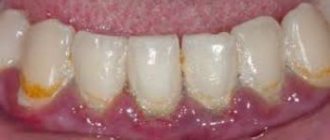
Pathologies of hard dental tissues are not always the result of caries and other inflammatory processes. A wedge-shaped tooth defect only superficially resembles an old carious lesion. The mechanism of development of this pathology is different and not fully understood.
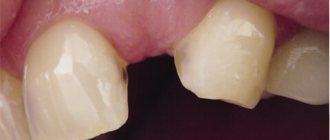
With a wedge-shaped defect, the enamel is deformed at the place where the dental crown adjoins the gum. At first it is a rough, matte hole, then the planes of the lesion close together and are shaped like a wedge (the letter V).
Why a wedge-shaped tooth defect develops is still unknown. There are several theories and they all consider excessive stress on tooth enamel.
Why wedges form on teeth and what to do about it
The defect can develop on both the upper and lower jaw, on one or more teeth. Most often, canines and premolars are affected - namely, they experience a large chewing load. The disease develops gradually and unnoticed. Over time, the defect deepens into the dentin, and the person feels pain. If the problem continues to be ignored, the base of the tooth becomes so thin that it can break.
A wedge-shaped defect appears in people of different ages, including teenagers. However, the older the person, the greater the risk of developing pathology.
The moment of appearance of the wedge-shaped defect cannot be tracked independently. But if you undergo regular examinations with a dentist, treatment will begin on time and will be completed with minimal time and money.
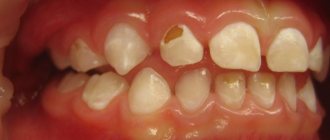
At first glance, a wedge-shaped defect can be confused with cervical caries. The affected teeth are marked with triangular-shaped spots and depressions, up to 4 mm in depth in the acute stage of development.
As for where wedges on teeth come from, there are three generally accepted theories:
- Chemical. The culprit is aggressive acids from food, drinks and resulting from an imbalance in the acid balance of the oral cavity.
- Mechanical. The defect is caused by an external load.
- Physico-mechanical. Pathology develops in response to improper chewing load.
How to treat initial cervical caries
At the white spot stage, caries can be treated using therapeutic procedures. It is necessary to restore the enamel structure by saturating it with minerals. First, the dentist will clean the affected tooth from plaque and tartar, and then apply a solution containing fluoride, magnesium, phosphorus and calcium to it. Under the influence of the active components, the enamel is remineralized and the pathological process is blocked. The patient is also prescribed mouth rinses with an antiseptic solution and toothpaste with fluoride.
How to treat superficial caries
If the carious area has managed to destroy the enamel, but has not penetrated into the hard tissues, remineralization is carried out, as in the first stage. The dentist grinds the affected area of the tooth, removes damaged tissue and applies a solution to the enamel to restore it. Several procedures may be required - 5-10 sessions. Throughout the treatment, the patient uses medicated toothpaste.
Treatment of cervical caries at the middle stage
As a rule, people consult a doctor when root caries has reached the third stage. At this stage, tooth filling is required. The doctor removes the affected tissue, carries out antiseptic treatment of the carious cavity and fills it with filling material. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many reasons for the appearance of a wedge-shaped defect. Among them
- Aggressive tooth brushing. We are talking about excessive pressure on the teeth, chaotic movement of the toothbrush. For daily care, the brush should be directed from top to bottom using soft scrubbing or circular movements. If you rub your teeth horizontally, you injure the enamel. Do not use brushes with hard bristles.
- Exposure to acids that come from food. Their suppliers are citrus juices and soda. Acid disrupts the natural protection of teeth and the enamel wears off faster when brushing your teeth or chewing food.
- Malocclusion. In this case, the load between the teeth is distributed incorrectly and additional pressure falls on the area of the transition of the crown to the root of the teeth. Additional risk factors are bruxism (teeth grinding), dystonia of the masticatory muscles, and dental defects.
