids that corrode tooth enamel. If you do not follow a set of hygienic measures, a carious cavity will form.
Oral hygiene includes disinfecting measures aimed at removing dental plaque. Maintaining these steps is an important step in preventing dental disease.
By following the rules of cleanliness you can achieve:
- fresh breath;
- healthy enamel color;
- destruction of pathogenic microflora;
- high quality teeth;
- prevention of caries, gum disease and periodontal disease.
Every person needs increased oral care, especially smokers and people with weak immune systems.
How does professional cleaning happen in the doctor's chair?
Hygienists have several professional teeth cleaning tools at their disposal. One of these tools using Air Flow
. This is a device that promotes hygiene with the help of a fine sand-like abrasive placed in this device, that is, it cleans the teeth and the surface of the teeth from soft and hard stone. I do my own oral hygiene this way - I like it. Air Flow is more gentle and gentle. And if you work with four hands with an assistant, it is very convenient for the patient.
But ideally, to ensure proper dental hygiene, you need to use the entire range of tools that exist.
In addition to Air Flow, there is also ultrasound - an ultrasonic scaler.
This is an attachment that is installed on the scaler itself.
Ultrasonic movements help remove hard plaque.
How to remove tartar in hard-to-reach places
In addition to ultrasound, there is mechanical cleaning using a Gracie curette
. This is a special instrument designed to do mechanical cleaning and hygiene began with these curettes.
Curettes are a handle with a working part on each side. The working part is a sharp edge. The angles of inclination on one side of the curette and on the other are different. The curette is convenient to work on both the upper and lower jaws. That is, it is convenient to get to - easy access.
An American housewife invented curettes. Part of the plaque is removed mechanically and then polished using a soft brush and paste. Great practical feminine approach, isn't it?
PS
Visiting the dentist twice a year was invented back in the Soviet Union under Soviet healthcare, and it was actually considered one of the best, by the way.
Treatment of teeth and gums in Moscow dentistry
During the pandemic, many people refuse to visit the dentist, believing that solving dental problems can be left “for later.” This opinion is erroneous, since the health of the entire body depends on the health of the teeth.
We offer the right solution to the existing problem with the health of teeth and gums - immediate treatment of dental diseases in a specialized center for family dentistry in Moscow - “Aesthetics”. To make your visit to the doctor as safe as possible for you, be sure to follow all preventive measures recommended by WHO.
In turn, specialists will do everything possible to protect their patients from any risks of contracting the coronavirus. Disinfection of work rooms, equipment and instruments used in treatment and diagnosis is carried out regularly. To minimize contact with strangers, we recommend making an appointment with a doctor by calling +7 (495) 66-574-55 for a specific day and time.
In our center you can receive professional dental care provided by qualified doctors. We have set affordable prices for all treatment and diagnostic procedures, and provide discounts on prosthetics and dental implantation to citizens of preferential categories.
All patients who leave their reviews on the site also receive a guaranteed 3% additional discount (in addition to the main one) on all dental services. Share your opinion, leave your reviews and don’t miss the opportunity to save your personal budget on dental treatment and prosthetics at the Aesthetics family dentistry center.
Local immunity
Local immunity provides local protection of the body from the penetration of foreign agents. Barrier functions are provided by the skin and mucous membranes. Any microtrauma to the skin and damage to the mucous membranes contribute to the unhindered penetration of harmful viruses and bacteria, which leads to the development of diseases.
Local mucosal immunity
provided by epithelial cells and the lymphoid apparatus of subepithelial spaces. Lymphoid cells secrete secretory immunoglobulins types A, G and M.
Local immunity of the oral cavity
Every day it resists the attack of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the oral cavity, therefore it is the most vulnerable place that should be given special attention.
How does local immunity differ from general immunity?
General immunity is the entire human immune system, which protects the body from foreign agents. It includes internal protective mechanisms: immune cells of various organs, lymph nodes, cerebrospinal fluid barrier, etc.
Local immunity is the first barrier of the body's immune defense, preventing further penetration of microorganisms, ensuring their death or cessation of vital activity. This is the main function of local immunity and its distinctive feature.
Types of hygiene
Measures to maintain the microflora of the oral cavity are divided into 2 types:
- Personal hygiene.
This is the basis for maintaining healthy teeth, preventing gum inflammation, caries and enamel destruction. High-quality and effective personal hygiene is not only about brushing your teeth. And it is advisable to know the basic measures to maintain “order” in the mouth from childhood.
- Professional cleaning.
It is performed by a dentist in a medical office.
It is important to note that these points do not exclude, but complement each other. It is necessary to undergo a preventive examination (2 times a year), observe the rules of personal hygiene and periodically resort to deep cleaning. All this will help prevent oral diseases and maintain the attractiveness of your smile.