- Frequent teeth whitening. Enamel is destroyed not only by uncontrolled home bleaching with lemon juice, soda and improvised abrasive substances, but by professional procedures if carried out more often than 1-2 times a year. To avoid becoming the owner of tooth enamel wearing away in the cervical area, replace frequent whitening with remineralization and fluoridation. Whitening pastes should also not be used constantly. They work great in courses lasting no more than 30 days, 1-2 times a year.
- Gastrointestinal diseases and hormonal imbalance. Increased stomach acidity can weaken the enamel and lead to the formation of a wedge-shaped defect. Women over 40 years of age are also at risk - hormonal changes lead to calcium leaching.
- Gum diseases. With periodontitis and periodontal disease, the necks of the teeth are exposed and their thin enamel is destroyed by acids and plaque bacteria.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking. Alcoholic drinks and tobacco smoke are aggressive to the microflora of the mouth. This leads to demineralization and tooth decay.
- Frequent consumption of solid foods.
- Incorrect treatment by an orthodontist.
- Heredity.
- Chemotherapy in the treatment of cancer.
Anomalies in tooth shape, treatment and causes.
Each tooth located in the dentition has a certain anatomical shape and size. An anomaly in tooth size and shape is a deviation from the normal size and shape of a tooth.
Anomaly of tooth shape is a congenital disorder of the anatomy of the crowns or roots of teeth. In the presence of such anomalies, problems arise when biting and chewing food, malocclusion and aesthetic disturbances occur. Treatment of anomalies is aimed at restoring the correct shape of the teeth, as well as their functions, through the use of orthopedic, surgical and therapeutic dentistry methods.
Causes of abnormal tooth shapes.
The main causes of tooth shape abnormalities include the following:
• Unfavorable heredity,
• Pathology of the formation and development of teeth in the prenatal period (for example, ARVI),
• Intrauterine infections (syphilis and other diseases)
In addition, abnormalities in the shape of teeth can appear due to a disorder of the endocrine system.
The basis for abnormal tooth shapes is the development of enamel hypoplasia, which occurs as a result of pathological processes during pregnancy, as well as due to metabolic disorders in the child’s body in the first years of his life.
There are various anomalies in tooth shape:
• Fournier teeth,
• Hutchinson's teeth,
• Pfluger's teeth,
• Spiked teeth,
• Ugly shaped teeth.
Hutchinson's teeth are upper central incisors with a screwdriver- and barrel-shaped crown (the size at the neck is larger than the cutting edge), having a semilunar notch on the cutting edge. The semilunar recess may be covered with enamel, but sometimes enamel is observed only at the corners of the tooth, and in the middle part the dentin is not covered with enamel.
Fournier's teeth are similar to Hutchinson's teeth, but without a semilunar notch along the cutting edge. Fournier and Hutchinson's teeth are found in congenital syphilis and other diseases.
Pflueger's teeth are the first large molars (sixes) in which the size of the crown near the neck is larger than that of the chewing surface, and the cusps are underdeveloped. The development of Pflueger's teeth is explained by the action of a syphilitic infection.
Spiny teeth - characterized by a conical shape of the funnel part and resemble a thorn. The reasons for the development of this anomaly are not known, but it is associated with the pathological development of tooth buds. Quite often, spiky teeth are caused by congenital partial edentia (absence of a tooth germ). There is also an anomaly in the form of a splitting of the lateral incisor into two spike-shaped teeth with a cleft palate.
Enamel hyperplasia , another type of tooth shape abnormality, is an excessive formation of hard tissue. Hyperplasia is accompanied by the appearance of enamel drops with a diameter of 1-4 mm on the chewing surface.
Giant teeth are an anomaly in the size of teeth. Most often these are the central upper or lateral incisors. Sometimes giant teeth are located in the anterior part of the lower jaw and in the premolar area. Such teeth can be formed due to:
- fusion of the roots of two fully formed adjacent teeth;
- fusion of the buds of two adjacent teeth;
- fusion or fusion of two teeth, one of which is normal and the other is supernumerary.
Diagnosis and treatment of dental abnormalities.
Diagnosing abnormalities in tooth shape is not particularly difficult. During a visual examination, the dentist will determine an abnormality in the shape of the teeth. To compile a complete etiological picture of the disease, doctors of other specializations may be involved. To determine deviations of the roots of the teeth, a computer study must be performed.
Treatment of teeth that have an anomaly in shape and size can be carried out using prosthetics: veneers, half-crowns, crowns.
Restoration of teeth using light-cured composite fillings using the direct method in one visit.
Prevention of the development of dental anomalies.
Prevention of the development of abnormalities in the shape of teeth is to ensure the normal development of the child inside the womb, as well as providing care and maintaining his health.
Preventive measures are aimed at ensuring a balanced diet, timely correction of endocrine system disorders and treatment of infectious and chronic diseases. We advise you to regularly visit your dentist for the prevention and timely diagnosis of dental development disorders.
Free consultation More about the clinic’s doctors
You can find out other details by calling clinic 8,
Stages of development of a wedge-shaped defect
The wedge-shaped defect develops gradually. The following stages of process development can be distinguished:
- First changes in enamel. A small area at the base of the tooth darkens slightly and loses its shine. Over time, it will develop pigmentation. At this stage, the future defect can only be seen using a special device.
- Superficial lesion. At the base of the tooth there is a noticeable crack, at its widest part not exceeding 3.5 mm. The gums sag, the neck of the tooth is exposed. The patient is uncomfortable with food that is too hot or cold, but the pain quickly goes away.
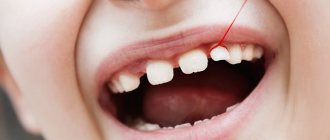
- Progressive stage. The wedge-shaped defect deepens to 4 mm, becomes yellowish-brown, matte. The shape of the triangle is already clearly visible - the two affected planes of the tooth converge at an angle of 45 degrees. Teeth react painfully to temperature stimuli and acidic foods. It is painful for the patient to brush his teeth. He feels the defect as a kind of step at the base of the tooth, where the remains of soft food are retained. At this stage, the diseased tooth is already noticeable to others when smiling and talking.
- Launched form. The enamel becomes thinner, dentin is affected, and in difficult cases, even the pulp. The wedge deepens to 0.5 cm, the neck of the tooth is exposed. If the destruction reaches the pulp, the neurovascular bundle of the tooth becomes inflamed. Acute paroxysmal pain appears, the tooth reacts to the temperature and taste of food, touch, the chewing process and causes a lot of inconvenience.
How to treat cervical caries on the front teeth
Cervical caries of the anterior teeth causes the most discomfort. Firstly, it develops and progresses faster than on molars and premolars. Secondly, the front teeth fall into the smile zone, so a cosmetic defect also occurs. Treatment is carried out according to the usual scheme, but the material for the filling is selected more carefully. It should not differ in color from the rest of the tooth, otherwise it will look unaesthetic. The cost of such a filling is significantly higher than the standard one.
Diagnostics
A wedge-shaped tooth defect is usually identified by a dentist during a routine examination or treatment. He evaluates the location and shape of the pathology, the density of the tooth tissue. It is important to confirm that we are not dealing with dental erosion, superficial, cervical caries or enamel necrosis.
The doctor examines the patient’s dental status (oral hygiene, number of caries-affected, filled and extracted teeth, gum condition) and conducts a thermal test. This is a tooth reaction to temperature stimuli.
Vital staining helps in establishing the diagnosis: the wedge-shaped defect is well stained with iodine solution, but retains its color when treated with methylene blue. It is also important to determine what malocclusion pathologies exist and how they affect the occurrence of the pathology.
To exclude the influence of somatic diseases, the doctor may refer the patient to an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist.
How is cervical caries diagnosed?
If the carious lesion is localized on the visible part of the tooth, the doctor makes a diagnosis after an external examination. But to confirm it, a special test is performed using a dye solution. It is applied to the enamel and left for 3-4 minutes. The affected area turns blue. After a few hours, the dye is completely washed out of the mouth.
The doctor may also prescribe an x-ray to assess the nature of the spread of caries, the depth of the carious cavity, the condition of the nerve endings, etc. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment method is selected. It is determined, first of all, by the stage of the disease.
Treatment
When treating a wedge-shaped tooth defect, the doctor first restores its integrity, then prevents its further destruction. If necessary, dentists of narrow specializations are involved in the treatment of a wedge-shaped defect: therapists, orthodontists, orthopedists.
The following will help restore the condition of the tooth:
- Installation of seals. The doctor removes the altered tissues in the cervical area, and installs filling material in their place. When restoring medium and complex defects, the doctor uses a light-curing fluid composite and compomer materials. They are quite elastic and can partially compensate for the load on the teeth. The best fillings are installed using the sandwich technique: the bottom layer is made of dental cement, the top layer is made of composite materials. For better aesthetics, your doctor may suggest installing ceramic veneers.
- Fluoridation and remineralization. The procedures restore the mineral content in the enamel, this heals the tooth and slows down the process of destruction;
- Prosthetics. If the tooth is severely damaged and there is a risk of fracture at the base of the crown, the doctor will be forced to install a denture. Usually this is permanent prosthetics made of metal-ceramics or using ceramic crowns.
If the wedge-shaped defect has just begun to develop, the following will help slow down the process:
- Remineralizing therapy. Applications with calcium and sodium preparations are applied to the affected part, and the patient is recommended to take a course of vitamin-containing complexes. Remineralization courses must be repeated regularly and they only help at the initial stage of the disease;
- Fluoridation. Effective in cases of deep damage to the enamel, applications with fluoride preparations seal the tubules of the tooth tissue and reduce its sensitivity;
- Laser therapy. Reduces tooth sensitivity and inhibits the development of the disease. Laser treatment is recommended for pregnant and lactating women and patients with allergies.
For home care, the doctor will recommend pastes and gels enriched with a special mineral composition.
What you can do at home
We described the features of caries treatment at different stages in the dentist's office. Many people are interested in the question of what to do if the disease develops at home, whether it can be stopped on their own. The only thing available to the patient is prevention. If a carious lesion has already begun, it is impossible to reverse it with the help of rinses or folk remedies.
However, you can slow it down or stop it if you follow a number of simple rules:
- brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after eating;
- give up sweet foods and sodas;
- quit bad habits, in particular smoking;
- use irrigators to clean the oral cavity.
In addition, do not forget to check your teeth every six months, even if you are not worried about caries symptoms.
How to prevent the development of a defect
If the wedge-shaped defect is not treated, the disease will develop and the tooth will collapse. But treatment methods have their drawbacks, they are not durable enough and do not guarantee that the pathology will not invade neighboring teeth.
To avoid an unpleasant disease, you need to take into account risk factors and take care of your own health and dental condition.
The most important preventive measures:
- brush your teeth correctly and choose oral hygiene products;
- undergo regular examinations in good dental clinics;
- trust dental manipulations only to a trusted orthodontist;
- correct the bite in time;
- promptly treat periodontal diseases;
- exclude soda and sour juices. Eat fresh foods containing enough vitamins and minerals;
- promptly identify and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and endocrine systems.
How is advanced cervical caries treated?
Deep caries is often accompanied by damage to the pulp, so depulpation is required. After this, root canal treatment and filling are performed. In some cases, nerve removal can be avoided. Then treatment is carried out according to the standard algorithm:
- Anesthesia.
- Removal of deposits and tartar.
- Selecting the shade of the future filling.
- Retraction of the gingival margin.
- Preparation of a carious cavity.
- Tooth isolation.
- Grinding.
- Filling.
- Polishing the filling.
The procedure can be more complicated if the carious lesion is located under the gum. It has to be cut to open access to the neck and root. After the main treatment, the doctor applies sutures, which dissolve within a few days.
If the patient goes to the doctor late and the tooth is almost completely destroyed, it is removed. The question arises about installing an implant.